Latest Articles
7 Best AI Startup Ideas for 2026 That Anyone Can Start
Today’s surge in real-world AI applications makes startup opportunities more achievable than ever, echoing the pot...
Hacking Vs Ethical Hacking: What Sets Them Apart?
It's no longer just about keeping people out, but instead building internal resilience. The stakes are gigantic: cyb...
5 Trends that can Shape Your Content Marketing
With content marketing rapidly maturing in 2025, understanding the trends driving this shift has become essential for bu...
How To Make A YouTube Video Viral?
Effective SMM doesn’t just increase visibility—it strengthens the chances of your YouTube content hitting vi...
How to Become a Game Developer: Steps, Skills and Career Guide
The global video game market is set to pass $320 billion in revenue by 2026. This shows that it is a huge and fast-growi...
Project Management Risk Assessment Senior Leaders Strategic Guide
In a recent global look at project results, 56% of those that failed report a weak or shallow way of predicting and hand...
20 Emerging Cybersecurity Trends to Watch Out in 2026
By 2026, losses from cybercrime globally will reach $20 trillion yearly, which would make cybercrime the world's thi...
Capacity Planning Definition Top Methods and Strategies
A surprising fact shows how big the challenge is in today's companies: only 13% of the organizations say their deman...
Tutorial on Importing Data in R Commander
A recent industry survey shows about 70% of professional data miners use R for their statistics and modeling. This makes...
Artificial Intelligence Algorithms: All you need to know
By 2030, more than $15.7 trillion will be added to the world's economy by the Artificial Intelligence market. This g...
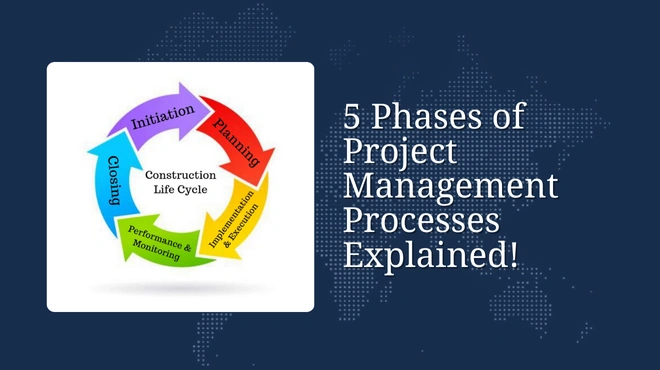
5 Phases of Project Management Processes Explained!
Looking ahead to the future of project management, mastering the five phases of project management processes ensures pro...
ARP Spoofing – Automating Ethical Hacking with Python
Combining Python’s beginner‑friendly syntax with hands‑on techniques like ARP Spoofing helps new ethical hacke...



.jpg)


.webp)