What are the 5 phases of Lean Six Sigma?

:
Lean Six Sigma (LSS) is a process of solving a problem in order to maintain the quality of the project. Lean and six sigma both are two different methods. Lean is a systematic approach to identify and reduce project activities that are not required. Six Sigma is a problem-solving methodology that focuses on continuous improvement with minimum defects. A combination of Lean and Six Sigma results in increased quality and revenue.
Lean Six Sigma certification is a quality management certification offered by the International Association of Six Sigma Certifications (IASSC™) designed to reduce variations and eliminate waste which ensures the quality of the process. It solves an existing problem with unknown causes.
LSS methodology is based on a problem-solving framework with a cycle called DMAIC. It is a data-driven quality strategy for improving the quality of the process. DMAIC is a five-phase process and is an acronym of:
- Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Improve
- Control
DMAIC is pronounced as, “duh-may-ik.”

Define
The first phase of Lean Six Sigma is to Define. The main aim of the define phase is to define the “problem statement” and plan the improvement initiative. In order to understand the overview of the project, ‘Project Charter’ is created.
The project charter is a key element that describes the whole project in brief. The project charter generally includes the objective of the project, stakeholders, requirements, high-level assumptions and constraints.
Define phase includes,
- Defining problems by developing a “problem statement” document
- Defining the project goal by developing “Goal Statement” document
- Defining the process of the project by developing a process map
- Defining the requirements from the customer
Problem statement: It is a document created to know about the symptoms of the problem and its effect. First, the indications of the issue are confirmed and then the problems are prioritized.
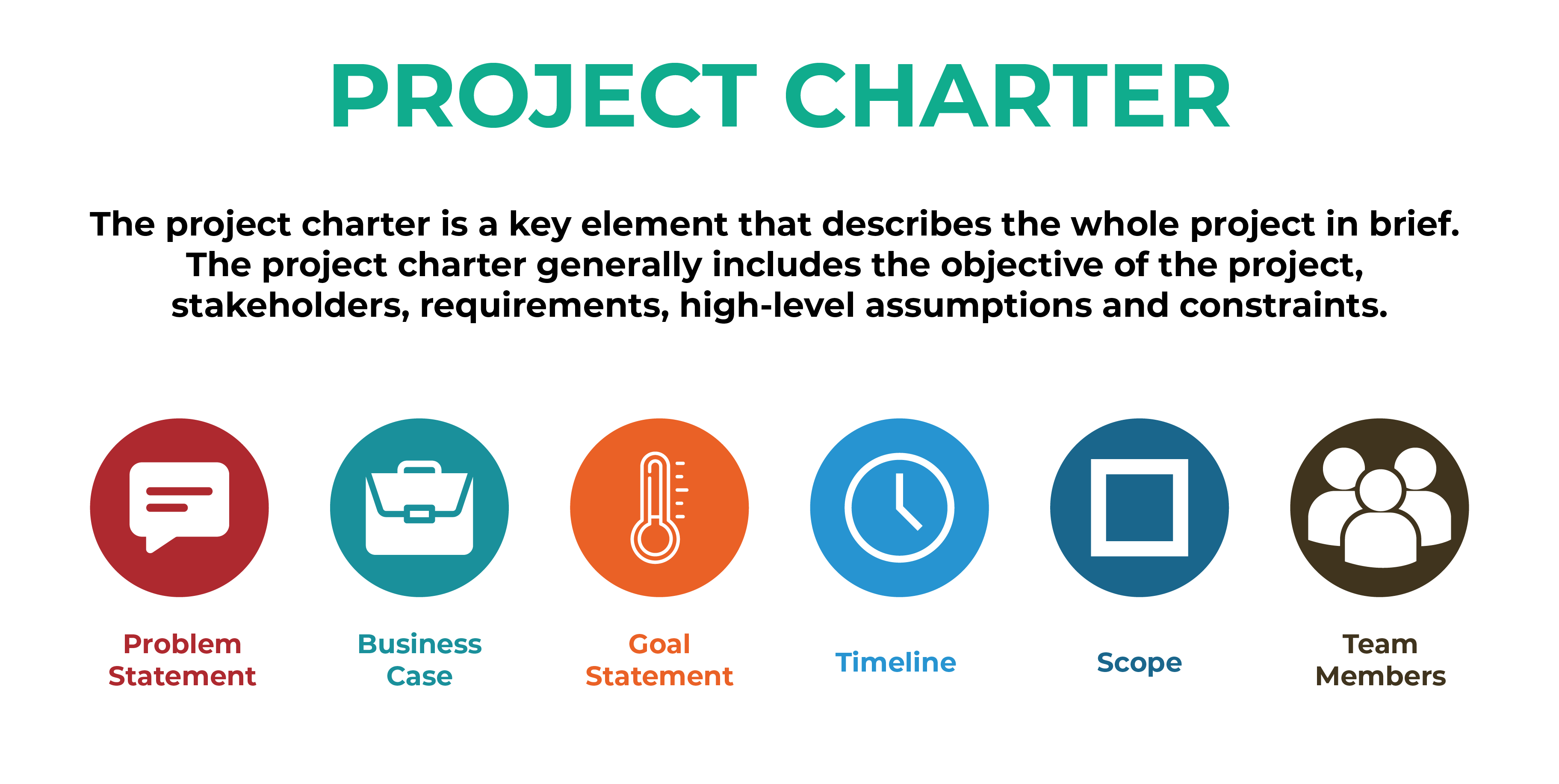
Tools used in defining phase:
A project charter is used to define Goal Statement
SIPOC: Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers. SIPOC is a high-level map used for developing process maps.
Similarly, Value Stream Map and Swimlane Maps are used.
In order to define the customer and their requirement Voice of the Customer (VOC), Translation Matrix and Tree Diagram are used.
After defining all the above statements, A3, Relationship Map and Stakeholder Analysis are used to inform others about the progress of the project.
Measure
In this phase, the magnitude of the problem is identified. In order to measure the problems, baseline or the start point is created. Before making any changes, the baseline is created. Measure phase is vital because the data collected for the project will be used throughout the project.
The Measure phase involves,
- Creating a baseline
- Root cause analysis is done for the problems identified
- Baseline Data collection
- Ensuring the data collected is reliable
- Update the project charter
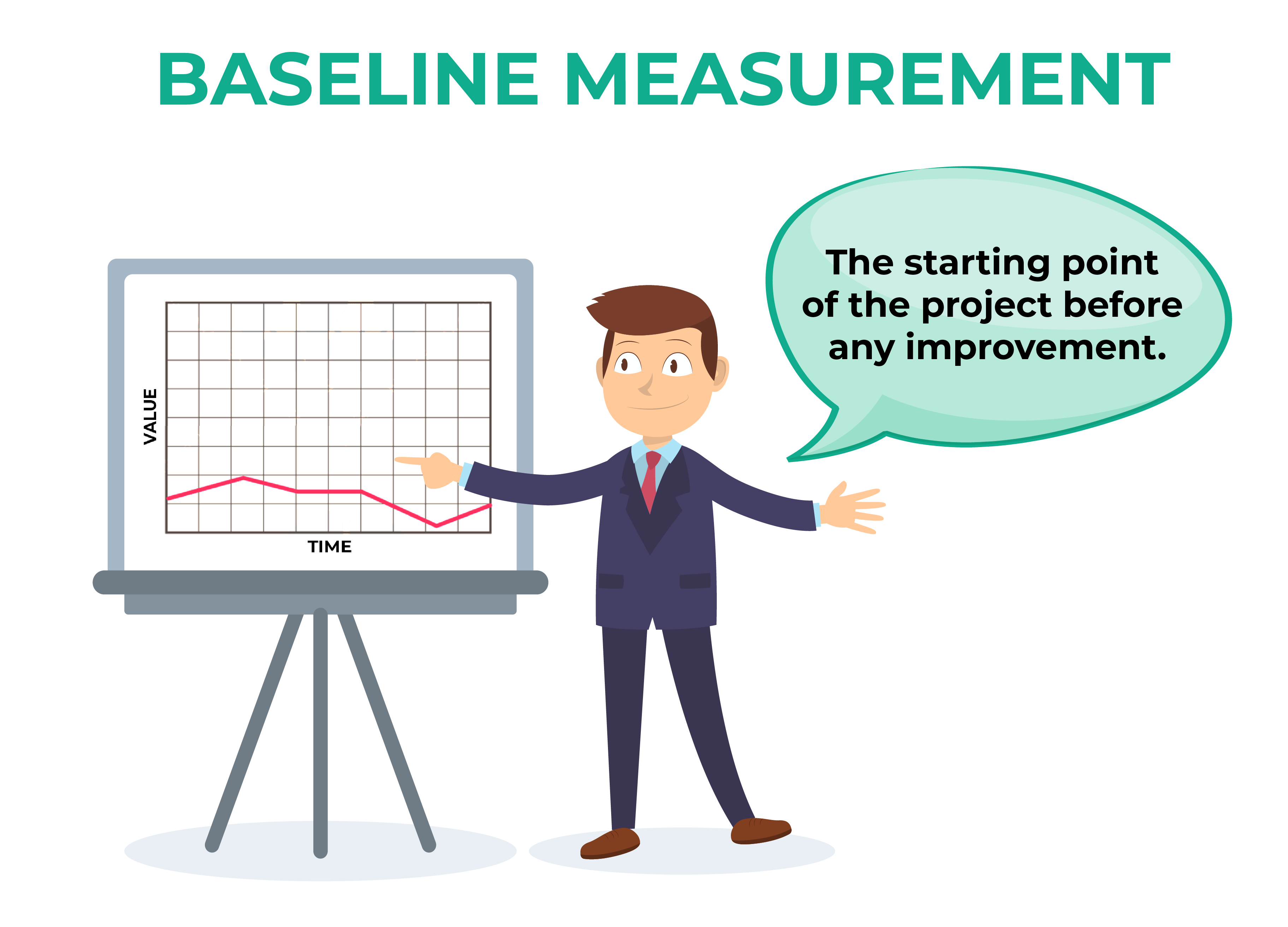
The main aim of this phase is to determine the current performance and refine the definition of each measure. This results in an improvement in quality and reduction in lead time.
The tools used in Measure phase are:
Data collection plan is used to define where to get the data, how much data is required, who will be responsible for data collection and how to collect the data.
Operational definitions are used to define and refine the processes that lead to collecting critical process information.
The check sheet is used to collect the baseline data
The collected data and the changes are updated in the Project charter.
Analyze
In order to get the solution, The problems have to be analyzed. This phase is carried out parallelly with the measure phase. When the data is reviewed in the measure phase, the person reviewing might adjust the additional data in the data project plan. The processes and the data are analyzed in order to verify the root cause of the defects.
This phase involves,
Examining the process: When the process maps are created in the Measure phase, the problems and defects are listed within the process. Then process analysis is carried out which consists of,
- Time Analysis: work time versus the waiting time.
- Value-Added Analysis: Analyzing the process through the customer’s point of view in terms of cost.
- Value Stream Mapping: Mapping of process data with value-added analysis in order to remove the waste.
Visually inspecting the data: Inspecting the data collected using charts and graphs
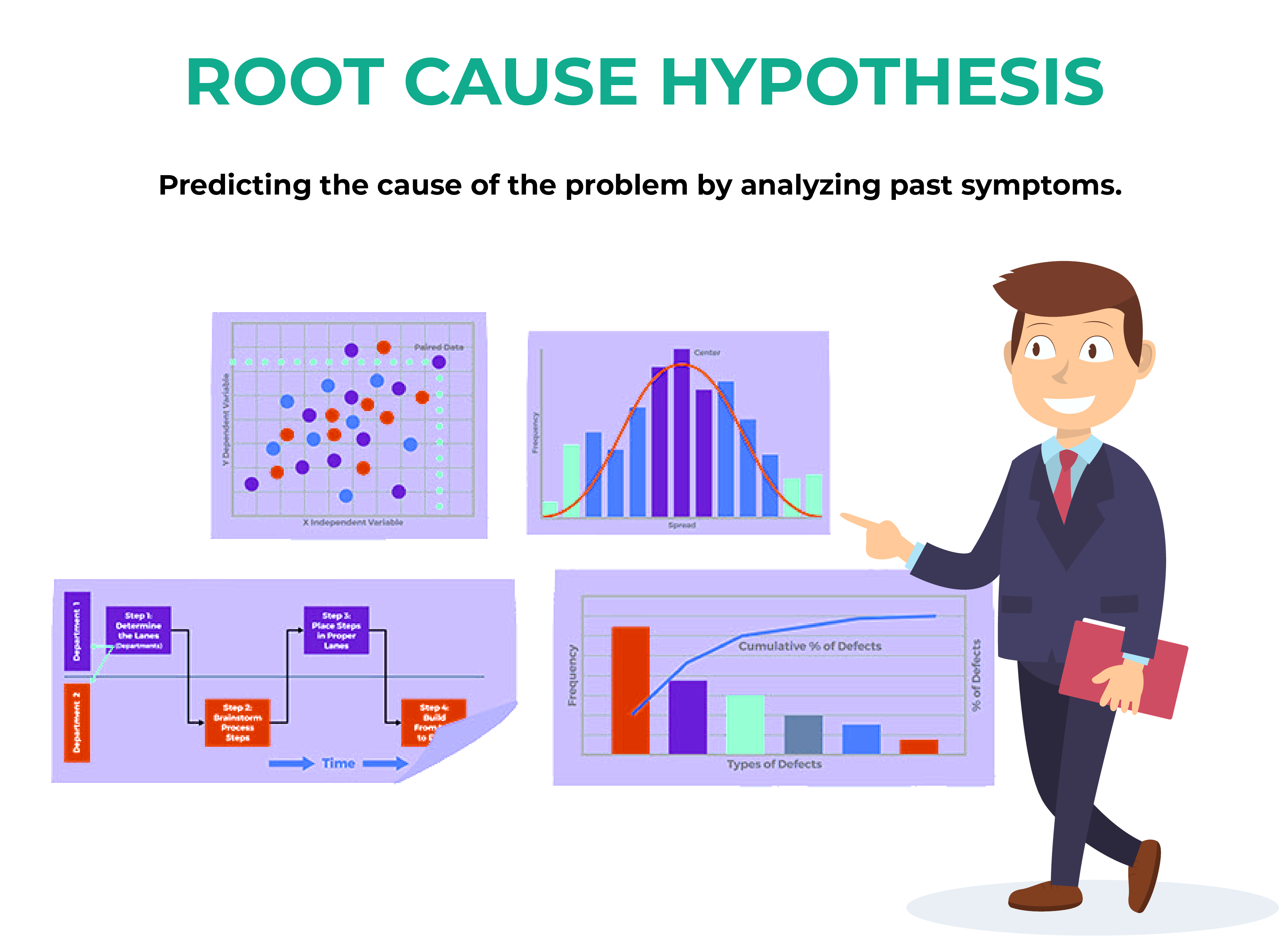
Analyzing the root causes by developing the theories on all the possible causes. The problems are analyzed by brainstorming together.
Verifying the causes of the defects through,
- Process analysis
- Data analysis
- Process observation
- Comparative analysis.
Updating the project charter after finalizing the process performance and scope of improvement.
The tools used in Analyze phase are:
Value stream mapping and Value-added Flow Analysis use to examine the process.
Run Charts, Histograms, Box Plots, and Pareto Charts are used to visually analyze the data.
Fishbone Diagram and the 5Whys are used to analyze the root cause.
Root Cause Hypothesis is used to verify the causes of the defects.
Improve
Once the root causes are determined, the solutions are developed and implemented. In this phase, the ideas are produced to solve the problem. In this phase, the team refines the ideas by collecting all the ideas, monitor process changes and finally implement the ideas.
This phase involves,
- Listing out all the possible ideas that might fix the problem: Techniques like, Cross-Training, Setup Reduction, Kanbans are used to bring out the innovative ideas for the defects or problems identified.
- Selecting the best of solutions.
- Process-based maps are developed based on different solutions
- Based on the process map, the best solution is decided
- The solution decided is implemented.
- Measurable improvement is recorded.
The tools used in this phase:
- To brainstorm solution Benchmarking and Classic lean improvements are used.
- Weighed Criteria Matrix is used to make the best decision and Impact Effort Matrix is used to assess the solutions providing the best impact.
- To-Be Map, Value Stream Map and Swimlane Maps are used to develop a process map.
- PDCA (Plan Do Check Act ) is used to select the solution. PDCA is a mini testing cycle carried out in order to select the best one.
- A pilot checklist is used to implement the plan
- Process changes are measured to check the improvement against the baseline.

Control
Once the problem is fixed, it is very essential to maintain it. This phase aims to create a monitoring plan, measure success, update process and develop a response plan if any dip is found.
Control phase is based on 4 principles:
- Value: To determine the steps which are important and are valued.
- Flow: The flow of the project process to be maintained smoothly.
- Pull: To ensure the customer’s demand is aligned with a process change.
- Perfection: The accuracy in the process.
This phase involves:
Ensuring the project process is continuously monitored using Lean. The response plan is prepared that involves the level at which the performance started to dip or reduce.
Recording the improved or changed process. Visual workspace is created to ensure others follow the new process.
Applying the improvement in all the areas. The knowledge gained in one project is applied in all the other areas of the organization.
Share the improvement and project success with everyone.
How to Get Lean Six Sigma Certified?
There is no such prerequisite to take any of the Lean Six Sigma Certification exams accredited by IASSC™. LSS has a hierarchy of certifications to progress in career path:
Who is the Target Audience for Lean Six Sigma Certification?
- Quality Managers
- Quality System Managers
- Quality Engineers
- Quality Supervisors
- Quality Analysts
- Quality Auditors
- Team Leaders
- Software Professionals
- Project Managers
- Improvement Managers
- Operational line managers
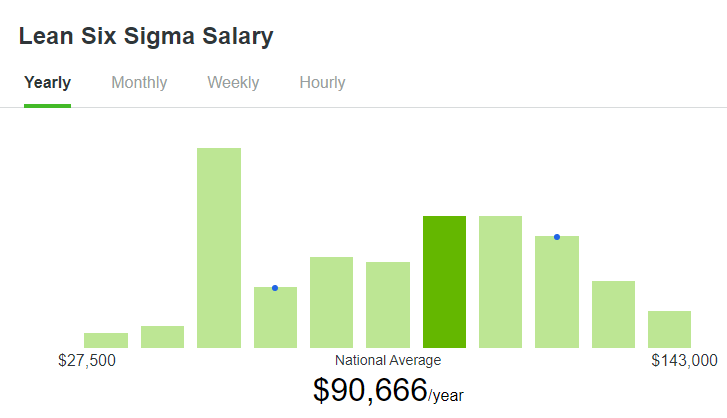
What is the average annual salary of Lean six sigma certified professionals?
According to ZipRecruiter, as dated on Feb 06, 2020,
The average annual salary for certified Lean Six Sigma professionals:
What is the exam format for the Lean Six Sigma Certification?
Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
60 multiple-choice questions
Duration: 2 hours
Qualifying points: 230 points out of 300 points
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
100 questions
Duration: 3 hours
Qualifying points: 385 points out of 500 points
Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
150 questions
Duration: 4 hours
Qualifying points: 580 points out of 750 points
How to maintain Lean Six Sigma Credentials?
Lean six sigma certifications have no expiry date.
For more information on how you can accelerate your career with these certifications, visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ or call now on +1-713-287-1213 / 1214 or e-mail us at info {at} icertglobal {dot} com.
We provide instructor-led classroom and instructor-led live online training across the globe. We also provide Corporate Training for enterprise workforce development.
Quality Management Training by iCert Global:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training by iCert Global:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training by iCert Global:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training by iCert Global:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
iCert Global both Instructor-led Classroom training workshops and Instructor-led Live Online Training sessions for learners from across the United States and around the world.
Please Contact Us for more information about our professional certification training courses to accelerate your career in the new year. Wish you all the best for your learning initiatives in the new year.
Which certifications are you aiming to achieve in 2020? Let us know your thoughts in the 'Comments' section below.
Thank you for reading this blog post. Hope you found it useful and interesting. Team iCert Global wishes you all the best for your learning endeavors.










Write a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked (*)