Articles on BigData
Why Data Architects Are the Backbone of Every Data-Driven Organization
While data visualization brings insights to life, it’s the data architects who ensure the backbone of these visual...
How Data Warehousing Powers Business Intelligence
Integrating big data analytics with a solid data warehousing strategy allows businesses to uncover trends, anticipate ch...
How to Create Effective Data Visualizations for Better Decision-Making
Big data analytics not only processes vast amounts of information but also enables the creation of visualizations that d...
How Data Mining Helps in Making Data-Driven Decisions
Big Data applications we encounter daily rely heavily on data mining to uncover patterns and insights that drive more in...
Is Hadoop Still Relevant in 2025? The Future of Big Data Ops
As big data operations evolve, grasping the fundamentals of data processing remains a key skill for professionals in the...
Leveraging Big Data Analytics to Predict Product Quality Trend
An American Society for Quality research found that 82% of companies think that big data analytics is important for qual...
Top 7 Applications of Big Data You See Every Day
From heat maps to dashboards, the right types of data visualization make the Top 7 Applications of Big Data You See Ever...
How Hadoop Distributed File System Works
Understanding data processing is incomplete without exploring Hadoop, the backbone of many big data systems.A recent stu...
The Best Practices for Business Intelligence
Understanding big data fundamentals explained clearly is essential for improving business intelligence, as it helps turn...
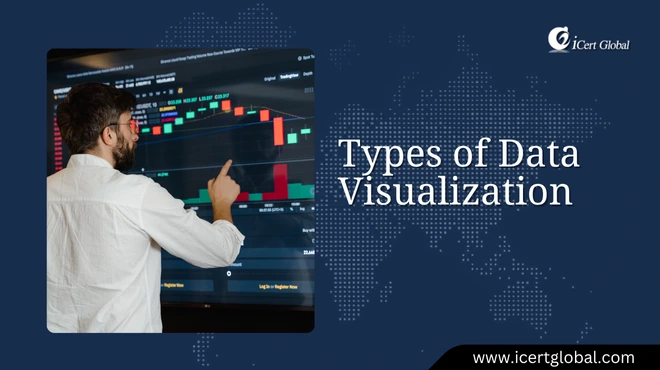
Types of Data Visualization
In the modern professional world, data is often called the new oil, but raw data alone holds little value. It's the ...
Strategy Pattern for Big Data:A Simple Guide
Different types of data visualization become far more powerful when combined with the Strategy Pattern, as it provides a...
Data Visualization Skills You Need for 2025
Mastering different types of data visualization is key to building the advanced skills needed to effectively communicate...

.webp)

.jpg)