Quick Enquiry Form
Categories
- Agile and Scrum (238)
- BigData (45)
- Business Analysis (98)
- Cirtix Client Administration (55)
- Cisco (63)
- Cloud Technology (121)
- Cyber Security (70)
- Data Science and Business Intelligence (67)
- Developement Courses (57)
- DevOps (17)
- Digital Marketing (67)
- Emerging Technology (211)
- IT Service Management (80)
- Microsoft (54)
- Other (396)
- Project Management (521)
- Quality Management (155)
- salesforce (68)
Latest posts
Business Analyst Roles That Pay..
Service Delivery Manager Role Explained..
GCP Services Explained Full Overview..
Free Resources
Subscribe to Newsletter
Step by step guide to the twenty six ITIL 4 processes
This is the initial process within the ITIL service lifecycle. It helps companies learn about their objectives and how to plan to satisfy customer needs. Companies can make good strategies by seeing what is required in the market and what they currently offer.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/0b1KqFKuRks?si=fWh70WclauG9KfcT" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen></iframe>
There are five major processes within the Service Strategy stage:
1. Service Level Management
This process assists an organization to plan and determine how the services are to be delivered. It also monitors performance in order to set whether the set targets are being met. The Service Level Agreement (SLA) document is employed to describe the anticipated service levels. The process involves four steps:
• Establishing what the customer requires and drafting the SLAs.
• Agreement and negotiations on the SLAs
2. Service Catalog Management
This guarantees that there is a well-defined and current list of services for the customers. This list is referred to as a service catalog. It assists the customers in finding and utilizing the services that they need. The four steps include:
• To explain what every service is.
• What to put into the catalog
3. Capacity Management
This methodology ensures the systems and services are sufficiently resilient to support business requirements without compromising. The five steps are:
• Observing the number of individuals utilizing the system
• Analyzing that information
4. Managing Availability
This is a procedure that ensures services to operate and be operational whenever customers need them. The five steps are:
• Verifying if services are accessible
• Checking availability data

5. IT Service Continuity Management
This process is designed to maintain the operation of services during disasters or disruptions. It assists in protecting the business from risk. The three steps are:
• Creating a plan to maintain services running
• Putting that plan into action
6. Information Security Management
This procedure protects data, systems, and users. It prevents penetration and resolves problems if they do happen. The five steps are:
• Learning security needs
• Writing security rules
7. Supplier Management
This process manages all of the external vendors and suppliers that the company uses. It makes sure they are honoring contracts and that their work is being done correctly. These five steps are:
• Setting supplier requirements
• Checking supplier options
8. Design Coordination
This approach guarantees that new service design is of high quality and addresses business requirements. It looks at resources, planning, and risk. The four stages are:
• Creating rules and plans
• Planning staff and equipment required
Service Transition
It is the third phase in the ITIL lifecycle. It enables services to move seamlessly from one phase to another, for example, when change or significant changes take place. It maintains services in a stable state while introducing new ones, and it minimizes risks. There are seven processes in it.
1. Managing Change
This procedure helps firms manage change while ensuring service quality. The six steps are:
• Sorting and logging change
• Risk and impact studies
2. Change Evaluation
This process checks how well the changes will be applied before and after making them. These three steps are:
• Planning the evaluation
• Confirming what is expected to occur
3. Releases and Deployments Management
This procedure is in charge of allowing new software to be introduced in the business. Its purpose is basically to avoid such modifications affecting the existing systems negatively. The five steps are:
• Planning the release
• Release development and validation
4. Service Testing and Validation
This is the process of checking whether the service is sufficient before it starts. It also checks whether to use or improve the service. The six steps are:
• Planning and designing tests
• Checking test plans

5. Service Asset and Configuration Management
This procedure records all the significant items utilized to deliver IT services, such as computers, software, and files. These are referred to as configuration items (CIs). The five steps are:
• Process and planning management
• Identifying what is being tracked
6. Knowledge Management
This process gathers and organizes helpful information so users and technicians can repair problems more simply. The five steps are:
• Developing a knowledge sharing plan
• Browsing and gathering useful information
7. Transition Planning and Support
It assists in planning and organizing the introduction of new or altered services into daily use. Although it is not utilized daily, it is necessary when utilized. The four steps are:
• Creating a transition plan
•Preparing for the change
Service Operation
It is the fourth stage of the ITIL lifecycle. It runs services on a daily basis and maintains them in an optimal state. It aims to deliver value to customers while maintaining adaptability to evolving business requirements and technology. It consists of five significant processes:
1. Handling Incidents
This procedure corrects service issues in real-time. They can range from resetting passwords to fixing printer errors. The five steps are as follows:
• Classifying and recording the problem
• Setting its priority
2. Problem Management
This is a process which examines what failed and tries to prevent them from happening again. There are five steps:
• Problem identification and documentation
• Grouping it
3. Event Management
This process searches for incidents within the system and stops them from creating service problems. Incidents might originate from applications or other products. The five steps are:
• Seeing when something occurs
• Finding the event
4. Access Management
This procedure determines who is authorized to access the system. Only authorized personnel are allowed access. The five steps are:
• Receiving access requests
• Checking the request
5. Fulfilling Service Requests
This process manages all users' service requests. It can be for assistance, information, or access. There are five steps:
• Logging the request
• Checking if it’s valid
How to obtain ITIL certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion:
The ITIL guideline assists companies in managing their IT services more effectively through well-defined processes. Every phase of the ITIL lifecycle, from strategy to continuous improvement, plays a crucial role in delivering good, effective, and customer-focused services. Adhering to these phases enables companies to respond to evolving needs, reduce risks, and deliver greater value in the long run.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
This is the initial process within the ITIL service lifecycle. It helps companies learn about their objectives and how to plan to satisfy customer needs. Companies can make good strategies by seeing what is required in the market and what they currently offer.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/0b1KqFKuRks?si=fWh70WclauG9KfcT" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen></iframe>
There are five major processes within the Service Strategy stage:
1. Service Level Management
This process assists an organization to plan and determine how the services are to be delivered. It also monitors performance in order to set whether the set targets are being met. The Service Level Agreement (SLA) document is employed to describe the anticipated service levels. The process involves four steps:
• Establishing what the customer requires and drafting the SLAs.
• Agreement and negotiations on the SLAs
2. Service Catalog Management
This guarantees that there is a well-defined and current list of services for the customers. This list is referred to as a service catalog. It assists the customers in finding and utilizing the services that they need. The four steps include:
• To explain what every service is.
• What to put into the catalog
3. Capacity Management
This methodology ensures the systems and services are sufficiently resilient to support business requirements without compromising. The five steps are:
• Observing the number of individuals utilizing the system
• Analyzing that information
4. Managing Availability
This is a procedure that ensures services to operate and be operational whenever customers need them. The five steps are:
• Verifying if services are accessible
• Checking availability data
5. IT Service Continuity Management
This process is designed to maintain the operation of services during disasters or disruptions. It assists in protecting the business from risk. The three steps are:
• Creating a plan to maintain services running
• Putting that plan into action
6. Information Security Management
This procedure protects data, systems, and users. It prevents penetration and resolves problems if they do happen. The five steps are:
• Learning security needs
• Writing security rules
7. Supplier Management
This process manages all of the external vendors and suppliers that the company uses. It makes sure they are honoring contracts and that their work is being done correctly. These five steps are:
• Setting supplier requirements
• Checking supplier options
8. Design Coordination
This approach guarantees that new service design is of high quality and addresses business requirements. It looks at resources, planning, and risk. The four stages are:
• Creating rules and plans
• Planning staff and equipment required
Service Transition
It is the third phase in the ITIL lifecycle. It enables services to move seamlessly from one phase to another, for example, when change or significant changes take place. It maintains services in a stable state while introducing new ones, and it minimizes risks. There are seven processes in it.
1. Managing Change
This procedure helps firms manage change while ensuring service quality. The six steps are:
• Sorting and logging change
• Risk and impact studies
2. Change Evaluation
This process checks how well the changes will be applied before and after making them. These three steps are:
• Planning the evaluation
• Confirming what is expected to occur
3. Releases and Deployments Management
This procedure is in charge of allowing new software to be introduced in the business. Its purpose is basically to avoid such modifications affecting the existing systems negatively. The five steps are:
• Planning the release
• Release development and validation
4. Service Testing and Validation
This is the process of checking whether the service is sufficient before it starts. It also checks whether to use or improve the service. The six steps are:
• Planning and designing tests
• Checking test plans
5. Service Asset and Configuration Management
This procedure records all the significant items utilized to deliver IT services, such as computers, software, and files. These are referred to as configuration items (CIs). The five steps are:
• Process and planning management
• Identifying what is being tracked
6. Knowledge Management
This process gathers and organizes helpful information so users and technicians can repair problems more simply. The five steps are:
• Developing a knowledge sharing plan
• Browsing and gathering useful information
7. Transition Planning and Support
It assists in planning and organizing the introduction of new or altered services into daily use. Although it is not utilized daily, it is necessary when utilized. The four steps are:
• Creating a transition plan
•Preparing for the change
Service Operation
It is the fourth stage of the ITIL lifecycle. It runs services on a daily basis and maintains them in an optimal state. It aims to deliver value to customers while maintaining adaptability to evolving business requirements and technology. It consists of five significant processes:
1. Handling Incidents
This procedure corrects service issues in real-time. They can range from resetting passwords to fixing printer errors. The five steps are as follows:
• Classifying and recording the problem
• Setting its priority
2. Problem Management
This is a process which examines what failed and tries to prevent them from happening again. There are five steps:
• Problem identification and documentation
• Grouping it
3. Event Management
This process searches for incidents within the system and stops them from creating service problems. Incidents might originate from applications or other products. The five steps are:
• Seeing when something occurs
• Finding the event
4. Access Management
This procedure determines who is authorized to access the system. Only authorized personnel are allowed access. The five steps are:
• Receiving access requests
• Checking the request
5. Fulfilling Service Requests
This process manages all users' service requests. It can be for assistance, information, or access. There are five steps:
• Logging the request
• Checking if it’s valid
How to obtain ITIL certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion:
The ITIL guideline assists companies in managing their IT services more effectively through well-defined processes. Every phase of the ITIL lifecycle, from strategy to continuous improvement, plays a crucial role in delivering good, effective, and customer-focused services. Adhering to these phases enables companies to respond to evolving needs, reduce risks, and deliver greater value in the long run.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Key Steps and Aspects of Strategic Implementation
It is difficult to set new company objectives. Regardless of how great your staff is, you require a strategy to get everybody and every facility working together in a way to reach these new objectives. This is where strategy implementation comes in.
Implementing a strategy is a part of planning management. It considers how you are going to execute your plan by figuring out who does what, when, where, and how in an attempt to realize the objectives.
Why Strategy Implementation Matters
Putting a strategy into practice is important because it is about doing, not discussing. It persuades the team that the strategy can work. It also improves the team because everyone is engaged. Being successful needs good communication and proper tools.
Key Components of Strategy Execution
The principal constituents are:
• Integrated Process: Every aspect of executing the strategy works in conjunction with one another. For example, marketing efforts need to occur in proper order and complement one another.
• Action Focus: Action must be taken on a plan. This is accomplished through planning and organizing. Managers not only plan but also ensure plans are implemented.
• Various Skills: Implementation of strategy requires numerous skills such as knowledge, good attitude, and organizing. These skills assist in utilizing resources, creating rules, and establishing teams.
• Team Work: All members of the organization are involved. Leaders at every level define the plan in a way that all can understand and no one gets confused.
• Broad Range: It comprises numerous tasks. For instance, in order to implement a marketing strategy, you need to establish a budget, do market research, create ad plans, test the product, introduce it, and receive customer feedback.

How Strategy Implementation Functions
After you have a project or goal, strategy implementation illustrates how you can execute your plan. Strategy implementation assists you in figuring out what to utilize, what policies to enact, and who will assist you in completing the work.
As an administration, consider the following:
• Are we equipped with the appropriate skills and experience to ensure this plan works?
•Do we have sufficient time and funds to do it?
• Is our management ready for open communication and regular meetings?
• Do we possess the technology to achieve our objectives?
• Before you start, review your plan and make sure your team is well equipped to bring it to fruition.
Key Elements of Strategy Implementation
Having the plan and executing it complement one another. These serve to make the plan function effectively:
• Encourage a supportive company culture and working environment that supports the plan. If you reward and motivate employees, the plan is more effective.
• Use a skilled labor pool to perform different aspects of the plan.
• Enhance communication so that all receive the support and information needed.
• Create rules or protocols to enable teams to achieve their objectives.
• Establish a defined budget and bring in the required funds for the plan.

Everyone has to be involved in strategy implementation. Management drives the project, and the teams implement the work. Make sure the appropriate systems and structure enable the teams to work effectively. Employees need to know their roles, their immediate managers, as well as the tools available to assist them.
7 Must Steps to Execute Strategy
1. Set Goals
Ensure that goals are specific and attainable. Ensure that goals are attainable with the available resources and time. Define if goals are for the entire company or for specific teams. Define any possible challenges that may occur and take necessary measures in advance.
2. Choose Roles
Inform the team of the plan. Explain what each group will do and tell them the steps that everyone will have to follow.
3. Assign Tasks
Delegate work to team members. Each must know the over-riding goal and how their assignment helps achieve it. Exchange deadlines to maintain the project on track.
4. Work and Monitor Progress
Begin executing the plan. Provide all the required things to everyone. Monitor from time to time to evaluate the progress and solve any problem.
5. Change and Improve
When something goes awry, change your plan if it's necessary. Notify your stakeholders and your team. Flexibility is what makes the project shine.
6. Finish the Job
Verify that the task is running according to schedule and no further help is required. Notify everyone regarding important updates or setbacks.
7. Look Back and Learn
Finally, reflect on how the plan went. Consider what worked and what did not. Use those experiences to make it better the next time.
Strategies for Effective Implementation of a Strategy
A team can complete their work quicker and know more about the company and project if they employ an efficient approach. Some recommendations are as follows:
• Keep Communication Clear
Use technology such as text messaging programs or project software to stay in contact. Be available to ask questions or brainstorm by having open office hours or email.
• Give the Right Tools
Your intuition won't do it if your team isn't also prepared with the right tools. Make sure that your team is prepared with the requisite tools to continue and succeed in achieving the goal.
• Be honest
You need to be truthful, not only to your team but even to yourself. Honesty at work benefits everyone and strengthens the team. It creates trust among the members of the team. Analyze your team's issues objectively and provide real feedback on the issue.
• Make Things Clear
Clear goals and plans are crucial for a strategy to be effective. When people are aware of what is expected of them, their roles, objectives, and how to attain them, they are able to work more effectively and efficiently.
• Provide Help
A support group pools all their knowledge to address problems in a timely manner. Members should be encouraged to assist each other by talking openly and showing them what it is like to have good support.

How to obtain certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
Successful execution of strategies requires precise goals, honest cooperation, and strong support. By taking required actions and using the right tools, organizations can implement their plans easily. Familiarity with these strategies will help you improve, and with the support of iCert Global, you can learn how to implement strategies for real success.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
It is difficult to set new company objectives. Regardless of how great your staff is, you require a strategy to get everybody and every facility working together in a way to reach these new objectives. This is where strategy implementation comes in.
Implementing a strategy is a part of planning management. It considers how you are going to execute your plan by figuring out who does what, when, where, and how in an attempt to realize the objectives.
Why Strategy Implementation Matters
Putting a strategy into practice is important because it is about doing, not discussing. It persuades the team that the strategy can work. It also improves the team because everyone is engaged. Being successful needs good communication and proper tools.
Key Components of Strategy Execution
The principal constituents are:
• Integrated Process: Every aspect of executing the strategy works in conjunction with one another. For example, marketing efforts need to occur in proper order and complement one another.
• Action Focus: Action must be taken on a plan. This is accomplished through planning and organizing. Managers not only plan but also ensure plans are implemented.
• Various Skills: Implementation of strategy requires numerous skills such as knowledge, good attitude, and organizing. These skills assist in utilizing resources, creating rules, and establishing teams.
• Team Work: All members of the organization are involved. Leaders at every level define the plan in a way that all can understand and no one gets confused.
• Broad Range: It comprises numerous tasks. For instance, in order to implement a marketing strategy, you need to establish a budget, do market research, create ad plans, test the product, introduce it, and receive customer feedback.
How Strategy Implementation Functions
After you have a project or goal, strategy implementation illustrates how you can execute your plan. Strategy implementation assists you in figuring out what to utilize, what policies to enact, and who will assist you in completing the work.
As an administration, consider the following:
• Are we equipped with the appropriate skills and experience to ensure this plan works?
•Do we have sufficient time and funds to do it?
• Is our management ready for open communication and regular meetings?
• Do we possess the technology to achieve our objectives?
• Before you start, review your plan and make sure your team is well equipped to bring it to fruition.
Key Elements of Strategy Implementation
Having the plan and executing it complement one another. These serve to make the plan function effectively:
• Encourage a supportive company culture and working environment that supports the plan. If you reward and motivate employees, the plan is more effective.
• Use a skilled labor pool to perform different aspects of the plan.
• Enhance communication so that all receive the support and information needed.
• Create rules or protocols to enable teams to achieve their objectives.
• Establish a defined budget and bring in the required funds for the plan.
Everyone has to be involved in strategy implementation. Management drives the project, and the teams implement the work. Make sure the appropriate systems and structure enable the teams to work effectively. Employees need to know their roles, their immediate managers, as well as the tools available to assist them.
7 Must Steps to Execute Strategy
1. Set Goals
Ensure that goals are specific and attainable. Ensure that goals are attainable with the available resources and time. Define if goals are for the entire company or for specific teams. Define any possible challenges that may occur and take necessary measures in advance.
2. Choose Roles
Inform the team of the plan. Explain what each group will do and tell them the steps that everyone will have to follow.
3. Assign Tasks
Delegate work to team members. Each must know the over-riding goal and how their assignment helps achieve it. Exchange deadlines to maintain the project on track.
4. Work and Monitor Progress
Begin executing the plan. Provide all the required things to everyone. Monitor from time to time to evaluate the progress and solve any problem.
5. Change and Improve
When something goes awry, change your plan if it's necessary. Notify your stakeholders and your team. Flexibility is what makes the project shine.
6. Finish the Job
Verify that the task is running according to schedule and no further help is required. Notify everyone regarding important updates or setbacks.
7. Look Back and Learn
Finally, reflect on how the plan went. Consider what worked and what did not. Use those experiences to make it better the next time.
Strategies for Effective Implementation of a Strategy
A team can complete their work quicker and know more about the company and project if they employ an efficient approach. Some recommendations are as follows:
• Keep Communication Clear
Use technology such as text messaging programs or project software to stay in contact. Be available to ask questions or brainstorm by having open office hours or email.
• Give the Right Tools
Your intuition won't do it if your team isn't also prepared with the right tools. Make sure that your team is prepared with the requisite tools to continue and succeed in achieving the goal.
• Be honest
You need to be truthful, not only to your team but even to yourself. Honesty at work benefits everyone and strengthens the team. It creates trust among the members of the team. Analyze your team's issues objectively and provide real feedback on the issue.
• Make Things Clear
Clear goals and plans are crucial for a strategy to be effective. When people are aware of what is expected of them, their roles, objectives, and how to attain them, they are able to work more effectively and efficiently.
• Provide Help
A support group pools all their knowledge to address problems in a timely manner. Members should be encouraged to assist each other by talking openly and showing them what it is like to have good support.
How to obtain certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
Successful execution of strategies requires precise goals, honest cooperation, and strong support. By taking required actions and using the right tools, organizations can implement their plans easily. Familiarity with these strategies will help you improve, and with the support of iCert Global, you can learn how to implement strategies for real success.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
5 Vital Functions of ITIL Service Strategy
ITIL means Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is a set of simple rules that help software and IT workers provide the best service they can. These rules were made by observing and learning from successful methods over time.
What are ITIL processes?
ITIL contains several processes, which make it easy to implement in different companies. ITIL processes contain clear steps, where things go in, things get done, and things come out.
1. Service Strategy
This is the initial step of the ITIL process. This assists the companies in knowing what their goal is and how to achieve it. Through the evaluation of the market and what they want, they can plan the services appropriately.
There are five primary processes in this phase:
• Service Portfolio Management
This encapsulates all the IT services the company provides. It ensures the services are aligned with the business objectives.
• Financial Management
This takes care of the money part, like making budgets, keeping records, and sending bills.
• Managing Strategy for IT Services
This looks at how IT services are performing in the market. The steps include looking at the market, creating a strategy, taking action, and checking the results.
• Demand Management
This takes into account what the consumer requires and to what extent. This allows the business to prepare for various levels of demand.
• Managing Business Relationships
This establishes positive relationships with customers. It is helpful to know customers' desires and to make sure their desires are met.

2. Services Design
This is the second process in the ITIL service lifecycle. In this stage, businesses plan and design the system, tools, and services they require to deliver the best experience to their customers. All—like rules of the service, technology, and infrastructure—is planned in detail to suit what the business and customers demand.
There are eight significant processes in this stage:
1. Service Level Management
This helps to set objectives for the way services should operate. It checks if the objectives were met and how to do better next time. It employs something referred to as Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to compare plans with reality.
2. Service Catalog Management
This has an updated list of all the IT services a business offers. It makes it simple for users to find the services they need.
3. Capacity Management
This is how systems operate and can accomplish all of the things that they have to accomplish. Activities included are keeping an eye on performance, searching for issues, repairing things, building schedules, and optimizing.
4. Availability Management
This guarantees the services are always available when customers need them. It considers how frequently the services operate, monitors issues, and provides for avoiding downtime.
5. IT Service Continuity Management
This enables services to operate even when issues or crises exist. It protects the business and enables it to continue operating.
6. Information Security Management
This safeguards the information, systems, and users of the company. It includes identifying risks, setting rules, using equipment for safety, and looking for risks.
7. Supplier Management
This procedure tests the performance of the outside suppliers (vendors). It holds them accountable to agreements and deliver as they agreed. The steps include identifying what is required, verifying the suppliers, selecting the best ones, tracking their performance, and renewing or terminating agreements.
8. Design Coordination
This ensures that the designing process is properly planned and executed. It confirms that the design is suitable for the needs of the company.

3. Service Transition
This is the third stage in the ITIL service lifecycle. During this stage, companies ensure that when they launch new services or execute change, everything continues to function optimally. It is used to minimize risks and make change simpler for all.
There are seven key processes in this phase:
1. Managing Change
This process assists in controlling changes safely and in a sequential manner. It makes services resilient and flexible as business conditions vary.
2. Change Evaluation
This is a trial of how something will work before it happens. It also compares what was supposed to happen with what happened.
3. Release and Deployment Management
This procedure is responsible for installing new software or updates into operation. It attempts to minimize issues when it makes changes.
4. Service Testing and Validation
This verifies if a new change or service functions as intended.
5. Service Asset and Configuration Management
This process monitors all parts of the IT service—like who they are owned by, how they relate to each other, and their history. These parts are known as configuration items (CIs).
6. Knowledge Management
This stores useful information so that the employees and clients can quickly resolve issues.
7. Planning and Assistance for Change
This is the task of getting ready to implement a new or revised service. It is used to put everything in place to make the change go smoothly.

4. Service Operations
This is the fourth stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. It assists in the management of the day-to-day delivery of IT services. The primary goal is to deliver value to customers and stay in line with evolving business requirements and new technology.
5. Continuous Service Improvement (CSI)
This is the last phase in the ITIL cycle. It is all about making IT services better with time. This phase considers past information to determine what is right and what should be altered.
What are ITIL process standards in day-to-day life?
If you wish to implement ITIL in your organization, you first need to know how it works. There are numerous training courses and certification programs that can assist you and your team in learning how to implement ITIL at work.
How to obtain ITIL certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
ITIL training and deployment enable organizations to improve their IT services in stages. With the proper tools, training, and collaboration, your business can fix problems faster and better serve customers. To improve your IT abilities and better understand service management, consider enrolling in the ITIL training courses provided by iCert Global.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
ITIL means Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is a set of simple rules that help software and IT workers provide the best service they can. These rules were made by observing and learning from successful methods over time.
What are ITIL processes?
ITIL contains several processes, which make it easy to implement in different companies. ITIL processes contain clear steps, where things go in, things get done, and things come out.
1. Service Strategy
This is the initial step of the ITIL process. This assists the companies in knowing what their goal is and how to achieve it. Through the evaluation of the market and what they want, they can plan the services appropriately.
There are five primary processes in this phase:
• Service Portfolio Management
This encapsulates all the IT services the company provides. It ensures the services are aligned with the business objectives.
• Financial Management
This takes care of the money part, like making budgets, keeping records, and sending bills.
• Managing Strategy for IT Services
This looks at how IT services are performing in the market. The steps include looking at the market, creating a strategy, taking action, and checking the results.
• Demand Management
This takes into account what the consumer requires and to what extent. This allows the business to prepare for various levels of demand.
• Managing Business Relationships
This establishes positive relationships with customers. It is helpful to know customers' desires and to make sure their desires are met.
2. Services Design
This is the second process in the ITIL service lifecycle. In this stage, businesses plan and design the system, tools, and services they require to deliver the best experience to their customers. All—like rules of the service, technology, and infrastructure—is planned in detail to suit what the business and customers demand.
There are eight significant processes in this stage:
1. Service Level Management
This helps to set objectives for the way services should operate. It checks if the objectives were met and how to do better next time. It employs something referred to as Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to compare plans with reality.
2. Service Catalog Management
This has an updated list of all the IT services a business offers. It makes it simple for users to find the services they need.
3. Capacity Management
This is how systems operate and can accomplish all of the things that they have to accomplish. Activities included are keeping an eye on performance, searching for issues, repairing things, building schedules, and optimizing.
4. Availability Management
This guarantees the services are always available when customers need them. It considers how frequently the services operate, monitors issues, and provides for avoiding downtime.
5. IT Service Continuity Management
This enables services to operate even when issues or crises exist. It protects the business and enables it to continue operating.
6. Information Security Management
This safeguards the information, systems, and users of the company. It includes identifying risks, setting rules, using equipment for safety, and looking for risks.
7. Supplier Management
This procedure tests the performance of the outside suppliers (vendors). It holds them accountable to agreements and deliver as they agreed. The steps include identifying what is required, verifying the suppliers, selecting the best ones, tracking their performance, and renewing or terminating agreements.
8. Design Coordination
This ensures that the designing process is properly planned and executed. It confirms that the design is suitable for the needs of the company.
3. Service Transition
This is the third stage in the ITIL service lifecycle. During this stage, companies ensure that when they launch new services or execute change, everything continues to function optimally. It is used to minimize risks and make change simpler for all.
There are seven key processes in this phase:
1. Managing Change
This process assists in controlling changes safely and in a sequential manner. It makes services resilient and flexible as business conditions vary.
2. Change Evaluation
This is a trial of how something will work before it happens. It also compares what was supposed to happen with what happened.
3. Release and Deployment Management
This procedure is responsible for installing new software or updates into operation. It attempts to minimize issues when it makes changes.
4. Service Testing and Validation
This verifies if a new change or service functions as intended.
5. Service Asset and Configuration Management
This process monitors all parts of the IT service—like who they are owned by, how they relate to each other, and their history. These parts are known as configuration items (CIs).
6. Knowledge Management
This stores useful information so that the employees and clients can quickly resolve issues.
7. Planning and Assistance for Change
This is the task of getting ready to implement a new or revised service. It is used to put everything in place to make the change go smoothly.
4. Service Operations
This is the fourth stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. It assists in the management of the day-to-day delivery of IT services. The primary goal is to deliver value to customers and stay in line with evolving business requirements and new technology.
5. Continuous Service Improvement (CSI)
This is the last phase in the ITIL cycle. It is all about making IT services better with time. This phase considers past information to determine what is right and what should be altered.
What are ITIL process standards in day-to-day life?
If you wish to implement ITIL in your organization, you first need to know how it works. There are numerous training courses and certification programs that can assist you and your team in learning how to implement ITIL at work.
How to obtain ITIL certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
ITIL training and deployment enable organizations to improve their IT services in stages. With the proper tools, training, and collaboration, your business can fix problems faster and better serve customers. To improve your IT abilities and better understand service management, consider enrolling in the ITIL training courses provided by iCert Global.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Essential ITSM Tools and Software for 2025
IT Service Management (ITSM) is a method of aligning business processes with IT services. The primary focus is to ensure that IT operations and services support business objectives to expand and prosper.
There is a multitude of IT service management software tools available and that can complicate the decision-making process. Below is a list of some of the industry's best ITSM software, including common features and some of the most recent download links. This is a compilation of FREE (open source) and PAID (commercial) ITSM software.What Is Information Technology Service Management (ITSM)?
What to look for in ITSM Tools ?
What should IT service management software contain? If you are an IT manager ensure that the ITSM tools have substance with the designed ability to support ITIL Service Operation and ITIL Continual Service Improvement. These are the supported anchors that further assist you in your day to day work responsibilities.

13 Best ITSM Tools and Software
What is ITSM software? Let's check out some of the best ITSM tools that can help you manage IT services.
1. SolarWinds Service Desk
SolarWinds Service Desk is a tool that helps manage help desks and IT services. It works in the cloud and helps businesses keep track of their assets and tasks.
2. Atera Helpdesk Software
Atera Helpdesk Software assists you in monitoring and maintaining IT systems. It is constantly searching for problems and is able to send alerts to the support personnel.
3. SuperOps Service Desk
SuperOps Service Desk is a tool that helps manage IT support teams, especially for companies that use or provide IT services. It can also assist with projects and tasks.
4. NinjaOne
NinjaOne is a cloud based way to manage your IT systems. NinjaOne keeps your support teams in-the-loop with everything without requiring them to be in the office.
5. ManageEngine ServiceDesk
Plus ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus is an IT Service Desk and a database capability for handling things like service requests, maintenance, and contracts for customers. Additionally, ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus is good for managing IT assets including equipment and software.

6. N-able N-sight
N-able N-sight is intended to help organizations monitor and manage IT systems. Using N-able N-sight companies can gain a comprehensive look at their clients IT needs, and keep track of every operation required to manage them.
7. Freshservice
Freshservice is an online tool that helps IT teams and service companies manage and solve tech problems easily. The platform is intuitive and has various levels for various needs.
8. ServiceNow
ServiceNow is a cloud-based IT service management system. ServiceNow helps track spending and handle IT requests in one place.
9. Alloy Navigator
Alloy Navigator has two options. The more expensive is Alloy Navigator Enterprise which has an entire ITSM feature set. If you don’t need the full set of ITSM features then you can purchase Alloy Navigator Express at a lower cost.
10. SysAid
SysAid is ITSM software that provides anything from a basic help desk to a full ITSM package. SysAid is cloud-based software or can be installed.
11. InvGate Service Desk
InvGate Service Desk is ITSM software compliant to ITIL and can be used either on-premise or in the cloud. It helps with handling problems, fixing issues, making changes, and completing requests.
12. Kaseya
Kaseya has tools for Managed Service Providers (MSPs) to manage IT service delivery. Kaseya VSA helps with remote monitoring and Kaseya BMS is an IT Operations solution that involves automation.
13. Vivantio
Vivantio is cloud based ITSM, in that it has 4 plans, and fits for organizations of any size and has different levels of complexity and the plans offer similar features.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
All in all, an ITSM is an important tool to help your organization meet the needs of users and businesses under your umbrella, but at the same time, it is important to choose the right solution. More importantly, find the best solution that meets your future business and organizational needs. Selecting the wrong solution will set your organization back a few years, so take your time to research before committing. Being an informed buyer will always help you in the end.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
IT Service Management (ITSM) is a method of aligning business processes with IT services. The primary focus is to ensure that IT operations and services support business objectives to expand and prosper.
There is a multitude of IT service management software tools available and that can complicate the decision-making process. Below is a list of some of the industry's best ITSM software, including common features and some of the most recent download links. This is a compilation of FREE (open source) and PAID (commercial) ITSM software.What Is Information Technology Service Management (ITSM)?
What to look for in ITSM Tools ?
What should IT service management software contain? If you are an IT manager ensure that the ITSM tools have substance with the designed ability to support ITIL Service Operation and ITIL Continual Service Improvement. These are the supported anchors that further assist you in your day to day work responsibilities.
13 Best ITSM Tools and Software
What is ITSM software? Let's check out some of the best ITSM tools that can help you manage IT services.
1. SolarWinds Service Desk
SolarWinds Service Desk is a tool that helps manage help desks and IT services. It works in the cloud and helps businesses keep track of their assets and tasks.
2. Atera Helpdesk Software
Atera Helpdesk Software assists you in monitoring and maintaining IT systems. It is constantly searching for problems and is able to send alerts to the support personnel.
3. SuperOps Service Desk
SuperOps Service Desk is a tool that helps manage IT support teams, especially for companies that use or provide IT services. It can also assist with projects and tasks.
4. NinjaOne
NinjaOne is a cloud based way to manage your IT systems. NinjaOne keeps your support teams in-the-loop with everything without requiring them to be in the office.
5. ManageEngine ServiceDesk
Plus ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus is an IT Service Desk and a database capability for handling things like service requests, maintenance, and contracts for customers. Additionally, ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus is good for managing IT assets including equipment and software.
6. N-able N-sight
N-able N-sight is intended to help organizations monitor and manage IT systems. Using N-able N-sight companies can gain a comprehensive look at their clients IT needs, and keep track of every operation required to manage them.
7. Freshservice
Freshservice is an online tool that helps IT teams and service companies manage and solve tech problems easily. The platform is intuitive and has various levels for various needs.
8. ServiceNow
ServiceNow is a cloud-based IT service management system. ServiceNow helps track spending and handle IT requests in one place.
9. Alloy Navigator
Alloy Navigator has two options. The more expensive is Alloy Navigator Enterprise which has an entire ITSM feature set. If you don’t need the full set of ITSM features then you can purchase Alloy Navigator Express at a lower cost.
10. SysAid
SysAid is ITSM software that provides anything from a basic help desk to a full ITSM package. SysAid is cloud-based software or can be installed.
11. InvGate Service Desk
InvGate Service Desk is ITSM software compliant to ITIL and can be used either on-premise or in the cloud. It helps with handling problems, fixing issues, making changes, and completing requests.
12. Kaseya
Kaseya has tools for Managed Service Providers (MSPs) to manage IT service delivery. Kaseya VSA helps with remote monitoring and Kaseya BMS is an IT Operations solution that involves automation.
13. Vivantio
Vivantio is cloud based ITSM, in that it has 4 plans, and fits for organizations of any size and has different levels of complexity and the plans offer similar features.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
All in all, an ITSM is an important tool to help your organization meet the needs of users and businesses under your umbrella, but at the same time, it is important to choose the right solution. More importantly, find the best solution that meets your future business and organizational needs. Selecting the wrong solution will set your organization back a few years, so take your time to research before committing. Being an informed buyer will always help you in the end.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Top Highest-Paying Programming Languages to Learn in 2025
The tech industry is changing fast, so staying ahead is key to boosting your earnings. Knowing the right programming languages can lead to high-paying jobs in 2025 and later. In this article, we’ll look at the top programming languages that are in demand. We’ll cover their main uses and the industries that value these skills the most. Let’s dive in!
Why Choosing the Right Programming Language Matters
Some programming languages are better than others. Companies are ready to pay extra for developers who focus on these languages. To future-proof your career and increase your earnings, focus on languages that are in demand now and are expected to grow in the future.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the top programming languages that can help you earn the big bucks in 2025.
5. Kotlin: The Go-To Language for Android Development
Key Uses & Industries
Kotlin is the official language for Android app development. It is used by top companies such as Google, Netflix, and Uber to create mobile applications. Its seamless fit with Android and its role in boosting developer productivity make it a desired language.
Why Kotlin Pays Well
Kotlin is ideal for building robust and scalable mobile applications, which power some of the world’s most popular platforms. Companies in the mobile tech and app development space are actively hiring Kotlin developers for their expertise.
Salary Insights
Average salary for experienced Kotlin developers: $105,000+ per year.
If you’re interested in mobile development, Kotlin is your go-to choice. Its increasing popularity and endorsement from Google make it a top choice for Android app development. There are also many well-paying job opportunities.
4. Swift: The Language of iOS Development
Key Uses & Industries
Swift is the primary language for iOS app development and is widely used in industries like fintech, healthcare, and gaming for developing apps within the Apple ecosystem.
Why Swift Pays Well
Swift’s role in the Apple ecosystem makes it essential for creating high-quality, user-friendly apps. As iOS continues to dominate the mobile market, Swift developers are in high demand to create innovative apps across various industries.
Salary Insights
Average salary for experienced Swift developers: $115,000+ per year.
As Apple’s ecosystem keeps expanding, Swift developers are highly sought after for iOS app development. Swift runs smoothly and helps developers make great apps. This makes it a smart choice for earning money in mobile development.
3. Python: The High-Demand Language Powering AI & Automation
Key Uses & Industries
Python is a versatile programming language widely used in AI, data science, web development, and automation. Industries like finance, healthcare, and machine learning rely on Python for its efficiency and extensive libraries, including TensorFlow, Pandas, and Flask.
Why Python Pays Well
Python’s role in AI, automation, and big data drives high demand. Companies like Google, Tesla, and Amazon use Python to develop scalable solutions. As automation and AI adoption grow, so does the need for Python experts.
Salary Insights
Entry-level: $80,000−$80,000−$100,000
Mid-level: $100,000−$100,000−$130,000
Senior/AI-focused: $120,000+
With remote and freelance opportunities, skilled Python developers can further increase their earnings.
If you’re interested in AI, automation, or finance, Python is a must-learn. Its broad applicability and future-proof demand make it one of the top-paying languages today.
2. Go (Golang): The Powerhouse Behind Cloud Computing & Backend Development
Key Uses & Industries
Go, also known as Golang, was created by Google to handle large-scale computing efficiently. It is widely used in cloud computing, DevOps, and backend development. Companies like Google, Dropbox, and Uber rely on Go for their backend infrastructure.
Why Go Pays Well
Go’s efficiency makes it perfect for cloud-native applications and large-scale backend systems. As more businesses shift to distributed computing and containerised applications, Go developers are in high demand.
Salary Insights
Entry-level: $90,000–$90,000–$110,000
Mid-level: $110,000−$110,000−$140,000
Senior/Cloud-focused: $130,000+
With remote work and freelance opportunities, Go developers can maximise their earnings.
Want to work with cloud-native applications or backend development? Then learning Go is a great investment. Its efficiency and growing demand in critical infrastructure make it a top contender for high-paying roles.
1. Rust: The Secure and High-Performance Language for System Programming
Key Uses and Industries
Developers love Rust because it is memory safe, fast, and reliable. This makes it a top pick for system programming. It has extensive applications in cybersecurity, embedded systems, and blockchain development. Mozilla, Microsoft, and many blockchain startups use Rust. They build systems that are both efficient and safe.
Why Rust Pays Well
Rust is fast and safe. This makes it vital in industries where security and performance matter most. It's becoming popular in blockchain, cryptography, and Web3. This is because it can create secure and efficient smart contracts.
Salary Insights
Entry-level: $100,000–$120,000
Mid-level: $120,000–$150,000
Senior/Blockchain-focused: $140,000+
Demand for cybersecurity and blockchain is rising. Rust developers have got excellent job options and can work from home.
Rust is gaining popularity for high-performance applications. Developers who know Rust are in great demand. Its focus on security and performance makes it a strong choice for good, future-proof jobs.
Honourable Mentions: More High-Paying Tech Languages
1. C++ – Powering Games & High-Performance Computing
C++ is a go-to language for game development and high-performance computing. It’s used in places where speed and efficiency are key, like video games, real-time systems, and finance.
2. SQL – The Backbone of Data Management
SQL is essential for data analytics and database management. Industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce use it a lot for large data sets.
3. Solidity – The language of smart contracts
Solidity is used for developing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It is crucial in blockchain, DeFi (Decentralised Finance), and cryptocurrency platforms.
These languages also offer excellent earning potential, especially in fields like gaming, blockchain, and data engineering. Mastering one of these can unlock some of the most exciting and high-paying opportunities in tech today!
How to Get Started & Maximise Your Earnings
1. Take online courses.
Enroll in online courses to build a strong foundation in your chosen languages.
2. Build real-world projects.
Start building real-world projects that demonstrate your abilities. Showcase these projects on GitHub. This way, potential employers and clients can view your online portfolio.
3. Contribute to open-source projects
Contribute to open-source projects to gain practical experience and strengthen your résumé. It’s a great way to learn from experienced developers while making valuable contributions to the community.
4. Network on LinkedIn and GitHub.
Build a strong network on LinkedIn and GitHub to connect with industry professionals and recruiters. Engage with communities, share your projects, and seek advice from experienced developers.
5. Freelance or do internships.
Take on freelance projects or internships to gain hands-on experience and build your portfolio. Real-world experience will give you the practical skills that employers are looking for.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
The tech industry is changing fast, so staying ahead is key to boosting your earnings. Knowing the right programming languages can lead to high-paying jobs in 2025 and later. In this article, we’ll look at the top programming languages that are in demand. We’ll cover their main uses and the industries that value these skills the most. Let’s dive in!
Why Choosing the Right Programming Language Matters
Some programming languages are better than others. Companies are ready to pay extra for developers who focus on these languages. To future-proof your career and increase your earnings, focus on languages that are in demand now and are expected to grow in the future.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the top programming languages that can help you earn the big bucks in 2025.
5. Kotlin: The Go-To Language for Android Development
Key Uses & Industries
Kotlin is the official language for Android app development. It is used by top companies such as Google, Netflix, and Uber to create mobile applications. Its seamless fit with Android and its role in boosting developer productivity make it a desired language.
Why Kotlin Pays Well
Kotlin is ideal for building robust and scalable mobile applications, which power some of the world’s most popular platforms. Companies in the mobile tech and app development space are actively hiring Kotlin developers for their expertise.
Salary Insights
Average salary for experienced Kotlin developers: $105,000+ per year.
If you’re interested in mobile development, Kotlin is your go-to choice. Its increasing popularity and endorsement from Google make it a top choice for Android app development. There are also many well-paying job opportunities.
4. Swift: The Language of iOS Development
Key Uses & Industries
Swift is the primary language for iOS app development and is widely used in industries like fintech, healthcare, and gaming for developing apps within the Apple ecosystem.
Why Swift Pays Well
Swift’s role in the Apple ecosystem makes it essential for creating high-quality, user-friendly apps. As iOS continues to dominate the mobile market, Swift developers are in high demand to create innovative apps across various industries.
Salary Insights
Average salary for experienced Swift developers: $115,000+ per year.
As Apple’s ecosystem keeps expanding, Swift developers are highly sought after for iOS app development. Swift runs smoothly and helps developers make great apps. This makes it a smart choice for earning money in mobile development.
3. Python: The High-Demand Language Powering AI & Automation
Key Uses & Industries
Python is a versatile programming language widely used in AI, data science, web development, and automation. Industries like finance, healthcare, and machine learning rely on Python for its efficiency and extensive libraries, including TensorFlow, Pandas, and Flask.
Why Python Pays Well
Python’s role in AI, automation, and big data drives high demand. Companies like Google, Tesla, and Amazon use Python to develop scalable solutions. As automation and AI adoption grow, so does the need for Python experts.
Salary Insights
Entry-level: $80,000−$80,000−$100,000
Mid-level: $100,000−$100,000−$130,000
Senior/AI-focused: $120,000+
With remote and freelance opportunities, skilled Python developers can further increase their earnings.
If you’re interested in AI, automation, or finance, Python is a must-learn. Its broad applicability and future-proof demand make it one of the top-paying languages today.
2. Go (Golang): The Powerhouse Behind Cloud Computing & Backend Development
Key Uses & Industries
Go, also known as Golang, was created by Google to handle large-scale computing efficiently. It is widely used in cloud computing, DevOps, and backend development. Companies like Google, Dropbox, and Uber rely on Go for their backend infrastructure.
Why Go Pays Well
Go’s efficiency makes it perfect for cloud-native applications and large-scale backend systems. As more businesses shift to distributed computing and containerised applications, Go developers are in high demand.
Salary Insights
Entry-level: $90,000–$90,000–$110,000
Mid-level: $110,000−$110,000−$140,000
Senior/Cloud-focused: $130,000+
With remote work and freelance opportunities, Go developers can maximise their earnings.
Want to work with cloud-native applications or backend development? Then learning Go is a great investment. Its efficiency and growing demand in critical infrastructure make it a top contender for high-paying roles.
1. Rust: The Secure and High-Performance Language for System Programming
Key Uses and Industries
Developers love Rust because it is memory safe, fast, and reliable. This makes it a top pick for system programming. It has extensive applications in cybersecurity, embedded systems, and blockchain development. Mozilla, Microsoft, and many blockchain startups use Rust. They build systems that are both efficient and safe.
Why Rust Pays Well
Rust is fast and safe. This makes it vital in industries where security and performance matter most. It's becoming popular in blockchain, cryptography, and Web3. This is because it can create secure and efficient smart contracts.
Salary Insights
Entry-level: $100,000–$120,000
Mid-level: $120,000–$150,000
Senior/Blockchain-focused: $140,000+
Demand for cybersecurity and blockchain is rising. Rust developers have got excellent job options and can work from home.
Rust is gaining popularity for high-performance applications. Developers who know Rust are in great demand. Its focus on security and performance makes it a strong choice for good, future-proof jobs.
Honourable Mentions: More High-Paying Tech Languages
1. C++ – Powering Games & High-Performance Computing
C++ is a go-to language for game development and high-performance computing. It’s used in places where speed and efficiency are key, like video games, real-time systems, and finance.
2. SQL – The Backbone of Data Management
SQL is essential for data analytics and database management. Industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce use it a lot for large data sets.
3. Solidity – The language of smart contracts
Solidity is used for developing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It is crucial in blockchain, DeFi (Decentralised Finance), and cryptocurrency platforms.
These languages also offer excellent earning potential, especially in fields like gaming, blockchain, and data engineering. Mastering one of these can unlock some of the most exciting and high-paying opportunities in tech today!
How to Get Started & Maximise Your Earnings
1. Take online courses.
Enroll in online courses to build a strong foundation in your chosen languages.
2. Build real-world projects.
Start building real-world projects that demonstrate your abilities. Showcase these projects on GitHub. This way, potential employers and clients can view your online portfolio.
3. Contribute to open-source projects
Contribute to open-source projects to gain practical experience and strengthen your résumé. It’s a great way to learn from experienced developers while making valuable contributions to the community.
4. Network on LinkedIn and GitHub.
Build a strong network on LinkedIn and GitHub to connect with industry professionals and recruiters. Engage with communities, share your projects, and seek advice from experienced developers.
5. Freelance or do internships.
Take on freelance projects or internships to gain hands-on experience and build your portfolio. Real-world experience will give you the practical skills that employers are looking for.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Essential Topics in ISO 20000 IT Service Management Training
One such critical standard is ISO/IEC 20000. It is the global standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). ISO 20000 certification shows an organization's commitment to best practices in service delivery. It boosts efficiency, customer satisfaction, and business continuity.
What is ISO 20000?
ISO/IEC 20000 is an international standard for IT service management. The standard aims to make IT services efficient and reliable. It also ensures they meet business and customer needs.
The standard consists of two key parts:
- ISO/IEC 20000-1: It specifies the requirements for certification. An organization must fulfill them to get certified.
- ISO/IEC 20000-2: Offers guidelines and best practices for implementation.
Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification
ISO 20000 certification provides several advantages, including:
1. Enhanced Service Quality
ISO 20000 certification proves an organization follows best IT service management practices. These are globally recognized. This leads to consistent, high-quality service delivery, reducing errors, downtime, and service interruptions. Structured ITSM processes let organizations fix service issues and improve operations.
2. Increased Customer Satisfaction
Customer expectations for IT services are higher than ever. ISO 20000 certification ensures that services meet customers' needs and goals. It improves the customer experience. A structured approach to service management lets organizations provide fast, efficient support. This builds trust and long-term relationships with clients.
3. Operational Efficiency and Process Improvement
ISO 20000 certification drives operational efficiency by standardizing IT service management processes. Automated workflows, clear roles, and performance monitoring can help. They can optimize resources and reduce waste. This structured approach eliminates redundant processes and improves overall productivity.
4. Competitive Advantage
ISO 20000 certification gives organizations an edge in today's competitive market. ISO 20000 certification proves compliance with global ITSM standards. It helps attract new clients, retain existing ones, and expand business. Many government contracts and large firms require suppliers to have ISO 20000 certification. This certification opens new markets to those suppliers.
5. Regulatory and Legal Compliance
Many industries and government bodies have strict regulatory requirements for IT service management. ISO 20000 helps organizations meet legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations. It does this by ensuring their ITSM processes are structured and well-documented. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties and enhances the organization's credibility.
6. Improved Risk Management and Business Continuity
One of the core components of ISO 20000 is risk management. The certification ensures that organizations can identify and manage IT service risks. Organizations can reduce downtime by using incident management and recovery strategies. This helps ensure smooth operations during crises.
7. Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
ISO 20000 helps organizations. It optimizes IT resources, cuts costs, and improves budgets. Additionally, proactive problem management reduces costly downtime and service failures.
8. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
ISO 20000's ITSM framework improves collaboration between departments in an organization. Clear roles, responsibilities, and communication improve teamwork. They reduce misunderstandings and boost service coordination. This leads to a more cohesive and agile IT environment.
9. Continuous Improvement Culture
ISO 20000 promotes continuous improvement. It encourages organizations to monitor, review, and enhance their IT service management processes.
10. Better Supplier and Third-Party Management
Many organizations rely on third-party vendors for IT services. ISO 20000 certification ensures organizations have good processes for managing suppliers. This cuts risks with outsourced services. It ensures external providers meet service standards.
Who Should Attend ISO 20000 Training?
ISO 20000 training is suitable for a wide range of professionals, including:
- IT Service Managers
- IT Consultants
- IT Support and Operations Teams
- Quality and Process Managers
- Business Analysts
- IT Auditors
- Professionals looking to enhance their ITSM knowledge
Key Topics Covered in ISO 20000 Training
ISO 20000 IT Service Management (ITSM) Certification Training is for ITSM professionals. It provides a thorough learning experience. The goal is to understand and apply the ISO 20000 standard for IT service management. This training covers many essential topics. It will help professionals improve IT service management systems (ITSMS) in their organizations. Here is a detailed explanation of the key topics in ISO 20000 training programs.
1. Introduction to IT Service Management (ITSM) & ISO 20000
- A strong grasp of IT Service Management and ISO 20000 is key for certification. In this section, participants are introduced to:
- IT Service Management (ITSM) is a set of policies, processes, and procedures. Organizations use them to design, deliver, manage, and improve IT services for customers. ITSM aims to align IT services with the business and its customers. It seeks to deliver services that are efficient, cost-effective, and high-quality.
- ISO/IEC 20000 Framework: ISO 20000 offers a framework for IT service management. It outlines what an organization must do to set up, run, monitor, review, and improve its ITSMS. We must understand how ISO 20000 helps organizations. It provides reliable, consistent, high-quality IT services.
- ISO 20000 Certification shows an org's commitment to IT service management best practices. Participants learn this. ISO 20000 certification proves that an organization's IT services meet global standards. It improves customer satisfaction, efficiency, and risk management.
2. Overview of ISO 20000 Requirements
- The ISO 20000 standard has many requirements. An organization must implement them to get certified. These include:
- ISO 20000-1: This part lists the requirements for certification. It focuses on setting up an ITSMS. This includes managing resources, processes, and ongoing improvement efforts.
- ISO 20000-2: It provides extra guidelines for implementing an ITSMS. These are based on the requirements in ISO 20000-1. ISO 20000-2 helps organizations customize the framework to their needs. It guides them on the best practices for certification.
It's vital to know the link between ISO 20000-1 and ISO 20000-2. This knowledge is key to creating an ITSMS that meets international standards.
3. Planning and Implementing an IT Service Management System (ITSMS)
A key part of ISO 20000 training is to learn to develop and implement an IT Service Management System (ITSMS). This process involves several key steps:
- Service Design: This is about planning and designing IT services. They must align with customer needs and business goals. Effective service design includes three steps. First, define service objectives. Next, identify service requirements. Lastly, establish the necessary resources and processes.
- Service Transition: The process of transitioning IT services from development to operation. This includes testing and validating services for deployment. Do this with minimal disruption to business operations.
- Service Delivery and Support: This section covers the management of IT services. This includes incident management, problem management, and service desk operations.
- Service Improvement: ISO 20000 training emphasizes the importance of continuous service improvement. The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle helps organizations track performance. It lets them find areas needing improvement. Then, they can make changes to improve service delivery and ITSM processes.
4. Service Management System (SMS) Processes
- ISO 20000 certification requires an organization to implement key processes. They ensure IT services are managed effectively. In training, professionals gain in-depth knowledge of these key processes:
- Service Level Management: This process defines, negotiates, and manages service level agreements (SLAs). It ensures IT services meet agreed-upon performance levels. ISO 20000 training teaches pros to monitor and report on service performance. It helps them manage customer expectations and improve service delivery using feedback.
- Incident and Problem Management: These processes work together. They aim to fix service disruptions and stop issues from happening again.
- Incident management fixes service interruptions quickly and efficiently. Problem management finds and removes root causes to prevent future incidents.
- This minimizes disruptions to service.
- Capacity and Availability Management: They help IT services meet demand and stay online. Capacity management helps organizations plan for future demand. Availability management aims to maximize service uptime and minimize downtime. It does this through proactive monitoring and planning.
- ISO 20000 stresses the need for disaster recovery and business continuity planning. This ensures IT services stay operational during a crisis.
5. ISO 20000 Certification Process
The ISO 20000 training program covers the steps to gain and keep certification. These steps include:
- Achieving Certification: Participants learn the process for applying for ISO 20000 certification. ISO 20000 training must cover audits, both internal and external.
- Continuous Improvement Strategies: ISO 20000 certification is not a one-time process. It's a commitment to continuous improvement. ISO 20000 training teaches how to create improvement strategies. They ensure IT service management processes are regularly reviewed and improved. This is based on performance data and changing business needs.
6. Roles and Responsibilities in ITSM
ISO 20000 training highlights the key responsibilities associated with these roles, including:
- Leadership Commitment: Top management is key to ITSM's success. Training helps professionals learn to secure leadership support. It's vital for implementing ISO 20000.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involving different stakeholders is crucial. This includes service owners, process owners, and vendors. This ensures the ITSMS aligns with business goals and customer needs. The training covers how to communicate with and manage these stakeholders effectively.
7. ISO 20000 Audit and Compliance
- ISO 20000 training also covers how to prepare for audits and keep your certification.
- Preparing for Internal Audits: Internal audits are essential for compliance with ISO 20000. Training provides strategies for effective auditing, including audit planning, execution, and reporting.
- Ensuring Compliance and Maintaining Certification ISO 20000 certification needs to be renewed periodically. This training ensures professionals can comply with the standard and its updates.
- ISO 20000 IT Service Management: Certification Training covers a wide range of topics. It trains pros to implement and manage IT service management systems. They must meet global standards.
Types of ISO 20000 Training
ISO 20000 training comes in various formats to meet diverse learning needs.
- Foundation Training: Covers the basics of ISO 20000 and ITSM principles.
- Lead Implementer Training: Focuses on implementing and managing an ITSMS.
- Lead Auditor Training: Prepares professionals to conduct internal and external audits.
- Self-paced Online Courses: Flexible learning options for busy professionals.
- Instructor-led Training: Classroom or virtual training with expert guidance.
Steps to Achieve ISO 20000 Certification
Organizations seeking ISO 20000 certification should follow these steps:
- Understand ISO 20000 Requirements
- Gain knowledge through training and certification programs.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis
- Identify current ITSM gaps and areas for improvement.
- Develop an Implementation Plan
- Define ITSMS objectives, policies, and procedures.
- Implement ITSM Processes
- Establish service management practices and align with business goals.
- Train Employees
- Ensure staff members understand and adhere to ITSMS guidelines.
- Perform Internal Audits
- Conduct internal audits to assess readiness.
- Undergo External Audit
- Get audited by a certified body for official certification.
- Maintain and Continuously Improve ITSMS
- Monitor, review, and enhance IT service management practices.
Choosing the Right ISO 20000 Training Provider
Selecting a reputable training provider is crucial for successful certification. Consider the following when choosing a provider:
- Accreditation: Ensure the provider is accredited by recognized certification bodies.
- Course Content: Verify that the training covers all essential aspects of ISO 20000.
- Trainer Expertise: Look for experienced instructors with industry knowledge.
- Learning Format: Choose between online, classroom, or blended learning.
- Reviews and Testimonials: Check feedback from past learners.
- Post-training Support: Opt for providers offering post-training resources.
How to obtain ISO 20000 IT Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
ISO 20000 IT Service Management Certification Training is a great investment. It helps IT pros and organizations improve service quality, efficiency, and compliance. With the right training and approach, organizations can get certified. They can also improve IT service management.
It's a step in the right direction. Start your journey today. Gain the knowledge to excel in IT service management!
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
One such critical standard is ISO/IEC 20000. It is the global standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). ISO 20000 certification shows an organization's commitment to best practices in service delivery. It boosts efficiency, customer satisfaction, and business continuity.
What is ISO 20000?
ISO/IEC 20000 is an international standard for IT service management. The standard aims to make IT services efficient and reliable. It also ensures they meet business and customer needs.
The standard consists of two key parts:
- ISO/IEC 20000-1: It specifies the requirements for certification. An organization must fulfill them to get certified.
- ISO/IEC 20000-2: Offers guidelines and best practices for implementation.
Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification
ISO 20000 certification provides several advantages, including:
1. Enhanced Service Quality
ISO 20000 certification proves an organization follows best IT service management practices. These are globally recognized. This leads to consistent, high-quality service delivery, reducing errors, downtime, and service interruptions. Structured ITSM processes let organizations fix service issues and improve operations.
2. Increased Customer Satisfaction
Customer expectations for IT services are higher than ever. ISO 20000 certification ensures that services meet customers' needs and goals. It improves the customer experience. A structured approach to service management lets organizations provide fast, efficient support. This builds trust and long-term relationships with clients.
3. Operational Efficiency and Process Improvement
ISO 20000 certification drives operational efficiency by standardizing IT service management processes. Automated workflows, clear roles, and performance monitoring can help. They can optimize resources and reduce waste. This structured approach eliminates redundant processes and improves overall productivity.
4. Competitive Advantage
ISO 20000 certification gives organizations an edge in today's competitive market. ISO 20000 certification proves compliance with global ITSM standards. It helps attract new clients, retain existing ones, and expand business. Many government contracts and large firms require suppliers to have ISO 20000 certification. This certification opens new markets to those suppliers.
5. Regulatory and Legal Compliance
Many industries and government bodies have strict regulatory requirements for IT service management. ISO 20000 helps organizations meet legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations. It does this by ensuring their ITSM processes are structured and well-documented. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties and enhances the organization's credibility.
6. Improved Risk Management and Business Continuity
One of the core components of ISO 20000 is risk management. The certification ensures that organizations can identify and manage IT service risks. Organizations can reduce downtime by using incident management and recovery strategies. This helps ensure smooth operations during crises.
7. Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
ISO 20000 helps organizations. It optimizes IT resources, cuts costs, and improves budgets. Additionally, proactive problem management reduces costly downtime and service failures.
8. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
ISO 20000's ITSM framework improves collaboration between departments in an organization. Clear roles, responsibilities, and communication improve teamwork. They reduce misunderstandings and boost service coordination. This leads to a more cohesive and agile IT environment.
9. Continuous Improvement Culture
ISO 20000 promotes continuous improvement. It encourages organizations to monitor, review, and enhance their IT service management processes.
10. Better Supplier and Third-Party Management
Many organizations rely on third-party vendors for IT services. ISO 20000 certification ensures organizations have good processes for managing suppliers. This cuts risks with outsourced services. It ensures external providers meet service standards.
Who Should Attend ISO 20000 Training?
ISO 20000 training is suitable for a wide range of professionals, including:
- IT Service Managers
- IT Consultants
- IT Support and Operations Teams
- Quality and Process Managers
- Business Analysts
- IT Auditors
- Professionals looking to enhance their ITSM knowledge
Key Topics Covered in ISO 20000 Training
ISO 20000 IT Service Management (ITSM) Certification Training is for ITSM professionals. It provides a thorough learning experience. The goal is to understand and apply the ISO 20000 standard for IT service management. This training covers many essential topics. It will help professionals improve IT service management systems (ITSMS) in their organizations. Here is a detailed explanation of the key topics in ISO 20000 training programs.
1. Introduction to IT Service Management (ITSM) & ISO 20000
- A strong grasp of IT Service Management and ISO 20000 is key for certification. In this section, participants are introduced to:
- IT Service Management (ITSM) is a set of policies, processes, and procedures. Organizations use them to design, deliver, manage, and improve IT services for customers. ITSM aims to align IT services with the business and its customers. It seeks to deliver services that are efficient, cost-effective, and high-quality.
- ISO/IEC 20000 Framework: ISO 20000 offers a framework for IT service management. It outlines what an organization must do to set up, run, monitor, review, and improve its ITSMS. We must understand how ISO 20000 helps organizations. It provides reliable, consistent, high-quality IT services.
- ISO 20000 Certification shows an org's commitment to IT service management best practices. Participants learn this. ISO 20000 certification proves that an organization's IT services meet global standards. It improves customer satisfaction, efficiency, and risk management.
2. Overview of ISO 20000 Requirements
- The ISO 20000 standard has many requirements. An organization must implement them to get certified. These include:
- ISO 20000-1: This part lists the requirements for certification. It focuses on setting up an ITSMS. This includes managing resources, processes, and ongoing improvement efforts.
- ISO 20000-2: It provides extra guidelines for implementing an ITSMS. These are based on the requirements in ISO 20000-1. ISO 20000-2 helps organizations customize the framework to their needs. It guides them on the best practices for certification.
It's vital to know the link between ISO 20000-1 and ISO 20000-2. This knowledge is key to creating an ITSMS that meets international standards.
3. Planning and Implementing an IT Service Management System (ITSMS)
A key part of ISO 20000 training is to learn to develop and implement an IT Service Management System (ITSMS). This process involves several key steps:
- Service Design: This is about planning and designing IT services. They must align with customer needs and business goals. Effective service design includes three steps. First, define service objectives. Next, identify service requirements. Lastly, establish the necessary resources and processes.
- Service Transition: The process of transitioning IT services from development to operation. This includes testing and validating services for deployment. Do this with minimal disruption to business operations.
- Service Delivery and Support: This section covers the management of IT services. This includes incident management, problem management, and service desk operations.
- Service Improvement: ISO 20000 training emphasizes the importance of continuous service improvement. The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle helps organizations track performance. It lets them find areas needing improvement. Then, they can make changes to improve service delivery and ITSM processes.
4. Service Management System (SMS) Processes
- ISO 20000 certification requires an organization to implement key processes. They ensure IT services are managed effectively. In training, professionals gain in-depth knowledge of these key processes:
- Service Level Management: This process defines, negotiates, and manages service level agreements (SLAs). It ensures IT services meet agreed-upon performance levels. ISO 20000 training teaches pros to monitor and report on service performance. It helps them manage customer expectations and improve service delivery using feedback.
- Incident and Problem Management: These processes work together. They aim to fix service disruptions and stop issues from happening again.
- Incident management fixes service interruptions quickly and efficiently. Problem management finds and removes root causes to prevent future incidents.
- This minimizes disruptions to service.
- Capacity and Availability Management: They help IT services meet demand and stay online. Capacity management helps organizations plan for future demand. Availability management aims to maximize service uptime and minimize downtime. It does this through proactive monitoring and planning.
- ISO 20000 stresses the need for disaster recovery and business continuity planning. This ensures IT services stay operational during a crisis.
5. ISO 20000 Certification Process
The ISO 20000 training program covers the steps to gain and keep certification. These steps include:
- Achieving Certification: Participants learn the process for applying for ISO 20000 certification. ISO 20000 training must cover audits, both internal and external.
- Continuous Improvement Strategies: ISO 20000 certification is not a one-time process. It's a commitment to continuous improvement. ISO 20000 training teaches how to create improvement strategies. They ensure IT service management processes are regularly reviewed and improved. This is based on performance data and changing business needs.
6. Roles and Responsibilities in ITSM
ISO 20000 training highlights the key responsibilities associated with these roles, including:
- Leadership Commitment: Top management is key to ITSM's success. Training helps professionals learn to secure leadership support. It's vital for implementing ISO 20000.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involving different stakeholders is crucial. This includes service owners, process owners, and vendors. This ensures the ITSMS aligns with business goals and customer needs. The training covers how to communicate with and manage these stakeholders effectively.
7. ISO 20000 Audit and Compliance
- ISO 20000 training also covers how to prepare for audits and keep your certification.
- Preparing for Internal Audits: Internal audits are essential for compliance with ISO 20000. Training provides strategies for effective auditing, including audit planning, execution, and reporting.
- Ensuring Compliance and Maintaining Certification ISO 20000 certification needs to be renewed periodically. This training ensures professionals can comply with the standard and its updates.
- ISO 20000 IT Service Management: Certification Training covers a wide range of topics. It trains pros to implement and manage IT service management systems. They must meet global standards.
Types of ISO 20000 Training
ISO 20000 training comes in various formats to meet diverse learning needs.
- Foundation Training: Covers the basics of ISO 20000 and ITSM principles.
- Lead Implementer Training: Focuses on implementing and managing an ITSMS.
- Lead Auditor Training: Prepares professionals to conduct internal and external audits.
- Self-paced Online Courses: Flexible learning options for busy professionals.
- Instructor-led Training: Classroom or virtual training with expert guidance.
Steps to Achieve ISO 20000 Certification
Organizations seeking ISO 20000 certification should follow these steps:
- Understand ISO 20000 Requirements
- Gain knowledge through training and certification programs.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis
- Identify current ITSM gaps and areas for improvement.
- Develop an Implementation Plan
- Define ITSMS objectives, policies, and procedures.
- Implement ITSM Processes
- Establish service management practices and align with business goals.
- Train Employees
- Ensure staff members understand and adhere to ITSMS guidelines.
- Perform Internal Audits
- Conduct internal audits to assess readiness.
- Undergo External Audit
- Get audited by a certified body for official certification.
- Maintain and Continuously Improve ITSMS
- Monitor, review, and enhance IT service management practices.
Choosing the Right ISO 20000 Training Provider
Selecting a reputable training provider is crucial for successful certification. Consider the following when choosing a provider:
- Accreditation: Ensure the provider is accredited by recognized certification bodies.
- Course Content: Verify that the training covers all essential aspects of ISO 20000.
- Trainer Expertise: Look for experienced instructors with industry knowledge.
- Learning Format: Choose between online, classroom, or blended learning.
- Reviews and Testimonials: Check feedback from past learners.
- Post-training Support: Opt for providers offering post-training resources.
How to obtain ISO 20000 IT Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
ISO 20000 IT Service Management Certification Training is a great investment. It helps IT pros and organizations improve service quality, efficiency, and compliance. With the right training and approach, organizations can get certified. They can also improve IT service management.
It's a step in the right direction. Start your journey today. Gain the knowledge to excel in IT service management!
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
COBIT 5 Foundation: Bridging IT and Business Objectives
One such framework is COBIT® 5. It is a global standard. It provides a structure for managing and governing enterprise IT. This blog covers COBIT® 5 Foundation. It highlights its principles, benefits, and uses for modern organizations.
What is COBIT® 5?
COBIT® 5 is a global framework for IT governance and management. ISACA developed it. The framework connects business goals with IT processes. It helps organizations use technology to achieve their strategic objectives.
Released in 2012, COBIT® 5 is the fifth version of the framework. It builds on earlier versions and includes the latest tech and business trends. It covers IT governance, including risk, compliance, and performance. It's a versatile tool for organizations of all sizes and industries.
COBIT® 5 is Built on Five Core Principles
COBIT® 5, developed by ISACA, is based on five core principles. They give the framework a strong structure and ensure its use across industries. These principles guide organizations in their IT governance and management. They must align with business goals and stakeholders' needs. Let’s delve deeper into each of these five core principles:
1. Meeting Stakeholder Needs
A key part of COBIT® 5 is its focus on stakeholders. It aims to meet their diverse needs. An organization's stakeholders can be internal or external. Internal stakeholders include employees, managers, and board members. External stakeholders are customers, suppliers, and regulators. COBIT® 5 stresses aligning IT goals with stakeholders' needs. This ensures tech investments are effective and create value for all.
For example, IT can add great value if it aligns with stakeholders' interests. Key areas are regulatory compliance, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity.
2. Covering the Enterprise End-to-End
COBIT® 5 adopts a holistic, integrated approach to IT governance. Unlike frameworks that see IT as a separate function, COBIT® 5 does not. It recognizes that IT is linked to every part of the enterprise. It addresses the IT department's role in business processes and goals. This "enterprise end-to-end" principle aligns all business areas with IT. It minimizes silos and fosters collaboration across departments.
COBIT® 5 links IT governance with business processes. This creates a clear framework for managing IT alongside the overall business strategy. This ensures that tech investments support the organization's mission and goals.
3. Applying a Single Integrated Framework
COBIT® 5 is designed to work with other, popular, industry standards and frameworks. COBIT® 5 fits nicely with ITIL® for IT service management. It also aligns with ISO/IEC 27001 and PRINCE2® standards. The former is for information security, the latter for project management. It allows a unified approach to governance and management.
This approach helps businesses use the strengths of multiple frameworks. It avoids duplications or conflicts in governance practices. It ensures all frameworks and methods work together. This will achieve consistent governance and better decision-making across the organization.
4. Enabling a Holistic Approach
COBIT® 5 identifies seven key enablers that are essential to successful IT governance. These enablers provide the tools and processes for effective governance. They help organizations to implement and sustain it. The enablers include principles, policies, frameworks, organizational structures, culture, information, services, and infrastructure.
COBIT® 5 shows that IT governance goes beyond technology. It must embed governance practices in the organization's culture and structures. These enablers create an ecosystem. In it, technology aligns with business goals. It drives improvement and value across the enterprise.
5. Separating Governance from Management
A key distinction in COBIT® 5 is the separation between governance and management. Governance sets strategic goals, monitors performance, and ensures accountability. Management handles the daily planning, building, running, and monitoring of IT activities.
COBIT® 5 clearly separates these two functions. It ensures that governance (strategic oversight) is distinct from management (operational activities). This separation clarifies roles and responsibilities. It reduces confusion and boosts efficiency. Governance sets the "why" and "what." Management handles the "how" and "when." Each must work effectively in its domain and toward the same goals.
In conclusion, COBIT® 5 has five core principles. They form its backbone. They provide a framework for IT management. It aligns with business goals, meets stakeholders' needs, and drives improvement. These principles guide the framework's use. They also align IT governance with the business strategy. This, in turn, supports the organization's long-term success.
COBIT® 5 benefits organizations. It improves IT governance and management, aligning them with business goals. The framework helps organizations manage technology as a strategic asset. It ensures tech boosts growth, efficiency, and risk management.
Key Components of COBIT® 5 COBIT® 5 has several key parts.
1. COBIT® 5 defines 37 governance and management objectives. They align with enterprise goals. These objectives are in five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM). This is a governance domain. It focuses on setting direction and monitoring performance. Align, Plan, and Organize (APO): Management domain covering strategic planning and resource allocation. Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI): A management domain. It covers developing and deploying IT solutions. Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS): This domain is about service delivery and support. Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA): Management domain for performance evaluation and compliance monitoring.
2. Process Reference Model The Process Reference Model (PRM) is a key part of COBIT® 5. It provides a structured view of IT processes. Each process includes inputs, outputs, roles, and responsibilities. This keeps things clear and consistent during implementation.
3. Goals Cascade The Goals Cascade links enterprise goals to IT goals. It ensures alignment across the organization. This alignment facilitates the achievement of strategic objectives through effective use of technology.
4. Implementation Guidance COBIT® 5 has practical advice for using the framework. It helps organizations customize it to their needs. The implementation approach is iterative and adaptive, ensuring continuous improvement.
COBIT® 5 Certification
ISACA offers the COBIT® 5 Foundation certification. It is for professionals who want to deepen their understanding of COBIT® 5. This entry-level certification tests a person's knowledge of the framework's principles and uses.
Certification Benefits
Obtaining the COBIT® 5 Foundation certification provides several advantages, including:
- Enhanced career prospects in IT governance and management roles.
- Recognition as a qualified professional in the field.
- Improved ability to implement and optimize COBIT® 5 practices within organizations.
Examination Details
The COBIT® 5 Foundation exam is a multiple-choice test consisting of 50 questions. Candidates must achieve a score of 50% or higher to pass. The exam covers key topics: the framework's principles, enablers, and its implementation process.
Practical Applications of COBIT® 5
COBIT® 5 is a strong, complete IT governance framework. It helps organizations manage and optimize their IT systems. COBIT® 5 was created by ISACA. It has changed to fit the needs of our digital world. It offers a strategic way to manage IT resources and align them with business goals. This section shows COBIT® 5's practical uses. It highlights its value in transforming IT governance in organizations.
1. IT Governance Framework
A fundamental application of COBIT® 5 is as an IT governance framework. In all organizations, it's crucial to set clear IT guidelines. They must ensure tech investments align with business goals. COBIT® 5 addresses this. It provides a structured approach to governance. It incorporates best practices that ensure IT supports the organization's long-term goals.
COBIT® 5 helps organizations build a strong governance structure. This structure allows for better oversight and decision-making. It ensures IT is part of every business level. COBIT® 5 is vital for firms wanting to improve IT governance. It meets stakeholders' needs. It gives a clear way to manage IT risks and performance.
COBIT® 5 helps align business goals with IT objectives. This alignment is key. It helps technology initiatives provide value and meet organizational goals. For example, COBIT® 5 can guide decisions on tech investments. It can help prioritize projects and manage resources to maximize business outcomes.
2. Risk Management and Compliance
A key use of COBIT® 5 is managing IT risks and meeting regulatory needs. As businesses face pressure to secure data and protect privacy, COBIT® 5 offers a solution. It provides a way to manage compliance with regulations.
COBIT® 5 focuses on risk management. It helps organizations find, assess, and reduce threats to IT systems. This includes strategic and operational risks. These are cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and system failures. COBIT® 5's structured approach helps firms manage risk. It protects against disruptions and ensures business continuity.
COBIT® 5 helps with risk management and ensures compliance with laws. Many organizations work in regulated industries, like healthcare and finance. They must follow standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. COBIT® 5 gives clear guidelines for aligning IT processes with these rules. It reduces the risk of non-compliance and its penalties. The framework helps organizations set up controls and monitoring. This way, they can meet compliance obligations and keep high governance standards.
3. Performance Monitoring
Another key application of COBIT® 5 is in performance monitoring. Organizations must constantly assess their IT systems. They must ensure these systems deliver value and support business success. COBIT® 5 is a strong framework. It defines, tracks, and evaluates IT process performance.
COBIT® 5 has key performance indicators (KPIs). They help organizations monitor their IT operations' efficiency and effectiveness. These KPIs help organizations measure IT system performance. They identify areas for improvement and ensure IT investments yield results. For example, COBIT® 5 can help organizations assess their IT security. It can also measure service delivery efficiency and track IT project success.
COBIT® 5's performance monitoring helps ensure IT services meet user expectations and SLAs. By tracking performance against benchmarks, organizations can make data-driven decisions. They can then optimize IT processes, improve service delivery, and boost customer satisfaction.
4. Project Management
In many organizations, IT projects are key to strategic goals. So, managing them well is essential for success. COBIT® 5 works well with project management methods like PRINCE2® and PMI's PMBOK®. It ensures IT projects meet business goals and finish on time and on budget.
COBIT® 5 gives a structured approach to project management. It defines clear objectives, roles, and responsibilities. It guides how to plan, run, and monitor IT projects. It ensures all project lifecycle phases are managed well. COBIT® 5 principles can help organizations. They can boost project success, cut risks, and ensure IT projects add value.
Also, COBIT® 5's focus on stakeholders ensures IT projects meet their needs. This focus helps organizations deliver IT projects that meet business goals.
5. Business and IT Alignment
A key strength of COBIT® 5 is its ability to facilitate the alignment of IT with business goals. In many organizations, IT and business units work separately. This can create inefficiencies and result in missed chances to collaborate. COBIT® 5 helps bridge this gap. It ensures IT strategies align with the organization's goals.
COBIT® 5 helps firms align IT with business needs. It ensures tech investments support initiatives that boost growth. The framework promotes teamwork between IT and other units. It ensures technology enhances processes, improves decisions, and fosters innovation.
COBIT® 5 aligns IT with business goals. It ensures technology helps achieve organizational objectives. These include greater efficiency, better customer satisfaction, and improved competitiveness. It also helps organizations avoid wasting money on IT projects that lack value.
6. Continuous Improvement
COBIT® 5 promotes a culture of continuous improvement. It urges organizations to assess and refine their IT governance practices over time. The framework's iterative approach helps organizations. It allows them to find areas to improve, make changes, and track progress toward their goals.
A focus on improvement helps organizations stay competitive in a fast-changing tech world. Organizations can adapt to new challenges by improving their IT processes. This helps them adopt new technologies and stay ahead in performance and innovation.
How to obtain COBIT® 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
COBIT® 5 is a framework for IT management and governance. It helps organizations meet business goals, reduce risks, ensure compliance, and improve continuously. It applies to many areas of IT governance. These include performance monitoring, project management, risk management, and business-IT alignment.
Using COBIT® 5 helps organizations improve IT operations. It also ensures good governance and supports strategic business goals. COBIT® 5 helps businesses use technology to drive success. It improves decision-making, manages risks, and builds stakeholder trust.
Adopting COBIT® 5 is not just about compliance or efficiency. It is about creating an IT governance structure. It should help organizations thrive in the digital age.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
One such framework is COBIT® 5. It is a global standard. It provides a structure for managing and governing enterprise IT. This blog covers COBIT® 5 Foundation. It highlights its principles, benefits, and uses for modern organizations.
What is COBIT® 5?
COBIT® 5 is a global framework for IT governance and management. ISACA developed it. The framework connects business goals with IT processes. It helps organizations use technology to achieve their strategic objectives.
Released in 2012, COBIT® 5 is the fifth version of the framework. It builds on earlier versions and includes the latest tech and business trends. It covers IT governance, including risk, compliance, and performance. It's a versatile tool for organizations of all sizes and industries.
COBIT® 5 is Built on Five Core Principles
COBIT® 5, developed by ISACA, is based on five core principles. They give the framework a strong structure and ensure its use across industries. These principles guide organizations in their IT governance and management. They must align with business goals and stakeholders' needs. Let’s delve deeper into each of these five core principles:
1. Meeting Stakeholder Needs
A key part of COBIT® 5 is its focus on stakeholders. It aims to meet their diverse needs. An organization's stakeholders can be internal or external. Internal stakeholders include employees, managers, and board members. External stakeholders are customers, suppliers, and regulators. COBIT® 5 stresses aligning IT goals with stakeholders' needs. This ensures tech investments are effective and create value for all.
For example, IT can add great value if it aligns with stakeholders' interests. Key areas are regulatory compliance, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity.
2. Covering the Enterprise End-to-End
COBIT® 5 adopts a holistic, integrated approach to IT governance. Unlike frameworks that see IT as a separate function, COBIT® 5 does not. It recognizes that IT is linked to every part of the enterprise. It addresses the IT department's role in business processes and goals. This "enterprise end-to-end" principle aligns all business areas with IT. It minimizes silos and fosters collaboration across departments.
COBIT® 5 links IT governance with business processes. This creates a clear framework for managing IT alongside the overall business strategy. This ensures that tech investments support the organization's mission and goals.
3. Applying a Single Integrated Framework
COBIT® 5 is designed to work with other, popular, industry standards and frameworks. COBIT® 5 fits nicely with ITIL® for IT service management. It also aligns with ISO/IEC 27001 and PRINCE2® standards. The former is for information security, the latter for project management. It allows a unified approach to governance and management.
This approach helps businesses use the strengths of multiple frameworks. It avoids duplications or conflicts in governance practices. It ensures all frameworks and methods work together. This will achieve consistent governance and better decision-making across the organization.
4. Enabling a Holistic Approach
COBIT® 5 identifies seven key enablers that are essential to successful IT governance. These enablers provide the tools and processes for effective governance. They help organizations to implement and sustain it. The enablers include principles, policies, frameworks, organizational structures, culture, information, services, and infrastructure.
COBIT® 5 shows that IT governance goes beyond technology. It must embed governance practices in the organization's culture and structures. These enablers create an ecosystem. In it, technology aligns with business goals. It drives improvement and value across the enterprise.
5. Separating Governance from Management
A key distinction in COBIT® 5 is the separation between governance and management. Governance sets strategic goals, monitors performance, and ensures accountability. Management handles the daily planning, building, running, and monitoring of IT activities.
COBIT® 5 clearly separates these two functions. It ensures that governance (strategic oversight) is distinct from management (operational activities). This separation clarifies roles and responsibilities. It reduces confusion and boosts efficiency. Governance sets the "why" and "what." Management handles the "how" and "when." Each must work effectively in its domain and toward the same goals.
In conclusion, COBIT® 5 has five core principles. They form its backbone. They provide a framework for IT management. It aligns with business goals, meets stakeholders' needs, and drives improvement. These principles guide the framework's use. They also align IT governance with the business strategy. This, in turn, supports the organization's long-term success.
COBIT® 5 benefits organizations. It improves IT governance and management, aligning them with business goals. The framework helps organizations manage technology as a strategic asset. It ensures tech boosts growth, efficiency, and risk management.
Key Components of COBIT® 5 COBIT® 5 has several key parts.
1. COBIT® 5 defines 37 governance and management objectives. They align with enterprise goals. These objectives are in five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM). This is a governance domain. It focuses on setting direction and monitoring performance. Align, Plan, and Organize (APO): Management domain covering strategic planning and resource allocation. Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI): A management domain. It covers developing and deploying IT solutions. Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS): This domain is about service delivery and support. Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA): Management domain for performance evaluation and compliance monitoring.
2. Process Reference Model The Process Reference Model (PRM) is a key part of COBIT® 5. It provides a structured view of IT processes. Each process includes inputs, outputs, roles, and responsibilities. This keeps things clear and consistent during implementation.
3. Goals Cascade The Goals Cascade links enterprise goals to IT goals. It ensures alignment across the organization. This alignment facilitates the achievement of strategic objectives through effective use of technology.
4. Implementation Guidance COBIT® 5 has practical advice for using the framework. It helps organizations customize it to their needs. The implementation approach is iterative and adaptive, ensuring continuous improvement.
COBIT® 5 Certification
ISACA offers the COBIT® 5 Foundation certification. It is for professionals who want to deepen their understanding of COBIT® 5. This entry-level certification tests a person's knowledge of the framework's principles and uses.
Certification Benefits
Obtaining the COBIT® 5 Foundation certification provides several advantages, including:
- Enhanced career prospects in IT governance and management roles.
- Recognition as a qualified professional in the field.
- Improved ability to implement and optimize COBIT® 5 practices within organizations.
Examination Details
The COBIT® 5 Foundation exam is a multiple-choice test consisting of 50 questions. Candidates must achieve a score of 50% or higher to pass. The exam covers key topics: the framework's principles, enablers, and its implementation process.
Practical Applications of COBIT® 5
COBIT® 5 is a strong, complete IT governance framework. It helps organizations manage and optimize their IT systems. COBIT® 5 was created by ISACA. It has changed to fit the needs of our digital world. It offers a strategic way to manage IT resources and align them with business goals. This section shows COBIT® 5's practical uses. It highlights its value in transforming IT governance in organizations.
1. IT Governance Framework
A fundamental application of COBIT® 5 is as an IT governance framework. In all organizations, it's crucial to set clear IT guidelines. They must ensure tech investments align with business goals. COBIT® 5 addresses this. It provides a structured approach to governance. It incorporates best practices that ensure IT supports the organization's long-term goals.
COBIT® 5 helps organizations build a strong governance structure. This structure allows for better oversight and decision-making. It ensures IT is part of every business level. COBIT® 5 is vital for firms wanting to improve IT governance. It meets stakeholders' needs. It gives a clear way to manage IT risks and performance.
COBIT® 5 helps align business goals with IT objectives. This alignment is key. It helps technology initiatives provide value and meet organizational goals. For example, COBIT® 5 can guide decisions on tech investments. It can help prioritize projects and manage resources to maximize business outcomes.
2. Risk Management and Compliance
A key use of COBIT® 5 is managing IT risks and meeting regulatory needs. As businesses face pressure to secure data and protect privacy, COBIT® 5 offers a solution. It provides a way to manage compliance with regulations.
COBIT® 5 focuses on risk management. It helps organizations find, assess, and reduce threats to IT systems. This includes strategic and operational risks. These are cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and system failures. COBIT® 5's structured approach helps firms manage risk. It protects against disruptions and ensures business continuity.
COBIT® 5 helps with risk management and ensures compliance with laws. Many organizations work in regulated industries, like healthcare and finance. They must follow standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. COBIT® 5 gives clear guidelines for aligning IT processes with these rules. It reduces the risk of non-compliance and its penalties. The framework helps organizations set up controls and monitoring. This way, they can meet compliance obligations and keep high governance standards.
3. Performance Monitoring
Another key application of COBIT® 5 is in performance monitoring. Organizations must constantly assess their IT systems. They must ensure these systems deliver value and support business success. COBIT® 5 is a strong framework. It defines, tracks, and evaluates IT process performance.
COBIT® 5 has key performance indicators (KPIs). They help organizations monitor their IT operations' efficiency and effectiveness. These KPIs help organizations measure IT system performance. They identify areas for improvement and ensure IT investments yield results. For example, COBIT® 5 can help organizations assess their IT security. It can also measure service delivery efficiency and track IT project success.
COBIT® 5's performance monitoring helps ensure IT services meet user expectations and SLAs. By tracking performance against benchmarks, organizations can make data-driven decisions. They can then optimize IT processes, improve service delivery, and boost customer satisfaction.
4. Project Management
In many organizations, IT projects are key to strategic goals. So, managing them well is essential for success. COBIT® 5 works well with project management methods like PRINCE2® and PMI's PMBOK®. It ensures IT projects meet business goals and finish on time and on budget.
COBIT® 5 gives a structured approach to project management. It defines clear objectives, roles, and responsibilities. It guides how to plan, run, and monitor IT projects. It ensures all project lifecycle phases are managed well. COBIT® 5 principles can help organizations. They can boost project success, cut risks, and ensure IT projects add value.
Also, COBIT® 5's focus on stakeholders ensures IT projects meet their needs. This focus helps organizations deliver IT projects that meet business goals.
5. Business and IT Alignment
A key strength of COBIT® 5 is its ability to facilitate the alignment of IT with business goals. In many organizations, IT and business units work separately. This can create inefficiencies and result in missed chances to collaborate. COBIT® 5 helps bridge this gap. It ensures IT strategies align with the organization's goals.
COBIT® 5 helps firms align IT with business needs. It ensures tech investments support initiatives that boost growth. The framework promotes teamwork between IT and other units. It ensures technology enhances processes, improves decisions, and fosters innovation.
COBIT® 5 aligns IT with business goals. It ensures technology helps achieve organizational objectives. These include greater efficiency, better customer satisfaction, and improved competitiveness. It also helps organizations avoid wasting money on IT projects that lack value.
6. Continuous Improvement
COBIT® 5 promotes a culture of continuous improvement. It urges organizations to assess and refine their IT governance practices over time. The framework's iterative approach helps organizations. It allows them to find areas to improve, make changes, and track progress toward their goals.
A focus on improvement helps organizations stay competitive in a fast-changing tech world. Organizations can adapt to new challenges by improving their IT processes. This helps them adopt new technologies and stay ahead in performance and innovation.
How to obtain COBIT® 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
COBIT® 5 is a framework for IT management and governance. It helps organizations meet business goals, reduce risks, ensure compliance, and improve continuously. It applies to many areas of IT governance. These include performance monitoring, project management, risk management, and business-IT alignment.
Using COBIT® 5 helps organizations improve IT operations. It also ensures good governance and supports strategic business goals. COBIT® 5 helps businesses use technology to drive success. It improves decision-making, manages risks, and builds stakeholder trust.
Adopting COBIT® 5 is not just about compliance or efficiency. It is about creating an IT governance structure. It should help organizations thrive in the digital age.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Top 5 Frontend Frameworks to Watch in 2025 for Developers
Frontend development is key to modern web apps. It ensures users have an engaging, interactive experience. With so many frameworks to choose from, selecting the right one can be overwhelming. But, it's crucial for developers to make careful choices. The framework will impact both productivity and the user experience.
For this video, we have identified the top 5 frontend frameworks to learn in 2025, based on three key factors:
1. Popularity – The framework’s adoption rate in the developer community.
2. Community Support – A large, active community that contributes to improvements, troubleshooting, and growth.
3. Future Potential – The framework's ability to adapt as technology changes.
Now, let’s dive into these frameworks and explore why they are the best choices for developers in 2025!
Framework 1: React
Overview of Features
React is a powerful front-end framework by Facebook. It allows developers to build dynamic and efficient user interfaces. Here are some of its standout features:
Component-Based Architecture:
React organises the UI into independent, reusable components. This modular approach makes it easier to manage and update code. It boosts development speed and long-term maintainability.
- Virtual DOM:
React uses a Virtual DOM to improve performance. When changes occur, React only updates the parts that need changing. It does not update the whole page. This selective update process results in faster rendering and a more responsive application.
---
Popularity and community support
React’s popularity is a key factor in its success:
Widespread adoption:
React is a popular framework among developers worldwide. Small startups and large tech giants like Facebook, Instagram, and Airbnb use it. Its adoption rate continues to grow year on year.
- Active Community:
React's large community provides continuous support. It includes open-source contributions, libraries, and frameworks built around React. This community-driven ecosystem helps developers solve problems faster and share knowledge.
---
Job Market Demand
The demand for React developers is high.
- High Job Demand:
React is now a staple in web development. Companies want developers skilled in it. The rising use of React in web and mobile apps creates a strong job market for skilled developers.
- Career Opportunities:
Mastering React opens doors to many front-end development jobs. It can help you work for a tech giant or a growing startup.
---
Conclusion
React has an efficient architecture, a strong community, and high demand. So, it is one of the best frameworks to learn for 2025. Its evolution makes it a reliable choice for developers. They want to build cutting-edge web applications.
Framework 2: Angular
Overview of Features
Angular is a comprehensive and robust front-end framework developed by Google. It provides a complete solution for building dynamic, scalable web apps. Here are some key features of Angular:
- Full-Featured Framework:
Unlike some frameworks that focus on UI rendering, Angular has a full suite of features. It includes routing, state management, and form validation. This all-in-one approach means developers don't need external libraries to build complex apps.
- TypeScript Support:
Angular is built using TypeScript, a statically typed superset of JavaScript. TypeScript helps developers catch errors and write better code. It has strong typing, object-oriented features, and better tooling support. This makes code more maintainable and scalable. It’s ideal for larger applications and teams.
---
Usage in Large-Scale Enterprise Applications
Angular is particularly well-suited for building large-scale enterprise applications:
- Scalability and Structure:
Angular's strict structure and patterns suit large teams and complex projects. Its powerful tools make it easier to manage large codebases. They include dependency injection and routing. They are more efficient too.
- Built for Complex Applications:
Angular is for complex, feature-rich web apps. It is popular for enterprise-level solutions. Companies like Microsoft and IBM use Angular for their apps. Their use shows it can handle large projects.
---
Google’s Backing and Long-Term Updates
Angular benefits from strong Google support, ensuring long-term development and stability:
- Google’s Backing:
Angular is a framework developed and maintained by Google. It is assured of continuous updates and improvements. Google's support gives confidence. The framework will evolve with web development trends.
- Long-Term Updates:
Angular's long-term update policy will keep it relevant and secure for years. This makes Angular ideal for enterprises needing long-term app support.
---
Conclusion
Angular is a powerful, feature-rich framework designed for large-scale web applications. Its full features, TypeScript support, and Google's backing make it a top choice for firms. In 2025, Angular is the best framework for complex, large-scale apps. So, it is worth mastering.
Framework 3: Vue.js
Overview of Features
Vue.js is a lightweight, flexible frontend framework. It is a favourite among developers. People know Vue for its simplicity and progressive nature. It allows developers to integrate it into existing projects with minimal effort. Or, they can use it to build full applications.
- Simplicity:
Vue is often praised for its gentle learning curve. It has a simple, clear API. It lets developers build apps with minimal setup. Vue's declarative rendering and reactivity system make it easy to use. This is especially true for developers familiar with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Flexibility:
Vue is a progressive framework, which allows developers to adopt it in stages. Developers can use it to improve parts of an app or to build apps from scratch. This flexibility makes Vue suitable for projects of all sizes.
---
Popularity and Growth in Projects
Vue.js is rapidly gaining traction in the web development world:
- Rising Popularity:
Vue has garnered significant attention and adoption in recent years. Its simple syntax and easy integration make it popular. Individual developers, startups, and large organizations love it.
- Small and Large Projects:
Vue's adaptability allows its use in small projects and enterprise apps. Vue handles it all with ease. It can build interactive components in legacy systems and complex SPAs.
---
Example Use Cases of Vue.js in Modern Applications
Vue is being used in a variety of modern applications across industries:
- Small Projects:
Vue is ideal for projects that require a quick and efficient solution. Developers use it to build fast, lightweight, dynamic UIs, interactive elements, and PWAs.
- Large-Scale Applications:
Despite its simplicity, Vue is fully capable of handling larger, more complex applications. Companies like Alibaba and Xiaomi use Vue.js on their websites and apps. This shows it can scale and perform well for enterprise use.
---
Conclusion
Vue.js is an excellent choice for developers. It is a simple, flexible, and powerful frontend framework. Its popularity is rising. Its adaptability suits both small and large projects. Vue.js is a framework that can grow with your needs. It works for both a simple interactive interface and a large-scale app.
Framework 4: Svelte
Introduction to Svelte's Unique Approach
Svelte is a modern frontend framework. It has a unique way to build web apps. Unlike other frameworks like React or Angular, Svelte doesn’t use a virtual DOM or require a runtime. Instead, it compiles the application at build time into highly optimized, vanilla JavaScript.
Compilation at build time:
Svelte compiles your code during the build process. It turns it into code that, with an imperative approach, efficiently and directly manipulates the DOM. This eliminates the need for a framework runtime, making the app lighter and faster.
---
Advantages of Svelte in Producing Faster and Smaller Apps
One of Svelte's biggest advantages is its ability to produce smaller, faster apps.
No Virtual DOM:
Since Svelte compiles to vanilla JavaScript at build time, there is no need for a virtual DOM. This leads to faster rendering and lower memory usage.
Optimised Output:
Svelte’s build process optimises the code for production. It keeps the bundle size small. It reduces the JavaScript the browser must download and run. This results in quicker page loads and better performance.
---
Emerging Trends and Why It Is Becoming a Developer Favourite
Svelte is gaining traction at a fast pace within the developer community.
Simplicity and performance:
Developers love Svelte for its simplicity. It needs less boilerplate code than traditional frameworks. The lack of a virtual DOM and runtime also leads to better performance out of the box.
Growing Popularity:
As developers seek better performance, Svelte is gaining popularity. Startups, developers, and larger apps needing a performance boost are adopting it.
---
Conclusion
Svelte's unique approach to frontend development sets it apart from traditional frameworks. It compiles at build time for better performance. Svelte can make smaller, faster apps. It's growing in popularity among developers. So, it's a framework to watch in 2025.
Framework 5: Next.js
Overview of Next.js as a framework for React
Next.js is a powerful framework built on React. It lets developers easily create full-stack web apps. It adds key features to React. So, it's a top choice for high-performance apps.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR):
One of the standout features of Next.js is its built-in support for server-side rendering. It means that web pages are pre-rendered on the server. The system sends them to the browser in the form of fully constructed HTML. This improves load times and ensures that search engines can access the content.
Static Site Generation (SSG):
Besides SSR, Next.js supports static site generation. This lets developers create static HTML pages at build time. It gives ultra-fast load times and a better user experience. This is key for content-heavy sites.
---
Adoption of performance-focused and SEO-friendly applications.
Developers prefer Next.js for fast, SEO-optimised apps.
- Performance:
Next.js uses SSR and SSG to serve web pages on time. This holds true for complex content or dynamic data. This is ideal for performance-sensitive apps, like e-commerce and news sites. Their speed is critical.
Not possible to remove the adverb.
Next.js renders pages on the server. Search engines can crawl and index the content with ease. This makes it great for SEO-focused apps. This is crucial for businesses seeking to boost their search engine visibility.
---
Real-World Implementations of Next.js
Many high-profile companies and projects have adopted Next.js.
- Real-World Use Cases:
Next.js powers fast, scalable apps at Twitch, Hulu, and TikTok. It uses server-side rendering and static site generation. These companies use Next.js for its speed and scalability. It handles dynamic content well.
---
Conclusion
Next.js is an excellent framework for React developers. It helps them create apps that are friendly to SEO and perform at a high level. It is great for web dev in 2025. It supports server-side rendering and static site generation. Next.js has gained widespread adoption in real projects. It is a great tool for building fast, dynamic, and scalable apps. Its value will grow as its use continues.
6. Conclusion
Recap of the Top 5 Frameworks
In this video, we have explored the top five front-end frameworks to learn in 2025:
React: The flexible, component-based framework with a huge community.
Angular: The full-featured, enterprise-ready framework backed by Google.
Vue.js: The simple and progressive framework for projects of all sizes.
Svelte: A unique, performance-focused framework that compiles at build time.
Next.js: The React framework for server-side rendering and static site generation.
---
Encouragement to Explore Based on Project Needs and Career Goals
The right framework depends on your project's needs and your career goals. If you're building a complex enterprise application, Angular might be the way to go. For smaller, high-performance applications, Vue or Svelte could be great choices. React and Next.js are great for any project. They are very scalable and flexible.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
Frontend development is key to modern web apps. It ensures users have an engaging, interactive experience. With so many frameworks to choose from, selecting the right one can be overwhelming. But, it's crucial for developers to make careful choices. The framework will impact both productivity and the user experience.
For this video, we have identified the top 5 frontend frameworks to learn in 2025, based on three key factors:
1. Popularity – The framework’s adoption rate in the developer community.
2. Community Support – A large, active community that contributes to improvements, troubleshooting, and growth.
3. Future Potential – The framework's ability to adapt as technology changes.
Now, let’s dive into these frameworks and explore why they are the best choices for developers in 2025!
Framework 1: React
Overview of Features
React is a powerful front-end framework by Facebook. It allows developers to build dynamic and efficient user interfaces. Here are some of its standout features:
Component-Based Architecture:
React organises the UI into independent, reusable components. This modular approach makes it easier to manage and update code. It boosts development speed and long-term maintainability.
- Virtual DOM:
React uses a Virtual DOM to improve performance. When changes occur, React only updates the parts that need changing. It does not update the whole page. This selective update process results in faster rendering and a more responsive application.
---
Popularity and community support
React’s popularity is a key factor in its success:
Widespread adoption:
React is a popular framework among developers worldwide. Small startups and large tech giants like Facebook, Instagram, and Airbnb use it. Its adoption rate continues to grow year on year.
- Active Community:
React's large community provides continuous support. It includes open-source contributions, libraries, and frameworks built around React. This community-driven ecosystem helps developers solve problems faster and share knowledge.
---
Job Market Demand
The demand for React developers is high.
- High Job Demand:
React is now a staple in web development. Companies want developers skilled in it. The rising use of React in web and mobile apps creates a strong job market for skilled developers.
- Career Opportunities:
Mastering React opens doors to many front-end development jobs. It can help you work for a tech giant or a growing startup.
---
Conclusion
React has an efficient architecture, a strong community, and high demand. So, it is one of the best frameworks to learn for 2025. Its evolution makes it a reliable choice for developers. They want to build cutting-edge web applications.
Framework 2: Angular
Overview of Features
Angular is a comprehensive and robust front-end framework developed by Google. It provides a complete solution for building dynamic, scalable web apps. Here are some key features of Angular:
- Full-Featured Framework:
Unlike some frameworks that focus on UI rendering, Angular has a full suite of features. It includes routing, state management, and form validation. This all-in-one approach means developers don't need external libraries to build complex apps.
- TypeScript Support:
Angular is built using TypeScript, a statically typed superset of JavaScript. TypeScript helps developers catch errors and write better code. It has strong typing, object-oriented features, and better tooling support. This makes code more maintainable and scalable. It’s ideal for larger applications and teams.
---
Usage in Large-Scale Enterprise Applications
Angular is particularly well-suited for building large-scale enterprise applications:
- Scalability and Structure:
Angular's strict structure and patterns suit large teams and complex projects. Its powerful tools make it easier to manage large codebases. They include dependency injection and routing. They are more efficient too.
- Built for Complex Applications:
Angular is for complex, feature-rich web apps. It is popular for enterprise-level solutions. Companies like Microsoft and IBM use Angular for their apps. Their use shows it can handle large projects.
---
Google’s Backing and Long-Term Updates
Angular benefits from strong Google support, ensuring long-term development and stability:
- Google’s Backing:
Angular is a framework developed and maintained by Google. It is assured of continuous updates and improvements. Google's support gives confidence. The framework will evolve with web development trends.
- Long-Term Updates:
Angular's long-term update policy will keep it relevant and secure for years. This makes Angular ideal for enterprises needing long-term app support.
---
Conclusion
Angular is a powerful, feature-rich framework designed for large-scale web applications. Its full features, TypeScript support, and Google's backing make it a top choice for firms. In 2025, Angular is the best framework for complex, large-scale apps. So, it is worth mastering.
Framework 3: Vue.js
Overview of Features
Vue.js is a lightweight, flexible frontend framework. It is a favourite among developers. People know Vue for its simplicity and progressive nature. It allows developers to integrate it into existing projects with minimal effort. Or, they can use it to build full applications.
- Simplicity:
Vue is often praised for its gentle learning curve. It has a simple, clear API. It lets developers build apps with minimal setup. Vue's declarative rendering and reactivity system make it easy to use. This is especially true for developers familiar with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Flexibility:
Vue is a progressive framework, which allows developers to adopt it in stages. Developers can use it to improve parts of an app or to build apps from scratch. This flexibility makes Vue suitable for projects of all sizes.
---
Popularity and Growth in Projects
Vue.js is rapidly gaining traction in the web development world:
- Rising Popularity:
Vue has garnered significant attention and adoption in recent years. Its simple syntax and easy integration make it popular. Individual developers, startups, and large organizations love it.
- Small and Large Projects:
Vue's adaptability allows its use in small projects and enterprise apps. Vue handles it all with ease. It can build interactive components in legacy systems and complex SPAs.
---
Example Use Cases of Vue.js in Modern Applications
Vue is being used in a variety of modern applications across industries:
- Small Projects:
Vue is ideal for projects that require a quick and efficient solution. Developers use it to build fast, lightweight, dynamic UIs, interactive elements, and PWAs.
- Large-Scale Applications:
Despite its simplicity, Vue is fully capable of handling larger, more complex applications. Companies like Alibaba and Xiaomi use Vue.js on their websites and apps. This shows it can scale and perform well for enterprise use.
---
Conclusion
Vue.js is an excellent choice for developers. It is a simple, flexible, and powerful frontend framework. Its popularity is rising. Its adaptability suits both small and large projects. Vue.js is a framework that can grow with your needs. It works for both a simple interactive interface and a large-scale app.
Framework 4: Svelte
Introduction to Svelte's Unique Approach
Svelte is a modern frontend framework. It has a unique way to build web apps. Unlike other frameworks like React or Angular, Svelte doesn’t use a virtual DOM or require a runtime. Instead, it compiles the application at build time into highly optimized, vanilla JavaScript.
Compilation at build time:
Svelte compiles your code during the build process. It turns it into code that, with an imperative approach, efficiently and directly manipulates the DOM. This eliminates the need for a framework runtime, making the app lighter and faster.
---
Advantages of Svelte in Producing Faster and Smaller Apps
One of Svelte's biggest advantages is its ability to produce smaller, faster apps.
No Virtual DOM:
Since Svelte compiles to vanilla JavaScript at build time, there is no need for a virtual DOM. This leads to faster rendering and lower memory usage.
Optimised Output:
Svelte’s build process optimises the code for production. It keeps the bundle size small. It reduces the JavaScript the browser must download and run. This results in quicker page loads and better performance.
---
Emerging Trends and Why It Is Becoming a Developer Favourite
Svelte is gaining traction at a fast pace within the developer community.
Simplicity and performance:
Developers love Svelte for its simplicity. It needs less boilerplate code than traditional frameworks. The lack of a virtual DOM and runtime also leads to better performance out of the box.
Growing Popularity:
As developers seek better performance, Svelte is gaining popularity. Startups, developers, and larger apps needing a performance boost are adopting it.
---
Conclusion
Svelte's unique approach to frontend development sets it apart from traditional frameworks. It compiles at build time for better performance. Svelte can make smaller, faster apps. It's growing in popularity among developers. So, it's a framework to watch in 2025.
Framework 5: Next.js
Overview of Next.js as a framework for React
Next.js is a powerful framework built on React. It lets developers easily create full-stack web apps. It adds key features to React. So, it's a top choice for high-performance apps.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR):
One of the standout features of Next.js is its built-in support for server-side rendering. It means that web pages are pre-rendered on the server. The system sends them to the browser in the form of fully constructed HTML. This improves load times and ensures that search engines can access the content.
Static Site Generation (SSG):
Besides SSR, Next.js supports static site generation. This lets developers create static HTML pages at build time. It gives ultra-fast load times and a better user experience. This is key for content-heavy sites.
---
Adoption of performance-focused and SEO-friendly applications.
Developers prefer Next.js for fast, SEO-optimised apps.
- Performance:
Next.js uses SSR and SSG to serve web pages on time. This holds true for complex content or dynamic data. This is ideal for performance-sensitive apps, like e-commerce and news sites. Their speed is critical.
Not possible to remove the adverb.
Next.js renders pages on the server. Search engines can crawl and index the content with ease. This makes it great for SEO-focused apps. This is crucial for businesses seeking to boost their search engine visibility.
---
Real-World Implementations of Next.js
Many high-profile companies and projects have adopted Next.js.
- Real-World Use Cases:
Next.js powers fast, scalable apps at Twitch, Hulu, and TikTok. It uses server-side rendering and static site generation. These companies use Next.js for its speed and scalability. It handles dynamic content well.
---
Conclusion
Next.js is an excellent framework for React developers. It helps them create apps that are friendly to SEO and perform at a high level. It is great for web dev in 2025. It supports server-side rendering and static site generation. Next.js has gained widespread adoption in real projects. It is a great tool for building fast, dynamic, and scalable apps. Its value will grow as its use continues.
6. Conclusion
Recap of the Top 5 Frameworks
In this video, we have explored the top five front-end frameworks to learn in 2025:
React: The flexible, component-based framework with a huge community.
Angular: The full-featured, enterprise-ready framework backed by Google.
Vue.js: The simple and progressive framework for projects of all sizes.
Svelte: A unique, performance-focused framework that compiles at build time.
Next.js: The React framework for server-side rendering and static site generation.
---
Encouragement to Explore Based on Project Needs and Career Goals
The right framework depends on your project's needs and your career goals. If you're building a complex enterprise application, Angular might be the way to go. For smaller, high-performance applications, Vue or Svelte could be great choices. React and Next.js are great for any project. They are very scalable and flexible.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Chatbots in ITSM: Enhancing Speed and User Experience!!
In today's fast-paced digital age, it's tough to deliver IT services. Organizations must ensure a smooth user experience, too. IT Service Management (ITSM) has evolved to meet these demands. A standout innovation is the integration of chatbots. AI has transformed IT service delivery through chatbots. They help organizations be more efficient, reduce response times, and improve user satisfaction.
The Growing Role of Chatbots in ITSM
Chatbots are AI-powered virtual assistants. They can mimic human conversations to answer queries and assist with tasks. In ITSM, they automate tasks, provide instant support, and streamline workflows. They can operate 24/7. This makes them vital in IT. Downtime and delays can have serious consequences.
Key Benefits of Chatbots in ITSM
1. Faster Response Times:
Chatbots significantly reduce the time it takes to address user queries. Unlike traditional ticketing systems, users often wait for agents. Chatbots provide immediate responses. This ensures users get help promptly.
2. Round-the-Clock Support:
One of the standout features of chatbots is their availability. They operate 24/7. Users can access support outside regular hours. This is particularly beneficial for global organizations with teams across multiple time zones.
3. Cost Efficiency:
Chatbots reduce IT support teams' workload. They handle repetitive queries and automate routine tasks. It cuts the need for extra staff. It lets agents focus on complex issues, optimising resources.
4. Enhanced User Experience:
Chatbots improve the overall user experience by providing quick and accurate responses. Many advanced chatbots use natural language processing (NLP). It helps them better understand user queries. This makes interactions more intuitive and less frustrating.
5. Data-Driven Insights:
Chatbots can analyse user interactions. They can identify common issues, track performance, and provide insights. These analytics help IT teams identify trends, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions.
Use Cases of Chatbots in ITSM
1. Incident Management:
Chatbots can assist in reporting and resolving incidents. For example, if a user encounters a system error, they can interact with a chatbot to report the issue. The chatbot can log the incident, provide troubleshooting steps, or escalate it to the right team if needed.
2. Password Resets:
Password-related queries are among the most common in IT support. Chatbots can automate password resets. They can verify user identity. They can also guide users through secure steps to reset their credentials.
3. Knowledge Base Access:
Chatbots can act as gateways to an organization’s knowledge base. Users can ask questions. The chatbot can fetch relevant articles or guides. This reduces the need to navigate complex systems manually.
4. Service Requests:
Chatbots can help users raise service requests. They can do this from provisioning new hardware to software installations. They can also provide updates on the status of these requests, keeping users informed.
5. Onboarding Support:
For new employees, chatbots can speed up onboarding. They can answer common questions, provide resources, and guide users through setup tasks.
How Chatbots Enhance User Experience
1. Personalization:
Modern chatbots can integrate with ITSM tools. They can then access user profiles and preferences. This allows them to provide tailored responses, making interactions feel more personalized.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP enables chatbots to understand and respond to queries in a conversational tone. This reduces the frustration often associated with rigid, keyword-based systems.
3. Omnichannel Support:
Many chatbots can work on multiple platforms, like email and messaging apps. This ensures users can access support through their preferred channels.
4. Proactive Assistance:
Advanced chatbots can predict user needs based on historical data. For example, if a user often faces the same issue, the chatbot can offer solutions before the user asks for help.
Challenges in Implementing Chatbots in ITSM
While chatbots offer numerous advantages, their implementation is not without challenges. Organizations need to address the following:
1. Complex Queries:
Chatbots excel at simple, repetitive tasks. But, they may struggle with complex queries. Ensuring seamless handoffs to human agents is crucial to maintaining user satisfaction.
2. Integration with Existing Systems:
Chatbots must integrate with ITSM tools, databases, and other systems to work effectively. Poor integration can lead to inefficiencies and limited functionality.
3. Data Security:
Chatbots often deal with sensitive user information. It is vital to have strong security to prevent data breaches and maintain user trust.
4. User Adoption:
Some users may be hesitant to engage with chatbots, preferring human interaction. Educating users about chatbots' benefits can help overcome this barrier.
Best Practices for Deploying Chatbots in ITSM
1. Start with High-Impact Use Cases:
Start by automating repetitive, time-consuming tasks. Examples are password resets and incident logging. This ensures immediate value and builds confidence in the system.
2. Ensure Robust Training:
Train chatbots using real-world data and scenarios to improve their accuracy and effectiveness. Regular updates are essential to keep them aligned with changing user needs.
3. Focus on User Experience:
Design chatbots with a user-centric approach. Ensure they have a conversational tone, clear instructions, and easy navigation options.
4. Enable Seamless Escalation:
Ensure chatbots can transfer users to human agents when needed. Provide agents with the context of previous interactions to avoid repetition and frustration.
5. Monitor and Optimize:
Regularly check chatbot performance. Use metrics like resolution time, user satisfaction, and error rates. Use these insights to make continuous improvements.
The Future of Chatbots in ITSM
The role of chatbots in ITSM is poised to grow as AI technologies advance. Future developments may include:
- Voice-Activated Chatbots: Integrating voice recognition to provide hands-free support.
- Predictive Capabilities: Using AI to predict and resolve issues before they occur.
- Deeper Integration with IoT: Managing and troubleshooting IoT devices through chatbots.
- Hyper-Personalization: Leveraging advanced analytics to offer highly tailored support.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
Chatbots are now vital in ITSM. They help firms provide faster, more efficient, and user-friendly support. They help IT teams focus on strategy. They do this by automating routine tasks, providing instant help, and improving the user experience. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, robust training, and ongoing optimization. As AI technology evolves, chatbots will shape the future of ITSM. They will help organizations stay ahead in the competitive digital landscape.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital age, it's tough to deliver IT services. Organizations must ensure a smooth user experience, too. IT Service Management (ITSM) has evolved to meet these demands. A standout innovation is the integration of chatbots. AI has transformed IT service delivery through chatbots. They help organizations be more efficient, reduce response times, and improve user satisfaction.
The Growing Role of Chatbots in ITSM
Chatbots are AI-powered virtual assistants. They can mimic human conversations to answer queries and assist with tasks. In ITSM, they automate tasks, provide instant support, and streamline workflows. They can operate 24/7. This makes them vital in IT. Downtime and delays can have serious consequences.
Key Benefits of Chatbots in ITSM
1. Faster Response Times:
Chatbots significantly reduce the time it takes to address user queries. Unlike traditional ticketing systems, users often wait for agents. Chatbots provide immediate responses. This ensures users get help promptly.
2. Round-the-Clock Support:
One of the standout features of chatbots is their availability. They operate 24/7. Users can access support outside regular hours. This is particularly beneficial for global organizations with teams across multiple time zones.
3. Cost Efficiency:
Chatbots reduce IT support teams' workload. They handle repetitive queries and automate routine tasks. It cuts the need for extra staff. It lets agents focus on complex issues, optimising resources.
4. Enhanced User Experience:
Chatbots improve the overall user experience by providing quick and accurate responses. Many advanced chatbots use natural language processing (NLP). It helps them better understand user queries. This makes interactions more intuitive and less frustrating.
5. Data-Driven Insights:
Chatbots can analyse user interactions. They can identify common issues, track performance, and provide insights. These analytics help IT teams identify trends, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions.
Use Cases of Chatbots in ITSM
1. Incident Management:
Chatbots can assist in reporting and resolving incidents. For example, if a user encounters a system error, they can interact with a chatbot to report the issue. The chatbot can log the incident, provide troubleshooting steps, or escalate it to the right team if needed.
2. Password Resets:
Password-related queries are among the most common in IT support. Chatbots can automate password resets. They can verify user identity. They can also guide users through secure steps to reset their credentials.
3. Knowledge Base Access:
Chatbots can act as gateways to an organization’s knowledge base. Users can ask questions. The chatbot can fetch relevant articles or guides. This reduces the need to navigate complex systems manually.
4. Service Requests:
Chatbots can help users raise service requests. They can do this from provisioning new hardware to software installations. They can also provide updates on the status of these requests, keeping users informed.
5. Onboarding Support:
For new employees, chatbots can speed up onboarding. They can answer common questions, provide resources, and guide users through setup tasks.
How Chatbots Enhance User Experience
1. Personalization:
Modern chatbots can integrate with ITSM tools. They can then access user profiles and preferences. This allows them to provide tailored responses, making interactions feel more personalized.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP enables chatbots to understand and respond to queries in a conversational tone. This reduces the frustration often associated with rigid, keyword-based systems.
3. Omnichannel Support:
Many chatbots can work on multiple platforms, like email and messaging apps. This ensures users can access support through their preferred channels.
4. Proactive Assistance:
Advanced chatbots can predict user needs based on historical data. For example, if a user often faces the same issue, the chatbot can offer solutions before the user asks for help.
Challenges in Implementing Chatbots in ITSM
While chatbots offer numerous advantages, their implementation is not without challenges. Organizations need to address the following:
1. Complex Queries:
Chatbots excel at simple, repetitive tasks. But, they may struggle with complex queries. Ensuring seamless handoffs to human agents is crucial to maintaining user satisfaction.
2. Integration with Existing Systems:
Chatbots must integrate with ITSM tools, databases, and other systems to work effectively. Poor integration can lead to inefficiencies and limited functionality.
3. Data Security:
Chatbots often deal with sensitive user information. It is vital to have strong security to prevent data breaches and maintain user trust.
4. User Adoption:
Some users may be hesitant to engage with chatbots, preferring human interaction. Educating users about chatbots' benefits can help overcome this barrier.
Best Practices for Deploying Chatbots in ITSM
1. Start with High-Impact Use Cases:
Start by automating repetitive, time-consuming tasks. Examples are password resets and incident logging. This ensures immediate value and builds confidence in the system.
2. Ensure Robust Training:
Train chatbots using real-world data and scenarios to improve their accuracy and effectiveness. Regular updates are essential to keep them aligned with changing user needs.
3. Focus on User Experience:
Design chatbots with a user-centric approach. Ensure they have a conversational tone, clear instructions, and easy navigation options.
4. Enable Seamless Escalation:
Ensure chatbots can transfer users to human agents when needed. Provide agents with the context of previous interactions to avoid repetition and frustration.
5. Monitor and Optimize:
Regularly check chatbot performance. Use metrics like resolution time, user satisfaction, and error rates. Use these insights to make continuous improvements.
The Future of Chatbots in ITSM
The role of chatbots in ITSM is poised to grow as AI technologies advance. Future developments may include:
- Voice-Activated Chatbots: Integrating voice recognition to provide hands-free support.
- Predictive Capabilities: Using AI to predict and resolve issues before they occur.
- Deeper Integration with IoT: Managing and troubleshooting IoT devices through chatbots.
- Hyper-Personalization: Leveraging advanced analytics to offer highly tailored support.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
Chatbots are now vital in ITSM. They help firms provide faster, more efficient, and user-friendly support. They help IT teams focus on strategy. They do this by automating routine tasks, providing instant help, and improving the user experience. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, robust training, and ongoing optimization. As AI technology evolves, chatbots will shape the future of ITSM. They will help organizations stay ahead in the competitive digital landscape.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Optimize IT Service Management with ISO 20000 Certification
In today's fast, tech-driven world, businesses rely on IT services to run. As we depend more on IT, we must ensure it works well, fast, and safely. Enter ISO 20000. It is a global standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). It helps organizations align their IT services with business needs. This ensures consistent quality and better performance.
ISO 20000 is a framework for organizations. It helps them deliver high-quality IT services, cut costs, and boost customer satisfaction. This blog will explore ISO 20000. It will cover its role in IT service management and its benefits to organizations.
What is ISO 20000?
ISO 20000 is a series of global standards. They help organizations manage IT services. The standard has a complete set of requirements. An organization must meet them to manage its IT services effectively.
ISO 20000 aims to create a reliable framework for managing IT services. It ensures they meet business and customer expectations. It follows best practices for service management. It aligns with other frameworks, like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library).
The standard is divided into two parts:
- ISO 20000-1: Service Management System Requirements. This part outlines the requirements for an IT service management system. It covers its establishment, implementation, operation, monitoring, review, and improvement.
- ISO 20000-2: Code of Practice for Service Management. It gives guidelines for implementing ISO 20000-1. It also offers best practices.
Why is ISO 20000 Important for IT Service Management?
- Improves Service Quality: ISO 20000's main benefit is it ensures high-quality IT services. This standard will help organizations. It will ensure their IT services meet SLAs. This will reduce service disruptions and customer dissatisfaction.
- Increases Customer Satisfaction: ISO 20000 helps organizations meet customer IT service needs. Clear processes, performance monitoring, and improvement can help. They can make services reliable, timely, and responsive. This will increase customer satisfaction.
- Boosts Efficiency: ISO 20000 helps organizations improve IT service management. It streamlines processes, eliminates redundancies, and fixes inefficiencies. This leads to better resource utilization, lower costs, and faster service delivery.
- A Competitive Edge: ISO 20000 certification shows a commitment to service excellence. It can boost an organization's reputation and give it an edge in the market. This can be particularly beneficial when bidding for contracts or building partnerships.
- Strengthens Risk Management: ISO 20000 helps organizations reduce risks in IT service delivery. It does this by enforcing standardized processes. The standard encourages a proactive approach to managing incidents and problems. This helps ensure business continuity by preventing disruptions.
- Adopting ISO 20000 can ensure compliance with IT service laws and contracts. It also provides a clear, auditable trail of compliance. This can help during audits.
Key Components of ISO 20000 IT Service Management
ISO 20000 defines several key processes and components. To meet the standard, organizations must implement them. These processes include:
- Service Management System (SMS): ISO 20000 is based on a strong IT SMS. This includes creating a service management policy and defining roles. It must ensure the system aligns with business goals.
- Service Design and Transition: It is about designing IT services for the business. It also ensures smooth transitions from development to live environments. It ensures that new services are introduced in a structured and controlled manner.
- Incident Management: Its goal is to restore normal service after disruptions. It includes processes to identify, log, and resolve incidents. This minimizes downtime and its impact on the business.
- Problem Management: It aims to find and fix the causes of recurring incidents. It seeks long-term solutions to prevent them. It works closely with incident management to ensure issues are thoroughly addressed.
- Change Management: This process ensures that IT updates cause minimal disruption. It involves assessing, approving, and managing changes in a controlled manner.
- Service Level Management (SLM): SLM defines, agrees, and monitors SLAs with customers. It ensures IT services meet agreed performance standards and customers' expectations.
- Capacity Management: It ensures the IT infrastructure can meet current and future demands. It involves monitoring, forecasting, and optimizing capacity to avoid performance bottlenecks.
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI): CSI is a key principle of ISO 20000. It involves regularly reviewing and improving IT service management processes. This keeps them aligned with business goals and customer needs. This ensures that services evolve in response to changing market conditions.
Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification
- ISO 20000 sets a clear standard for IT service management across an organization. It improves service delivery and reduces variability in IT services.
- Cost Reduction: By optimizing processes and minimizing inefficiencies, organizations can reduce operational costs. ISO 20000 urges organizations to manage resources, cut waste, and use cost-effective practices.
- Better Communication and Collaboration: ISO 20000 fosters teamwork and clear communication across departments. It promotes alignment between IT teams and business units. IT services should support business goals and customer needs.
- Enhanced Reputation and Trust: ISO 20000 certification builds trust with customers and stakeholders. It is a mark of excellence. Certified organizations prove their commitment to quality and improvement. They aim to satisfy customers.
- ISO 20000 certification helps regulated industries meet IT service management laws. It also ensures IT services meet industry standards and best practices.
- Business Continuity: ISO 20000 emphasizes risk management and incident response. It aims to fix problems before they occur, ensuring IT service resilience. This minimizes interruptions and ensures business continuity.
How to Implement ISO 20000 in Your Organization
Implementing ISO 20000 in your organization involves several key steps:
- Conduct a Gap Analysis. Assess your IT service management processes. Compare them to the ISO 20000 requirements. Find areas needing improvement. Then, create a plan to meet the standard.
- Create an SMS. It should define policies, procedures, and roles for managing IT services. The system must align with business goals. It must deliver quality services.
- Train Your Team: Educate your team on the principles of ISO 20000 and its benefits. Train on the standard's requirements and best practices in IT service management.
- Monitor and Measure Performance: Set up systems to track your IT services' performance. Use KPIs to measure service quality and find areas to improve.
- Continuous Improvement: Use a process to improve your IT service management. Regularly review and enhance your practices. Use feedback from customers, employees, and performance metrics to drive ongoing improvements.
- Obtain Certification: The certification process includes an audit of your SMS. It must meet the standard's requiremen
How to obtain ISO 20000 Optimizing IT Service Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
ISO 20000 is a key framework for organizations. It helps them improve the quality, efficiency, and resilience of their IT services. This standard helps organizations align IT services with business goals. This will boost customer satisfaction and drive improvement. ISO 20000 also has many benefits. It standardizes processes, manages risks, reduces costs, and improves compliance.
In a digital world, businesses must be competitive. So, they must implement ISO 20000. It's not just a smart choice—it’s essential. ISO 20000 can improve IT service management for any business, big or small. It will prepare you for tomorrow's digital challenges.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
In today's fast, tech-driven world, businesses rely on IT services to run. As we depend more on IT, we must ensure it works well, fast, and safely. Enter ISO 20000. It is a global standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). It helps organizations align their IT services with business needs. This ensures consistent quality and better performance.
ISO 20000 is a framework for organizations. It helps them deliver high-quality IT services, cut costs, and boost customer satisfaction. This blog will explore ISO 20000. It will cover its role in IT service management and its benefits to organizations.
What is ISO 20000?
ISO 20000 is a series of global standards. They help organizations manage IT services. The standard has a complete set of requirements. An organization must meet them to manage its IT services effectively.
ISO 20000 aims to create a reliable framework for managing IT services. It ensures they meet business and customer expectations. It follows best practices for service management. It aligns with other frameworks, like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library).
The standard is divided into two parts:
- ISO 20000-1: Service Management System Requirements. This part outlines the requirements for an IT service management system. It covers its establishment, implementation, operation, monitoring, review, and improvement.
- ISO 20000-2: Code of Practice for Service Management. It gives guidelines for implementing ISO 20000-1. It also offers best practices.
Why is ISO 20000 Important for IT Service Management?
- Improves Service Quality: ISO 20000's main benefit is it ensures high-quality IT services. This standard will help organizations. It will ensure their IT services meet SLAs. This will reduce service disruptions and customer dissatisfaction.
- Increases Customer Satisfaction: ISO 20000 helps organizations meet customer IT service needs. Clear processes, performance monitoring, and improvement can help. They can make services reliable, timely, and responsive. This will increase customer satisfaction.
- Boosts Efficiency: ISO 20000 helps organizations improve IT service management. It streamlines processes, eliminates redundancies, and fixes inefficiencies. This leads to better resource utilization, lower costs, and faster service delivery.
- A Competitive Edge: ISO 20000 certification shows a commitment to service excellence. It can boost an organization's reputation and give it an edge in the market. This can be particularly beneficial when bidding for contracts or building partnerships.
- Strengthens Risk Management: ISO 20000 helps organizations reduce risks in IT service delivery. It does this by enforcing standardized processes. The standard encourages a proactive approach to managing incidents and problems. This helps ensure business continuity by preventing disruptions.
- Adopting ISO 20000 can ensure compliance with IT service laws and contracts. It also provides a clear, auditable trail of compliance. This can help during audits.
Key Components of ISO 20000 IT Service Management
ISO 20000 defines several key processes and components. To meet the standard, organizations must implement them. These processes include:
- Service Management System (SMS): ISO 20000 is based on a strong IT SMS. This includes creating a service management policy and defining roles. It must ensure the system aligns with business goals.
- Service Design and Transition: It is about designing IT services for the business. It also ensures smooth transitions from development to live environments. It ensures that new services are introduced in a structured and controlled manner.
- Incident Management: Its goal is to restore normal service after disruptions. It includes processes to identify, log, and resolve incidents. This minimizes downtime and its impact on the business.
- Problem Management: It aims to find and fix the causes of recurring incidents. It seeks long-term solutions to prevent them. It works closely with incident management to ensure issues are thoroughly addressed.
- Change Management: This process ensures that IT updates cause minimal disruption. It involves assessing, approving, and managing changes in a controlled manner.
- Service Level Management (SLM): SLM defines, agrees, and monitors SLAs with customers. It ensures IT services meet agreed performance standards and customers' expectations.
- Capacity Management: It ensures the IT infrastructure can meet current and future demands. It involves monitoring, forecasting, and optimizing capacity to avoid performance bottlenecks.
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI): CSI is a key principle of ISO 20000. It involves regularly reviewing and improving IT service management processes. This keeps them aligned with business goals and customer needs. This ensures that services evolve in response to changing market conditions.
Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification
- ISO 20000 sets a clear standard for IT service management across an organization. It improves service delivery and reduces variability in IT services.
- Cost Reduction: By optimizing processes and minimizing inefficiencies, organizations can reduce operational costs. ISO 20000 urges organizations to manage resources, cut waste, and use cost-effective practices.
- Better Communication and Collaboration: ISO 20000 fosters teamwork and clear communication across departments. It promotes alignment between IT teams and business units. IT services should support business goals and customer needs.
- Enhanced Reputation and Trust: ISO 20000 certification builds trust with customers and stakeholders. It is a mark of excellence. Certified organizations prove their commitment to quality and improvement. They aim to satisfy customers.
- ISO 20000 certification helps regulated industries meet IT service management laws. It also ensures IT services meet industry standards and best practices.
- Business Continuity: ISO 20000 emphasizes risk management and incident response. It aims to fix problems before they occur, ensuring IT service resilience. This minimizes interruptions and ensures business continuity.
How to Implement ISO 20000 in Your Organization
Implementing ISO 20000 in your organization involves several key steps:
- Conduct a Gap Analysis. Assess your IT service management processes. Compare them to the ISO 20000 requirements. Find areas needing improvement. Then, create a plan to meet the standard.
- Create an SMS. It should define policies, procedures, and roles for managing IT services. The system must align with business goals. It must deliver quality services.
- Train Your Team: Educate your team on the principles of ISO 20000 and its benefits. Train on the standard's requirements and best practices in IT service management.
- Monitor and Measure Performance: Set up systems to track your IT services' performance. Use KPIs to measure service quality and find areas to improve.
- Continuous Improvement: Use a process to improve your IT service management. Regularly review and enhance your practices. Use feedback from customers, employees, and performance metrics to drive ongoing improvements.
- Obtain Certification: The certification process includes an audit of your SMS. It must meet the standard's requiremen
How to obtain ISO 20000 Optimizing IT Service Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2025 are:
Conclusion
ISO 20000 is a key framework for organizations. It helps them improve the quality, efficiency, and resilience of their IT services. This standard helps organizations align IT services with business goals. This will boost customer satisfaction and drive improvement. ISO 20000 also has many benefits. It standardizes processes, manages risks, reduces costs, and improves compliance.
In a digital world, businesses must be competitive. So, they must implement ISO 20000. It's not just a smart choice—it’s essential. ISO 20000 can improve IT service management for any business, big or small. It will prepare you for tomorrow's digital challenges.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Data Science for IT Process Management and Optimization
The digital age has made data central to innovation and efficiency. It drives decisions and operations. To stay competitive, organizations must use data science in IT process management. It has become a game-changer. This mix of advanced analytics and IT operations offers unmatched opportunities. It can optimize, predict, and automate. This blog will explore data science in IT process management. We'll cover its applications, benefits, challenges, and future potential.
The Role of Data Science in IT Process Management
Data science is about finding insights in large, mixed datasets. It uses techniques like machine learning, statistical analysis, and data visualization. Data science helps IT process management. It streamlines operations, finds inefficiencies, and improves service delivery.
IT process management includes many activities. These are incident management, change management, problem resolution, and service optimization. Traditionally, these processes relied on manual intervention and historical data analysis. Data science enables real-time analysis and predictions. It revolutionizes IT departments.
Key Applications of Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses machine learning to analyze past data. It predicts potential system failures. By identifying patterns and anomalies, IT teams can fix issues before they escalate. This minimizes downtime and improves service reliability.
2. Incident Management
Data science can greatly improve incident management. It can automate detecting and classifying incidents. NLP algorithms can analyze ticket descriptions and route them to the right teams. This reduces resolution times and improves customer satisfaction.
3. Capacity Planning
Data science helps in capacity planning. It does this by analyzing past usage data and forecasting future demand. IT teams can optimally allocate resources. They can prevent overloads and avoid wasting money on underused resources.
4. Root Cause Analysis
Machine learning algorithms can sift through vast datasets. They can find the root causes of recurring problems. This proactive approach helps IT teams find long-term solutions. They won't just keep fixing symptoms.
5. Service Level Agreement (SLA) Compliance
Data science tools monitor SLA metrics in real-time, alerting teams to potential breaches. Predictive models can forecast SLA violations. This lets IT teams act quickly.
6. IT Security
Data science plays a critical role in identifying security threats. It can detect anomalies that indicate cyberattacks. It does this by analyzing network traffic patterns and user behavior. This enables faster responses to security breaches.
7. Process Automation
RPA, combined with data science, automates repetitive IT tasks. These include system updates, backups, and patch management. This reduces human error and frees up IT staff for strategic initiatives.
Benefits of Integrating Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Automation and predictive insights reduce manual work. This lets IT teams focus on strategic tasks and deliver services more efficiently.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Data-driven insights empower IT managers to make informed decisions. This includes resource allocation and process optimization.
3. Cost Savings
Predictive maintenance and capacity planning cut costs. They do this by preventing system failures and optimising resource use.
4. Proactive Problem-Solving
Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics help IT teams. They can fix issues before they impact end-users. This boosts service quality.
5. Scalability
Data science tools can adapt to the growing complexity of IT. They keep processes efficient as organizations expand.
6. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Higher customer satisfaction comes from faster incident resolution, reliable services, and proactive problem-solving.
Challenges in Implementing Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Data Quality
The effectiveness of data science depends on the quality of data. Incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate data can lead to erroneous insights and decisions.
2. Integration Complexities
Integrating data science tools with existing IT systems can be tough. It takes a lot of time and resources.
3. Skill Gaps
Implementing data science solutions requires skilled professionals. They must be proficient in data analysis, machine learning, and IT operations. Bridging this skills gap is a major hurdle for many organizations.
4. Cost of Implementation
The initial investment in data science tools, infrastructure, and talent can be high. This is a barrier for smaller organizations.
5. Data Security and Privacy
Sensitive IT data needs strong security. This prevents unauthorized access and complies with data protection laws.
6. Change Management
Introducing data science into IT processes often requires a cultural shift. Resistance to change can hinder successful implementation.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Start Small
Start with pilot projects to show the value of data science in IT process management. Use these successes to build momentum for broader adoption.
2. Invest in Training
Upskill IT teams in data science methodologies and tools. Consider hiring data scientists or partnering with experts to close the skills gap.
3. Ensure Data Quality
Implement robust data governance policies to maintain high-quality, accurate, and consistent data.
4. Collaborate Across Teams
Foster collaboration between IT, data science, and business teams. This will align their objectives and maximise the impact of data science projects.
5. Leverage Automation
Combine data science with automation tools to enhance efficiency and scalability.
6. Monitor and Refine
Continuously monitor and refine data science models to adapt to changing IT environments.
The Future of Data Science in IT Process Management
Data science in IT process management is still in its early stages. But, the potential is immense. As technologies evolve, we can expect more sophisticated applications, such as:
- AI-Driven IT Operations (AIOps): AI and machine learning will become key to IT operations. They will automate complex tasks and provide real-time insights.
- Edge Computing: Data science will be key in managing IT processes at the edge. It will enable faster decision-making and better performance.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced analytics will reveal new security threats. This will enable stronger defenses.
Sustainability: Data science will help cut energy use and IT's carbon footprint.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Data science is transforming IT process management. It helps organizations to work more efficiently. It can predict and prevent issues, and it delivers better services. Despite some challenges, the benefits far outweigh the obstacles. So, it's a worthwhile investment for forward-thinking organizations. By embracing data science, IT can be a strategic enabler of business success. It can drive innovation and resilience in a digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
The digital age has made data central to innovation and efficiency. It drives decisions and operations. To stay competitive, organizations must use data science in IT process management. It has become a game-changer. This mix of advanced analytics and IT operations offers unmatched opportunities. It can optimize, predict, and automate. This blog will explore data science in IT process management. We'll cover its applications, benefits, challenges, and future potential.
The Role of Data Science in IT Process Management
Data science is about finding insights in large, mixed datasets. It uses techniques like machine learning, statistical analysis, and data visualization. Data science helps IT process management. It streamlines operations, finds inefficiencies, and improves service delivery.
IT process management includes many activities. These are incident management, change management, problem resolution, and service optimization. Traditionally, these processes relied on manual intervention and historical data analysis. Data science enables real-time analysis and predictions. It revolutionizes IT departments.
Key Applications of Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses machine learning to analyze past data. It predicts potential system failures. By identifying patterns and anomalies, IT teams can fix issues before they escalate. This minimizes downtime and improves service reliability.
2. Incident Management
Data science can greatly improve incident management. It can automate detecting and classifying incidents. NLP algorithms can analyze ticket descriptions and route them to the right teams. This reduces resolution times and improves customer satisfaction.
3. Capacity Planning
Data science helps in capacity planning. It does this by analyzing past usage data and forecasting future demand. IT teams can optimally allocate resources. They can prevent overloads and avoid wasting money on underused resources.
4. Root Cause Analysis
Machine learning algorithms can sift through vast datasets. They can find the root causes of recurring problems. This proactive approach helps IT teams find long-term solutions. They won't just keep fixing symptoms.
5. Service Level Agreement (SLA) Compliance
Data science tools monitor SLA metrics in real-time, alerting teams to potential breaches. Predictive models can forecast SLA violations. This lets IT teams act quickly.
6. IT Security
Data science plays a critical role in identifying security threats. It can detect anomalies that indicate cyberattacks. It does this by analyzing network traffic patterns and user behavior. This enables faster responses to security breaches.
7. Process Automation
RPA, combined with data science, automates repetitive IT tasks. These include system updates, backups, and patch management. This reduces human error and frees up IT staff for strategic initiatives.
Benefits of Integrating Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Automation and predictive insights reduce manual work. This lets IT teams focus on strategic tasks and deliver services more efficiently.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Data-driven insights empower IT managers to make informed decisions. This includes resource allocation and process optimization.
3. Cost Savings
Predictive maintenance and capacity planning cut costs. They do this by preventing system failures and optimising resource use.
4. Proactive Problem-Solving
Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics help IT teams. They can fix issues before they impact end-users. This boosts service quality.
5. Scalability
Data science tools can adapt to the growing complexity of IT. They keep processes efficient as organizations expand.
6. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Higher customer satisfaction comes from faster incident resolution, reliable services, and proactive problem-solving.
Challenges in Implementing Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Data Quality
The effectiveness of data science depends on the quality of data. Incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate data can lead to erroneous insights and decisions.
2. Integration Complexities
Integrating data science tools with existing IT systems can be tough. It takes a lot of time and resources.
3. Skill Gaps
Implementing data science solutions requires skilled professionals. They must be proficient in data analysis, machine learning, and IT operations. Bridging this skills gap is a major hurdle for many organizations.
4. Cost of Implementation
The initial investment in data science tools, infrastructure, and talent can be high. This is a barrier for smaller organizations.
5. Data Security and Privacy
Sensitive IT data needs strong security. This prevents unauthorized access and complies with data protection laws.
6. Change Management
Introducing data science into IT processes often requires a cultural shift. Resistance to change can hinder successful implementation.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Science in IT Process Management
1. Start Small
Start with pilot projects to show the value of data science in IT process management. Use these successes to build momentum for broader adoption.
2. Invest in Training
Upskill IT teams in data science methodologies and tools. Consider hiring data scientists or partnering with experts to close the skills gap.
3. Ensure Data Quality
Implement robust data governance policies to maintain high-quality, accurate, and consistent data.
4. Collaborate Across Teams
Foster collaboration between IT, data science, and business teams. This will align their objectives and maximise the impact of data science projects.
5. Leverage Automation
Combine data science with automation tools to enhance efficiency and scalability.
6. Monitor and Refine
Continuously monitor and refine data science models to adapt to changing IT environments.
The Future of Data Science in IT Process Management
Data science in IT process management is still in its early stages. But, the potential is immense. As technologies evolve, we can expect more sophisticated applications, such as:
- AI-Driven IT Operations (AIOps): AI and machine learning will become key to IT operations. They will automate complex tasks and provide real-time insights.
- Edge Computing: Data science will be key in managing IT processes at the edge. It will enable faster decision-making and better performance.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced analytics will reveal new security threats. This will enable stronger defenses.
Sustainability: Data science will help cut energy use and IT's carbon footprint.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Data science is transforming IT process management. It helps organizations to work more efficiently. It can predict and prevent issues, and it delivers better services. Despite some challenges, the benefits far outweigh the obstacles. So, it's a worthwhile investment for forward-thinking organizations. By embracing data science, IT can be a strategic enabler of business success. It can drive innovation and resilience in a digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
The Crucial Role of Change Management in ITSM Success!!
In today's fast-paced business world, organizations must evolve. They must keep up with new tech, industry standards, and customer expectations. As a result, changes to IT systems, processes, and services are inevitable. But, if unmanaged, these changes can disrupt operations, harm security, or cause inefficiencies. This is where Change Management in IT Service Management (ITSM) becomes crucial. Effective Change Management makes changes in a controlled, efficient way. It minimizes negative impacts and maximizes value.
What is Change Management in ITSM?
Change Management, part of ITSM, manages changes to IT systems and services. It controls, documents, and implements them. It aims to manage changes and align them with the organization's goals. Change Management helps prevent problems from poorly implemented changes. These changes may involve hardware, software, infrastructure, or processes.
At its core, Change Management in ITSM focuses on three key aspects:
-
Change Management minimizes service disruption risks. It assesses changes for potential risks and implements strategies to mitigate them.
-
Accountability: The process requires clear docs, approvals, and communication. This ensures accountability and transparency at every step.
-
Change Management aligns changes with business goals. It ensures they provide value.
Why Change Management is Important in ITSM
Change is unavoidable in the IT world, but it doesn’t have to be chaotic or detrimental. Effective Change Management is essential for several reasons:
1. Risk Mitigation and Service Continuity
Unmanaged changes can cause major disruptions, like downtime, data loss, or security risks. A change, no matter how small, could have unforeseen consequences. A software update might introduce a bug that crashes the system. A configuration change might break a critical application.
Change Management reduces the risk of service disruptions. It does this by assessing and evaluating the impact of proposed changes. A structured approach can help. Organizations can assess risks, test changes, and schedule changes for low-impact hours. This will reduce the chance of service outages or unexpected failures.
2. Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Managing change without a structured approach often leads to confusion, inefficiencies, and rework. For example, without proper docs or approvals, IT teams might repeat work or create conflicts. This would waste resources and increase costs.
By using Change Management processes, IT teams can streamline their workflows. It tracks, reviews, and implements all changes per a set procedure. This reduces the chance of mistakes. Also, changes are planned and scheduled in advance. It allows for efficient resource use. It avoids costly, urgent fixes from last-minute surprises.
3. Ensuring Compliance and Security
For organizations that must comply with regulations, proper Change Management is critical. This includes GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. Uncontrolled changes could violate compliance requirements. They might breach sensitive data or introduce security vulnerabilities.
Change Management processes must document changes and audit trails. They are essential for compliance with regulations. Also, it ensures that security measures are reviewed and updated during changes. This prevents potential risks. This includes data encryption and access controls.
4. Better Communication and Collaboration
Change Management creates a framework for clear communication and teamwork across teams. This is vital in large organizations with many teams. These include development, operations, security, and service management. They all implement changes.
Structured change requests, approvals, and notifications keep all stakeholders informed about upcoming changes. It reduces confusion. It helps teams work together better. So, changes are made smoothly. For example, if a system upgrade is planned, the ITSM tool can notify the helpdesk team. This will prepare them for a rise in support tickets or user inquiries after the upgrade.
5. Aligning IT Changes with Business Objectives
In many organizations, IT is viewed as a cost center rather than a strategic asset. However, IT can contribute to business success if it is aligned with business goals. Change Management ensures that any IT change supports the business's goals.
For example, an organization may launch a new CRM system to improve customer service. Effective Change Management ensures a smooth, documented transition to the new system. It must have support. It enables the business to reap the CRM system's benefits without major disruptions.
6. Increased Customer Satisfaction
In today’s customer-centric world, delivering uninterrupted service is essential. Frequent outages or slowdowns in IT systems will harm customers. They will be dissatisfied and may take their business elsewhere.
ITSM's Change Management ensures changes have minimal impact on end-users. Reducing service disruptions and ensuring consistent delivery will give customers a seamless experience. For example, a new software release or patch is tested before deployment. If issues arise, they can be fixed quickly to minimize impact on customers.
The Change Management Process in ITSM
The Change Management process typically includes the following stages:
-
Change Request Submission: A team or stakeholder submits a request for change (RFC). It details the change, its benefits, and any risks or impacts.
-
Change Assessment: A Change Advisory Board (CAB) or relevant stakeholders evaluate the change. The team assesses the potential risks, benefits, and resource requirements.
-
Approval or Rejection: The change is either approved or rejected. This is based on the assessment. If approved, a timeline for implementation is established.
-
Change Implementation: The change is made per the approved plan. Rollback procedures are often in place in case of issues.
-
Post-Change Review: After the change is made, a review is done. It checks for success, finds any issues, and ensures the goals are met.
-
Documentation: All details of the change are documented. This includes decisions, approvals, and outcomes. This documentation serves as an audit trail for future reference.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
With tech vital to business, Change Management in ITSM is a must, not just a best practice. Without a change management process, organizations risk disruptions, breaches, and lost opportunities. Change Management helps businesses implement changes efficiently. It minimizes impacts on services, compliance, and security. It also helps organizations align IT with business goals. This improves efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall success.
An effective Change Management process takes time, effort, and resources. But, its long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. It makes sure IT is a strategic asset. It should drive innovation and support business growth.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
In today's fast-paced business world, organizations must evolve. They must keep up with new tech, industry standards, and customer expectations. As a result, changes to IT systems, processes, and services are inevitable. But, if unmanaged, these changes can disrupt operations, harm security, or cause inefficiencies. This is where Change Management in IT Service Management (ITSM) becomes crucial. Effective Change Management makes changes in a controlled, efficient way. It minimizes negative impacts and maximizes value.
What is Change Management in ITSM?
Change Management, part of ITSM, manages changes to IT systems and services. It controls, documents, and implements them. It aims to manage changes and align them with the organization's goals. Change Management helps prevent problems from poorly implemented changes. These changes may involve hardware, software, infrastructure, or processes.
At its core, Change Management in ITSM focuses on three key aspects:
-
Change Management minimizes service disruption risks. It assesses changes for potential risks and implements strategies to mitigate them.
-
Accountability: The process requires clear docs, approvals, and communication. This ensures accountability and transparency at every step.
-
Change Management aligns changes with business goals. It ensures they provide value.
Why Change Management is Important in ITSM
Change is unavoidable in the IT world, but it doesn’t have to be chaotic or detrimental. Effective Change Management is essential for several reasons:
1. Risk Mitigation and Service Continuity
Unmanaged changes can cause major disruptions, like downtime, data loss, or security risks. A change, no matter how small, could have unforeseen consequences. A software update might introduce a bug that crashes the system. A configuration change might break a critical application.
Change Management reduces the risk of service disruptions. It does this by assessing and evaluating the impact of proposed changes. A structured approach can help. Organizations can assess risks, test changes, and schedule changes for low-impact hours. This will reduce the chance of service outages or unexpected failures.
2. Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Managing change without a structured approach often leads to confusion, inefficiencies, and rework. For example, without proper docs or approvals, IT teams might repeat work or create conflicts. This would waste resources and increase costs.
By using Change Management processes, IT teams can streamline their workflows. It tracks, reviews, and implements all changes per a set procedure. This reduces the chance of mistakes. Also, changes are planned and scheduled in advance. It allows for efficient resource use. It avoids costly, urgent fixes from last-minute surprises.
3. Ensuring Compliance and Security
For organizations that must comply with regulations, proper Change Management is critical. This includes GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. Uncontrolled changes could violate compliance requirements. They might breach sensitive data or introduce security vulnerabilities.
Change Management processes must document changes and audit trails. They are essential for compliance with regulations. Also, it ensures that security measures are reviewed and updated during changes. This prevents potential risks. This includes data encryption and access controls.
4. Better Communication and Collaboration
Change Management creates a framework for clear communication and teamwork across teams. This is vital in large organizations with many teams. These include development, operations, security, and service management. They all implement changes.
Structured change requests, approvals, and notifications keep all stakeholders informed about upcoming changes. It reduces confusion. It helps teams work together better. So, changes are made smoothly. For example, if a system upgrade is planned, the ITSM tool can notify the helpdesk team. This will prepare them for a rise in support tickets or user inquiries after the upgrade.
5. Aligning IT Changes with Business Objectives
In many organizations, IT is viewed as a cost center rather than a strategic asset. However, IT can contribute to business success if it is aligned with business goals. Change Management ensures that any IT change supports the business's goals.
For example, an organization may launch a new CRM system to improve customer service. Effective Change Management ensures a smooth, documented transition to the new system. It must have support. It enables the business to reap the CRM system's benefits without major disruptions.
6. Increased Customer Satisfaction
In today’s customer-centric world, delivering uninterrupted service is essential. Frequent outages or slowdowns in IT systems will harm customers. They will be dissatisfied and may take their business elsewhere.
ITSM's Change Management ensures changes have minimal impact on end-users. Reducing service disruptions and ensuring consistent delivery will give customers a seamless experience. For example, a new software release or patch is tested before deployment. If issues arise, they can be fixed quickly to minimize impact on customers.
The Change Management Process in ITSM
The Change Management process typically includes the following stages:
-
Change Request Submission: A team or stakeholder submits a request for change (RFC). It details the change, its benefits, and any risks or impacts.
-
Change Assessment: A Change Advisory Board (CAB) or relevant stakeholders evaluate the change. The team assesses the potential risks, benefits, and resource requirements.
-
Approval or Rejection: The change is either approved or rejected. This is based on the assessment. If approved, a timeline for implementation is established.
-
Change Implementation: The change is made per the approved plan. Rollback procedures are often in place in case of issues.
-
Post-Change Review: After the change is made, a review is done. It checks for success, finds any issues, and ensures the goals are met.
-
Documentation: All details of the change are documented. This includes decisions, approvals, and outcomes. This documentation serves as an audit trail for future reference.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
With tech vital to business, Change Management in ITSM is a must, not just a best practice. Without a change management process, organizations risk disruptions, breaches, and lost opportunities. Change Management helps businesses implement changes efficiently. It minimizes impacts on services, compliance, and security. It also helps organizations align IT with business goals. This improves efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall success.
An effective Change Management process takes time, effort, and resources. But, its long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. It makes sure IT is a strategic asset. It should drive innovation and support business growth.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
ITSM for Effective Digital Workplace Transformation Solution
In today's fast-paced digital world, the traditional office environment is quickly evolving into a more dynamic, flexible, and digitally driven workplace. As businesses continue to embrace the shift to remote, hybrid, and cloud-based models, IT Service Management (ITSM) has become a critical enabler of this transformation. In this blog, we will explore how ITSM is facilitating the digital workplace transformation and the role it plays in creating more efficient, collaborative, and agile working environments.
What is ITSM?
IT Service Management (ITSM) refers to the activities, processes, and policies that an organization uses to design, deliver, manage, and improve IT services for its customers. Traditionally, ITSM frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) have focused on delivering high-quality IT services, ensuring efficiency, minimizing downtime, and maximizing productivity. As organizations transition to digital-first operations, ITSM has expanded to address not just the needs of IT departments but also those of employees, customers, and end-users across various digital platforms.
The Rise of the Digital Workplace
The digital workplace is a tech-driven, virtual environment. It lets employees work from anywhere, using any device and digital tools. In this new world, work's traditional boundaries have changed. Flexible, collaborative, real-time communication tools now empower teams to work efficiently. Gartner's research shows that nearly 70% of employees will work in hybrid models by 2025. This will increase the need for better tech integration and IT services.
The digital workplace transformation includes many elements. They are cloud computing, AI collaboration tools, digital workflows, automation, and better cybersecurity. However, a truly effective digital workplace needs more than new tech. It requires an overhaul of how IT services are managed and delivered. This is where ITSM comes into play.
The Role of ITSM in Digital Workplace Transformation
ITSM is key to the digital workplace transformation. It ensures IT services and support are agile, efficient, and aligned with business needs. Here are the key ways ITSM supports this transformation:
1. Improved Service Delivery and Support
In a digital workplace, employees rely on digital tools to do their tasks. Any downtime or service interruptions can disrupt productivity. ITSM ensures IT services are delivered efficiently and with minimal disruption. Support must always be available when needed. ITSM frameworks like ITIL aim to improve service desk operations. They focus on incident management and request fulfillment. The goal is to ensure a smooth experience for end-users.
Cloud-based ITSM platforms let businesses manage services remotely. They can support employees in different locations. This is crucial in hybrid or remote work. IT teams must provide support, no matter the location.
2. Automation and Streamlining Processes
A key benefit of digital workplace transformation is automating routine tasks. ITSM facilitates automation by standardizing workflows and processes across the organization. ITSM allows employees to use automated ticketing and self-service portals. They can resolve issues without waiting for IT support.
Automation speeds up service delivery. It also reduces the burden on IT staff. They can then focus on more strategic initiatives. ITSM tools like ServiceNow and Freshservice have powerful automation features. They include AI chatbots that help with ticket triage and incident management.
3. Collaboration and Communication
A successful digital workplace thrives on effective communication and collaboration among teams. ITSM supports these goals by integrating with tools like Teams, Slack, and Zoom. By using these integrations, IT teams can improve service desk support. They can share knowledge and discuss issues and solutions in real time.
Moreover, ITSM encourages knowledge management repositories. They help employees find solutions to common issues on their own. This self-service approach boosts employee satisfaction. It also frees IT teams to focus on complex tasks.
4. Employee Experience Enhancement
The digital workplace aims to improve employee experience. It does this by providing flexibility, collaboration, and seamless IT services. ITSM helps by focusing on the user experience. It ensures employees can access high-quality IT support when they need it. ITSM uses feedback loops and user-centric design. This ensures services meet the workforce's needs.
ITSM platforms often include self-service portals and mobile apps. They let employees submit service requests, track incidents, and find info on-demand. This improves satisfaction and productivity.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
A key part of digital workplace transformation is making data-driven decisions. ITSM platforms generate a lot of data from requests, incidents, and changes. Businesses can gain insights by analyzing this data. They can find areas to improve, optimize IT service delivery, and predict disruptions.
For example, IT teams can use data to find recurring issues, track SLA performance, and fix system flaws. ITSM solutions with AI and machine learning are more powerful. They can predict trends and automate decision-making.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
As organizations expand and evolve, their IT infrastructure needs to scale accordingly. ITSM provides the framework to manage this growth effectively. Cloud-based ITSM solutions are key to digital workplace transformation. They let businesses scale services as needed. ITSM ensures that IT services can be scaled without losing quality. This applies when an organization adds users, adopts new tools, or expands into new areas.
7. Security and Compliance
Digital workplace transformation raises the need for strong security and compliance. ITSM helps organizations keep a secure, compliant IT environment. It does this by providing structured processes for change, incident, and risk management. ITSM practices help businesses. They can implement policies to protect data, reduce risks, and comply with GDPR and HIPAA.
ITSM also helps businesses handle security incidents better.
It does this by ensuring clear procedures for:
-
Identifying,
-
Assessing, and
-
Mitigating security risks.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
ITSM is now key to digital workplace transformation, not just managing IT services. ITSM helps organizations adapt to the fast-changing digital world. It does this by improving service delivery, automating processes, and enhancing collaboration. It also ensures a smooth employee experience. With more remote and hybrid work, ITSM will shape the future of work. Its role will be critical.
ITSM must be done right in the digital workplace. This needs the right tools, a user-centric approach, and alignment with broader goals. In 2024, firms using ITSM in their workplace strategy will be better able to face challenges. They will deliver great services and stay competitive in a fast-changing digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, the traditional office environment is quickly evolving into a more dynamic, flexible, and digitally driven workplace. As businesses continue to embrace the shift to remote, hybrid, and cloud-based models, IT Service Management (ITSM) has become a critical enabler of this transformation. In this blog, we will explore how ITSM is facilitating the digital workplace transformation and the role it plays in creating more efficient, collaborative, and agile working environments.
What is ITSM?
IT Service Management (ITSM) refers to the activities, processes, and policies that an organization uses to design, deliver, manage, and improve IT services for its customers. Traditionally, ITSM frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) have focused on delivering high-quality IT services, ensuring efficiency, minimizing downtime, and maximizing productivity. As organizations transition to digital-first operations, ITSM has expanded to address not just the needs of IT departments but also those of employees, customers, and end-users across various digital platforms.
The Rise of the Digital Workplace
The digital workplace is a tech-driven, virtual environment. It lets employees work from anywhere, using any device and digital tools. In this new world, work's traditional boundaries have changed. Flexible, collaborative, real-time communication tools now empower teams to work efficiently. Gartner's research shows that nearly 70% of employees will work in hybrid models by 2025. This will increase the need for better tech integration and IT services.
The digital workplace transformation includes many elements. They are cloud computing, AI collaboration tools, digital workflows, automation, and better cybersecurity. However, a truly effective digital workplace needs more than new tech. It requires an overhaul of how IT services are managed and delivered. This is where ITSM comes into play.
The Role of ITSM in Digital Workplace Transformation
ITSM is key to the digital workplace transformation. It ensures IT services and support are agile, efficient, and aligned with business needs. Here are the key ways ITSM supports this transformation:
1. Improved Service Delivery and Support
In a digital workplace, employees rely on digital tools to do their tasks. Any downtime or service interruptions can disrupt productivity. ITSM ensures IT services are delivered efficiently and with minimal disruption. Support must always be available when needed. ITSM frameworks like ITIL aim to improve service desk operations. They focus on incident management and request fulfillment. The goal is to ensure a smooth experience for end-users.
Cloud-based ITSM platforms let businesses manage services remotely. They can support employees in different locations. This is crucial in hybrid or remote work. IT teams must provide support, no matter the location.
2. Automation and Streamlining Processes
A key benefit of digital workplace transformation is automating routine tasks. ITSM facilitates automation by standardizing workflows and processes across the organization. ITSM allows employees to use automated ticketing and self-service portals. They can resolve issues without waiting for IT support.
Automation speeds up service delivery. It also reduces the burden on IT staff. They can then focus on more strategic initiatives. ITSM tools like ServiceNow and Freshservice have powerful automation features. They include AI chatbots that help with ticket triage and incident management.
3. Collaboration and Communication
A successful digital workplace thrives on effective communication and collaboration among teams. ITSM supports these goals by integrating with tools like Teams, Slack, and Zoom. By using these integrations, IT teams can improve service desk support. They can share knowledge and discuss issues and solutions in real time.
Moreover, ITSM encourages knowledge management repositories. They help employees find solutions to common issues on their own. This self-service approach boosts employee satisfaction. It also frees IT teams to focus on complex tasks.
4. Employee Experience Enhancement
The digital workplace aims to improve employee experience. It does this by providing flexibility, collaboration, and seamless IT services. ITSM helps by focusing on the user experience. It ensures employees can access high-quality IT support when they need it. ITSM uses feedback loops and user-centric design. This ensures services meet the workforce's needs.
ITSM platforms often include self-service portals and mobile apps. They let employees submit service requests, track incidents, and find info on-demand. This improves satisfaction and productivity.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
A key part of digital workplace transformation is making data-driven decisions. ITSM platforms generate a lot of data from requests, incidents, and changes. Businesses can gain insights by analyzing this data. They can find areas to improve, optimize IT service delivery, and predict disruptions.
For example, IT teams can use data to find recurring issues, track SLA performance, and fix system flaws. ITSM solutions with AI and machine learning are more powerful. They can predict trends and automate decision-making.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
As organizations expand and evolve, their IT infrastructure needs to scale accordingly. ITSM provides the framework to manage this growth effectively. Cloud-based ITSM solutions are key to digital workplace transformation. They let businesses scale services as needed. ITSM ensures that IT services can be scaled without losing quality. This applies when an organization adds users, adopts new tools, or expands into new areas.
7. Security and Compliance
Digital workplace transformation raises the need for strong security and compliance. ITSM helps organizations keep a secure, compliant IT environment. It does this by providing structured processes for change, incident, and risk management. ITSM practices help businesses. They can implement policies to protect data, reduce risks, and comply with GDPR and HIPAA.
ITSM also helps businesses handle security incidents better.
It does this by ensuring clear procedures for:
-
Identifying,
-
Assessing, and
-
Mitigating security risks.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
ITSM is now key to digital workplace transformation, not just managing IT services. ITSM helps organizations adapt to the fast-changing digital world. It does this by improving service delivery, automating processes, and enhancing collaboration. It also ensures a smooth employee experience. With more remote and hybrid work, ITSM will shape the future of work. Its role will be critical.
ITSM must be done right in the digital workplace. This needs the right tools, a user-centric approach, and alignment with broader goals. In 2024, firms using ITSM in their workplace strategy will be better able to face challenges. They will deliver great services and stay competitive in a fast-changing digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Future-Proof Your ITSM Strategy for 2025 and Beyond Today!
As tech changes quickly, ITSM is vital for smooth IT operations. However, traditional ITSM strategies may not suffice against trends like automation, AI, and multi-cloud systems. To stay competitive, organizations must future-proof their ITSM strategies. They must adapt to shifts in technology, operations, and culture. This blog explores key steps to prepare an ITSM approach for 2025 and beyond.
1. Understand Emerging Trends in ITSM
To future-proof your ITSM strategy, know the trends in ITSM. They are shaping its landscape.
AI and Automation: AI tools are redefining service desks. They enable faster ticket resolution, predictive maintenance, and personalized user experiences.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid IT: Organizations are using more multi-cloud and hybrid setups. They need ITSM tools that work well across different infrastructures.
- DevOps and Agile Integration: ITSM's merge with DevOps and Agile stresses teamwork and improvement.
- Enterprise Service Management (ESM): There's a trend to extend ITSM practices beyond IT to HR, finance, and other departments. This is enhancing efficiency.
Anticipating and adapting to these trends will ensure your ITSM strategy remains relevant.
2. Adopt AI-Driven Solutions
AI and machine learning are not just buzzwords but practical solutions transforming ITSM. Consider the following applications:
AI chatbots handle routine inquiries. This frees service desk staff to focus on complex issues.
Predictive Analytics: Using historical data, predictive analytics can forecast system failures. This enables proactive maintenance.
- Intelligent Automation: Automating tasks, like password resets, improves efficiency. It also reduces errors.
Investing in AI today will prepare your ITSM for tomorrow's demands.
3. Embrace Flexibility with Cloud-Native ITSM
Cloud adoption is accelerating, with organizations leveraging its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Future-proof ITSM strategies must:
- Ensure Compatibility: Choose ITSM tools that work with all cloud types.
- Enable Remote Management: Cloud ITSM platforms let IT teams manage services from anywhere. This is vital in a world of remote work.
- Enhance Security: As cloud environments grow, strong security is vital. Use encryption, access controls, and compliance tracking.
Aligning ITSM with cloud-first strategies can help organizations. It can handle the growing complexity of IT ecosystems.
4. Prioritize User-Centric Design
User expectations are evolving, demanding faster resolutions, intuitive interfaces, and self-service options. Future-proof ITSM must cater to these needs by:
- Implementing Self-Service Portals: Give users a knowledge base and tools to fix their issues.
- Focusing on UX/UI: Invest in ITSM platforms with intuitive designs. They must be easy to use for both IT staff and end-users.
- Gathering Feedback: Ask users for feedback to find pain points and improve the service.
Putting users at the heart of your ITSM strategy boosts satisfaction and efficiency.
5. Integrate DevOps and Agile Practices
The divide between ITSM and DevOps is fading. Organizations are embracing a culture of collaboration and agility. To integrate these methodologies:
- Adopt Agile Service Management: Use Agile principles in ITSM. They include iterative improvement and continuous feedback.
- Automate CI/CD Pipelines: Add automation to deployment workflows. This will ensure faster, more reliable software updates.
- Foster Collaboration: Align cross-functional teams on goals. This will reduce friction between ITSM and DevOps initiatives.
A seamless integration of DevOps and ITSM will accelerate innovation and operational efficiency.
6. Expand ITSM into ESM
Enterprise Service Management (ESM) applies ITSM principles to non-IT departments. It improves resource allocation and standardizes processes. To transition effectively:
Use ITSM frameworks like ITIL to standardize HR, finance, and customer service processes.
- Use Unified Tools: Use one platform to manage service requests and tickets across departments.
- Demonstrate Value: Show the benefits of ESM. It resolves issues faster and improves collaboration across departments.
Expanding ITSM to an enterprise level fosters organizational agility and efficiency.
7. Focus on Security and Compliance
As cyber threats grow, strong security is vital for ITSM. It must be future-proof. Key considerations include:
- Embedding Security into ITSM: Integrate security into ITSM, including incident and change management.
- Compliance Monitoring: Stay updated on regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Ensure ITSM tools support compliance efforts.
- Training Staff: Teach your IT team about new security threats and best practices.
A proactive approach to security safeguards both ITSM processes and organizational data.
8. Leverage Data and Analytics
Data-driven decision-making is a cornerstone of modern ITSM. Future-proof strategies should incorporate:
- Real-Time Dashboards: Use dashboards to track KPIs, like ticket resolution time and system uptime.
- Incident Trend Analysis: Analyse incident data to find recurring issues. Prioritise fixing them.
- Capacity Planning: Use historical data to predict resource needs. This will prevent service disruptions.
Harnessing analytics ensures continuous improvement in ITSM operations.
9. Invest in Skill Development
The success of your ITSM strategy hinges on the skills of your IT team. Prepare your workforce for the future by:
- Providing Ongoing Training: Certify staff in ITIL, DevOps, or cloud tech to keep their skills up to date.
- Encourage Cross-Training: Let team members learn multiple skills to foster versatility.
- Promoting a Growth Mindset: Encourage innovation and experimentation. Create a culture of continuous improvement.
An empowered IT team is essential for navigating future challenges.
10. Adopt a Continuous Improvement Mindset
Future-proofing is an ongoing process, not a one-time effort. Cultivate a mindset of continuous improvement by:
- Conducting Regular Audits: Assess ITSM processes. Find ways to improve.
- Encouraging Feedback: Actively seek input from IT staff, users, and business leaders.
- Staying Informed: Keep up with industry trends and new tech. Adapt strategies as needed.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Future-proofing your ITSM strategy is about adaptability, innovation, and alignment with organizational goals. By embracing trends and user-focused designs, organizations can make their ITSM framework effective and resilient. They should also integrate Agile and DevOps. They should also invest in security and skills development.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
As tech changes quickly, ITSM is vital for smooth IT operations. However, traditional ITSM strategies may not suffice against trends like automation, AI, and multi-cloud systems. To stay competitive, organizations must future-proof their ITSM strategies. They must adapt to shifts in technology, operations, and culture. This blog explores key steps to prepare an ITSM approach for 2025 and beyond.
1. Understand Emerging Trends in ITSM
To future-proof your ITSM strategy, know the trends in ITSM. They are shaping its landscape.
AI and Automation: AI tools are redefining service desks. They enable faster ticket resolution, predictive maintenance, and personalized user experiences.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid IT: Organizations are using more multi-cloud and hybrid setups. They need ITSM tools that work well across different infrastructures.
- DevOps and Agile Integration: ITSM's merge with DevOps and Agile stresses teamwork and improvement.
- Enterprise Service Management (ESM): There's a trend to extend ITSM practices beyond IT to HR, finance, and other departments. This is enhancing efficiency.
Anticipating and adapting to these trends will ensure your ITSM strategy remains relevant.
2. Adopt AI-Driven Solutions
AI and machine learning are not just buzzwords but practical solutions transforming ITSM. Consider the following applications:
AI chatbots handle routine inquiries. This frees service desk staff to focus on complex issues.
Predictive Analytics: Using historical data, predictive analytics can forecast system failures. This enables proactive maintenance.
- Intelligent Automation: Automating tasks, like password resets, improves efficiency. It also reduces errors.
Investing in AI today will prepare your ITSM for tomorrow's demands.
3. Embrace Flexibility with Cloud-Native ITSM
Cloud adoption is accelerating, with organizations leveraging its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Future-proof ITSM strategies must:
- Ensure Compatibility: Choose ITSM tools that work with all cloud types.
- Enable Remote Management: Cloud ITSM platforms let IT teams manage services from anywhere. This is vital in a world of remote work.
- Enhance Security: As cloud environments grow, strong security is vital. Use encryption, access controls, and compliance tracking.
Aligning ITSM with cloud-first strategies can help organizations. It can handle the growing complexity of IT ecosystems.
4. Prioritize User-Centric Design
User expectations are evolving, demanding faster resolutions, intuitive interfaces, and self-service options. Future-proof ITSM must cater to these needs by:
- Implementing Self-Service Portals: Give users a knowledge base and tools to fix their issues.
- Focusing on UX/UI: Invest in ITSM platforms with intuitive designs. They must be easy to use for both IT staff and end-users.
- Gathering Feedback: Ask users for feedback to find pain points and improve the service.
Putting users at the heart of your ITSM strategy boosts satisfaction and efficiency.
5. Integrate DevOps and Agile Practices
The divide between ITSM and DevOps is fading. Organizations are embracing a culture of collaboration and agility. To integrate these methodologies:
- Adopt Agile Service Management: Use Agile principles in ITSM. They include iterative improvement and continuous feedback.
- Automate CI/CD Pipelines: Add automation to deployment workflows. This will ensure faster, more reliable software updates.
- Foster Collaboration: Align cross-functional teams on goals. This will reduce friction between ITSM and DevOps initiatives.
A seamless integration of DevOps and ITSM will accelerate innovation and operational efficiency.
6. Expand ITSM into ESM
Enterprise Service Management (ESM) applies ITSM principles to non-IT departments. It improves resource allocation and standardizes processes. To transition effectively:
Use ITSM frameworks like ITIL to standardize HR, finance, and customer service processes.
- Use Unified Tools: Use one platform to manage service requests and tickets across departments.
- Demonstrate Value: Show the benefits of ESM. It resolves issues faster and improves collaboration across departments.
Expanding ITSM to an enterprise level fosters organizational agility and efficiency.
7. Focus on Security and Compliance
As cyber threats grow, strong security is vital for ITSM. It must be future-proof. Key considerations include:
- Embedding Security into ITSM: Integrate security into ITSM, including incident and change management.
- Compliance Monitoring: Stay updated on regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Ensure ITSM tools support compliance efforts.
- Training Staff: Teach your IT team about new security threats and best practices.
A proactive approach to security safeguards both ITSM processes and organizational data.
8. Leverage Data and Analytics
Data-driven decision-making is a cornerstone of modern ITSM. Future-proof strategies should incorporate:
- Real-Time Dashboards: Use dashboards to track KPIs, like ticket resolution time and system uptime.
- Incident Trend Analysis: Analyse incident data to find recurring issues. Prioritise fixing them.
- Capacity Planning: Use historical data to predict resource needs. This will prevent service disruptions.
Harnessing analytics ensures continuous improvement in ITSM operations.
9. Invest in Skill Development
The success of your ITSM strategy hinges on the skills of your IT team. Prepare your workforce for the future by:
- Providing Ongoing Training: Certify staff in ITIL, DevOps, or cloud tech to keep their skills up to date.
- Encourage Cross-Training: Let team members learn multiple skills to foster versatility.
- Promoting a Growth Mindset: Encourage innovation and experimentation. Create a culture of continuous improvement.
An empowered IT team is essential for navigating future challenges.
10. Adopt a Continuous Improvement Mindset
Future-proofing is an ongoing process, not a one-time effort. Cultivate a mindset of continuous improvement by:
- Conducting Regular Audits: Assess ITSM processes. Find ways to improve.
- Encouraging Feedback: Actively seek input from IT staff, users, and business leaders.
- Staying Informed: Keep up with industry trends and new tech. Adapt strategies as needed.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Future-proofing your ITSM strategy is about adaptability, innovation, and alignment with organizational goals. By embracing trends and user-focused designs, organizations can make their ITSM framework effective and resilient. They should also integrate Agile and DevOps. They should also invest in security and skills development.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Evolution of Self-Service Portals in IT Service Management
In today's fast-paced digital world, firms want to: boost efficiency, cut costs, and improve user experience. IT Service Management (ITSM) has been key to achieving these goals. Self-service portals are a transformative innovation. Over time, these portals have evolved. They started as basic ticket-logging systems. Now, they are advanced platforms. They offer personalized, automated, and proactive IT support. This blog explores the journey of self-service portals in ITSM. It covers their impact and the trends driving their evolution.
What Are Self-Service Portals in ITSM?
Self-service portals are web-based platforms. They let users—employees, customers, or stakeholders—access IT services. This includes knowledge bases and support without IT staff's help. These portals typically include functionalities such as:
- Logging and tracking IT tickets.
- Accessing FAQs or knowledge articles.
- Resetting passwords or troubleshooting common issues.
- Requesting new hardware, software, or services.
Self-service portals empower users to solve routine issues. This frees IT teams to focus on complex tasks. It drives efficiency and productivity.
The Early Days of Self-Service Portals
At first, self-service portals were rudimentary. They served as digital ticketing systems. They allowed users to log IT requests or report incidents, which were then addressed by the IT team. These portals had limited functionality. They relied on users to state their problems accurately. They also relied on IT staff to resolve them manually.
These early systems were simple. But, they were a big step forward. They centralized IT requests and standardized some processes. However, they were often criticized for their lack of user-friendliness, leading to low adoption rates.
The Shift to User-Centric Designs
As technology advanced and users' expectations grew, organizations needed to improve self-service portals. They needed to make them more usable and accessible. This led to the adoption of user-centric design principles, focusing on:
1. Intuitive Interfaces: Easy-to-use portals with simple navigation and nice layouts.
2. Search Optimization: Robust search functionalities to help users find relevant information quickly.
3. Mobile Accessibility: Portals were optimized for mobile devices. This let users access support anytime, anywhere.
These changes boosted user adoption and satisfaction. They made self-service portals a valuable resource for end-users, not just an IT tool.
Automation and AI Integration
The next phase of evolution came with automation and AI. These technologies revolutionized self-service portals by enabling features like:
1. Automated Workflows
- Automated ticket routing to appropriate IT teams.
- Workflow approvals for service requests without manual intervention.
2. Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
AI chatbots began to handle common queries. They provided instant replies and guided users through troubleshooting steps. This not only reduced response times but also alleviated the burden on IT staff.
3. Predictive Support
Machine learning-enabled predictive analytics helped portals anticipate users' needs using historical data. For example, the system could suggest articles or solutions based on the user's query.
Automation and AI upgraded self-service portals into tools. They can now resolve issues before they disrupt workflows.
The Role of Personalization
Modern self-service portals now emphasize personalization, delivering tailored experiences to individual users. Key advancements include:
- Custom Dashboards: Users can view dashboards with relevant services, tickets, and updates. They are personalized.
- Adaptive Knowledge Bases: Recommendations are based on users' behaviour, preferences, and roles.
- Localized Content: Support materials are in the user's preferred language or region.
Personalized self-service portals align IT support with user expectations. This fosters engagement and trust.
The Impact of Self-Service Portals on Organizations
The evolution of self-service portals has brought numerous benefits to organizations, including:
1. Cost Reduction
Automating routine tasks and cutting help desk calls lowers costs.
2. Enhanced Productivity
Independent issue resolution saves employees time. It lets them focus on their core tasks.
3. Improved IT Efficiency
IT teams are freed from mundane tasks. They can now focus on strategic initiatives.
4. Greater User Satisfaction
Fast, accessible, and reliable self-service portals enhance the overall user experience.
5. Data-Driven Insights
Portals offer data on user behaviour and common issues. This helps organisations optimise IT services.
Challenges in Adopting Self-Service Portals
Despite their advantages, implementing self-service portals comes with challenges:
1. Low User Adoption: Users may resist new systems due to unfamiliarity or complexity.
2. Knowledge Management: Keeping knowledge bases accurate, comprehensive, and up-to-date requires significant effort.
3. Integration Issues: Integrating with existing ITSM tools and workflows can be complex.
4. Security Concerns: Managing access control and protecting sensitive information is critical.
Organizations must tackle these challenges. They need effective change management, user training, and strong IT governance.
Future Trends in Self-Service Portals
The evolution of self-service portals is far from over. Emerging trends indicate a shift toward even more intelligent and integrated systems:
1. Conversational AI
Advanced NLP will make virtual assistants more conversational. They will handle complex queries better.
2. Hyper-Personalization
AI will enable portals to deliver more precise, personalised content. They will better anticipate user needs.
3. Integration with IoT
As IoT adoption grows, self-service portals will help manage and troubleshoot devices in connected environments.
4. Unified Service Portals
Portals will expand beyond IT. They will offer self-service for HR, facilities, and other functions. This aligns with the Enterprise Service Management (ESM) model.
5. Enhanced Analytics
Real-time analytics and reporting will help organizations measure portal performance. They can then use this data to improve the user experience.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Self-service portals in ITSM have evolved. They now reflect a shift to user-centric, data-driven, and automated IT services. Self-service portals are now vital for modern organizations. They empower users, reduce IT workload, and cut costs.
As technology advances, these portals will grow more sophisticated. They will drive innovation and set new standards for efficiency and user satisfaction. For organizations that haven't embraced self-service portals, now is the time to invest in them. This will ensure they stay competitive in a digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, firms want to: boost efficiency, cut costs, and improve user experience. IT Service Management (ITSM) has been key to achieving these goals. Self-service portals are a transformative innovation. Over time, these portals have evolved. They started as basic ticket-logging systems. Now, they are advanced platforms. They offer personalized, automated, and proactive IT support. This blog explores the journey of self-service portals in ITSM. It covers their impact and the trends driving their evolution.
What Are Self-Service Portals in ITSM?
Self-service portals are web-based platforms. They let users—employees, customers, or stakeholders—access IT services. This includes knowledge bases and support without IT staff's help. These portals typically include functionalities such as:
- Logging and tracking IT tickets.
- Accessing FAQs or knowledge articles.
- Resetting passwords or troubleshooting common issues.
- Requesting new hardware, software, or services.
Self-service portals empower users to solve routine issues. This frees IT teams to focus on complex tasks. It drives efficiency and productivity.
The Early Days of Self-Service Portals
At first, self-service portals were rudimentary. They served as digital ticketing systems. They allowed users to log IT requests or report incidents, which were then addressed by the IT team. These portals had limited functionality. They relied on users to state their problems accurately. They also relied on IT staff to resolve them manually.
These early systems were simple. But, they were a big step forward. They centralized IT requests and standardized some processes. However, they were often criticized for their lack of user-friendliness, leading to low adoption rates.
The Shift to User-Centric Designs
As technology advanced and users' expectations grew, organizations needed to improve self-service portals. They needed to make them more usable and accessible. This led to the adoption of user-centric design principles, focusing on:
1. Intuitive Interfaces: Easy-to-use portals with simple navigation and nice layouts.
2. Search Optimization: Robust search functionalities to help users find relevant information quickly.
3. Mobile Accessibility: Portals were optimized for mobile devices. This let users access support anytime, anywhere.
These changes boosted user adoption and satisfaction. They made self-service portals a valuable resource for end-users, not just an IT tool.
Automation and AI Integration
The next phase of evolution came with automation and AI. These technologies revolutionized self-service portals by enabling features like:
1. Automated Workflows
- Automated ticket routing to appropriate IT teams.
- Workflow approvals for service requests without manual intervention.
2. Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
AI chatbots began to handle common queries. They provided instant replies and guided users through troubleshooting steps. This not only reduced response times but also alleviated the burden on IT staff.
3. Predictive Support
Machine learning-enabled predictive analytics helped portals anticipate users' needs using historical data. For example, the system could suggest articles or solutions based on the user's query.
Automation and AI upgraded self-service portals into tools. They can now resolve issues before they disrupt workflows.
The Role of Personalization
Modern self-service portals now emphasize personalization, delivering tailored experiences to individual users. Key advancements include:
- Custom Dashboards: Users can view dashboards with relevant services, tickets, and updates. They are personalized.
- Adaptive Knowledge Bases: Recommendations are based on users' behaviour, preferences, and roles.
- Localized Content: Support materials are in the user's preferred language or region.
Personalized self-service portals align IT support with user expectations. This fosters engagement and trust.
The Impact of Self-Service Portals on Organizations
The evolution of self-service portals has brought numerous benefits to organizations, including:
1. Cost Reduction
Automating routine tasks and cutting help desk calls lowers costs.
2. Enhanced Productivity
Independent issue resolution saves employees time. It lets them focus on their core tasks.
3. Improved IT Efficiency
IT teams are freed from mundane tasks. They can now focus on strategic initiatives.
4. Greater User Satisfaction
Fast, accessible, and reliable self-service portals enhance the overall user experience.
5. Data-Driven Insights
Portals offer data on user behaviour and common issues. This helps organisations optimise IT services.
Challenges in Adopting Self-Service Portals
Despite their advantages, implementing self-service portals comes with challenges:
1. Low User Adoption: Users may resist new systems due to unfamiliarity or complexity.
2. Knowledge Management: Keeping knowledge bases accurate, comprehensive, and up-to-date requires significant effort.
3. Integration Issues: Integrating with existing ITSM tools and workflows can be complex.
4. Security Concerns: Managing access control and protecting sensitive information is critical.
Organizations must tackle these challenges. They need effective change management, user training, and strong IT governance.
Future Trends in Self-Service Portals
The evolution of self-service portals is far from over. Emerging trends indicate a shift toward even more intelligent and integrated systems:
1. Conversational AI
Advanced NLP will make virtual assistants more conversational. They will handle complex queries better.
2. Hyper-Personalization
AI will enable portals to deliver more precise, personalised content. They will better anticipate user needs.
3. Integration with IoT
As IoT adoption grows, self-service portals will help manage and troubleshoot devices in connected environments.
4. Unified Service Portals
Portals will expand beyond IT. They will offer self-service for HR, facilities, and other functions. This aligns with the Enterprise Service Management (ESM) model.
5. Enhanced Analytics
Real-time analytics and reporting will help organizations measure portal performance. They can then use this data to improve the user experience.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Self-service portals in ITSM have evolved. They now reflect a shift to user-centric, data-driven, and automated IT services. Self-service portals are now vital for modern organizations. They empower users, reduce IT workload, and cut costs.
As technology advances, these portals will grow more sophisticated. They will drive innovation and set new standards for efficiency and user satisfaction. For organizations that haven't embraced self-service portals, now is the time to invest in them. This will ensure they stay competitive in a digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Achieving Regulatory Compliance Through COBIT 5 Framework
In today's digital age, compliance is crucial for organizations. It helps maintain trust, protect data, and avoid fines. COBIT 5 is a popular framework for IT governance. It helps achieve compliance with regulations. This framework gives a set of principles, processes, and controls. Organizations can use them to manage and govern their IT systems and meet regulations.
Understanding COBIT 5 Compliance
COBIT 5 stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) developed it. The framework helps organizations govern and control their IT. The framework defines processes and best practices for IT governance. It includes risk management, compliance, and IT audit.
Organizations must understand COBIT 5 compliance. It aligns IT governance with business goals and meets regulations. The framework promotes risk management. It helps organizations identify and reduce IT-related risks. This, in turn, boosts accountability and performance. COBIT 5 gives a structured way to comply. It supports improvement and value creation. It ensures IT processes are efficient and aligned with strategic goals.
What are the key principles of COBIT 5?
The key principles of COBIT 5 include:
-
Meeting stakeholder needs
-
Covering the enterprise end-to-end
-
Applying a single integrated framework
-
Enabling a holistic approach
-
Separating governance from management By adhering to these principles, organizations can ensure that their IT governance practices align with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Implementing COBIT 5 for Regulatory Compliance
Implementing COBIT 5 can bring numerous benefits to organizations looking to achieve regulatory compliance, including:
-
Enhanced risk management: COBIT 5 helps organizations identify and mitigate IT-related risks, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Better compliance management: The framework gives clear guidelines. They help organizations meet regulations and avoid legal issues.
-
Strengthened IT controls: COBIT 5 helps firms create strong IT controls and audit trails. They monitor compliance and detect deviations.
-
Comprehensive compliance framework: COBIT 5 offers a structured approach to compliance management, covering all aspects of IT governance and regulatory requirements.
Steps to Achieve Regulatory Compliance with COBIT 5
To achieve regulatory compliance with COBIT 5, organizations can follow a structured approach that includes:
-
Conducting a gap analysis: Identify areas where the organization's current IT governance practices fall short of regulatory requirements.
-
Develop a compliance roadmap. It should outline steps to align IT governance with COBIT 5 principles and regulations.
-
Implement COBIT controls: Set up policies, processes, and controls to meet regulations.
-
Monitor and measure compliance: Regularly check the organization's compliance with COBIT 5 and the regulations. Identify areas for improvement.
-
Continuously improve compliance practices. Use feedback to enhance IT governance and comply with regulations. By using COBIT 5 and these steps, organizations can improve compliance. They can also build a strong IT governance foundation.
How to obtain COBIT 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Organizations must comply with COBIT 5 to meet IT governance and data security rules. Using the framework's principles, organizations can align their IT with regulations. This will reduce risks and protect sensitive data. COBIT 5 helps organizations build a strong compliance framework. It meets regulations and improves IT governance.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
In today's digital age, compliance is crucial for organizations. It helps maintain trust, protect data, and avoid fines. COBIT 5 is a popular framework for IT governance. It helps achieve compliance with regulations. This framework gives a set of principles, processes, and controls. Organizations can use them to manage and govern their IT systems and meet regulations.
Understanding COBIT 5 Compliance
COBIT 5 stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) developed it. The framework helps organizations govern and control their IT. The framework defines processes and best practices for IT governance. It includes risk management, compliance, and IT audit.
Organizations must understand COBIT 5 compliance. It aligns IT governance with business goals and meets regulations. The framework promotes risk management. It helps organizations identify and reduce IT-related risks. This, in turn, boosts accountability and performance. COBIT 5 gives a structured way to comply. It supports improvement and value creation. It ensures IT processes are efficient and aligned with strategic goals.
What are the key principles of COBIT 5?
The key principles of COBIT 5 include:
-
Meeting stakeholder needs
-
Covering the enterprise end-to-end
-
Applying a single integrated framework
-
Enabling a holistic approach
-
Separating governance from management By adhering to these principles, organizations can ensure that their IT governance practices align with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Implementing COBIT 5 for Regulatory Compliance
Implementing COBIT 5 can bring numerous benefits to organizations looking to achieve regulatory compliance, including:
-
Enhanced risk management: COBIT 5 helps organizations identify and mitigate IT-related risks, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Better compliance management: The framework gives clear guidelines. They help organizations meet regulations and avoid legal issues.
-
Strengthened IT controls: COBIT 5 helps firms create strong IT controls and audit trails. They monitor compliance and detect deviations.
-
Comprehensive compliance framework: COBIT 5 offers a structured approach to compliance management, covering all aspects of IT governance and regulatory requirements.
Steps to Achieve Regulatory Compliance with COBIT 5
To achieve regulatory compliance with COBIT 5, organizations can follow a structured approach that includes:
-
Conducting a gap analysis: Identify areas where the organization's current IT governance practices fall short of regulatory requirements.
-
Develop a compliance roadmap. It should outline steps to align IT governance with COBIT 5 principles and regulations.
-
Implement COBIT controls: Set up policies, processes, and controls to meet regulations.
-
Monitor and measure compliance: Regularly check the organization's compliance with COBIT 5 and the regulations. Identify areas for improvement.
-
Continuously improve compliance practices. Use feedback to enhance IT governance and comply with regulations. By using COBIT 5 and these steps, organizations can improve compliance. They can also build a strong IT governance foundation.
How to obtain COBIT 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Organizations must comply with COBIT 5 to meet IT governance and data security rules. Using the framework's principles, organizations can align their IT with regulations. This will reduce risks and protect sensitive data. COBIT 5 helps organizations build a strong compliance framework. It meets regulations and improves IT governance.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Cloud Native & Hybrid ITSM Solutions for Modern Enterprises
In today's fast-changing digital world, businesses are using cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions. They want to improve IT operations and boost digital transformation. As cloud tech and complex IT rise, firms seek better IT service management and efficiency.
What are Cloud-Native ITSM Solutions?
Cloud-native ITSM solutions are built for cloud environments. They use the latest cloud-native tech to deliver agile, scalable IT services. These solutions are designed for a cloud-native architecture. They use cloud services and platforms to improve IT operations and service delivery. Cloud-native technology lets organizations manage their IT infrastructure better. It offers more flexibility, speed, and cost savings.
Why Choose Hybrid ITSM Solutions?
Hybrid ITSM solutions combine the best of both worlds. They merge traditional on-premises ITSM tools with cloud-based services. This hybrid approach lets organizations use both environments. It integrates their on-premises systems with cloud services for more agility and flexibility. Hybrid ITSM solutions can help businesses balance on-premises systems and cloud services. They want the security of on-premises systems. They also want the scalability of cloud services.
Cloud-Native Technology in IT Service Management
Cloud-native tech has changed IT service management. It helps firms modernize their IT and adapt to a fast-paced digital world. Cloud-native ITSM solutions let businesses automate IT processes. They improve service delivery and user experience. Organizations can use cloud-native technology to accelerate their digital transformation. It will help them outpace the competition.
Cloud-native technology is changing IT Service Management (ITSM). It lets organizations build, deploy, and scale applications in the cloud, more efficiently. Using microservices, containers, and orchestration tools, IT teams can improve service delivery. They can respond better to changing business needs. This will enhance the user experience. As cloud adoption rises, organizations must integrate cloud-native solutions into ITSM frameworks. This is key to staying competitive and agile in today's digital world.
Hybrid Cloud Strategy for IT Operations
A hybrid cloud strategy is key to optimizing IT in today's complex environments. Combining on-premises infrastructure with cloud services gives organizations more flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. A hybrid cloud lets businesses adjust their IT resources based on workload demands. This ensures peak performance and resource use.
A hybrid cloud strategy for IT uses on-premises systems and public and private clouds. It helps organizations optimize resources and improve flexibility. This approach lets businesses run sensitive workloads in a private cloud. They can use the public cloud's scalability for less critical tasks. This ensures both security and cost-effectiveness.
IT Automation and Governance in the Cloud
IT automation is vital in cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions. It helps organizations streamline IT processes, reduce manual work, and improve efficiency. Automation of routine tasks can free up IT resources. They can then focus on more strategic initiatives. Also, proper IT governance ensures compliance with industry regulations. It mitigates risks and secures IT operations.
It involves using automation tools to streamline cloud operations. It must also ensure compliance with governance policies. Automation in governance can improve efficiency. It can reduce errors and ensure oversight of cloud environments. This approach supports agile development and deployment. It also boosts security and compliance. So, it's essential for modern cloud management.
Best Practices for Implementing ITSM Solutions
When using cloud-native or hybrid ITSM solutions, organizations should follow industry best practices. This will maximize the benefits of these technologies. Some key best practices include:
-
Conducting a thorough assessment of current ITSM processes and identifying areas for improvement
-
Developing a comprehensive ITSM strategy aligned with business goals and objectives
-
Implementing robust ITSM tools and platforms that support cloud integration and automation
-
Establishing clear IT governance frameworks to ensure compliance and security
-
Regularly monitoring and evaluating ITSM performance to drive continuous improvement and innovation
Choosing the Right ITSM Solution Provider
Choosing the right ITSM provider is vital for your IT operations. Find a provider with cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions, tailored to your needs. When choosing an ITSM vendor, consider scalability, reliability, security, and support. This will ensure seamless integration and peak performance.
Choosing the right ITSM provider is crucial. It ensures your organization can manage IT services and improve efficiency. Look for providers with robust features tailored to your needs. These include automation, reporting tools, and user-friendly interfaces. Also, consider the provider's reputation and support. Their ability to scale with your business is important too. These factors can greatly affect your ITSM implementation's success.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions are vital for modern businesses. They must streamline IT, drive digital change, and compete in today's digital economy. Cloud-native tech and a hybrid ITSM can improve IT management. They will gain flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. To optimize your IT service management, choose the right ITSM provider. This is key to long-term success.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Read More
In today's fast-changing digital world, businesses are using cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions. They want to improve IT operations and boost digital transformation. As cloud tech and complex IT rise, firms seek better IT service management and efficiency.
What are Cloud-Native ITSM Solutions?
Cloud-native ITSM solutions are built for cloud environments. They use the latest cloud-native tech to deliver agile, scalable IT services. These solutions are designed for a cloud-native architecture. They use cloud services and platforms to improve IT operations and service delivery. Cloud-native technology lets organizations manage their IT infrastructure better. It offers more flexibility, speed, and cost savings.
Why Choose Hybrid ITSM Solutions?
Hybrid ITSM solutions combine the best of both worlds. They merge traditional on-premises ITSM tools with cloud-based services. This hybrid approach lets organizations use both environments. It integrates their on-premises systems with cloud services for more agility and flexibility. Hybrid ITSM solutions can help businesses balance on-premises systems and cloud services. They want the security of on-premises systems. They also want the scalability of cloud services.
Cloud-Native Technology in IT Service Management
Cloud-native tech has changed IT service management. It helps firms modernize their IT and adapt to a fast-paced digital world. Cloud-native ITSM solutions let businesses automate IT processes. They improve service delivery and user experience. Organizations can use cloud-native technology to accelerate their digital transformation. It will help them outpace the competition.
Cloud-native technology is changing IT Service Management (ITSM). It lets organizations build, deploy, and scale applications in the cloud, more efficiently. Using microservices, containers, and orchestration tools, IT teams can improve service delivery. They can respond better to changing business needs. This will enhance the user experience. As cloud adoption rises, organizations must integrate cloud-native solutions into ITSM frameworks. This is key to staying competitive and agile in today's digital world.
Hybrid Cloud Strategy for IT Operations
A hybrid cloud strategy is key to optimizing IT in today's complex environments. Combining on-premises infrastructure with cloud services gives organizations more flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. A hybrid cloud lets businesses adjust their IT resources based on workload demands. This ensures peak performance and resource use.
A hybrid cloud strategy for IT uses on-premises systems and public and private clouds. It helps organizations optimize resources and improve flexibility. This approach lets businesses run sensitive workloads in a private cloud. They can use the public cloud's scalability for less critical tasks. This ensures both security and cost-effectiveness.
IT Automation and Governance in the Cloud
IT automation is vital in cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions. It helps organizations streamline IT processes, reduce manual work, and improve efficiency. Automation of routine tasks can free up IT resources. They can then focus on more strategic initiatives. Also, proper IT governance ensures compliance with industry regulations. It mitigates risks and secures IT operations.
It involves using automation tools to streamline cloud operations. It must also ensure compliance with governance policies. Automation in governance can improve efficiency. It can reduce errors and ensure oversight of cloud environments. This approach supports agile development and deployment. It also boosts security and compliance. So, it's essential for modern cloud management.
Best Practices for Implementing ITSM Solutions
When using cloud-native or hybrid ITSM solutions, organizations should follow industry best practices. This will maximize the benefits of these technologies. Some key best practices include:
-
Conducting a thorough assessment of current ITSM processes and identifying areas for improvement
-
Developing a comprehensive ITSM strategy aligned with business goals and objectives
-
Implementing robust ITSM tools and platforms that support cloud integration and automation
-
Establishing clear IT governance frameworks to ensure compliance and security
-
Regularly monitoring and evaluating ITSM performance to drive continuous improvement and innovation
Choosing the Right ITSM Solution Provider
Choosing the right ITSM provider is vital for your IT operations. Find a provider with cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions, tailored to your needs. When choosing an ITSM vendor, consider scalability, reliability, security, and support. This will ensure seamless integration and peak performance.
Choosing the right ITSM provider is crucial. It ensures your organization can manage IT services and improve efficiency. Look for providers with robust features tailored to your needs. These include automation, reporting tools, and user-friendly interfaces. Also, consider the provider's reputation and support. Their ability to scale with your business is important too. These factors can greatly affect your ITSM implementation's success.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud-native and hybrid ITSM solutions are vital for modern businesses. They must streamline IT, drive digital change, and compete in today's digital economy. Cloud-native tech and a hybrid ITSM can improve IT management. They will gain flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. To optimize your IT service management, choose the right ITSM provider. This is key to long-term success.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : 
Future Trends in IT Governance: Evolution of COBIT Framework
In the fast-paced IT world, governance has become vital. Organizations must align their IT systems with business goals. They must also comply with regulations and secure against cyber threats. As technology continues to evolve, so do the best practices and frameworks that guide IT governance. One framework at the forefront of IT governance is COBIT. It stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies.
Evolution of COBIT
COBIT, developed by ISACA, has been continuously evolving to keep pace with the changing IT landscape. COBIT, released in 1996, has been updated several times. These updates align it with industry trends, best practices, and regulations. COBIT 2019 builds on the success of COBIT 5. It adds new features to help organizations meet their governance goals.
COBIT's evolution reflects changes in IT governance. It shifted from a focus on IT control to a broader framework. This new approach emphasizes aligning IT with business goals. COBIT 5 integrated principles from various methodologies, including ITIL and ISO standards. It aimed to provide a comprehensive approach to governance, risk management, and compliance.
Importance of COBIT
COBIT is a framework. It helps organizations to align IT with business strategies. It does this by improving processes and establishing IT governance best practices. It enables organizations to manage risks, ensure compliance, and optimize IT resources. As IT environments grow more complex, so do cyber threats. COBIT is vital. It helps organizations with digital transformation and cybersecurity.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is vital for firms. It helps align IT strategies with business goals. It ensures governance and management practices are in sync. It offers a framework for organizations. It helps them manage risk and improve performance. It does this with defined processes and best practices. It also optimizes resources. Also, COBIT fosters a culture of accountability and transparency. It gives stakeholders confidence in the governance of IT investments.
COBIT Framework
The COBIT framework is built on five key principles: 1. Meet stakeholders' needs. 2. Cover the enterprise end-to-end. 3. Apply a single, integrated framework. 4. Enable a holistic approach. 5. Separate governance from management. These principles guide organizations in designing, implementing, and monitoring effective IT governance practices. COBIT has a maturity model. It helps organizations assess and improve their IT governance. The model consists of five maturity levels, ranging from ad hoc processes to optimized processes. Organizations can improve their IT governance by assessing their maturity. This will identify areas for improvement.
COBIT stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is a framework of guidelines. They help organizations manage and govern their IT assets. It stresses aligning IT goals with business objectives. IT must deliver value, manage risk, and optimize resources.
COBIT vs. ITIL
COBIT focuses on IT governance and risk management. ITIL, however, is about IT service management. Both frameworks address different aspects of IT. Organizations can benefit from implementing them together. This will create a more holistic approach to IT governance and service delivery.
COBIT and ITIL are two key IT management frameworks. Each has a distinct but complementary purpose. COBIT stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is for IT governance, risk management, and compliance. It is ideal for organizations needing to align IT with business goals and regulations. In contrast, ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is about managing IT services. It offers best practices for delivering high-quality IT services. They must meet customers' and businesses' needs.
COBIT Compliance and Benefits
Compliance with COBIT standards can benefit organizations in many ways. It can improve risk management and decision-making. It can also increase efficiency and align IT with business goals. The COBIT framework can help organizations improve their governance. It will help them succeed in the fast-changing IT world.
COBIT compliance gives organizations a framework to improve IT governance. It aligns business goals with IT strategies. By adopting COBIT, organizations can improve risk management and resource use. It will help them make better decisions. This will boost efficiency and ensure compliance with regulations. Also, organizations that follow COBIT principles gain stakeholders' trust. This enhances business relationships and gives a competitive edge.
How to obtain COBIT 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, as technology advances, IT governance is vital. It helps organizations manage IT resources, reduce risks, and meet business goals. By using frameworks like COBIT, organizations can thrive in the digital age. They can confidently navigate its complexities.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In the fast-paced IT world, governance has become vital. Organizations must align their IT systems with business goals. They must also comply with regulations and secure against cyber threats. As technology continues to evolve, so do the best practices and frameworks that guide IT governance. One framework at the forefront of IT governance is COBIT. It stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies.
Evolution of COBIT
COBIT, developed by ISACA, has been continuously evolving to keep pace with the changing IT landscape. COBIT, released in 1996, has been updated several times. These updates align it with industry trends, best practices, and regulations. COBIT 2019 builds on the success of COBIT 5. It adds new features to help organizations meet their governance goals.
COBIT's evolution reflects changes in IT governance. It shifted from a focus on IT control to a broader framework. This new approach emphasizes aligning IT with business goals. COBIT 5 integrated principles from various methodologies, including ITIL and ISO standards. It aimed to provide a comprehensive approach to governance, risk management, and compliance.
Importance of COBIT
COBIT is a framework. It helps organizations to align IT with business strategies. It does this by improving processes and establishing IT governance best practices. It enables organizations to manage risks, ensure compliance, and optimize IT resources. As IT environments grow more complex, so do cyber threats. COBIT is vital. It helps organizations with digital transformation and cybersecurity.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is vital for firms. It helps align IT strategies with business goals. It ensures governance and management practices are in sync. It offers a framework for organizations. It helps them manage risk and improve performance. It does this with defined processes and best practices. It also optimizes resources. Also, COBIT fosters a culture of accountability and transparency. It gives stakeholders confidence in the governance of IT investments.
COBIT Framework
The COBIT framework is built on five key principles: 1. Meet stakeholders' needs. 2. Cover the enterprise end-to-end. 3. Apply a single, integrated framework. 4. Enable a holistic approach. 5. Separate governance from management. These principles guide organizations in designing, implementing, and monitoring effective IT governance practices. COBIT has a maturity model. It helps organizations assess and improve their IT governance. The model consists of five maturity levels, ranging from ad hoc processes to optimized processes. Organizations can improve their IT governance by assessing their maturity. This will identify areas for improvement.
COBIT stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is a framework of guidelines. They help organizations manage and govern their IT assets. It stresses aligning IT goals with business objectives. IT must deliver value, manage risk, and optimize resources.
COBIT vs. ITIL
COBIT focuses on IT governance and risk management. ITIL, however, is about IT service management. Both frameworks address different aspects of IT. Organizations can benefit from implementing them together. This will create a more holistic approach to IT governance and service delivery.
COBIT and ITIL are two key IT management frameworks. Each has a distinct but complementary purpose. COBIT stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is for IT governance, risk management, and compliance. It is ideal for organizations needing to align IT with business goals and regulations. In contrast, ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is about managing IT services. It offers best practices for delivering high-quality IT services. They must meet customers' and businesses' needs.
COBIT Compliance and Benefits
Compliance with COBIT standards can benefit organizations in many ways. It can improve risk management and decision-making. It can also increase efficiency and align IT with business goals. The COBIT framework can help organizations improve their governance. It will help them succeed in the fast-changing IT world.
COBIT compliance gives organizations a framework to improve IT governance. It aligns business goals with IT strategies. By adopting COBIT, organizations can improve risk management and resource use. It will help them make better decisions. This will boost efficiency and ensure compliance with regulations. Also, organizations that follow COBIT principles gain stakeholders' trust. This enhances business relationships and gives a competitive edge.
How to obtain COBIT 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, as technology advances, IT governance is vital. It helps organizations manage IT resources, reduce risks, and meet business goals. By using frameworks like COBIT, organizations can thrive in the digital age. They can confidently navigate its complexities.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
The Resurgence of Configuration Management Databases (CMDB)
In IT infrastructure management, CMDBs are becoming popular again. These tools are vital for the smooth operation and security of IT systems. Let's explore the benefits, use, best practices, and trends of CMDB in IT.
Understanding CMDB and Its Importance
A Configuration Management Database is a central repository. It holds info on all components in an IT environment. It helps organizations track and manage configuration items. It also helps them understand their relationships. It sets a baseline for best practices in configuration management. CMDB is essential for maintaining the integrity and consistency of IT infrastructure.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is key in IT service management. It is a central store of an organization's IT assets, their configs, and their relationships. A CMDB gives visibility into the IT infrastructure. So, it is essential to understand it. It helps with decision-making, risk management, and meeting regulations. By managing configuration items and their dependencies, organizations can improve. It will help incident response times, change management, and service delivery.
Benefits of CMDB Implementation
-
Improved visibility and control over IT assets.
-
Enhanced change management and risk reduction.
-
Automation of configuration management processes.
-
Facilitation of compliance audits and reporting.
-
Integration with other IT service management tools for seamless operations.
-
Greater scalability and data quality in configuration management.
CMDB Deployment and Tools
Implementing a CMDB solution involves careful planning, deployment, and maintenance. Organizations can choose from many CMDB tools on the market. Each offers unique features and capabilities. Deploying a CMDB requires a clear strategy and governance. It also needs ongoing monitoring to ensure its effectiveness.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is vital for IT Service Management (ITSM). It is a central repository for all IT assets and their relationships. So, configuring and deploying a CMDB is essential. Modern CMDB tools allow real-time updates. They help organizations keep accurate records and make informed decisions. This is vital in fast-changing environments.
Modern CMDB Trends and Technology
CMDB technology has evolved. It has led to better, easier tools. Modern CMDBs use automation, AI, and machine learning. They streamline config management processes. They also support cloud-based deployment and scalability. They optimize datacenters for better performance and efficiency.
Modern CMDBs are using AI and machine learning. They aim to automate data collection and improve accuracy. This helps organizations maintain real-time visibility into their IT environments. AI-driven solutions improve incident response and service management. They provide context and insights into asset dependencies.
CMDB Integration and Automation
Integrating the CMDB with other IT tools is vital. It provides a complete view of the IT environment. Automation is key to CMDB accuracy. It reduces manual work and improves data correlation. CMDB integration and automation can help organizations. They can streamline operations, save costs, and ensure data consistency.
CMDB integration and automation are key to IT service management. They provide a central repository of IT assets and their relationships. This integration streamlines processes. It enables real-time visibility into infrastructure changes. It also improves decision-making on service delivery and risk management.
Challenges and Solutions in CMDB Implementation
While CMDB offers numerous benefits, organizations often face challenges during its implementation. Common issues include data synchronization, accuracy, scalability, and governance. Best practices, docs, and process control can help fix these issues. They can ensure CMDB initiatives succeed.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) can be hard to implement. It may have issues with data accuracy, system integration, and user adoption. Organizations often struggle to keep their CMDB data up to date. Real-time changes often lead to inaccuracies that undermine its effectiveness.
Future Benefits and Business Value of CMDB
As CMDB continues to evolve, its future holds promising benefits for organizations. The CMDB's automation, data modeling, metrics, and ROI should enhance config management. They should improve efficiency and innovation. Integrating CMDB with ITSM, asset management, and other systems can greatly benefit businesses. It can help them achieve operational excellence.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is key for organizations. It helps improve IT service management. A CMDB is a central place to manage IT assets and their relationships. This tool helps businesses make better decisions. It improves visibility of asset dependencies. This leads to better resource use and risk management.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, CMDBs are a big step in IT infrastructure management. Using CMDB best practices and modern tech, organizations can unlock its full potential. This will boost efficiency, compliance, and business value. They must also address implementation challenges.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In IT infrastructure management, CMDBs are becoming popular again. These tools are vital for the smooth operation and security of IT systems. Let's explore the benefits, use, best practices, and trends of CMDB in IT.
Understanding CMDB and Its Importance
A Configuration Management Database is a central repository. It holds info on all components in an IT environment. It helps organizations track and manage configuration items. It also helps them understand their relationships. It sets a baseline for best practices in configuration management. CMDB is essential for maintaining the integrity and consistency of IT infrastructure.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is key in IT service management. It is a central store of an organization's IT assets, their configs, and their relationships. A CMDB gives visibility into the IT infrastructure. So, it is essential to understand it. It helps with decision-making, risk management, and meeting regulations. By managing configuration items and their dependencies, organizations can improve. It will help incident response times, change management, and service delivery.
Benefits of CMDB Implementation
-
Improved visibility and control over IT assets.
-
Enhanced change management and risk reduction.
-
Automation of configuration management processes.
-
Facilitation of compliance audits and reporting.
-
Integration with other IT service management tools for seamless operations.
-
Greater scalability and data quality in configuration management.
CMDB Deployment and Tools
Implementing a CMDB solution involves careful planning, deployment, and maintenance. Organizations can choose from many CMDB tools on the market. Each offers unique features and capabilities. Deploying a CMDB requires a clear strategy and governance. It also needs ongoing monitoring to ensure its effectiveness.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is vital for IT Service Management (ITSM). It is a central repository for all IT assets and their relationships. So, configuring and deploying a CMDB is essential. Modern CMDB tools allow real-time updates. They help organizations keep accurate records and make informed decisions. This is vital in fast-changing environments.
Modern CMDB Trends and Technology
CMDB technology has evolved. It has led to better, easier tools. Modern CMDBs use automation, AI, and machine learning. They streamline config management processes. They also support cloud-based deployment and scalability. They optimize datacenters for better performance and efficiency.
Modern CMDBs are using AI and machine learning. They aim to automate data collection and improve accuracy. This helps organizations maintain real-time visibility into their IT environments. AI-driven solutions improve incident response and service management. They provide context and insights into asset dependencies.
CMDB Integration and Automation
Integrating the CMDB with other IT tools is vital. It provides a complete view of the IT environment. Automation is key to CMDB accuracy. It reduces manual work and improves data correlation. CMDB integration and automation can help organizations. They can streamline operations, save costs, and ensure data consistency.
CMDB integration and automation are key to IT service management. They provide a central repository of IT assets and their relationships. This integration streamlines processes. It enables real-time visibility into infrastructure changes. It also improves decision-making on service delivery and risk management.
Challenges and Solutions in CMDB Implementation
While CMDB offers numerous benefits, organizations often face challenges during its implementation. Common issues include data synchronization, accuracy, scalability, and governance. Best practices, docs, and process control can help fix these issues. They can ensure CMDB initiatives succeed.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) can be hard to implement. It may have issues with data accuracy, system integration, and user adoption. Organizations often struggle to keep their CMDB data up to date. Real-time changes often lead to inaccuracies that undermine its effectiveness.
Future Benefits and Business Value of CMDB
As CMDB continues to evolve, its future holds promising benefits for organizations. The CMDB's automation, data modeling, metrics, and ROI should enhance config management. They should improve efficiency and innovation. Integrating CMDB with ITSM, asset management, and other systems can greatly benefit businesses. It can help them achieve operational excellence.
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is key for organizations. It helps improve IT service management. A CMDB is a central place to manage IT assets and their relationships. This tool helps businesses make better decisions. It improves visibility of asset dependencies. This leads to better resource use and risk management.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, CMDBs are a big step in IT infrastructure management. Using CMDB best practices and modern tech, organizations can unlock its full potential. This will boost efficiency, compliance, and business value. They must also address implementation challenges.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Challenges of AI Implementation in IT Service Management
In today's fast-changing tech world, using AI in ITSM brings many challenges. Organizations face many obstacles in using AI in ITSM. They must navigate integration and deployment issues to reap its benefits.
AI in ITSM Challenges
A key challenge of using AI in ITSM is integrating it with existing ITSM tools and processes. AI needs a lot of data to work well. Integrating it with ITSM systems can be tough. Another challenge organizations face is the difficulty of deploying AI in ITSM environments. Deploying an AI solution can be complex and time-consuming. It involves choosing the right AI and training ITSM teams.
Integrating AI into IT Service Management (ITSM) poses challenges. Organizations must navigate them. A big hurdle is employees' resistance to change. They may fear for their jobs and doubt AI's effectiveness. Also, there are technical obstacles. These include ensuring data quality and integrating AI tools with existing ITSM frameworks. They can complicate deployment efforts.
Obstacles of AI Implementation in ITSM
There are several key obstacles that organizations encounter when implementing AI in ITSM. One major obstacle is the lack of AI adoption in IT service management. Many organizations may be hesitant to embrace AI technology due to concerns about its impact on ITSM processes and workflows. Also, the complexities of AI adoption in ITSM can challenge organizations. Organizations must develop an AI strategy. They must also overcome risks in implementation. Only then can they integrate AI successfully.
Implementing AI in IT Service Management (ITSM) can face many hurdles. Cultural resistance is one. Employees may fear job loss and less personal service.
AI Challenges in IT Service Management
One of the key challenges of AI adoption in ITSM is the potential risks associated with implementing AI technology. AI in ITSM operations has pitfalls. AI projects can also fail. So, organizations must assess and reduce these risks. This will ensure a successful AI deployment. Furthermore, organizations may face difficulties in implementing AI in ITSM projects. AI integration in ITSM systems is complex. Organizations must overcome the challenges of AI implementation. Only then can they fully benefit from AI in ITSM.
Integrating AI into IT Service Management (ITSM) poses challenges for organizations. They must navigate them. One major hurdle is ensuring data quality and consistency. AI systems rely on accurate data to provide effective service and insights. Cultural resistance in teams can hinder AI adoption. It shows the need for change management and training to foster acceptance.
Overcoming AI Implementation Challenges
AI in ITSM has challenges. But, organizations can take steps to overcome them. Organizations can integrate AI into their ITSM workflows. To do this, they must: 1. Develop a comprehensive AI strategy. 2. Assess and reduce risks. 3. Ensure effective deployment and training. Also, organizations can use AI tools to streamline ITSM processes and boost efficiency. Investing in the right AI solutions can help organizations. It can overcome the challenges of AI in ITSM and improve business outcomes.
Implementing AI in IT Service Management (ITSM) can be challenging. There may be resistance to change and poor data quality. To overcome these obstacles, organizations must prioritize training. Staff must learn to work effectively with AI systems. Also, a culture that embraces innovation can help. Involving stakeholders in the AI integration process can boost implementation efforts.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI in ITSM has big challenges. But, organizations can overcome them. They should develop an AI strategy, use AI tools, and manage the complexities of AI adoption in ITSM. By taking proactive steps to address these challenges, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI technology in ITSM and drive enhanced business performance.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-changing tech world, using AI in ITSM brings many challenges. Organizations face many obstacles in using AI in ITSM. They must navigate integration and deployment issues to reap its benefits.
AI in ITSM Challenges
A key challenge of using AI in ITSM is integrating it with existing ITSM tools and processes. AI needs a lot of data to work well. Integrating it with ITSM systems can be tough. Another challenge organizations face is the difficulty of deploying AI in ITSM environments. Deploying an AI solution can be complex and time-consuming. It involves choosing the right AI and training ITSM teams.
Integrating AI into IT Service Management (ITSM) poses challenges. Organizations must navigate them. A big hurdle is employees' resistance to change. They may fear for their jobs and doubt AI's effectiveness. Also, there are technical obstacles. These include ensuring data quality and integrating AI tools with existing ITSM frameworks. They can complicate deployment efforts.
Obstacles of AI Implementation in ITSM
There are several key obstacles that organizations encounter when implementing AI in ITSM. One major obstacle is the lack of AI adoption in IT service management. Many organizations may be hesitant to embrace AI technology due to concerns about its impact on ITSM processes and workflows. Also, the complexities of AI adoption in ITSM can challenge organizations. Organizations must develop an AI strategy. They must also overcome risks in implementation. Only then can they integrate AI successfully.
Implementing AI in IT Service Management (ITSM) can face many hurdles. Cultural resistance is one. Employees may fear job loss and less personal service.
AI Challenges in IT Service Management
One of the key challenges of AI adoption in ITSM is the potential risks associated with implementing AI technology. AI in ITSM operations has pitfalls. AI projects can also fail. So, organizations must assess and reduce these risks. This will ensure a successful AI deployment. Furthermore, organizations may face difficulties in implementing AI in ITSM projects. AI integration in ITSM systems is complex. Organizations must overcome the challenges of AI implementation. Only then can they fully benefit from AI in ITSM.
Integrating AI into IT Service Management (ITSM) poses challenges for organizations. They must navigate them. One major hurdle is ensuring data quality and consistency. AI systems rely on accurate data to provide effective service and insights. Cultural resistance in teams can hinder AI adoption. It shows the need for change management and training to foster acceptance.
Overcoming AI Implementation Challenges
AI in ITSM has challenges. But, organizations can take steps to overcome them. Organizations can integrate AI into their ITSM workflows. To do this, they must: 1. Develop a comprehensive AI strategy. 2. Assess and reduce risks. 3. Ensure effective deployment and training. Also, organizations can use AI tools to streamline ITSM processes and boost efficiency. Investing in the right AI solutions can help organizations. It can overcome the challenges of AI in ITSM and improve business outcomes.
Implementing AI in IT Service Management (ITSM) can be challenging. There may be resistance to change and poor data quality. To overcome these obstacles, organizations must prioritize training. Staff must learn to work effectively with AI systems. Also, a culture that embraces innovation can help. Involving stakeholders in the AI integration process can boost implementation efforts.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI in ITSM has big challenges. But, organizations can overcome them. They should develop an AI strategy, use AI tools, and manage the complexities of AI adoption in ITSM. By taking proactive steps to address these challenges, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI technology in ITSM and drive enhanced business performance.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Reviving CMDB Effectively Through IT Service Management
In IT operations, a fast-paced field, a central hub is vital. It must manage all configuration items. This is where Configuration Management Database (CMDB) comes into play. With the resurgence of CMDB, organizations see its value. A well-maintained, up-to-date database can streamline IT service management.
What is CMDB and Why is it Important?
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a central store. It holds information about all configuration items in an organization's IT infrastructure. This includes hardware assets, software assets, relationships between items, and more. CMDB is vital for asset, change, and incident management. It's also key for service desk operations. A complete CMDB helps organizations understand their IT environment. It reduces risks, improves decision-making, and boosts service delivery. It also plays a key role in ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) practices. It provides a foundation for implementing IT service management best practices.
Benefits of CMDB Implementation
-
Improved visibility and control over IT assets and configurations
-
Enhanced incident, change, and problem management processes
-
Streamlined service desk operations and increased efficiency
-
Better decision-making based on accurate and up-to-date information
-
Alignment with ITIL best practices and compliance requirements
-
Enhanced IT operations by reducing downtime and improving service quality
Best Practices for Successful CMDB Implementation
-
Define clear objectives and scope for the CMDB project
-
Align CMDB processes with IT service management goals
-
Engage stakeholders across different IT functions
-
Ensure data accuracy and quality through data reconciliation and regular updates
-
Implement automation for data collection and maintenance
-
Establish proper governance and security measures to protect sensitive information
-
Provide ongoing training for users and administrators
-
Regularly audit and monitor the CMDB for compliance and performance optimization
CMDB Integration and Architecture
It's crucial to integrate the CMDB with other IT tools. These include service, asset, and monitoring management systems. This will maximize its benefits. A well-planned CMDB architecture ensures scalability, security, and performance optimization. CMDB integration allows for smooth data exchange and relationship mapping between systems. It improves visibility and efficiency.
CMDB Integration and Architecture is vital. It ensures that all IT infrastructure components are accurately mapped and managed. A good CMDB improves visibility into asset relationships. It also helps decision-making and supports proactive IT service management. Integrating CMDBs with other IT tools can automate workflows. It also creates a single source of truth. This will boost efficiency and cut operational risks.
The Future of CMDB: Embracing Automation and Analytics
As technology evolves, the role of CMDB in IT operations is critical. Automation tools are being used to streamline data collection and updates. They also ensure data accuracy. Analytics are being added to CMDB systems. They will provide insights for better decision-making and monitoring.
The future of CMDBs is in automation and advanced analytics. They will help organizations streamline IT asset management. AI and machine learning can help businesses. They can improve data accuracy, decision-making, and responses to changes in IT. This evolution boosts efficiency. It helps organizations align IT with business goals. This fosters a more agile, responsive IT landscape.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, a renewed interest in CMDBs is changing IT asset management. Organizations can unlock the CMDB's full potential. They should use best practices. They must integrate with other IT tools. They should apply automation and analytics. This will improve IT service management and efficiency.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In IT operations, a fast-paced field, a central hub is vital. It must manage all configuration items. This is where Configuration Management Database (CMDB) comes into play. With the resurgence of CMDB, organizations see its value. A well-maintained, up-to-date database can streamline IT service management.
What is CMDB and Why is it Important?
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a central store. It holds information about all configuration items in an organization's IT infrastructure. This includes hardware assets, software assets, relationships between items, and more. CMDB is vital for asset, change, and incident management. It's also key for service desk operations. A complete CMDB helps organizations understand their IT environment. It reduces risks, improves decision-making, and boosts service delivery. It also plays a key role in ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) practices. It provides a foundation for implementing IT service management best practices.
Benefits of CMDB Implementation
-
Improved visibility and control over IT assets and configurations
-
Enhanced incident, change, and problem management processes
-
Streamlined service desk operations and increased efficiency
-
Better decision-making based on accurate and up-to-date information
-
Alignment with ITIL best practices and compliance requirements
-
Enhanced IT operations by reducing downtime and improving service quality
Best Practices for Successful CMDB Implementation
-
Define clear objectives and scope for the CMDB project
-
Align CMDB processes with IT service management goals
-
Engage stakeholders across different IT functions
-
Ensure data accuracy and quality through data reconciliation and regular updates
-
Implement automation for data collection and maintenance
-
Establish proper governance and security measures to protect sensitive information
-
Provide ongoing training for users and administrators
-
Regularly audit and monitor the CMDB for compliance and performance optimization
CMDB Integration and Architecture
It's crucial to integrate the CMDB with other IT tools. These include service, asset, and monitoring management systems. This will maximize its benefits. A well-planned CMDB architecture ensures scalability, security, and performance optimization. CMDB integration allows for smooth data exchange and relationship mapping between systems. It improves visibility and efficiency.
CMDB Integration and Architecture is vital. It ensures that all IT infrastructure components are accurately mapped and managed. A good CMDB improves visibility into asset relationships. It also helps decision-making and supports proactive IT service management. Integrating CMDBs with other IT tools can automate workflows. It also creates a single source of truth. This will boost efficiency and cut operational risks.
The Future of CMDB: Embracing Automation and Analytics
As technology evolves, the role of CMDB in IT operations is critical. Automation tools are being used to streamline data collection and updates. They also ensure data accuracy. Analytics are being added to CMDB systems. They will provide insights for better decision-making and monitoring.
The future of CMDBs is in automation and advanced analytics. They will help organizations streamline IT asset management. AI and machine learning can help businesses. They can improve data accuracy, decision-making, and responses to changes in IT. This evolution boosts efficiency. It helps organizations align IT with business goals. This fosters a more agile, responsive IT landscape.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, a renewed interest in CMDBs is changing IT asset management. Organizations can unlock the CMDB's full potential. They should use best practices. They must integrate with other IT tools. They should apply automation and analytics. This will improve IT service management and efficiency.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Key Benefits of Adopting COBIT® 5 in Your IT Organization
In today's fast-changing tech world, IT governance is vital. It ensures that technology meets organizational goals. COBIT® 5 is a framework by ISACA. It guides the management and governance of enterprise IT. COBIT® 5 can help organizations. It improves IT governance and management. It aligns IT with business goals. It drives better performance and risk management. This article explores the key benefits of adopting COBIT® 5 in your IT organization.
Table Of Contents
- Enhanced Alignment Between IT and Business Goals
- Improved Risk Management
- Enhanced IT process efficiency
- Strengthened IT governance
- Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
- Conclusion
Enhanced Alignment Between IT and Business Goals
A key benefit of COBIT® 5 is its focus on aligning IT with business goals. COBIT® 5 provides a way to ensure that IT work supports business goals.
- COBIT® 5 helps align IT with business goals. It ensures IT investments and projects deliver value to the organization. This alignment helps rank IT initiatives. Their contributions to business goals form the basis.
- Value Delivery: The framework emphasizes delivering measurable value from IT investments. It helps organizations manage the benefits, costs, and risks of IT projects. This ensures the effective use of IT resources.
Aligning IT strategies with business goals can boost performance. It helps organizations achieve their objectives with greater efficiency.
Improved Risk Management
Effective risk management is critical for protecting organizational assets and ensuring business continuity. COBIT® 5 offers a robust approach to managing IT-related risks.
- Risk Identification: The framework helps in identifying potential IT risks and vulnerabilities. COBIT® 5 provides a complete set of risk management practices. It ensures the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks.
- Risk Response: COBIT® 5 offers guidance on developing and implementing risk response strategies. This includes defining risk tolerance levels, establishing controls, and monitoring risk management activities.
- Compliance and Security: The framework meets regulations and boosts IT security. Integrating risk management into IT processes helps protect sensitive data and ensures compliance.
COBIT® 5's risk management practices can help reduce IT risks. They can also protect assets.
Enhanced IT process efficiency
COBIT® 5 offers best practices and frameworks. They help organizations optimize their IT operations.
- Process Optimization: The framework outlines best practices for IT process management. It will make them more efficient and effective. This includes streamlining workflows, reducing redundancies, and enhancing process performance.
- Performance Measurement: COBIT® 5 has metrics to assess IT processes. By monitoring performance, organizations can find areas to improve. They can then make the necessary changes.
- Resource Management: The framework helps organizations manage IT resources: personnel, technology, and budgets. Effective resource management maximizes IT investments and ensures the efficient use of resources.
Using COBIT® 5 to improve IT processes boosts performance and saves costs.
Strengthened IT governance
COBIT® 5 offers a complete method for IT governance. It ensures that IT management aligns with corporate governance principles.
- Governance Framework: The framework sets clear IT management structures, roles, and responsibilities. This includes defining decision-making processes, accountability mechanisms, and oversight functions.
- Compliance Management: COBIT® 5 supports compliance with internal policies and external regulations. Governance practices in IT processes can ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
- Strategic Decision-Making: The framework helps with strategic decisions. It provides a structured way to test IT investments and initiatives. This helps in making informed decisions that support long-term business objectives.
Strengthening IT governance through COBIT® 5 enhances organizational control, accountability, and compliance.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
COBIT® 5 promotes a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability within IT organizations.
- Continuous Improvement: The framework encourages regular evaluation and improvement of IT processes. A mindset of continuous improvement helps organizations stay competitive. It allows them to respond to changes in business needs and new technologies.
- Adaptability: COBIT® 5 supports it with a flexible, customizable framework. It can fit different organizations and needs. This allows organizations to adjust their IT governance and management as needed.
- Benchmarking and Best Practices: The framework includes benchmarking techniques. They compare IT performance to industry standards and best practices. This helps organizations identify gaps and install improvements based on proven methods.
COBIT® 5 helps organizations stay agile in a fast-changing world. It does this by promoting a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability.
How to obtain Cobit 5 certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, COBIT® 5 has many benefits for IT organizations. It improves alignment between IT and business goals. It also boosts risk management and IT process efficiency. It strengthens IT governance and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. COBIT® 5 helps organizations align IT with business goals. It also manages risks, optimizes IT processes, and strengthens governance. As technology evolves, COBIT® 5 offers a framework. It helps manage complex IT and drives organizational success.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-changing tech world, IT governance is vital. It ensures that technology meets organizational goals. COBIT® 5 is a framework by ISACA. It guides the management and governance of enterprise IT. COBIT® 5 can help organizations. It improves IT governance and management. It aligns IT with business goals. It drives better performance and risk management. This article explores the key benefits of adopting COBIT® 5 in your IT organization.
Table Of Contents
- Enhanced Alignment Between IT and Business Goals
- Improved Risk Management
- Enhanced IT process efficiency
- Strengthened IT governance
- Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
- Conclusion
Enhanced Alignment Between IT and Business Goals
A key benefit of COBIT® 5 is its focus on aligning IT with business goals. COBIT® 5 provides a way to ensure that IT work supports business goals.
- COBIT® 5 helps align IT with business goals. It ensures IT investments and projects deliver value to the organization. This alignment helps rank IT initiatives. Their contributions to business goals form the basis.
- Value Delivery: The framework emphasizes delivering measurable value from IT investments. It helps organizations manage the benefits, costs, and risks of IT projects. This ensures the effective use of IT resources.
Aligning IT strategies with business goals can boost performance. It helps organizations achieve their objectives with greater efficiency.
Improved Risk Management
Effective risk management is critical for protecting organizational assets and ensuring business continuity. COBIT® 5 offers a robust approach to managing IT-related risks.
- Risk Identification: The framework helps in identifying potential IT risks and vulnerabilities. COBIT® 5 provides a complete set of risk management practices. It ensures the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks.
- Risk Response: COBIT® 5 offers guidance on developing and implementing risk response strategies. This includes defining risk tolerance levels, establishing controls, and monitoring risk management activities.
- Compliance and Security: The framework meets regulations and boosts IT security. Integrating risk management into IT processes helps protect sensitive data and ensures compliance.
COBIT® 5's risk management practices can help reduce IT risks. They can also protect assets.
Enhanced IT process efficiency
COBIT® 5 offers best practices and frameworks. They help organizations optimize their IT operations.
- Process Optimization: The framework outlines best practices for IT process management. It will make them more efficient and effective. This includes streamlining workflows, reducing redundancies, and enhancing process performance.
- Performance Measurement: COBIT® 5 has metrics to assess IT processes. By monitoring performance, organizations can find areas to improve. They can then make the necessary changes.
- Resource Management: The framework helps organizations manage IT resources: personnel, technology, and budgets. Effective resource management maximizes IT investments and ensures the efficient use of resources.
Using COBIT® 5 to improve IT processes boosts performance and saves costs.
Strengthened IT governance
COBIT® 5 offers a complete method for IT governance. It ensures that IT management aligns with corporate governance principles.
- Governance Framework: The framework sets clear IT management structures, roles, and responsibilities. This includes defining decision-making processes, accountability mechanisms, and oversight functions.
- Compliance Management: COBIT® 5 supports compliance with internal policies and external regulations. Governance practices in IT processes can ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
- Strategic Decision-Making: The framework helps with strategic decisions. It provides a structured way to test IT investments and initiatives. This helps in making informed decisions that support long-term business objectives.
Strengthening IT governance through COBIT® 5 enhances organizational control, accountability, and compliance.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
COBIT® 5 promotes a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability within IT organizations.
- Continuous Improvement: The framework encourages regular evaluation and improvement of IT processes. A mindset of continuous improvement helps organizations stay competitive. It allows them to respond to changes in business needs and new technologies.
- Adaptability: COBIT® 5 supports it with a flexible, customizable framework. It can fit different organizations and needs. This allows organizations to adjust their IT governance and management as needed.
- Benchmarking and Best Practices: The framework includes benchmarking techniques. They compare IT performance to industry standards and best practices. This helps organizations identify gaps and install improvements based on proven methods.
COBIT® 5 helps organizations stay agile in a fast-changing world. It does this by promoting a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability.
How to obtain Cobit 5 certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, COBIT® 5 has many benefits for IT organizations. It improves alignment between IT and business goals. It also boosts risk management and IT process efficiency. It strengthens IT governance and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. COBIT® 5 helps organizations align IT with business goals. It also manages risks, optimizes IT processes, and strengthens governance. As technology evolves, COBIT® 5 offers a framework. It helps manage complex IT and drives organizational success.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
ITIL 4: Transforming Modern IT Governance for Efficiency
In today's fast-paced digital world, IT governance is vital for success. One popular framework that plays a key role in modern IT governance is ITIL 4. In this article, we will explore the significance of ITIL 4 and how it can benefit organizations in achieving their IT goals.
What is ITIL 4?
ITIL 4 stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is a set of best practices for IT service management. It gives organizations a way to manage IT services and operations.
Why is ITIL 4 Important for Modern IT Governance?
ITIL 4 is vital for modern IT governance. It helps align IT services with business goals, improve service delivery, and boost customer satisfaction. ITIL 4 practices help organizations run IT operations efficiently. They will then support their business goals.
ITIL 4 is key for IT governance. It aligns IT services with business needs and goals. It is a complete framework. By focusing on value creation, and service management, it ensures IT operations are efficient and effective. Integrating ITIL 4 practices can help organizations. It can improve governance, service quality, and adaptation to the digital world.
ITIL 4 is vital for modern IT governance. It offers a flexible, scalable way to manage IT services. It meets the demands of today's fast-paced digital world. The focus on the SVS and four dimensions model ensures a complete view of service management. It aligns IT with business goals and boosts efficiency. Also, ITIL 4 promotes a culture of improvement and agility. It helps organizations quickly adapt to changes and achieve lasting success.
How Does ITIL 4 Benefit Organizations?
ITIL 4 gives organizations a modern way to manage IT services. It emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continual improvement. By aligning IT services with business needs, it helps companies deliver value and adapt to change. ITIL 4 practices can help organizations. They improve service quality and streamline operations. This leads to better overall outcomes.
-
ITIL 4 helps organizations improve service management and delivery.
-
Improved Processes: Using ITIL 4 practices can optimize IT processes and boost efficiency.
-
Better Customer Experience: ITIL 4 aims for customer-focused service. This improves customer satisfaction.
-
Increased Productivity: ITIL 4 principles and practices boost productivity and results.
ITIL 4 Implementation and Challenges
ITIL 4 has great benefits. But, its implementation can be hard for organizations. Some common challenges include resistance to change, lack of awareness, and insufficient resources. With proper training, tools, and support, organizations can overcome these challenges. They can then reap the rewards of ITIL 4 implementation.
ITIL 4 can greatly improve IT service management. It offers a flexible, complete framework that aligns IT services with business needs. However, organizations often face challenges. These include resistance to change, adapting processes, and training all stakeholders. We must take a strategic approach to address these hurdles. It needs clear communication, phased implementation, and ongoing support to succeed.
ITIL 4 Best Practices
ITIL 4 takes a holistic approach to IT service management. It blends modern practices with traditional ITIL principles. It emphasizes value co-creation and continuous improvement. ITIL 4's best practices can help. They focus on the Service Value System (SVS) and use agile methods. This aligns IT services with business goals and customer needs. These practices help teams to improve service, efficiency, and innovation in a fast-changing tech world.
ITIL 4 encompasses a range of best practices that organizations can leverage to improve their IT service management. Some key ITIL 4 best practices include:
-
Incident Management: Resolving IT incidents promptly and efficiently to minimize downtime.
-
Change Management: Managing changes to IT systems in a controlled and systematic manner to reduce risks.
-
Service Level Management: Defining, monitoring, and improving service levels to meet business requirements.
-
Continual Improvement: Regularly reviewing and improving IT services and processes. This drives ongoing improvement.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, ITIL 4 is vital to modern IT governance. It gives a framework for managing IT services effectively. ITIL 4's principles and best practices can help organizations. They can improve service delivery, processes, and business outcomes. With the right approach and commitment, organizations can harness the power of ITIL 4 to drive success in today's digital age.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, IT governance is vital for success. One popular framework that plays a key role in modern IT governance is ITIL 4. In this article, we will explore the significance of ITIL 4 and how it can benefit organizations in achieving their IT goals.
What is ITIL 4?
ITIL 4 stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is a set of best practices for IT service management. It gives organizations a way to manage IT services and operations.
Why is ITIL 4 Important for Modern IT Governance?
ITIL 4 is vital for modern IT governance. It helps align IT services with business goals, improve service delivery, and boost customer satisfaction. ITIL 4 practices help organizations run IT operations efficiently. They will then support their business goals.
ITIL 4 is key for IT governance. It aligns IT services with business needs and goals. It is a complete framework. By focusing on value creation, and service management, it ensures IT operations are efficient and effective. Integrating ITIL 4 practices can help organizations. It can improve governance, service quality, and adaptation to the digital world.
ITIL 4 is vital for modern IT governance. It offers a flexible, scalable way to manage IT services. It meets the demands of today's fast-paced digital world. The focus on the SVS and four dimensions model ensures a complete view of service management. It aligns IT with business goals and boosts efficiency. Also, ITIL 4 promotes a culture of improvement and agility. It helps organizations quickly adapt to changes and achieve lasting success.
How Does ITIL 4 Benefit Organizations?
ITIL 4 gives organizations a modern way to manage IT services. It emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continual improvement. By aligning IT services with business needs, it helps companies deliver value and adapt to change. ITIL 4 practices can help organizations. They improve service quality and streamline operations. This leads to better overall outcomes.
-
ITIL 4 helps organizations improve service management and delivery.
-
Improved Processes: Using ITIL 4 practices can optimize IT processes and boost efficiency.
-
Better Customer Experience: ITIL 4 aims for customer-focused service. This improves customer satisfaction.
-
Increased Productivity: ITIL 4 principles and practices boost productivity and results.
ITIL 4 Implementation and Challenges
ITIL 4 has great benefits. But, its implementation can be hard for organizations. Some common challenges include resistance to change, lack of awareness, and insufficient resources. With proper training, tools, and support, organizations can overcome these challenges. They can then reap the rewards of ITIL 4 implementation.
ITIL 4 can greatly improve IT service management. It offers a flexible, complete framework that aligns IT services with business needs. However, organizations often face challenges. These include resistance to change, adapting processes, and training all stakeholders. We must take a strategic approach to address these hurdles. It needs clear communication, phased implementation, and ongoing support to succeed.
ITIL 4 Best Practices
ITIL 4 takes a holistic approach to IT service management. It blends modern practices with traditional ITIL principles. It emphasizes value co-creation and continuous improvement. ITIL 4's best practices can help. They focus on the Service Value System (SVS) and use agile methods. This aligns IT services with business goals and customer needs. These practices help teams to improve service, efficiency, and innovation in a fast-changing tech world.
ITIL 4 encompasses a range of best practices that organizations can leverage to improve their IT service management. Some key ITIL 4 best practices include:
-
Incident Management: Resolving IT incidents promptly and efficiently to minimize downtime.
-
Change Management: Managing changes to IT systems in a controlled and systematic manner to reduce risks.
-
Service Level Management: Defining, monitoring, and improving service levels to meet business requirements.
-
Continual Improvement: Regularly reviewing and improving IT services and processes. This drives ongoing improvement.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, ITIL 4 is vital to modern IT governance. It gives a framework for managing IT services effectively. ITIL 4's principles and best practices can help organizations. They can improve service delivery, processes, and business outcomes. With the right approach and commitment, organizations can harness the power of ITIL 4 to drive success in today's digital age.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
How to Align Business Goals with IT Objectives Using COBIT 5
In today's fast-paced business world, IT must align with business goals. It's vital for success. COBIT® 5 is a global IT governance and management framework. It provides a complete way to achieve this alignment. This framework links IT and business. It ensures tech investments support business goals, reduce risks, and maximize value. This guide shows how COBIT® 5 can help organizations. It aligns IT objectives with business goals. This drives better decisions and boosts performance.
Table Of Contents
- Understanding the Importance of IT-Business Alignment
- Leveraging COBIT® 5 principles for strategic alignment
- Implementing COBIT® 5 enablers for effective alignment
- Measuring and Monitoring Alignment with COBIT® 5
- Case Studies: Successful Alignment Using COBIT® 5
- Conclusion
Understanding the Importance of IT-Business Alignment
IT-business alignment is the sync of IT and business strategies to achieve goals. It's important. It ensures that IT investments and initiatives are directly contributing to business objectives.
- Challenges of Misalignment: Misalignment can lead to inefficiencies, wasted resources, and missed opportunities. Common challenges include communication gaps, conflicting priorities, and a lack of strategic oversight.
- Role of COBIT® 5: COBIT® 5 is a framework. It helps organizations align IT with the business. It does this by defining clear governance principles, processes, and enablers. It focuses on creating value through effective risk management and resource optimization.
IT-business alignment is vital for organizations aiming to remain competitive and innovative. When IT goals don't align with business ones, organizations face problems. They may become less efficient, incur higher costs, and miss growth opportunities. COBIT® 5, with its governance principles and processes, offers a solution. It ensures that IT initiatives align with business goals. This alignment leads to better decision-making, optimized resource utilization, and enhanced risk management.
Leveraging COBIT® 5 principles for strategic alignment
COBIT® 5 stresses the need to meet stakeholders. IT initiatives must support business goals.
- End-to-End Governance: The framework provides a full view of governance. It covers all IT activities and aligns them with business processes.
- Using a Single Integrated Framework: COBIT® 5 integrates with other frameworks and standards. It enables a consistent approach to governance and management across the organization.
COBIT® 5 is built on five principles that guide the alignment of IT with business goals. The first principle, "Meeting Stakeholder Needs," ensures IT projects meet the business's needs. By focusing on stakeholders' expectations, organizations can prioritize IT projects. This will provide the most value. The second principle, "End-to-End Governance," ensures all IT work aligns with business processes. It provides a holistic view of governance. COBIT® 5's third principle, 'Applying a Single Integrated Framework,' says to integrate it with other frameworks. It seeks a consistent, unified approach to governance.
Implementing COBIT® 5 enablers for effective alignment
COBIT® 5 outlines governance and management objectives. They align IT initiatives with business strategies. The focus is on value creation, risk management, and resource optimization.
- Enabler Models: The framework uses enabler models to align. These include processes, structures, and culture. These enablers support the achievement of governance and management objectives.
- Critical Enablers: The seven COBIT® 5 enablers are: principles, policies, frameworks, processes, structures, culture, information, services, infrastructure, applications, and skills. Also, infrastructure and competencies.
COBIT® 5 names enablers to help organizations align IT with business goals. These enablers include governance and management objectives. They aim for value creation, risk management, and resource optimization. The framework's enabler models, like processes and culture, provide the tools to align. By focusing on seven key enablers, organizations can align IT with business goals. This will improve performance and drive better outcomes.
Measuring and Monitoring Alignment with COBIT® 5
Performance Measurement: COBIT® 5 includes practices to measure performance. They help organizations track and assess how well IT aligns with business goals.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Use KPIs to assess IT governance and management. They should support business goals.
- Continuous Improvement: COBIT® 5 promotes a continuous improvement approach. Regularly reviewing and adjusting ensures that we maintain alignment over time.
Measuring and monitoring IT's alignment with business goals is vital for success. COBIT® 5 offers practices to measure performance. They enable organizations to track their IT governance and management. Organizations can use KPIs to see if IT projects are valuable and meeting goals. COBIT® 5 emphasizes continuous improvement. It calls for organizations to reassess their alignment strategies periodically. They must adapt to changing business needs.
Case Studies: Successful Alignment Using COBIT® 5
Real-World Examples: Study organizations that have used COBIT® 5. They aligned their IT and business goals.
- Lessons Learned: Key takeaways from the case studies. They include best practices and pitfalls to avoid.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Explain using COBIT® 5 in small to large businesses.
Case studies offer insights into how organizations used COBIT® 5. They aligned their IT and business goals. These examples show the framework's real-world use. They share best practices and lessons learned. The case studies teach us three key lessons. First, engage stakeholders. Second, have a clear governance structure. Monitor development and make adjustments as needed. Also, COBIT® 5 demonstrates scalability and flexibility. The framework can adapt to different organizations and sizes.
How to obtain COBIT 5 certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Aligning IT with business goals is key to success today. COBIT® 5 offers a strong framework for this alignment. It provides clear governance principles, enablers, and ways to measure performance. COBIT® 5 can help organizations. It ensures their IT investments support business goals. It also optimizes resources and manages risks. As a result, businesses can improve their strategies, efficiency, and growth.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-paced business world, IT must align with business goals. It's vital for success. COBIT® 5 is a global IT governance and management framework. It provides a complete way to achieve this alignment. This framework links IT and business. It ensures tech investments support business goals, reduce risks, and maximize value. This guide shows how COBIT® 5 can help organizations. It aligns IT objectives with business goals. This drives better decisions and boosts performance.
Table Of Contents
- Understanding the Importance of IT-Business Alignment
- Leveraging COBIT® 5 principles for strategic alignment
- Implementing COBIT® 5 enablers for effective alignment
- Measuring and Monitoring Alignment with COBIT® 5
- Case Studies: Successful Alignment Using COBIT® 5
- Conclusion
Understanding the Importance of IT-Business Alignment
IT-business alignment is the sync of IT and business strategies to achieve goals. It's important. It ensures that IT investments and initiatives are directly contributing to business objectives.
- Challenges of Misalignment: Misalignment can lead to inefficiencies, wasted resources, and missed opportunities. Common challenges include communication gaps, conflicting priorities, and a lack of strategic oversight.
- Role of COBIT® 5: COBIT® 5 is a framework. It helps organizations align IT with the business. It does this by defining clear governance principles, processes, and enablers. It focuses on creating value through effective risk management and resource optimization.
IT-business alignment is vital for organizations aiming to remain competitive and innovative. When IT goals don't align with business ones, organizations face problems. They may become less efficient, incur higher costs, and miss growth opportunities. COBIT® 5, with its governance principles and processes, offers a solution. It ensures that IT initiatives align with business goals. This alignment leads to better decision-making, optimized resource utilization, and enhanced risk management.
Leveraging COBIT® 5 principles for strategic alignment
COBIT® 5 stresses the need to meet stakeholders. IT initiatives must support business goals.
- End-to-End Governance: The framework provides a full view of governance. It covers all IT activities and aligns them with business processes.
- Using a Single Integrated Framework: COBIT® 5 integrates with other frameworks and standards. It enables a consistent approach to governance and management across the organization.
COBIT® 5 is built on five principles that guide the alignment of IT with business goals. The first principle, "Meeting Stakeholder Needs," ensures IT projects meet the business's needs. By focusing on stakeholders' expectations, organizations can prioritize IT projects. This will provide the most value. The second principle, "End-to-End Governance," ensures all IT work aligns with business processes. It provides a holistic view of governance. COBIT® 5's third principle, 'Applying a Single Integrated Framework,' says to integrate it with other frameworks. It seeks a consistent, unified approach to governance.
Implementing COBIT® 5 enablers for effective alignment
COBIT® 5 outlines governance and management objectives. They align IT initiatives with business strategies. The focus is on value creation, risk management, and resource optimization.
- Enabler Models: The framework uses enabler models to align. These include processes, structures, and culture. These enablers support the achievement of governance and management objectives.
- Critical Enablers: The seven COBIT® 5 enablers are: principles, policies, frameworks, processes, structures, culture, information, services, infrastructure, applications, and skills. Also, infrastructure and competencies.
COBIT® 5 names enablers to help organizations align IT with business goals. These enablers include governance and management objectives. They aim for value creation, risk management, and resource optimization. The framework's enabler models, like processes and culture, provide the tools to align. By focusing on seven key enablers, organizations can align IT with business goals. This will improve performance and drive better outcomes.
Measuring and Monitoring Alignment with COBIT® 5
Performance Measurement: COBIT® 5 includes practices to measure performance. They help organizations track and assess how well IT aligns with business goals.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Use KPIs to assess IT governance and management. They should support business goals.
- Continuous Improvement: COBIT® 5 promotes a continuous improvement approach. Regularly reviewing and adjusting ensures that we maintain alignment over time.
Measuring and monitoring IT's alignment with business goals is vital for success. COBIT® 5 offers practices to measure performance. They enable organizations to track their IT governance and management. Organizations can use KPIs to see if IT projects are valuable and meeting goals. COBIT® 5 emphasizes continuous improvement. It calls for organizations to reassess their alignment strategies periodically. They must adapt to changing business needs.
Case Studies: Successful Alignment Using COBIT® 5
Real-World Examples: Study organizations that have used COBIT® 5. They aligned their IT and business goals.
- Lessons Learned: Key takeaways from the case studies. They include best practices and pitfalls to avoid.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Explain using COBIT® 5 in small to large businesses.
Case studies offer insights into how organizations used COBIT® 5. They aligned their IT and business goals. These examples show the framework's real-world use. They share best practices and lessons learned. The case studies teach us three key lessons. First, engage stakeholders. Second, have a clear governance structure. Monitor development and make adjustments as needed. Also, COBIT® 5 demonstrates scalability and flexibility. The framework can adapt to different organizations and sizes.
How to obtain COBIT 5 certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Aligning IT with business goals is key to success today. COBIT® 5 offers a strong framework for this alignment. It provides clear governance principles, enablers, and ways to measure performance. COBIT® 5 can help organizations. It ensures their IT investments support business goals. It also optimizes resources and manages risks. As a result, businesses can improve their strategies, efficiency, and growth.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
ISO 20000: Driving Continuous Improvement in IT Services.
In today's fast-paced digital world, IT services must be efficient and high-quality. They are vital to business success. ISO 20000 is the international standard for IT service management (ITSM). It provides a framework for managing and delivering quality IT services. A core principle is continuous improvement. It ensures that IT services meet changing business needs. And, it improves them. This article shows how ISO 20000 boosts IT service improvement. It provides a structured way to optimize IT operations.
Table Of Contents
- Understanding ISO 20000: A Brief Overview
- The Role of Continuous Improvement in ITSM
- Implementing ISO 20000: Key Steps for Success
- The Benefits of ISO 20000 and Continuous Improvement
- Challenges in Maintaining Continuous Improvement
- Conclusion
Understanding ISO 20000: A Brief Overview
ISO 20000 is the first international standard for IT service management. It harmonizes IT services with business requirements and provides efficient delivery. The standard integrates processes and mirrors ITIL's framework. It consists of two main parts:
- ISO 20000-1: A specification. It outlines what an organization must do to improve its IT service management system (SMS).
- ISO 20000-2: The code of practice that provides guidance on the application of the SMS.
ISO 20000 helps organizations manage risks, boost customer satisfaction, and improve services. The standard stresses the need to plan, install, and improve IT services. It also calls for monitoring and reviewing them.
The Role of Continuous Improvement in ITSM
Continuous improvement is key to ISO 20000 and IT service management. It uses a systematic method to find ways to improve. It then implements changes and measures their impact. ITSM's continuous improvement process revolves around the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle.
- Plan: Identify areas for improvement and develop a plan to address them.
- Do: Install the planned changes.
- Check and test the results of the changes.
- Act: Take action based on the results to further refine and optimize the process.
This cycle is iterative. It means that improvement is ongoing, not a one-time event. Continuous improvement helps organizations adapt to change. It improves service quality and outcomes.
Implementing ISO 20000: Key Steps for Success
Implementing ISO 20000 involves several key steps. Each step aims at continuous improvement.
- Gap Analysis: Assess your IT service management processes against ISO 20000. Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Service Management Plan: Create a plan to install changes to meet ISO 20000. This plan should include clear objectives, roles, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Process Development and Documentation: Define and document the ISO 20000 ITSM processes. Align these processes with business needs. They should support continuous improvement.
- Training and Awareness: Train staff on the new processes. They must know their roles in continuous improvement.
- Internal Audits and Management Reviews: Conduct regular internal audits and management reviews. They will check compliance with ISO 20000 and find improvement opportunities.
These steps help organizations install ISO 20000. They also build a culture of continuous improvement in IT services.
The Benefits of ISO 20000 and Continuous Improvement
Implementing ISO 20000 and embracing continuous improvement offers many benefits to organizations:
- Continuous improvement leads to better IT services. This boosts customer satisfaction and reduces disruptions.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes and reviews cut inefficiencies and costs.
- Risk Management: ISO 20000's ITSM approach helps firms find and reduce risks. It leads to more reliable and secure IT services.
- ISO 20000 certification shows a commitment to quality and improvement. It enhances an organization's reputation and its competitive edge in the market.
- Employee Engagement: Involving employees in improvement projects boosts collaboration and innovation. This raises job satisfaction and productivity.
These benefits make ISO 20000 a wise investment. It helps organizations improve their IT services and succeed long-term.
Challenges in Maintaining Continuous Improvement
While continuous improvement is essential, it is not without challenges. Organizations may face several obstacles in IT services. They must maintain a culture of continuous improvement.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist new processes or role changes. This can hinder improvement efforts.
- Resource Constraints: Continuous improvement requires time, effort, and resources. Organizations must ensure they have the necessary support to sustain improvement initiatives.
- Complex IT environments are tough to improve. It's hard to find areas to fix and to make changes. Organizations must have a clear understanding of their IT infrastructure and processes.
- Measuring Improvement: It's hard to gauge the short-term impacts of improvement initiatives. Organizations need effective metrics and monitoring systems to track progress.
We must overcome these challenges. We need strong leadership, clear communication, and a commitment to learning and growth.
How to obtain ISO 20000 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, ISO 20000 is a strong IT service management framework. It focuses on continuous improvement. ISO 20000 helps organizations improve their IT services. It ensures they meet the business's changing needs and deliver value to customers. Continuous improvement is not a one-time effort. It is an ongoing journey. It requires dedication, resources, and a willingness to adapt to change. It will help organizations excel and manage risks. They will stay competitive in today's fast-changing world.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, IT services must be efficient and high-quality. They are vital to business success. ISO 20000 is the international standard for IT service management (ITSM). It provides a framework for managing and delivering quality IT services. A core principle is continuous improvement. It ensures that IT services meet changing business needs. And, it improves them. This article shows how ISO 20000 boosts IT service improvement. It provides a structured way to optimize IT operations.
Table Of Contents
- Understanding ISO 20000: A Brief Overview
- The Role of Continuous Improvement in ITSM
- Implementing ISO 20000: Key Steps for Success
- The Benefits of ISO 20000 and Continuous Improvement
- Challenges in Maintaining Continuous Improvement
- Conclusion
Understanding ISO 20000: A Brief Overview
ISO 20000 is the first international standard for IT service management. It harmonizes IT services with business requirements and provides efficient delivery. The standard integrates processes and mirrors ITIL's framework. It consists of two main parts:
- ISO 20000-1: A specification. It outlines what an organization must do to improve its IT service management system (SMS).
- ISO 20000-2: The code of practice that provides guidance on the application of the SMS.
ISO 20000 helps organizations manage risks, boost customer satisfaction, and improve services. The standard stresses the need to plan, install, and improve IT services. It also calls for monitoring and reviewing them.
The Role of Continuous Improvement in ITSM
Continuous improvement is key to ISO 20000 and IT service management. It uses a systematic method to find ways to improve. It then implements changes and measures their impact. ITSM's continuous improvement process revolves around the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle.
- Plan: Identify areas for improvement and develop a plan to address them.
- Do: Install the planned changes.
- Check and test the results of the changes.
- Act: Take action based on the results to further refine and optimize the process.
This cycle is iterative. It means that improvement is ongoing, not a one-time event. Continuous improvement helps organizations adapt to change. It improves service quality and outcomes.
Implementing ISO 20000: Key Steps for Success
Implementing ISO 20000 involves several key steps. Each step aims at continuous improvement.
- Gap Analysis: Assess your IT service management processes against ISO 20000. Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Service Management Plan: Create a plan to install changes to meet ISO 20000. This plan should include clear objectives, roles, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Process Development and Documentation: Define and document the ISO 20000 ITSM processes. Align these processes with business needs. They should support continuous improvement.
- Training and Awareness: Train staff on the new processes. They must know their roles in continuous improvement.
- Internal Audits and Management Reviews: Conduct regular internal audits and management reviews. They will check compliance with ISO 20000 and find improvement opportunities.
These steps help organizations install ISO 20000. They also build a culture of continuous improvement in IT services.
The Benefits of ISO 20000 and Continuous Improvement
Implementing ISO 20000 and embracing continuous improvement offers many benefits to organizations:
- Continuous improvement leads to better IT services. This boosts customer satisfaction and reduces disruptions.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes and reviews cut inefficiencies and costs.
- Risk Management: ISO 20000's ITSM approach helps firms find and reduce risks. It leads to more reliable and secure IT services.
- ISO 20000 certification shows a commitment to quality and improvement. It enhances an organization's reputation and its competitive edge in the market.
- Employee Engagement: Involving employees in improvement projects boosts collaboration and innovation. This raises job satisfaction and productivity.
These benefits make ISO 20000 a wise investment. It helps organizations improve their IT services and succeed long-term.
Challenges in Maintaining Continuous Improvement
While continuous improvement is essential, it is not without challenges. Organizations may face several obstacles in IT services. They must maintain a culture of continuous improvement.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist new processes or role changes. This can hinder improvement efforts.
- Resource Constraints: Continuous improvement requires time, effort, and resources. Organizations must ensure they have the necessary support to sustain improvement initiatives.
- Complex IT environments are tough to improve. It's hard to find areas to fix and to make changes. Organizations must have a clear understanding of their IT infrastructure and processes.
- Measuring Improvement: It's hard to gauge the short-term impacts of improvement initiatives. Organizations need effective metrics and monitoring systems to track progress.
We must overcome these challenges. We need strong leadership, clear communication, and a commitment to learning and growth.
How to obtain ISO 20000 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, ISO 20000 is a strong IT service management framework. It focuses on continuous improvement. ISO 20000 helps organizations improve their IT services. It ensures they meet the business's changing needs and deliver value to customers. Continuous improvement is not a one-time effort. It is an ongoing journey. It requires dedication, resources, and a willingness to adapt to change. It will help organizations excel and manage risks. They will stay competitive in today's fast-changing world.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Service Management in the Era of Digital Transformation
In today's fast-changing tech world, service management is vital. It ensures success for organizations undergoing digital transformation. As businesses rely more on technology, service management has evolved. It now has many tools. They manage IT, deliver services, and improve customer experiences.
The Impact of Digital Transformation on Service Management
Digital transformation has changed how organizations operate. It uses cloud computing, automation, and agile methods. These technologies streamline processes, boost efficiency, and drive innovation. As businesses go digital, service management's role becomes vital. It must ensure a smooth tech integration into their operations. Digital technologies are growing. Organizations now face new challenges. They must manage their IT infrastructure, data analytics, cybersecurity, and IT service management. To solve these challenges, service management must evolve for the digital era. It should adopt best practices like DevOps, continuous improvement, and change management.
Digital transformation is reshaping service management. It integrates advanced tech, like AI, automation, and cloud solutions. These tools streamline processes and boost efficiency. This evolution lets organizations provide better, more responsive customer experiences. It also improves service delivery using real-time data and predictive analytics. As businesses adapt to the digital shift, they must embrace new tools and strategies. This is to stay competitive and meet their customers' complex demands.
Leveraging Technology for Service Management
A key to effective service management today is adopting new tech. This includes AI, IoT, and virtualization. These technologies help organizations. They enhance network management, improve IT operations, and drive innovation in service delivery.
In today's fast-changing digital world, using technology is key to improving service management. Advanced tools, like AI analytics and automation, can help organizations. They can streamline operations, improve service, and boost customer satisfaction. These new technologies boost efficiency. They also empower service teams to fix issues and adapt to change.
By using AI and IoT, organizations can automate routine tasks. They can also improve decision-making and optimize service delivery. It improves efficiency and scalability. It helps organizations improve customer experience with real-time, personalized insights and services.
Best Practices for Service Management in the Digital Era
To succeed in the digital era, organizations must use best practices in service management. These should focus on efficiency, adaptability, and scalability. This includes using agile methods, cloud services, and SaaS. It also includes adopting ITIL for service desk management.
In the digital era, we must use new tech and agile methods to improve service management. This will boost efficiency and responsiveness. Best practices are to automate routine tasks. Use data analytics for decisions. Focus on customers to meet their changing expectations. By using these strategies, organizations can excel in service. They can also adapt to the fast-paced digital world.
Best practices can help organizations. They improve service, cut costs, and reduce risks. These include: service optimization, process automation, and service virtualization. It also involves ensuring compliance with regulations. It requires robust incident management and problem-solving processes. We must also monitor performance metrics to gauge user satisfaction.
The Future of Service Management
As technology evolves, the future of service management will be shaped by trends. These include the digital workforce, service request automation, and predictive analytics. To thrive in the digital age, organizations must modernize their IT. They should improve their service design and transition processes. They must also optimize service performance.
As technology evolves, the future of service management looks bright. It promises big gains in efficiency and customer experience. AI, automation, and predictive analytics will change service delivery. They will enable proactive solutions instead of reactive ones. Organizations must embrace these innovations to stay competitive. They must also meet their customers' ever-changing expectations.
A shift to agile, flexible frameworks is shaping the future of service management. It is driven by a need to adapt to new technologies and changing customer demands. 5G and IoT will revolutionize service delivery. They will provide real-time data and improve connectivity. To thrive in a changing world, organizations must invest in new tools and strategies. These must prioritize efficiency and great customer experiences.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, service management is vital in the digital age. It helps organizations innovate, improve processes, and boost customer experiences. Using technology and best practices, organizations can succeed in the fast-changing digital world. They must also optimize their services.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-changing tech world, service management is vital. It ensures success for organizations undergoing digital transformation. As businesses rely more on technology, service management has evolved. It now has many tools. They manage IT, deliver services, and improve customer experiences.
The Impact of Digital Transformation on Service Management
Digital transformation has changed how organizations operate. It uses cloud computing, automation, and agile methods. These technologies streamline processes, boost efficiency, and drive innovation. As businesses go digital, service management's role becomes vital. It must ensure a smooth tech integration into their operations. Digital technologies are growing. Organizations now face new challenges. They must manage their IT infrastructure, data analytics, cybersecurity, and IT service management. To solve these challenges, service management must evolve for the digital era. It should adopt best practices like DevOps, continuous improvement, and change management.
Digital transformation is reshaping service management. It integrates advanced tech, like AI, automation, and cloud solutions. These tools streamline processes and boost efficiency. This evolution lets organizations provide better, more responsive customer experiences. It also improves service delivery using real-time data and predictive analytics. As businesses adapt to the digital shift, they must embrace new tools and strategies. This is to stay competitive and meet their customers' complex demands.
Leveraging Technology for Service Management
A key to effective service management today is adopting new tech. This includes AI, IoT, and virtualization. These technologies help organizations. They enhance network management, improve IT operations, and drive innovation in service delivery.
In today's fast-changing digital world, using technology is key to improving service management. Advanced tools, like AI analytics and automation, can help organizations. They can streamline operations, improve service, and boost customer satisfaction. These new technologies boost efficiency. They also empower service teams to fix issues and adapt to change.
By using AI and IoT, organizations can automate routine tasks. They can also improve decision-making and optimize service delivery. It improves efficiency and scalability. It helps organizations improve customer experience with real-time, personalized insights and services.
Best Practices for Service Management in the Digital Era
To succeed in the digital era, organizations must use best practices in service management. These should focus on efficiency, adaptability, and scalability. This includes using agile methods, cloud services, and SaaS. It also includes adopting ITIL for service desk management.
In the digital era, we must use new tech and agile methods to improve service management. This will boost efficiency and responsiveness. Best practices are to automate routine tasks. Use data analytics for decisions. Focus on customers to meet their changing expectations. By using these strategies, organizations can excel in service. They can also adapt to the fast-paced digital world.
Best practices can help organizations. They improve service, cut costs, and reduce risks. These include: service optimization, process automation, and service virtualization. It also involves ensuring compliance with regulations. It requires robust incident management and problem-solving processes. We must also monitor performance metrics to gauge user satisfaction.
The Future of Service Management
As technology evolves, the future of service management will be shaped by trends. These include the digital workforce, service request automation, and predictive analytics. To thrive in the digital age, organizations must modernize their IT. They should improve their service design and transition processes. They must also optimize service performance.
As technology evolves, the future of service management looks bright. It promises big gains in efficiency and customer experience. AI, automation, and predictive analytics will change service delivery. They will enable proactive solutions instead of reactive ones. Organizations must embrace these innovations to stay competitive. They must also meet their customers' ever-changing expectations.
A shift to agile, flexible frameworks is shaping the future of service management. It is driven by a need to adapt to new technologies and changing customer demands. 5G and IoT will revolutionize service delivery. They will provide real-time data and improve connectivity. To thrive in a changing world, organizations must invest in new tools and strategies. These must prioritize efficiency and great customer experiences.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, service management is vital in the digital age. It helps organizations innovate, improve processes, and boost customer experiences. Using technology and best practices, organizations can succeed in the fast-changing digital world. They must also optimize their services.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Top 5 Reasons to Get COBIT 5 Foundation Certified in 2024
In today's fast-changing digital world, businesses rely on strong IT governance and management. As organizations seek to align IT with business goals, COBIT® 5 is essential.COBIT® 5 represents Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is a global framework. It offers guidance for governing and managing enterprise IT. In 2024, there is a greater focus on compliance, risk, and IT investment. So, COBIT® 5 Foundation certification is now more relevant than ever.
This article will share the top five reasons to get COBIT® 5 Foundation certified in 2024. This opportunity can transform your career and revolutionize your organization. If you're an IT pro, a business manager, or into GRC, know the benefits of COBIT® 5 certification. It will help you navigate today's complex IT and drive business success.
Table Of Contents
- Enhances Your Understanding of IT Governance
- Strengthens Risk Management Capabilities
- Facilitates regulatory compliance
- Boosts Career Opportunities and Earning Potential
- Supports Continuous Improvement and Value Creation
- Conclusion
Enhances Your Understanding of IT Governance
In the digital age, IT governance is vital to corporate governance. It is no longer a niche concern. COBIT® 5 is a strong framework. It helps organizations meet their IT governance goals. It does this by aligning IT processes with business objectives. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification teaches you to improve IT governance in your organization.
The certification covers the core principles of COBIT® 5. They are:
- Meeting stakeholders' needs;
- covering the enterprise end to
- Applying a single integrated framework.
- Enabling a holistic approach.
- Separating governance from management.
This knowledge is invaluable for IT managers. They must use IT resources well, manage risks, and maximize returns on IT investments. In 2024, scrutiny of IT practices will rise. Your IT governance skills will set you apart in the job market.
Strengthens Risk Management Capabilities
Risk management is key to any organization's success. In IT, it is even more critical. COBIT® 5 offers comprehensive guidance on identifying, assessing, and mitigating IT-related risks. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification will equip you to manage risks. It will help protect your organization from potential threats.
In today's business world, it's vital to optimize risk, not avoid it. So, the framework's focus on this is very relevant. COBIT® 5 stresses the need to balance risk and opportunity. IT investments should add business value without exposing the organization to excess risk. In 2024, cyber threats will evolve, and regulations will tighten. So, the ability to manage IT risks will be a sought-after skill.
Facilitates regulatory compliance
With data breaches in the news, compliance is a top priority for organizations. COBIT® 5 ensures IT processes meet laws, regulations, and industry standards. Certification will teach you to design and install IT controls. They must meet regulations and support business goals.
The certification will let you help your organization with complex regulations. It includes data protection laws like GDPR and industry standards like HIPAA. It also includes various national and international laws. In 2024, new regulations and stricter enforcement may come. A COBIT® 5 certification will show you are an expert in IT compliance. It will allow you to guide your organization through these challenges.
Boosts Career Opportunities and Earning Potential
The demand for GRC professionals is growing. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification can boost your career. The certification is globally recognized. It demonstrates mastery of a popular development platform. Organizations of all sizes and industries adopt it.
In 2024, demand for IT pros with GRC skills will be high. Companies need help to navigate complex IT environments. COBIT® 5 certification will make you a more appealing job candidate. It is especially useful for IT governance, risk, and compliance. Also, for IT auditors. Also, certified professionals often earn more than their non-certified peers. This makes the certification a valuable investment in your future.
Supports Continuous Improvement and Value Creation
One of the key benefits of COBIT® 5 is its focus on continuous improvement and value creation. The framework guides how to measure and improve IT performance. It ensures that IT helps the organization's success. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification will teach you to apply these principles in practice. This will help your organization achieve its strategic goals.
COBIT® 5 promotes a holistic view of IT governance. It involves all stakeholders in decision-making. IT initiatives must align with business goals. This approach boosts IT performance. It also drives innovation and value. In 2024, organizations will want to maximize their IT investments. Your ability to help with improvement initiatives will make you invaluable.
How to obtain Cobit 5 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, As we enter 2024, IT governance, risk management, and compliance are crucial. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification gives a deep understanding of these areas.COBIT® 5 certification can help you. It will boost your IT governance knowledge, improve risk management, and ensure compliance. It can also boost your career and support improvement efforts. The certification provides the tools you need to succeed.
In a world of rapid tech change, it's vital to stay ahead. Get COBIT® 5 Foundation certified in 2024. This will make you a leader in IT governance and a valuable asset to any organization. Make a real impact in IT management and governance.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-changing digital world, businesses rely on strong IT governance and management. As organizations seek to align IT with business goals, COBIT® 5 is essential.COBIT® 5 represents Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is a global framework. It offers guidance for governing and managing enterprise IT. In 2024, there is a greater focus on compliance, risk, and IT investment. So, COBIT® 5 Foundation certification is now more relevant than ever.
This article will share the top five reasons to get COBIT® 5 Foundation certified in 2024. This opportunity can transform your career and revolutionize your organization. If you're an IT pro, a business manager, or into GRC, know the benefits of COBIT® 5 certification. It will help you navigate today's complex IT and drive business success.
Table Of Contents
- Enhances Your Understanding of IT Governance
- Strengthens Risk Management Capabilities
- Facilitates regulatory compliance
- Boosts Career Opportunities and Earning Potential
- Supports Continuous Improvement and Value Creation
- Conclusion
Enhances Your Understanding of IT Governance
In the digital age, IT governance is vital to corporate governance. It is no longer a niche concern. COBIT® 5 is a strong framework. It helps organizations meet their IT governance goals. It does this by aligning IT processes with business objectives. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification teaches you to improve IT governance in your organization.
The certification covers the core principles of COBIT® 5. They are:
- Meeting stakeholders' needs;
- covering the enterprise end to
- Applying a single integrated framework.
- Enabling a holistic approach.
- Separating governance from management.
This knowledge is invaluable for IT managers. They must use IT resources well, manage risks, and maximize returns on IT investments. In 2024, scrutiny of IT practices will rise. Your IT governance skills will set you apart in the job market.
Strengthens Risk Management Capabilities
Risk management is key to any organization's success. In IT, it is even more critical. COBIT® 5 offers comprehensive guidance on identifying, assessing, and mitigating IT-related risks. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification will equip you to manage risks. It will help protect your organization from potential threats.
In today's business world, it's vital to optimize risk, not avoid it. So, the framework's focus on this is very relevant. COBIT® 5 stresses the need to balance risk and opportunity. IT investments should add business value without exposing the organization to excess risk. In 2024, cyber threats will evolve, and regulations will tighten. So, the ability to manage IT risks will be a sought-after skill.
Facilitates regulatory compliance
With data breaches in the news, compliance is a top priority for organizations. COBIT® 5 ensures IT processes meet laws, regulations, and industry standards. Certification will teach you to design and install IT controls. They must meet regulations and support business goals.
The certification will let you help your organization with complex regulations. It includes data protection laws like GDPR and industry standards like HIPAA. It also includes various national and international laws. In 2024, new regulations and stricter enforcement may come. A COBIT® 5 certification will show you are an expert in IT compliance. It will allow you to guide your organization through these challenges.
Boosts Career Opportunities and Earning Potential
The demand for GRC professionals is growing. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification can boost your career. The certification is globally recognized. It demonstrates mastery of a popular development platform. Organizations of all sizes and industries adopt it.
In 2024, demand for IT pros with GRC skills will be high. Companies need help to navigate complex IT environments. COBIT® 5 certification will make you a more appealing job candidate. It is especially useful for IT governance, risk, and compliance. Also, for IT auditors. Also, certified professionals often earn more than their non-certified peers. This makes the certification a valuable investment in your future.
Supports Continuous Improvement and Value Creation
One of the key benefits of COBIT® 5 is its focus on continuous improvement and value creation. The framework guides how to measure and improve IT performance. It ensures that IT helps the organization's success. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification will teach you to apply these principles in practice. This will help your organization achieve its strategic goals.
COBIT® 5 promotes a holistic view of IT governance. It involves all stakeholders in decision-making. IT initiatives must align with business goals. This approach boosts IT performance. It also drives innovation and value. In 2024, organizations will want to maximize their IT investments. Your ability to help with improvement initiatives will make you invaluable.
How to obtain Cobit 5 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional® (CISSP)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Big Data Certification
- Data Science Certification
- Certified In Risk And Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
Conclusion
In Conclusion, As we enter 2024, IT governance, risk management, and compliance are crucial. COBIT® 5 Foundation certification gives a deep understanding of these areas.COBIT® 5 certification can help you. It will boost your IT governance knowledge, improve risk management, and ensure compliance. It can also boost your career and support improvement efforts. The certification provides the tools you need to succeed.
In a world of rapid tech change, it's vital to stay ahead. Get COBIT® 5 Foundation certified in 2024. This will make you a leader in IT governance and a valuable asset to any organization. Make a real impact in IT management and governance.
Contact Us :
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Understanding the Service Level Agreements (SLAs) in ITSM
In IT Service Management (ITSM), SLAs are key. They define the expectations and responsibilities between service providers and customers. Let's explore SLAs. They are vital for efficient IT service delivery.
What are Service Level Agreements?
Service Level Agreements, or SLAs, are formal agreements. They outline the service levels a provider commits to delivering to its customers. These agreements define key metrics that the provider must meet. They include response times, resolution times, uptime, and performance.
Why are SLAs important in ITSM?
SLAs are essential in ITSM for several reasons:
1. SLAs define what the customer can expect from service levels. They help manage expectations and avoid misunderstandings.
2. Measuring Performance: SLAs set clear metrics and targets. They allow both the provider and customer to measure IT service performance.
3. Improving Service Quality: SLAs set a benchmark for service quality. They drive continuous improvement.
4. SLAs hold service providers accountable for agreed-upon service levels. This helps improve service reliability and customer satisfaction.
5. SLAs are crucial in ITSM. They set clear expectations for service delivery. They ensure both the provider and customer understand the performance standards and responsibilities. They also support accountability and improvement. They do this by setting targets, communication protocols, and dispute resolution methods. They also manage service quality.
6. SLAs are vital in ITSM. They set service expectations and performance metrics. This aligns the goals of the service provider and the customer. It boosts accountability, communication, and service. This raises customer satisfaction and IT reliability.
Components of an SLA
An SLA always has these core elements:
Service descriptions define what the vendor will deliver. Performance metrics quantify the service quality. Problem management outlines the process for issue resolution. Warranties and remediation specify penalties for non-compliance. Termination clauses state the conditions for agreement ending.
· Service Level Targets: Specific, measurable targets that the service provider commits to achieving.
· SLA Metrics: KPIs that measure IT service performance.
· Service Level Reporting: Regular reports on IT service performance vs. targets.
· SLA Enforcement: The process for enforcing the SLA, including penalties for non-compliance.
· SLA Reviews: Periodic reviews to assess and adjust the SLA's effectiveness.
· Monitoring and Reporting:
· Performance Monitoring: It is the tools that check service performance against the SLOs.
· Reporting Schedule: Frequency and format of performance reports provided to the customer.
· Penalties and Remedies:
Service Credits: Compensation to the customer if service levels are not met.
·Penalties: Consequences for failing to meet agreed-upon service levels.
· Review and Revision:
· Review Schedule: Frequency of SLA reviews to ensure they remain relevant and up-to-date.
· Amendment Process: Procedures for making changes to the SLA.
· Dispute Resolution:
· Resolution Mechanisms: Processes for settling disputes between the provider and the customer.
· Term and Termination:
· Contract Duration: Length of time the SLA is in effect.
·Termination Conditions: Conditions under which the SLA or service agreement can be terminated.
· Contact Information:
· Primary Contacts: Key contacts on both sides to manage the SLA.
Best Practices for SLAs in ITSM
To ensure the effectiveness of SLAs in ITSM, consider the following best practices:
· Align with Business Objectives: SLAs must support the organization's goals. They should match the business objectives.
Emphasize refining processes: Periodically reassess and refine service agreements. This will drive service improvement and keep them relevant.
·Monitor Performance: Use metrics and reports to check service levels. Address any deviations from the targets.
· Establish Clear Communication: Keep customers informed about the SLA and any changes.
Document Everything: Keep detailed records of SLA negotiations, agreements, and performance metrics. Also, record any disputes or exceptions. In conclusion, SLAs are vital to IT Service Management. They ensure providers deliver high-quality IT services that meet customers' expectations. Best practices and regular reviews of SLAs can improve services. This will boost customer satisfaction.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, SLAs are key to effective IT Service Management. They ensure providers deliver IT services that meet customer expectations. Organizations can drive service improvement and boost customer satisfaction. They should follow best practices and regularly update SLAs.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In IT Service Management (ITSM), SLAs are key. They define the expectations and responsibilities between service providers and customers. Let's explore SLAs. They are vital for efficient IT service delivery.
What are Service Level Agreements?
Service Level Agreements, or SLAs, are formal agreements. They outline the service levels a provider commits to delivering to its customers. These agreements define key metrics that the provider must meet. They include response times, resolution times, uptime, and performance.
Why are SLAs important in ITSM?
SLAs are essential in ITSM for several reasons:
1. SLAs define what the customer can expect from service levels. They help manage expectations and avoid misunderstandings.
2. Measuring Performance: SLAs set clear metrics and targets. They allow both the provider and customer to measure IT service performance.
3. Improving Service Quality: SLAs set a benchmark for service quality. They drive continuous improvement.
4. SLAs hold service providers accountable for agreed-upon service levels. This helps improve service reliability and customer satisfaction.
5. SLAs are crucial in ITSM. They set clear expectations for service delivery. They ensure both the provider and customer understand the performance standards and responsibilities. They also support accountability and improvement. They do this by setting targets, communication protocols, and dispute resolution methods. They also manage service quality.
6. SLAs are vital in ITSM. They set service expectations and performance metrics. This aligns the goals of the service provider and the customer. It boosts accountability, communication, and service. This raises customer satisfaction and IT reliability.
Components of an SLA
An SLA always has these core elements:
Service descriptions define what the vendor will deliver. Performance metrics quantify the service quality. Problem management outlines the process for issue resolution. Warranties and remediation specify penalties for non-compliance. Termination clauses state the conditions for agreement ending.
· Service Level Targets: Specific, measurable targets that the service provider commits to achieving.
· SLA Metrics: KPIs that measure IT service performance.
· Service Level Reporting: Regular reports on IT service performance vs. targets.
· SLA Enforcement: The process for enforcing the SLA, including penalties for non-compliance.
· SLA Reviews: Periodic reviews to assess and adjust the SLA's effectiveness.
· Monitoring and Reporting:
· Performance Monitoring: It is the tools that check service performance against the SLOs.
· Reporting Schedule: Frequency and format of performance reports provided to the customer.
· Penalties and Remedies:
Service Credits: Compensation to the customer if service levels are not met.
·Penalties: Consequences for failing to meet agreed-upon service levels.
· Review and Revision:
· Review Schedule: Frequency of SLA reviews to ensure they remain relevant and up-to-date.
· Amendment Process: Procedures for making changes to the SLA.
· Dispute Resolution:
· Resolution Mechanisms: Processes for settling disputes between the provider and the customer.
· Term and Termination:
· Contract Duration: Length of time the SLA is in effect.
·Termination Conditions: Conditions under which the SLA or service agreement can be terminated.
· Contact Information:
· Primary Contacts: Key contacts on both sides to manage the SLA.
Best Practices for SLAs in ITSM
To ensure the effectiveness of SLAs in ITSM, consider the following best practices:
· Align with Business Objectives: SLAs must support the organization's goals. They should match the business objectives.
Emphasize refining processes: Periodically reassess and refine service agreements. This will drive service improvement and keep them relevant.
·Monitor Performance: Use metrics and reports to check service levels. Address any deviations from the targets.
· Establish Clear Communication: Keep customers informed about the SLA and any changes.
Document Everything: Keep detailed records of SLA negotiations, agreements, and performance metrics. Also, record any disputes or exceptions. In conclusion, SLAs are vital to IT Service Management. They ensure providers deliver high-quality IT services that meet customers' expectations. Best practices and regular reviews of SLAs can improve services. This will boost customer satisfaction.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, SLAs are key to effective IT Service Management. They ensure providers deliver IT services that meet customer expectations. Organizations can drive service improvement and boost customer satisfaction. They should follow best practices and regularly update SLAs.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Improving ITSM with Process Mining & Automation for Success
Are you looking to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your IT Service Management (ITSM) processes? If so, incorporating process mining and automation techniques can revolutionize the way your IT operations function. In this article, we will explore how these innovative solutions can streamline your IT processes, optimize service delivery, and drive operational excellence in your organization.
\
Leveraging Process Mining for Enhanced Data Analysis
Process mining involves analyzing event logs generated by IT systems to gain insights into the actual execution of business processes. By visualizing and analyzing these logs, organizations can identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and deviations from standard procedures. This data-driven approach enables IT teams to make informed decisions for process improvement and optimization.
With the help of process mining tools, IT departments can track the flow of activities within their IT processes, identify root causes of issues, and pinpoint areas for enhancement. By harnessing the power of data analysis, organizations can achieve a deeper understanding of their workflows and make strategic improvements to drive efficiency and effectiveness.
Automating IT Processes for Enhanced Workflow Management
Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining IT processes and enhancing operational efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, IT teams can free up time and resources to focus on more strategic initiatives. Automation tools can be used to automate routine activities such as incident management, performance monitoring, and service desk operations.
Workflow automation not only reduces the risk of human error but also accelerates the execution of tasks, leading to faster resolution times and improved service quality. With the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, organizations can leverage automation to drive digital transformation and deliver cost-effective solutions.
Benefits of Process Mining and Automation in ITSM
-
Enhanced Data Insights: By combining process mining and automation, organizations can gain valuable insights into their IT workflows and identify areas for improvement.
-
Improved Workflows: Automation streamlines IT processes, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
-
Compliance and Governance: Automation ensures that IT processes adhere to industry regulations and internal governance policies.
-
Continuous Improvement: Process mining and automation facilitate ongoing process enhancements and optimization.
-
Service Efficiency: Automated workflows enable IT teams to deliver services more effectively and efficiently.
By investing in process mining and automation solutions, organizations can unlock a world of possibilities for their IT operations. From optimized IT workflows to streamlined processes and improved service delivery, these innovative technologies offer a blueprint for success in the digital age.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, improving ITSM with process mining and automation is essential for organizations looking to stay competitive in today's fast-paced digital landscape. By leveraging data-driven insights, automating workflows, and embracing innovative technologies, IT departments can achieve operational excellence, drive business efficiency, and deliver superior service quality. It's time to take your IT processes to the next level with process mining and automation.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
Are you looking to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your IT Service Management (ITSM) processes? If so, incorporating process mining and automation techniques can revolutionize the way your IT operations function. In this article, we will explore how these innovative solutions can streamline your IT processes, optimize service delivery, and drive operational excellence in your organization.
\
Leveraging Process Mining for Enhanced Data Analysis
Process mining involves analyzing event logs generated by IT systems to gain insights into the actual execution of business processes. By visualizing and analyzing these logs, organizations can identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and deviations from standard procedures. This data-driven approach enables IT teams to make informed decisions for process improvement and optimization.
With the help of process mining tools, IT departments can track the flow of activities within their IT processes, identify root causes of issues, and pinpoint areas for enhancement. By harnessing the power of data analysis, organizations can achieve a deeper understanding of their workflows and make strategic improvements to drive efficiency and effectiveness.
Automating IT Processes for Enhanced Workflow Management
Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining IT processes and enhancing operational efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, IT teams can free up time and resources to focus on more strategic initiatives. Automation tools can be used to automate routine activities such as incident management, performance monitoring, and service desk operations.
Workflow automation not only reduces the risk of human error but also accelerates the execution of tasks, leading to faster resolution times and improved service quality. With the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, organizations can leverage automation to drive digital transformation and deliver cost-effective solutions.
Benefits of Process Mining and Automation in ITSM
-
Enhanced Data Insights: By combining process mining and automation, organizations can gain valuable insights into their IT workflows and identify areas for improvement.
-
Improved Workflows: Automation streamlines IT processes, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
-
Compliance and Governance: Automation ensures that IT processes adhere to industry regulations and internal governance policies.
-
Continuous Improvement: Process mining and automation facilitate ongoing process enhancements and optimization.
-
Service Efficiency: Automated workflows enable IT teams to deliver services more effectively and efficiently.
By investing in process mining and automation solutions, organizations can unlock a world of possibilities for their IT operations. From optimized IT workflows to streamlined processes and improved service delivery, these innovative technologies offer a blueprint for success in the digital age.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, improving ITSM with process mining and automation is essential for organizations looking to stay competitive in today's fast-paced digital landscape. By leveraging data-driven insights, automating workflows, and embracing innovative technologies, IT departments can achieve operational excellence, drive business efficiency, and deliver superior service quality. It's time to take your IT processes to the next level with process mining and automation.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Exploring the COBIT Framework for IT Governance Mastery.
Do you want to enhance your organization's IT governance and ensure effective risk management and compliance practices? Look no further than the COBIT framework, a widely recognized and trusted set of guidelines designed to help businesses achieve their IT objectives while maintaining a high level of control over their systems and processes.
What is the COBIT Framework?
The COBIT framework, short for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a comprehensive framework developed by ISACA to help organizations align their IT strategies with their business goals. It provides a structured approach to IT governance and helps organizations improve their overall performance by implementing best practices and controls.
COBIT Principles and Concepts
At the core of the COBIT framework are a set of principles that guide organizations in achieving their goals and objectives. These principles include aligning IT with business goals, providing value to the organization, managing risk effectively, and optimizing resource utilization.
Components of the COBIT Framework
The COBIT framework is divided into five key components: principles, processes, organizational structures, culture, and information. These components work together to ensure that IT governance practices are effectively implemented and maintained throughout the organization.
COBIT Governance and Domains
One of the key aspects of the COBIT framework is its focus on governance, which involves defining roles and responsibilities, establishing clear decision-making processes, and ensuring accountability. The framework also includes four domains: planning and organization, acquisition and implementation, delivery and support, and monitoring and evaluation.
COBIT Implementation and Best Practices
Implementing the COBIT framework involves following a set of best practices that are outlined in the framework. These practices include defining and communicating IT roles and responsibilities, establishing clear performance metrics, and regularly monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of IT processes.
COBIT Controls and Benefits
The COBIT framework includes a set of controls that organizations can use to manage their IT processes effectively. These controls help organizations identify and mitigate risks, ensure compliance with regulations, and improve overall performance. By implementing the COBIT framework, organizations can benefit from improved IT governance, enhanced risk management practices, and increased transparency and accountability.
COBIT Certification and Training
For organizations looking to enhance their IT governance practices, COBIT certification and training programs are available. These programs help professionals gain a deeper understanding of the COBIT framework and learn how to implement it effectively within their organizations.
How to obtain COBIT certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the COBIT framework is an invaluable tool for organizations looking to improve their IT governance practices and achieve their business objectives. By following the principles, processes, and best practices outlined in the framework, organizations can enhance their overall performance, manage risks effectively, and ensure compliance with regulations. With its emphasis on governance, control, and risk management, the COBIT framework is a must-have for any organization looking to succeed in today's increasingly digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
Do you want to enhance your organization's IT governance and ensure effective risk management and compliance practices? Look no further than the COBIT framework, a widely recognized and trusted set of guidelines designed to help businesses achieve their IT objectives while maintaining a high level of control over their systems and processes.
What is the COBIT Framework?
The COBIT framework, short for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a comprehensive framework developed by ISACA to help organizations align their IT strategies with their business goals. It provides a structured approach to IT governance and helps organizations improve their overall performance by implementing best practices and controls.
COBIT Principles and Concepts
At the core of the COBIT framework are a set of principles that guide organizations in achieving their goals and objectives. These principles include aligning IT with business goals, providing value to the organization, managing risk effectively, and optimizing resource utilization.
Components of the COBIT Framework
The COBIT framework is divided into five key components: principles, processes, organizational structures, culture, and information. These components work together to ensure that IT governance practices are effectively implemented and maintained throughout the organization.
COBIT Governance and Domains
One of the key aspects of the COBIT framework is its focus on governance, which involves defining roles and responsibilities, establishing clear decision-making processes, and ensuring accountability. The framework also includes four domains: planning and organization, acquisition and implementation, delivery and support, and monitoring and evaluation.
COBIT Implementation and Best Practices
Implementing the COBIT framework involves following a set of best practices that are outlined in the framework. These practices include defining and communicating IT roles and responsibilities, establishing clear performance metrics, and regularly monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of IT processes.
COBIT Controls and Benefits
The COBIT framework includes a set of controls that organizations can use to manage their IT processes effectively. These controls help organizations identify and mitigate risks, ensure compliance with regulations, and improve overall performance. By implementing the COBIT framework, organizations can benefit from improved IT governance, enhanced risk management practices, and increased transparency and accountability.
COBIT Certification and Training
For organizations looking to enhance their IT governance practices, COBIT certification and training programs are available. These programs help professionals gain a deeper understanding of the COBIT framework and learn how to implement it effectively within their organizations.
How to obtain COBIT certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the COBIT framework is an invaluable tool for organizations looking to improve their IT governance practices and achieve their business objectives. By following the principles, processes, and best practices outlined in the framework, organizations can enhance their overall performance, manage risks effectively, and ensure compliance with regulations. With its emphasis on governance, control, and risk management, the COBIT framework is a must-have for any organization looking to succeed in today's increasingly digital world.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
The Impact of Emerging Technologies on IT Service Management
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, the impact of emerging technologies on IT service management cannot be overlooked. With constant advancements in technology trends such as digital transformation, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, cybersecurity, automation, big data, internet of things, data analytics, and more, IT service management professionals must adapt and evolve to meet the demands of the modern IT industry.
Evolution of IT Service Management
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, IT service management has undergone significant transformation. The traditional IT infrastructure is being replaced by innovative tech advancements, leading to the adoption of new and improved IT strategies. Organizations are increasingly leveraging emerging technologies to enhance their IT operations, driving the need for seamless technology integration and efficient change management practices.
Question: How has digital transformation impacted IT service management?
Answer: Digital transformation has revolutionized the way organizations approach IT service management, enabling them to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance overall business performance.
The Role of IT Professionals
With the emergence of new technologies and tech disruptions, IT professionals are faced with a myriad of challenges. From ensuring business continuity to implementing effective IT governance practices, IT professionals must navigate the complexities of the modern IT landscape. This requires a deep understanding of IT best practices, the ability to adapt to evolving technology trends, and a proactive approach to IT risk management.
-
IT Challenges: What challenges do IT professionals face in the era of emerging technologies?
-
IT Trends: How can IT professionals stay ahead of the latest technology trends in IT service management?
-
IT Innovation: What role does innovation play in driving success for IT professionals in the digital age?
Enhancing IT Operations
In order to stay competitive in today's digital economy, organizations must prioritize IT modernization and implement adaptive IT practices. This includes leveraging emerging IT tools, optimizing IT infrastructure, and embracing new software development methodologies. By embracing tech advancements and staying ahead of the curve, organizations can effectively enhance their IT operations and drive business growth.
Benefits of Technology Integration
-
Improved efficiency and productivity
-
Enhanced collaboration and communication
-
Streamlined processes and workflows
Challenges of Change Management
-
Resistance to change from employees
-
Integration issues with legacy systems
-
Training and upskilling requirements for IT professionals
The Future of IT Service Management
As technology continues to evolve, the future of IT service management holds endless possibilities. From AI-driven solutions to advanced cybersecurity measures, the IT industry is constantly innovating to address the diverse needs of organizations worldwide. By staying informed about the latest technology trends and embracing a proactive approach to IT service management, organizations can pave the way for a successful digital future.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of emerging technologies on IT service management is undeniable. To thrive in today's fast-paced digital landscape, IT professionals must continuously adapt, innovate, and evolve in order to meet the demands of the modern IT industry. By prioritizing IT modernization, embracing adaptive IT practices, and staying ahead of the latest technology trends, organizations can position themselves for long-term success in the ever-changing world of IT service management.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, the impact of emerging technologies on IT service management cannot be overlooked. With constant advancements in technology trends such as digital transformation, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, cybersecurity, automation, big data, internet of things, data analytics, and more, IT service management professionals must adapt and evolve to meet the demands of the modern IT industry.
Evolution of IT Service Management
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, IT service management has undergone significant transformation. The traditional IT infrastructure is being replaced by innovative tech advancements, leading to the adoption of new and improved IT strategies. Organizations are increasingly leveraging emerging technologies to enhance their IT operations, driving the need for seamless technology integration and efficient change management practices.
Question: How has digital transformation impacted IT service management?
Answer: Digital transformation has revolutionized the way organizations approach IT service management, enabling them to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance overall business performance.
The Role of IT Professionals
With the emergence of new technologies and tech disruptions, IT professionals are faced with a myriad of challenges. From ensuring business continuity to implementing effective IT governance practices, IT professionals must navigate the complexities of the modern IT landscape. This requires a deep understanding of IT best practices, the ability to adapt to evolving technology trends, and a proactive approach to IT risk management.
-
IT Challenges: What challenges do IT professionals face in the era of emerging technologies?
-
IT Trends: How can IT professionals stay ahead of the latest technology trends in IT service management?
-
IT Innovation: What role does innovation play in driving success for IT professionals in the digital age?
Enhancing IT Operations
In order to stay competitive in today's digital economy, organizations must prioritize IT modernization and implement adaptive IT practices. This includes leveraging emerging IT tools, optimizing IT infrastructure, and embracing new software development methodologies. By embracing tech advancements and staying ahead of the curve, organizations can effectively enhance their IT operations and drive business growth.
Benefits of Technology Integration
-
Improved efficiency and productivity
-
Enhanced collaboration and communication
-
Streamlined processes and workflows
Challenges of Change Management
-
Resistance to change from employees
-
Integration issues with legacy systems
-
Training and upskilling requirements for IT professionals
The Future of IT Service Management
As technology continues to evolve, the future of IT service management holds endless possibilities. From AI-driven solutions to advanced cybersecurity measures, the IT industry is constantly innovating to address the diverse needs of organizations worldwide. By staying informed about the latest technology trends and embracing a proactive approach to IT service management, organizations can pave the way for a successful digital future.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of emerging technologies on IT service management is undeniable. To thrive in today's fast-paced digital landscape, IT professionals must continuously adapt, innovate, and evolve in order to meet the demands of the modern IT industry. By prioritizing IT modernization, embracing adaptive IT practices, and staying ahead of the latest technology trends, organizations can position themselves for long-term success in the ever-changing world of IT service management.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
COBIT 5: Empowering Digital Transformation & IT Governance
In today's fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape, digital transformation is a crucial process that organizations need to undertake to stay competitive and relevant. One framework that can help businesses navigate this complex journey is COBIT® 5.
What is COBIT® 5?
COBIT® 5 is a comprehensive framework developed by ISACA that helps organizations effectively govern and manage their information and technology assets. It provides a set of best practices and guidelines that can be tailored to suit the specific needs of each organization.
Business Process
COBIT® 5 focuses on aligning IT goals with business objectives, ensuring that technology investments contribute to the overall success of the organization. By mapping out business processes and identifying areas for improvement, COBIT® 5 helps streamline operations and drive efficiency.
IT Governance
One of the key aspects of COBIT® 5 is IT governance, which involves setting clear roles and responsibilities, establishing decision-making processes, and ensuring accountability. This helps organizations make informed decisions about their IT investments and initiatives.
Risk Management
Risk management is another critical component of COBIT® 5. By identifying and assessing potential risks, organizations can take proactive measures to mitigate them and protect their assets. This proactive approach helps minimize disruptions and ensures continuity of operations.
Control Objectives
COBIT® 5 provides a set of control objectives that organizations can use to evaluate and monitor their IT processes. These objectives help ensure that technology systems are secure, reliable, and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Enterprise Architecture
COBIT® 5 also emphasizes the importance of building a solid enterprise architecture that supports the organization's strategic objectives. By aligning IT resources with business goals, organizations can drive innovation and create a competitive advantage.
Information Security
Information security is a top priority for organizations in the digital age. COBIT® 5 helps organizations implement robust security measures to protect their data and systems from cyber threats and breaches.
Compliance Requirements
Staying compliant with industry regulations and standards is crucial for organizations operating in highly regulated sectors. COBIT® 5 provides a roadmap for achieving compliance and maintaining a strong governance framework.
The Principles of COBIT® 5
The principles of COBIT® 5 are based on seven key factors that drive successful governance and management of IT assets. These principles include:
-
Aligning IT with business goals
-
Enabling a holistic approach to governance
-
Ensuring end-to-end coverage of IT processes
-
Applying a single integrated framework
-
Enabling a tailored approach to implementation
-
Focusing on organizational goals
-
Separating governance from management
By adhering to these principles, organizations can effectively leverage COBIT® 5 to drive digital transformation and achieve their strategic objectives.
COBIT® 5 Certification and Training
For professionals looking to enhance their knowledge and skills in IT governance and management, COBIT® 5 certification and training programs are available. These programs provide in-depth training on how to implement and leverage COBIT® 5 within an organization, enabling professionals to drive successful digital transformation initiatives.
How to obtain COBIT 5 certification?
We are an education technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5 is a powerful framework that can help organizations navigate the complexities of digital transformation. By implementing COBIT® 5 principles and guidelines, organizations can maximize the value of their IT investments, drive innovation, and ensure long-term success in today's competitive business environment. Embracing COBIT® 5 is not just an option—it's a necessity for organizations looking to thrive in the digital age.
Read More
In today's fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape, digital transformation is a crucial process that organizations need to undertake to stay competitive and relevant. One framework that can help businesses navigate this complex journey is COBIT® 5.
What is COBIT® 5?
COBIT® 5 is a comprehensive framework developed by ISACA that helps organizations effectively govern and manage their information and technology assets. It provides a set of best practices and guidelines that can be tailored to suit the specific needs of each organization.
Business Process
COBIT® 5 focuses on aligning IT goals with business objectives, ensuring that technology investments contribute to the overall success of the organization. By mapping out business processes and identifying areas for improvement, COBIT® 5 helps streamline operations and drive efficiency.
IT Governance
One of the key aspects of COBIT® 5 is IT governance, which involves setting clear roles and responsibilities, establishing decision-making processes, and ensuring accountability. This helps organizations make informed decisions about their IT investments and initiatives.
Risk Management
Risk management is another critical component of COBIT® 5. By identifying and assessing potential risks, organizations can take proactive measures to mitigate them and protect their assets. This proactive approach helps minimize disruptions and ensures continuity of operations.
Control Objectives
COBIT® 5 provides a set of control objectives that organizations can use to evaluate and monitor their IT processes. These objectives help ensure that technology systems are secure, reliable, and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Enterprise Architecture
COBIT® 5 also emphasizes the importance of building a solid enterprise architecture that supports the organization's strategic objectives. By aligning IT resources with business goals, organizations can drive innovation and create a competitive advantage.
Information Security
Information security is a top priority for organizations in the digital age. COBIT® 5 helps organizations implement robust security measures to protect their data and systems from cyber threats and breaches.
Compliance Requirements
Staying compliant with industry regulations and standards is crucial for organizations operating in highly regulated sectors. COBIT® 5 provides a roadmap for achieving compliance and maintaining a strong governance framework.
The Principles of COBIT® 5
The principles of COBIT® 5 are based on seven key factors that drive successful governance and management of IT assets. These principles include:
-
Aligning IT with business goals
-
Enabling a holistic approach to governance
-
Ensuring end-to-end coverage of IT processes
-
Applying a single integrated framework
-
Enabling a tailored approach to implementation
-
Focusing on organizational goals
-
Separating governance from management
By adhering to these principles, organizations can effectively leverage COBIT® 5 to drive digital transformation and achieve their strategic objectives.
COBIT® 5 Certification and Training
For professionals looking to enhance their knowledge and skills in IT governance and management, COBIT® 5 certification and training programs are available. These programs provide in-depth training on how to implement and leverage COBIT® 5 within an organization, enabling professionals to drive successful digital transformation initiatives.
How to obtain COBIT 5 certification?
We are an education technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5 is a powerful framework that can help organizations navigate the complexities of digital transformation. By implementing COBIT® 5 principles and guidelines, organizations can maximize the value of their IT investments, drive innovation, and ensure long-term success in today's competitive business environment. Embracing COBIT® 5 is not just an option—it's a necessity for organizations looking to thrive in the digital age.
Ensure IT Service Continuity for Stronger Infrastructure
In today's fast-paced digital world, IT service continuity management plays a crucial role in ensuring the protection and resilience of your organization's infrastructure. With the increasing reliance on technology for day-to-day operations, it is essential to have robust processes in place to prevent service interruptions and safeguard critical data and systems. Let's explore how you can effectively implement IT service continuity management to protect your infrastructure and ensure business continuity.
Importance of Infrastructure Protection in IT Service Management
IT service management encompasses various processes and practices aimed at delivering and supporting IT services to meet the needs of the organization. One of the key components of IT service management is continuity planning, which focuses on maintaining service availability and resilience in the face of disruptions. By implementing effective continuity planning, organizations can mitigate risks associated with service interruptions and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Data Protection and Disaster Recovery in IT Service Continuity Management
Data protection is a critical aspect of IT service continuity management, as it involves safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring its availability in case of data loss or corruption. Disaster recovery plans are essential for restoring IT systems and services in the event of a disaster or outage. By implementing robust data protection and disaster recovery measures, organizations can minimize downtime and mitigate the impact of potential disruptions on their operations.
Business Continuity and IT Infrastructure Security
Business continuity planning focuses on maintaining overall operational resilience and ensuring the continuity of critical business functions during unforeseen events. IT infrastructure security plays a vital role in protecting IT assets and preventing unauthorized access or data breaches. By integrating business continuity and IT infrastructure security measures, organizations can enhance their overall resilience and responsiveness to disruptions.
Implementing Service Continuity Framework and Incident Response
A comprehensive service continuity framework includes policies, procedures, and processes that support the organization's ability to maintain service availability and respond effectively to incidents. Incident response plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach, outage, or other disruptions. By proactively implementing a service continuity framework and incident response plans, organizations can minimize the impact of incidents on their operations and accelerate the recovery process.
Protecting IT Systems and Preventing Service Interruptions
Effective IT service continuity management involves implementing measures to protect IT systems from potential threats and vulnerabilities. By conducting regular infrastructure maintenance, organizations can enhance the stability and performance of their IT environment. Additionally, implementing robust security measures and continuity procedures can help prevent service interruptions and ensure the timely restoration of services in case of disruptions.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, ensuring IT service continuity management protects your infrastructure is essential for maintaining the resilience and reliability of your organization's IT operations. By implementing proactive measures to protect data, prevent service interruptions, and respond to incidents effectively, organizations can minimize downtime and ensure business continuity. With a holistic approach to IT service continuity management, organizations can enhance their infrastructure's security, reliability, and resilience in the face of potential risks and disruptions.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, IT service continuity management plays a crucial role in ensuring the protection and resilience of your organization's infrastructure. With the increasing reliance on technology for day-to-day operations, it is essential to have robust processes in place to prevent service interruptions and safeguard critical data and systems. Let's explore how you can effectively implement IT service continuity management to protect your infrastructure and ensure business continuity.
Importance of Infrastructure Protection in IT Service Management
IT service management encompasses various processes and practices aimed at delivering and supporting IT services to meet the needs of the organization. One of the key components of IT service management is continuity planning, which focuses on maintaining service availability and resilience in the face of disruptions. By implementing effective continuity planning, organizations can mitigate risks associated with service interruptions and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Data Protection and Disaster Recovery in IT Service Continuity Management
Data protection is a critical aspect of IT service continuity management, as it involves safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring its availability in case of data loss or corruption. Disaster recovery plans are essential for restoring IT systems and services in the event of a disaster or outage. By implementing robust data protection and disaster recovery measures, organizations can minimize downtime and mitigate the impact of potential disruptions on their operations.
Business Continuity and IT Infrastructure Security
Business continuity planning focuses on maintaining overall operational resilience and ensuring the continuity of critical business functions during unforeseen events. IT infrastructure security plays a vital role in protecting IT assets and preventing unauthorized access or data breaches. By integrating business continuity and IT infrastructure security measures, organizations can enhance their overall resilience and responsiveness to disruptions.
Implementing Service Continuity Framework and Incident Response
A comprehensive service continuity framework includes policies, procedures, and processes that support the organization's ability to maintain service availability and respond effectively to incidents. Incident response plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach, outage, or other disruptions. By proactively implementing a service continuity framework and incident response plans, organizations can minimize the impact of incidents on their operations and accelerate the recovery process.
Protecting IT Systems and Preventing Service Interruptions
Effective IT service continuity management involves implementing measures to protect IT systems from potential threats and vulnerabilities. By conducting regular infrastructure maintenance, organizations can enhance the stability and performance of their IT environment. Additionally, implementing robust security measures and continuity procedures can help prevent service interruptions and ensure the timely restoration of services in case of disruptions.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, ensuring IT service continuity management protects your infrastructure is essential for maintaining the resilience and reliability of your organization's IT operations. By implementing proactive measures to protect data, prevent service interruptions, and respond to incidents effectively, organizations can minimize downtime and ensure business continuity. With a holistic approach to IT service continuity management, organizations can enhance their infrastructure's security, reliability, and resilience in the face of potential risks and disruptions.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
A Complete Guide to Becoming a Successful Systems Analyst
Are you interested in pursuing a career in the fast-paced and dynamic field of information technology (IT)? Have you considered becoming a systems analyst? If you have a knack for problem-solving, a passion for technology, and excellent analytical skills, then this might be the perfect career path for you.
What is a Systems Analyst?
A systems analyst is responsible for analyzing, designing, implementing, and maintaining computer systems to meet the needs of an organization. They work closely with business stakeholders to understand their requirements and translate them into technical solutions. Systems analysts play a crucial role in ensuring that IT systems align with business goals and objectives.
Skills and Qualifications
To become a successful systems analyst, you will need a combination of technical skills, soft skills, and education. Some of the key skills and qualifications required for this role include:
-
Strong problem-solving skills
-
Excellent communication skills
-
Analytical thinking
-
Knowledge of technology and computer systems
-
Experience in business analysis
-
Familiarity with software development and programming
-
Project management skills
-
Critical thinking
-
Ability to work independently and in a team
-
Attention to detail
-
Strong documentation and workflow analysis skills
Job Role and Responsibilities
As a systems analyst, your main responsibilities will include:
-
Process Analysis: Analyzing and understanding existing business processes to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
-
System Design: Designing IT solutions to meet the needs of the organization, taking into account technical requirements and business objectives.
-
Data Modeling: Creating data models to ensure that the system meets the data management requirements of the organization.
-
Problem-Solving: Troubleshooting and resolving issues with computer systems and applications.
-
Communication: Collaborating with stakeholders to gather requirements, provide updates on projects, and offer support.
-
Technology: Staying up-to-date with the latest technology trends and tools to ensure the development of innovative solutions.
Education and Certifications
While a bachelor's degree in information technology, computer science, or a related field is typically required for a systems analyst role, some employers may prefer candidates with a master's degree or relevant certifications. Popular certifications for systems analysts include:
-
Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP)
-
CompTIA IT Fundamentals (ITF+)
-
Project Management Professional (PMP)
-
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Career Path and Development
The career path for a systems analyst typically starts with entry-level roles such as IT support or business analyst, with opportunities to specialize in areas such as data analysis, cybersecurity, or project management. As you gain experience and expertise in the field, you may progress to roles such as senior systems analyst, IT manager, or chief technology officer.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, becoming a systems analyst can be a rewarding and fulfilling career choice for individuals with a passion for technology and problem-solving. By developing the necessary skills, qualifications, and experience, you can embark on a successful career in the IT industry and make a significant impact on the organizations you work for. So, are you ready to take the first step towards becoming a systems analyst?.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
Are you interested in pursuing a career in the fast-paced and dynamic field of information technology (IT)? Have you considered becoming a systems analyst? If you have a knack for problem-solving, a passion for technology, and excellent analytical skills, then this might be the perfect career path for you.
What is a Systems Analyst?
A systems analyst is responsible for analyzing, designing, implementing, and maintaining computer systems to meet the needs of an organization. They work closely with business stakeholders to understand their requirements and translate them into technical solutions. Systems analysts play a crucial role in ensuring that IT systems align with business goals and objectives.
Skills and Qualifications
To become a successful systems analyst, you will need a combination of technical skills, soft skills, and education. Some of the key skills and qualifications required for this role include:
-
Strong problem-solving skills
-
Excellent communication skills
-
Analytical thinking
-
Knowledge of technology and computer systems
-
Experience in business analysis
-
Familiarity with software development and programming
-
Project management skills
-
Critical thinking
-
Ability to work independently and in a team
-
Attention to detail
-
Strong documentation and workflow analysis skills
Job Role and Responsibilities
As a systems analyst, your main responsibilities will include:
-
Process Analysis: Analyzing and understanding existing business processes to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
-
System Design: Designing IT solutions to meet the needs of the organization, taking into account technical requirements and business objectives.
-
Data Modeling: Creating data models to ensure that the system meets the data management requirements of the organization.
-
Problem-Solving: Troubleshooting and resolving issues with computer systems and applications.
-
Communication: Collaborating with stakeholders to gather requirements, provide updates on projects, and offer support.
-
Technology: Staying up-to-date with the latest technology trends and tools to ensure the development of innovative solutions.
Education and Certifications
While a bachelor's degree in information technology, computer science, or a related field is typically required for a systems analyst role, some employers may prefer candidates with a master's degree or relevant certifications. Popular certifications for systems analysts include:
-
Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP)
-
CompTIA IT Fundamentals (ITF+)
-
Project Management Professional (PMP)
-
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Career Path and Development
The career path for a systems analyst typically starts with entry-level roles such as IT support or business analyst, with opportunities to specialize in areas such as data analysis, cybersecurity, or project management. As you gain experience and expertise in the field, you may progress to roles such as senior systems analyst, IT manager, or chief technology officer.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, becoming a systems analyst can be a rewarding and fulfilling career choice for individuals with a passion for technology and problem-solving. By developing the necessary skills, qualifications, and experience, you can embark on a successful career in the IT industry and make a significant impact on the organizations you work for. So, are you ready to take the first step towards becoming a systems analyst?.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit :www.icertglobal.comEmail : info@icertglobal.com
IT Service Management Tools to Use in 2024 for Efficiency
Are you looking for the best IT service management tools that will help your business stay ahead in 2024? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the leading IT service management tools that are shaping the future of IT solutions and services.
Introduction to IT Service Management Tools
IT service management tools are crucial for businesses to effectively manage their IT infrastructure, processes, and operations. These tools help streamline IT services, enhance operational efficiency, and improve overall productivity. With the rapid advancement in technology, it is essential for businesses to leverage the latest IT service management tools to stay competitive in the market.
Best IT Tools for 2024
-
ServiceNow: ServiceNow is a cloud-based IT service management software that offers a comprehensive suite of IT solutions. It provides advanced IT services including IT asset management, IT operations management, and IT governance. With ServiceNow, businesses can enhance their IT service delivery and improve customer satisfaction.
-
BMC Helix: BMC Helix is a top IT management tool that offers innovative IT solutions for businesses. It provides cutting-edge IT services such as predictive analytics, IT automation, and AI-driven IT operations. BMC Helix helps businesses achieve digital transformation and drive operational excellence.
-
Zendesk: Zendesk is a leading IT service desk software that helps businesses streamline their IT support services. It offers remote IT tools, IT asset management, and scalable IT solutions. Zendesk is known for its user-friendly interface and exceptional customer support.
-
Splunk: Splunk is a powerful IT monitoring tool that provides real-time visibility into IT infrastructure and operations. It offers advanced features such as artificial intelligence in IT, predictive analytics, and IT automation. Splunk helps businesses proactively manage IT incidents and ensure optimal performance.
Emerging IT Tools for the Future
As we look towards the future of IT service management, there are several emerging IT tools that are set to revolutionize the industry. These tools focus on enhancing IT service delivery, improving IT processes, and driving digital transformation. Some of the key emerging IT tools include:
-
AI-powered IT automation tools
-
Cloud-based IT infrastructure solutions
-
Predictive analytics tools for IT operations
-
Cybersecurity tools for advanced threat detection
-
IT governance tools for compliance management
With these innovative IT solutions, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and adapt to the ever-changing IT landscape. By leveraging the latest IT tools, businesses can improve operational efficiency, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the leading IT service management tools of 2024 offer a wide range of advanced features and capabilities that can help businesses thrive in the digital age. From cloud-based IT tools to AI-driven solutions, these tools are shaping the future of IT service delivery. By investing in the right IT tools, businesses can stay competitive, drive innovation, and achieve success in a rapidly evolving IT environment. Embrace the future of IT service management with the best tools available in 2024.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
Are you looking for the best IT service management tools that will help your business stay ahead in 2024? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the leading IT service management tools that are shaping the future of IT solutions and services.
Introduction to IT Service Management Tools
IT service management tools are crucial for businesses to effectively manage their IT infrastructure, processes, and operations. These tools help streamline IT services, enhance operational efficiency, and improve overall productivity. With the rapid advancement in technology, it is essential for businesses to leverage the latest IT service management tools to stay competitive in the market.
Best IT Tools for 2024
-
ServiceNow: ServiceNow is a cloud-based IT service management software that offers a comprehensive suite of IT solutions. It provides advanced IT services including IT asset management, IT operations management, and IT governance. With ServiceNow, businesses can enhance their IT service delivery and improve customer satisfaction.
-
BMC Helix: BMC Helix is a top IT management tool that offers innovative IT solutions for businesses. It provides cutting-edge IT services such as predictive analytics, IT automation, and AI-driven IT operations. BMC Helix helps businesses achieve digital transformation and drive operational excellence.
-
Zendesk: Zendesk is a leading IT service desk software that helps businesses streamline their IT support services. It offers remote IT tools, IT asset management, and scalable IT solutions. Zendesk is known for its user-friendly interface and exceptional customer support.
-
Splunk: Splunk is a powerful IT monitoring tool that provides real-time visibility into IT infrastructure and operations. It offers advanced features such as artificial intelligence in IT, predictive analytics, and IT automation. Splunk helps businesses proactively manage IT incidents and ensure optimal performance.
Emerging IT Tools for the Future
As we look towards the future of IT service management, there are several emerging IT tools that are set to revolutionize the industry. These tools focus on enhancing IT service delivery, improving IT processes, and driving digital transformation. Some of the key emerging IT tools include:
-
AI-powered IT automation tools
-
Cloud-based IT infrastructure solutions
-
Predictive analytics tools for IT operations
-
Cybersecurity tools for advanced threat detection
-
IT governance tools for compliance management
With these innovative IT solutions, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and adapt to the ever-changing IT landscape. By leveraging the latest IT tools, businesses can improve operational efficiency, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the leading IT service management tools of 2024 offer a wide range of advanced features and capabilities that can help businesses thrive in the digital age. From cloud-based IT tools to AI-driven solutions, these tools are shaping the future of IT service delivery. By investing in the right IT tools, businesses can stay competitive, drive innovation, and achieve success in a rapidly evolving IT environment. Embrace the future of IT service management with the best tools available in 2024.
Contact Us For More Information:
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
ITSM and DevOps: Bridging the Gap for Better Collaboration
In today's fast-paced world of technology and information, the collaboration between ITSM (IT Service Management) and DevOps is crucial for success. By bridging the gap between these two key areas, organizations can improve efficiency, communication, and innovation in their IT operations. In this article, we will explore how ITSM and DevOps can work together to create a culture of collaboration and drive continuous improvement.
ITSM and DevOps: A Winning Combination
For many years, ITSM and DevOps have been viewed as separate entities within organizations. ITSM focuses on the delivery of quality IT services, while DevOps is centered around the rapid and continuous delivery of software. However, by integrating these two approaches, organizations can achieve greater alignment, efficiency, and innovation.
Why is Collaboration Important?
Collaboration between ITSM and DevOps is essential for ensuring that IT operations run smoothly and effectively. By working together, teams can streamline processes, improve workflows, and enhance overall productivity. Additionally, collaboration can help organizations respond more quickly to changing business needs and market demands.
Bridging the Gap: How to Foster Collaboration
To bridge the gap between ITSM and DevOps, organizations must focus on building a culture of teamwork and communication. This can be achieved by:
-
Implementing Agile Practices: Agile methodologies can help teams work together more effectively by promoting flexibility, adaptability, and transparency.
-
Embracing Automation: Automation tools can streamline processes and eliminate manual tasks, allowing teams to focus on higher-value work.
-
Encouraging Open Communication: Regular communication between ITSM and DevOps teams is crucial for sharing information, resolving issues, and aligning priorities.
-
Investing in Training and Development: Training programs can help team members develop new skills, stay up-to-date on the latest technologies, and foster a culture of continuous learning.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can create a collaborative environment where ITSM and DevOps teams can work together seamlessly to drive innovation and deliver value to the business.
Improving Efficiency and Performance
When ITSM and DevOps collaborate effectively, organizations can achieve significant improvements in efficiency and performance. By aligning processes, tools, and practices, teams can work more cohesively and deliver results faster. This leads to greater customer satisfaction, increased agility, and reduced time-to-market for new products and services.
Aligning Culture and Strategy
Collaboration between ITSM and DevOps also requires a shift in culture and strategy. Organizations must prioritize collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement to succeed in today's competitive landscape. By fostering a culture of teamwork, trust, and experimentation, teams can drive positive change and achieve better results.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, bridging the gap between ITSM and DevOps is essential for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of technology, information, and innovation. By fostering collaboration, improving communication, and aligning processes, organizations can create a culture of teamwork and drive continuous improvement in their IT operations. It is time for organizations to embrace the power of collaboration between ITSM and DevOps and unlock the full potential of their technology investments.
Contact Us For More Information
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Read More
In today's fast-paced world of technology and information, the collaboration between ITSM (IT Service Management) and DevOps is crucial for success. By bridging the gap between these two key areas, organizations can improve efficiency, communication, and innovation in their IT operations. In this article, we will explore how ITSM and DevOps can work together to create a culture of collaboration and drive continuous improvement.
ITSM and DevOps: A Winning Combination
For many years, ITSM and DevOps have been viewed as separate entities within organizations. ITSM focuses on the delivery of quality IT services, while DevOps is centered around the rapid and continuous delivery of software. However, by integrating these two approaches, organizations can achieve greater alignment, efficiency, and innovation.
Why is Collaboration Important?
Collaboration between ITSM and DevOps is essential for ensuring that IT operations run smoothly and effectively. By working together, teams can streamline processes, improve workflows, and enhance overall productivity. Additionally, collaboration can help organizations respond more quickly to changing business needs and market demands.
Bridging the Gap: How to Foster Collaboration
To bridge the gap between ITSM and DevOps, organizations must focus on building a culture of teamwork and communication. This can be achieved by:
-
Implementing Agile Practices: Agile methodologies can help teams work together more effectively by promoting flexibility, adaptability, and transparency.
-
Embracing Automation: Automation tools can streamline processes and eliminate manual tasks, allowing teams to focus on higher-value work.
-
Encouraging Open Communication: Regular communication between ITSM and DevOps teams is crucial for sharing information, resolving issues, and aligning priorities.
-
Investing in Training and Development: Training programs can help team members develop new skills, stay up-to-date on the latest technologies, and foster a culture of continuous learning.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can create a collaborative environment where ITSM and DevOps teams can work together seamlessly to drive innovation and deliver value to the business.
Improving Efficiency and Performance
When ITSM and DevOps collaborate effectively, organizations can achieve significant improvements in efficiency and performance. By aligning processes, tools, and practices, teams can work more cohesively and deliver results faster. This leads to greater customer satisfaction, increased agility, and reduced time-to-market for new products and services.
Aligning Culture and Strategy
Collaboration between ITSM and DevOps also requires a shift in culture and strategy. Organizations must prioritize collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement to succeed in today's competitive landscape. By fostering a culture of teamwork, trust, and experimentation, teams can drive positive change and achieve better results.
How to obtain ITSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php and https://www.icertglobal.com/index.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, bridging the gap between ITSM and DevOps is essential for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of technology, information, and innovation. By fostering collaboration, improving communication, and aligning processes, organizations can create a culture of teamwork and drive continuous improvement in their IT operations. It is time for organizations to embrace the power of collaboration between ITSM and DevOps and unlock the full potential of their technology investments.
Contact Us For More Information
Visit : www.icertglobal.com Email : info@icertglobal.com
Secure Your Business: Proven IT Risk Management Tactics
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses of all sizes face a multitude of IT risks that can pose significant threats to their operations, finances, and reputation. From cyber attract and data breaches to hardware failures and natural disasters, the potential risks are diverse and ever-present. To safeguard your business and ensure a secure future, it is essential to implement robust IT risk management strategies. In this article, we will explore proven tactics for mitigating IT risks and protecting your business from potential vulnerabilities.
Understanding IT Risk Management
IT risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks related to the use of information technology within an organization. By taking proactive steps to identify and address potential threats, businesses can minimize the impact of IT-related incidents and ensure continuity of operations. Effective IT risk management involves a combination of policies, procedures, technologies, and employee training to create a secure and resilient IT environment.
Assessing IT Risks
The first step in effective IT risk management is to conduct a comprehensive assessment of potential risks facing your business. This involves identifying all possible threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts on your organization. By understanding the specific risks you face, you can prioritize your efforts and allocate resources effectively to address the most critical areas of concern.
What are the key benefits of conducting an IT risk assessment?
A thorough IT risk assessment can help you identify vulnerabilities in your systems, prioritize remediation efforts, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
How can businesses conduct an IT risk assessment?
Businesses can conduct an IT risk assessment by using a combination of automated tools, manual inspections, vulnerability scans, and risk analysis techniques.
Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once you have identified and assessed the IT risks facing your business, the next step is to implement mitigation strategies to address these vulnerabilities. This may involve implementing security controls, updating software and hardware, and establishing backup and recovery processes to minimize the impact of potential incidents.
What are some effective risk mitigation strategies for businesses?
Some effective risk mitigation strategies include implementing robust access controls, encrypting sensitive data, conducting regular security audits, and providing ongoing staff training on cyber security best practices.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Effective IT risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance and monitoring to ensure the security and resilience of your IT systems. By regularly monitoring for potential risks, implementing updates and patches, and conducting regular security assessments, businesses can adapt to evolving threats and maintain a strong security posture.
How can businesses ensure continuous improvement in their IT risk management practices?
Businesses can ensure continuous improvement by staying informed about the latest cyber security trends, investing in advanced security technologies, and conducting regular reviews of their IT risk management policies and procedures.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governace Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Protecting your business from IT risks requires a proactive and comprehensive approach to risk management. By understanding the specific risks facing your organization, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and continuously monitoring for potential threats, you can shield your business from harm and ensure a secure future.
Read More
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses of all sizes face a multitude of IT risks that can pose significant threats to their operations, finances, and reputation. From cyber attract and data breaches to hardware failures and natural disasters, the potential risks are diverse and ever-present. To safeguard your business and ensure a secure future, it is essential to implement robust IT risk management strategies. In this article, we will explore proven tactics for mitigating IT risks and protecting your business from potential vulnerabilities.
Understanding IT Risk Management
IT risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks related to the use of information technology within an organization. By taking proactive steps to identify and address potential threats, businesses can minimize the impact of IT-related incidents and ensure continuity of operations. Effective IT risk management involves a combination of policies, procedures, technologies, and employee training to create a secure and resilient IT environment.
Assessing IT Risks
The first step in effective IT risk management is to conduct a comprehensive assessment of potential risks facing your business. This involves identifying all possible threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts on your organization. By understanding the specific risks you face, you can prioritize your efforts and allocate resources effectively to address the most critical areas of concern.
What are the key benefits of conducting an IT risk assessment?
A thorough IT risk assessment can help you identify vulnerabilities in your systems, prioritize remediation efforts, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
How can businesses conduct an IT risk assessment?
Businesses can conduct an IT risk assessment by using a combination of automated tools, manual inspections, vulnerability scans, and risk analysis techniques.
Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once you have identified and assessed the IT risks facing your business, the next step is to implement mitigation strategies to address these vulnerabilities. This may involve implementing security controls, updating software and hardware, and establishing backup and recovery processes to minimize the impact of potential incidents.
What are some effective risk mitigation strategies for businesses?
Some effective risk mitigation strategies include implementing robust access controls, encrypting sensitive data, conducting regular security audits, and providing ongoing staff training on cyber security best practices.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Effective IT risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance and monitoring to ensure the security and resilience of your IT systems. By regularly monitoring for potential risks, implementing updates and patches, and conducting regular security assessments, businesses can adapt to evolving threats and maintain a strong security posture.
How can businesses ensure continuous improvement in their IT risk management practices?
Businesses can ensure continuous improvement by staying informed about the latest cyber security trends, investing in advanced security technologies, and conducting regular reviews of their IT risk management policies and procedures.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governace Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Protecting your business from IT risks requires a proactive and comprehensive approach to risk management. By understanding the specific risks facing your organization, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and continuously monitoring for potential threats, you can shield your business from harm and ensure a secure future.
IT Governance Frameworks: An Essential Guide for Beginners
In today's fast-paced digital world, it is more important than ever for organizations to have a solid IT governance framework in place. Navigating the complex digital landscape can be overwhelming for beginners, but with the right guidance and knowledge, you can successfully implement an effective IT governance framework to protect your organization from potential cyber threats and ensure compliance with regulations.
Understanding IT Governance Frameworks
IT governance frameworks are essentially a set of guidelines and practices that organizations follow to ensure that their IT systems and processes are aligned with business objectives. These frameworks help organizations make informed decisions regarding technology strategy, cybersecurity policies, compliance, risk management, data protection, information technology controls, and best practices.
Why is IT Governance Important for Beginners?
As a beginner in the digital landscape, it is crucial to understand the importance of IT governance. Without a proper framework in place, organizations are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, data breaches, and other IT-related risks. By implementing an IT governance framework, beginners can ensure that their organization's IT systems are secure, compliant, and aligned with business goals.
Key Components of IT Governance Frameworks
-
Regulations: IT governance frameworks help organizations comply with industry regulations and standards to avoid legal consequences.
-
Framework Implementation: Beginners can use frameworks such as COBIT, ITIL, or NIST to implement IT governance best practices.
-
Audit Trails: Keeping detailed audit trails helps organizations track changes and monitor system activities effectively.
-
Guidelines and Procedures: Following established guidelines and procedures ensures consistency and efficiency in IT operations.
-
Software, Hardware, Network Security: Implementing robust security measures across software, hardware, and networks is essential for protecting sensitive data.
-
Incident Response: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place can help organizations mitigate the impact of cybersecurity incidents.
-
Training and Documentation: Training employees on IT governance practices and documenting processes are critical for successful framework implementation.
Choosing the Right Governance Structure
There are various governance models and practices to choose from, depending on the organization's size, industry, and specific needs. Beginners should carefully assess different governance standards before selecting a framework that best suits their organization.
Common Governance Models
-
Centralized Governance: In this model, decision-making authority is centralized, allowing for consistency and control over IT operations.
-
Decentralized Governance: Decentralized governance allows individual departments to make decisions based on their specific requirements.
-
Hybrid Governance: A combination of centralized and decentralized governance models can offer flexibility and efficiency in IT management.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Navigating the digital landscape as a beginner can be challenging, but with a solid IT governance framework in place, you can effectively manage risks, ensure compliance, and align technology with business objectives. By following best practices, implementing robust security measures, and choosing the right governance structure, beginners can successfully navigate the complex world of IT governance.
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, it is more important than ever for organizations to have a solid IT governance framework in place. Navigating the complex digital landscape can be overwhelming for beginners, but with the right guidance and knowledge, you can successfully implement an effective IT governance framework to protect your organization from potential cyber threats and ensure compliance with regulations.
Understanding IT Governance Frameworks
IT governance frameworks are essentially a set of guidelines and practices that organizations follow to ensure that their IT systems and processes are aligned with business objectives. These frameworks help organizations make informed decisions regarding technology strategy, cybersecurity policies, compliance, risk management, data protection, information technology controls, and best practices.
Why is IT Governance Important for Beginners?
As a beginner in the digital landscape, it is crucial to understand the importance of IT governance. Without a proper framework in place, organizations are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, data breaches, and other IT-related risks. By implementing an IT governance framework, beginners can ensure that their organization's IT systems are secure, compliant, and aligned with business goals.
Key Components of IT Governance Frameworks
-
Regulations: IT governance frameworks help organizations comply with industry regulations and standards to avoid legal consequences.
-
Framework Implementation: Beginners can use frameworks such as COBIT, ITIL, or NIST to implement IT governance best practices.
-
Audit Trails: Keeping detailed audit trails helps organizations track changes and monitor system activities effectively.
-
Guidelines and Procedures: Following established guidelines and procedures ensures consistency and efficiency in IT operations.
-
Software, Hardware, Network Security: Implementing robust security measures across software, hardware, and networks is essential for protecting sensitive data.
-
Incident Response: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place can help organizations mitigate the impact of cybersecurity incidents.
-
Training and Documentation: Training employees on IT governance practices and documenting processes are critical for successful framework implementation.
Choosing the Right Governance Structure
There are various governance models and practices to choose from, depending on the organization's size, industry, and specific needs. Beginners should carefully assess different governance standards before selecting a framework that best suits their organization.
Common Governance Models
-
Centralized Governance: In this model, decision-making authority is centralized, allowing for consistency and control over IT operations.
-
Decentralized Governance: Decentralized governance allows individual departments to make decisions based on their specific requirements.
-
Hybrid Governance: A combination of centralized and decentralized governance models can offer flexibility and efficiency in IT management.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Navigating the digital landscape as a beginner can be challenging, but with a solid IT governance framework in place, you can effectively manage risks, ensure compliance, and align technology with business objectives. By following best practices, implementing robust security measures, and choosing the right governance structure, beginners can successfully navigate the complex world of IT governance.
IT Project Management: Choosing the Optimal Method for Teams
In the world of information technology, project management methodologies play a crucial role in ensuring the successful completion of projects. From Agile to Waterfall to Hybrid approaches, choosing the right methodology can greatly impact the outcome of your IT projects. In this article, we will explore the different IT project management methodologies available and how you can determine which one is best suited for your team.
What are IT Project Management Methodologies?
IT project management methodologies are frameworks that guide the planning, execution, and monitoring of IT projects. These methodologies provide structure and guidelines for how projects should be managed from start to finish. By following a defined methodology, project managers can ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet the desired quality standards.
Agile Methodology
Agile is a popular iterative approach to project management that emphasizes flexibility and adaptability. In Agile methodology, projects are broken down into smaller, manageable tasks known as sprints. Teams work collaboratively, responding to changes and feedback quickly throughout the project. Agile is ideal for projects where requirements are likely to change or evolve over time.
Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall is a more traditional project management approach that follows a linear, sequential process. In this methodology, each phase of the project must be completed before moving on to the next phase. Waterfall is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and a clear scope. While it may lack the flexibility of Agile, Waterfall can be effective for projects where change is minimal.
Hybrid Methodology
Hybrid methodology combines elements of both Agile and Waterfall approaches. This flexible approach allows teams to tailor the project management process to meet the specific needs of the project. For example, teams may choose to use Agile for certain phases of the project and then switch to a more Waterfall-like approach for other phases. Hybrid methodology is ideal for teams that require a mix of flexibility and structure.
How to Choose the Right Methodology for Your Team
When selecting an IT project management methodology for your team, it's essential to consider factors such as the project's scope, requirements, and team dynamics. Here are some tips to help you choose the right methodology:
-
Assess Your Project: Evaluate the size, complexity, and uncertainty of your project to determine which methodology aligns best with your needs.
-
Understand Your Team: Consider your team's experience, skills, and working style to ensure that the chosen methodology is a good fit.
-
Client Requirements: Take into account any specific requirements or preferences of your clients or stakeholders when deciding on a methodology.
-
Iterate and Adapt: Don't be afraid to experiment with different methodologies and adapt them to better suit your team and project needs.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the IT project management methodology that will set your team up for success.
How to obtain IT Service Mangement & Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Choosing the right IT project management methodology is crucial for the success of your projects. Whether you opt for Agile, Waterfall, Hybrid, or another approach altogether, selecting the methodology that aligns best with your team's needs and project requirements is key. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can confidently navigate the world of IT project management and lead your team to project success.
Read More
In the world of information technology, project management methodologies play a crucial role in ensuring the successful completion of projects. From Agile to Waterfall to Hybrid approaches, choosing the right methodology can greatly impact the outcome of your IT projects. In this article, we will explore the different IT project management methodologies available and how you can determine which one is best suited for your team.
What are IT Project Management Methodologies?
IT project management methodologies are frameworks that guide the planning, execution, and monitoring of IT projects. These methodologies provide structure and guidelines for how projects should be managed from start to finish. By following a defined methodology, project managers can ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet the desired quality standards.
Agile Methodology
Agile is a popular iterative approach to project management that emphasizes flexibility and adaptability. In Agile methodology, projects are broken down into smaller, manageable tasks known as sprints. Teams work collaboratively, responding to changes and feedback quickly throughout the project. Agile is ideal for projects where requirements are likely to change or evolve over time.
Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall is a more traditional project management approach that follows a linear, sequential process. In this methodology, each phase of the project must be completed before moving on to the next phase. Waterfall is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and a clear scope. While it may lack the flexibility of Agile, Waterfall can be effective for projects where change is minimal.
Hybrid Methodology
Hybrid methodology combines elements of both Agile and Waterfall approaches. This flexible approach allows teams to tailor the project management process to meet the specific needs of the project. For example, teams may choose to use Agile for certain phases of the project and then switch to a more Waterfall-like approach for other phases. Hybrid methodology is ideal for teams that require a mix of flexibility and structure.
How to Choose the Right Methodology for Your Team
When selecting an IT project management methodology for your team, it's essential to consider factors such as the project's scope, requirements, and team dynamics. Here are some tips to help you choose the right methodology:
-
Assess Your Project: Evaluate the size, complexity, and uncertainty of your project to determine which methodology aligns best with your needs.
-
Understand Your Team: Consider your team's experience, skills, and working style to ensure that the chosen methodology is a good fit.
-
Client Requirements: Take into account any specific requirements or preferences of your clients or stakeholders when deciding on a methodology.
-
Iterate and Adapt: Don't be afraid to experiment with different methodologies and adapt them to better suit your team and project needs.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the IT project management methodology that will set your team up for success.
How to obtain IT Service Mangement & Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Choosing the right IT project management methodology is crucial for the success of your projects. Whether you opt for Agile, Waterfall, Hybrid, or another approach altogether, selecting the methodology that aligns best with your team's needs and project requirements is key. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can confidently navigate the world of IT project management and lead your team to project success.
The Role of Automation in IT Service Management:Key Benefits
Are you looking to streamline your IT service management processes and improve overall efficiency? Look no further than automation! Automation plays a crucial role in IT service management, offering a wide range of benefits and opportunities for organizations looking to optimize their operations. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of automation in IT service management, including its implementation, challenges, best practices, and future developments.
What is Automation in IT Service Management?
Automation in IT service management refers to the use of technology to perform manual tasks, processes, and workflows automatically. This can include automating routine tasks such as incident management, problem resolution, change management, and asset management. By leveraging automation tools and technologies, organizations can reduce human error, improve productivity, and enhance the overall quality of IT services.
Benefits of Automation in IT Service Management
-
Improved efficiency and productivity: By automating repetitive tasks, IT teams can focus on more strategic initiatives and projects.
-
Enhanced accuracy: Automation reduces the risk of human error, leading to higher data accuracy and consistency.
-
Faster response times: Automated workflows can respond to incidents and requests in real-time, leading to quicker resolution times.
-
Cost savings: Automation helps reduce operational costs by minimizing the need for manual intervention and streamlining processes.
-
Better scalability: With automation, IT service management processes can easily scale to support growing business needs and requirements.
Automation Tools in IT Service Management
Several automation tools are available in the market to support IT service management processes. These tools offer features such as workflow automation, ticket routing, alerting, and reporting capabilities. Some popular automation tools in IT service management include:
-
ServiceNow
-
BMC Helix
-
Cherwell
-
SolarWinds
-
Freshservice
Automation Strategies and Practices in IT Service Management
When implementing automation in IT service management, organizations should consider the following strategies and practices:
-
Identify key processes and tasks that can be automated to improve efficiency.
-
Establish clear objectives and goals for automation initiatives.
-
Train employees on how to use automation tools effectively.
-
Monitor and measure the impact of automation on IT service management processes.
-
Continuously optimize and improve automation workflows to adapt to changing business needs.
Automation Challenges and Solutions in IT Service Management
While automation offers numerous benefits, organizations may face challenges during implementation. Some common challenges include:
-
Resistance to change from employees.
-
Integration issues with existing systems.
-
Complexity of defining automation workflows.
-
Ensuring data security and compliance.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should focus on:
-
Communicating the benefits of automation to employees.
-
Investing in integration tools to connect different systems.
-
Collaborating with IT and business stakeholders to define automation workflows.
-
Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
Future of Automation in IT Service Management
The future of automation in IT service management looks promising, with advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation. These technologies will further enhance automation capabilities, enabling organizations to achieve higher levels of efficiency, agility, and innovation in their IT service management processes.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, automation plays a critical role in IT service management, offering a wide range of benefits and opportunities for organizations. By leveraging automation tools, strategies, and practices, organizations can streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and deliver higher quality IT services to their customers. Embrace automation today and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving world of IT service management!
Read More
Are you looking to streamline your IT service management processes and improve overall efficiency? Look no further than automation! Automation plays a crucial role in IT service management, offering a wide range of benefits and opportunities for organizations looking to optimize their operations. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of automation in IT service management, including its implementation, challenges, best practices, and future developments.
What is Automation in IT Service Management?
Automation in IT service management refers to the use of technology to perform manual tasks, processes, and workflows automatically. This can include automating routine tasks such as incident management, problem resolution, change management, and asset management. By leveraging automation tools and technologies, organizations can reduce human error, improve productivity, and enhance the overall quality of IT services.
Benefits of Automation in IT Service Management
-
Improved efficiency and productivity: By automating repetitive tasks, IT teams can focus on more strategic initiatives and projects.
-
Enhanced accuracy: Automation reduces the risk of human error, leading to higher data accuracy and consistency.
-
Faster response times: Automated workflows can respond to incidents and requests in real-time, leading to quicker resolution times.
-
Cost savings: Automation helps reduce operational costs by minimizing the need for manual intervention and streamlining processes.
-
Better scalability: With automation, IT service management processes can easily scale to support growing business needs and requirements.
Automation Tools in IT Service Management
Several automation tools are available in the market to support IT service management processes. These tools offer features such as workflow automation, ticket routing, alerting, and reporting capabilities. Some popular automation tools in IT service management include:
-
ServiceNow
-
BMC Helix
-
Cherwell
-
SolarWinds
-
Freshservice
Automation Strategies and Practices in IT Service Management
When implementing automation in IT service management, organizations should consider the following strategies and practices:
-
Identify key processes and tasks that can be automated to improve efficiency.
-
Establish clear objectives and goals for automation initiatives.
-
Train employees on how to use automation tools effectively.
-
Monitor and measure the impact of automation on IT service management processes.
-
Continuously optimize and improve automation workflows to adapt to changing business needs.
Automation Challenges and Solutions in IT Service Management
While automation offers numerous benefits, organizations may face challenges during implementation. Some common challenges include:
-
Resistance to change from employees.
-
Integration issues with existing systems.
-
Complexity of defining automation workflows.
-
Ensuring data security and compliance.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should focus on:
-
Communicating the benefits of automation to employees.
-
Investing in integration tools to connect different systems.
-
Collaborating with IT and business stakeholders to define automation workflows.
-
Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
Future of Automation in IT Service Management
The future of automation in IT service management looks promising, with advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation. These technologies will further enhance automation capabilities, enabling organizations to achieve higher levels of efficiency, agility, and innovation in their IT service management processes.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, automation plays a critical role in IT service management, offering a wide range of benefits and opportunities for organizations. By leveraging automation tools, strategies, and practices, organizations can streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and deliver higher quality IT services to their customers. Embrace automation today and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving world of IT service management!
IT Service Management Trends to Watch in 2024 and Beyond
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, staying abreast of the latest IT service management trends is essential for businesses to remain competitive and efficient. As we look ahead to 2024 and beyond, several key trends are poised to shape the future of IT service management, incorporating advancements in technology, innovation, automation, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, data analytics, cloud computing, digital transformation, customer experience, agile methodologies, remote work, and more.
Embracing Emerging Technologies
One of the most prominent trends in IT service management is the increasing adoption of emerging technologies. From artificial intelligence and machine learning to data analytics and cloud computing, businesses are leveraging these technologies to optimize their IT operations and deliver scalable solutions to their customers. By embracing these cutting-edge technologies, organizations can streamline their processes, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Shifting Towards Automation
Automation is another key trend that is transforming the field of IT service management. By automating routine tasks and processes, businesses can reduce manual errors, increase productivity, and free up their IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. From automating incident response and change management to implementing the ITIL framework for continuous improvement, automation is revolutionizing how IT services are delivered and managed.
Enhancing Cybersecurity Measures
With the increasing threat of cyberattacks and data breaches, cybersecurity continues to be a top priority for businesses. In 2024 and beyond, organizations will need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect their data, systems, and networks from evolving threats. This includes implementing best practices for IT security, vendor management, and mobile device security, as well as ensuring compliance with IT governance standards to safeguard sensitive information.
Enabling Remote Work Capabilities
The rise of remote work has become a permanent fixture in the modern workplace, driven by the global pandemic and the need for flexibility and collaboration. As businesses continue to support remote work environments, IT service management will need to adapt to meet the changing needs of a distributed workforce. This includes providing secure access to IT resources, supporting remote collaboration tools, and implementing agile methodologies to enhance productivity and communication.
Leveraging Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is playing an increasingly important role in IT service management, enabling organizations to anticipate and prevent potential issues before they occur. By analyzing historical data and trends, businesses can identify patterns, forecast future events, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their IT infrastructure and operations. This proactive approach helps businesses to mitigate risks, improve performance, and deliver superior customer service.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, IT service management is undergoing a significant transformation as we look ahead to 2024 and beyond. By embracing emerging technologies, shifting towards automation, enhancing cybersecurity measures, enabling remote work capabilities, and leveraging predictive analytics, businesses can position themselves for success in the digital age. As technology continues to evolve, staying ahead of these key trends will be crucial for organizations to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and deliver exceptional IT services to their customers.
Read More
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, staying abreast of the latest IT service management trends is essential for businesses to remain competitive and efficient. As we look ahead to 2024 and beyond, several key trends are poised to shape the future of IT service management, incorporating advancements in technology, innovation, automation, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, data analytics, cloud computing, digital transformation, customer experience, agile methodologies, remote work, and more.
Embracing Emerging Technologies
One of the most prominent trends in IT service management is the increasing adoption of emerging technologies. From artificial intelligence and machine learning to data analytics and cloud computing, businesses are leveraging these technologies to optimize their IT operations and deliver scalable solutions to their customers. By embracing these cutting-edge technologies, organizations can streamline their processes, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Shifting Towards Automation
Automation is another key trend that is transforming the field of IT service management. By automating routine tasks and processes, businesses can reduce manual errors, increase productivity, and free up their IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. From automating incident response and change management to implementing the ITIL framework for continuous improvement, automation is revolutionizing how IT services are delivered and managed.
Enhancing Cybersecurity Measures
With the increasing threat of cyberattacks and data breaches, cybersecurity continues to be a top priority for businesses. In 2024 and beyond, organizations will need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect their data, systems, and networks from evolving threats. This includes implementing best practices for IT security, vendor management, and mobile device security, as well as ensuring compliance with IT governance standards to safeguard sensitive information.
Enabling Remote Work Capabilities
The rise of remote work has become a permanent fixture in the modern workplace, driven by the global pandemic and the need for flexibility and collaboration. As businesses continue to support remote work environments, IT service management will need to adapt to meet the changing needs of a distributed workforce. This includes providing secure access to IT resources, supporting remote collaboration tools, and implementing agile methodologies to enhance productivity and communication.
Leveraging Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is playing an increasingly important role in IT service management, enabling organizations to anticipate and prevent potential issues before they occur. By analyzing historical data and trends, businesses can identify patterns, forecast future events, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their IT infrastructure and operations. This proactive approach helps businesses to mitigate risks, improve performance, and deliver superior customer service.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, IT service management is undergoing a significant transformation as we look ahead to 2024 and beyond. By embracing emerging technologies, shifting towards automation, enhancing cybersecurity measures, enabling remote work capabilities, and leveraging predictive analytics, businesses can position themselves for success in the digital age. As technology continues to evolve, staying ahead of these key trends will be crucial for organizations to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and deliver exceptional IT services to their customers.
Integrating ISO 20000 with Other QMS for Enhanced Efficiency
In today's fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve their processes and ensure the highest quality of service delivery. One way to achieve this is by integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems (QMS) to create a seamless and efficient system that aligns with industry standards and best practices.
Understanding ISO 20000
ISO 20000 is an international standard for IT Service Management that outlines the requirements for an organization to effectively deliver quality IT services. It focuses on ensuring the alignment of IT services with the needs of the business and the continuous improvement of service delivery processes.
Benefits of Integrating ISO 20000 with QMS
Integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems offers several benefits to organizations, including:
-
Improved efficiency and effectiveness of processes
-
Enhanced service delivery and customer satisfaction
-
Greater alignment with industry standards and best practices
-
Streamlined compliance with regulatory requirements
-
Increased visibility and control over service performance
-
Enhanced risk management and mitigation strategies
Strategies for Integration
When integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems, organizations should consider the following strategies:
-
Conduct a gap analysis to identify areas of overlap and areas that require alignment.
-
Develop a roadmap for integration that outlines the steps, timelines, and responsibilities.
-
Engage stakeholders from different departments to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
-
Monitor and measure the performance of the integrated system to identify areas for improvement.
Best Practices for Integration
To ensure a successful integration of ISO 20000 with QMS, organizations should consider the following best practices:
-
Ensure compatibility between systems to avoid conflicts and ensure seamless integration.
-
Align QMS standards with ISO 20000 requirements to create a unified approach to quality management.
-
Implement a framework for continuous improvement to drive efficiencies and enhance service delivery.
-
Focus on improving QMS processes to meet the requirements of ISO 20000 and enhance overall performance.
-
Establish guidelines and protocols for service delivery integration to ensure consistency and quality.
Achieving Certification and Compliance
By integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems, organizations can enhance their chances of achieving certification and compliance with industry standards. This not only demonstrates a commitment to quality and excellence but also opens doors to new business opportunities and partnerships.
How to obtain ISO 20000 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems is a strategic approach to improving service delivery, enhancing quality assurance, and driving efficiencies within an organization. By following best practices, engaging stakeholders, and focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can create a seamless and effective system that aligns with industry standards and best practices. Start integrating your ISO 20000 with QMS today to experience the benefits firsthand.
Read More
In today's fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve their processes and ensure the highest quality of service delivery. One way to achieve this is by integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems (QMS) to create a seamless and efficient system that aligns with industry standards and best practices.
Understanding ISO 20000
ISO 20000 is an international standard for IT Service Management that outlines the requirements for an organization to effectively deliver quality IT services. It focuses on ensuring the alignment of IT services with the needs of the business and the continuous improvement of service delivery processes.
Benefits of Integrating ISO 20000 with QMS
Integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems offers several benefits to organizations, including:
-
Improved efficiency and effectiveness of processes
-
Enhanced service delivery and customer satisfaction
-
Greater alignment with industry standards and best practices
-
Streamlined compliance with regulatory requirements
-
Increased visibility and control over service performance
-
Enhanced risk management and mitigation strategies
Strategies for Integration
When integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems, organizations should consider the following strategies:
-
Conduct a gap analysis to identify areas of overlap and areas that require alignment.
-
Develop a roadmap for integration that outlines the steps, timelines, and responsibilities.
-
Engage stakeholders from different departments to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
-
Monitor and measure the performance of the integrated system to identify areas for improvement.
Best Practices for Integration
To ensure a successful integration of ISO 20000 with QMS, organizations should consider the following best practices:
-
Ensure compatibility between systems to avoid conflicts and ensure seamless integration.
-
Align QMS standards with ISO 20000 requirements to create a unified approach to quality management.
-
Implement a framework for continuous improvement to drive efficiencies and enhance service delivery.
-
Focus on improving QMS processes to meet the requirements of ISO 20000 and enhance overall performance.
-
Establish guidelines and protocols for service delivery integration to ensure consistency and quality.
Achieving Certification and Compliance
By integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems, organizations can enhance their chances of achieving certification and compliance with industry standards. This not only demonstrates a commitment to quality and excellence but also opens doors to new business opportunities and partnerships.
How to obtain ISO 20000 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Integrating ISO 20000 with other Quality Management Systems is a strategic approach to improving service delivery, enhancing quality assurance, and driving efficiencies within an organization. By following best practices, engaging stakeholders, and focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can create a seamless and effective system that aligns with industry standards and best practices. Start integrating your ISO 20000 with QMS today to experience the benefits firsthand.
The Rise of Self-Service Portals in IT Service Management
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to streamline processes and enhance efficiency. One key area where significant advancements have been made is in IT service management, with the rise of self-service portals revolutionizing the way organizations deliver support to their users.
Self-Service Portals and IT Service Management
Self-service portals have quickly become a cornerstone of modern IT service management. These portals empower users to find solutions to their problems independently, without the need to rely on IT support staff. By providing users with a centralized hub where they can access knowledge articles, submit service requests, and track the status of their tickets, self-service portals offer a level of convenience and autonomy that was previously unheard of.
The Benefits of Automation
Automation lies at the heart of self-service portals, enabling organizations to streamline repetitive tasks and free up their IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. By automating routine processes such as ticket routing, incident categorization, and request fulfillment, organizations can significantly reduce response times and improve overall service delivery.
Enhanced User Experience
Self-service portals also play a critical role in enhancing the user experience. By providing users with a user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation, organizations can ensure that users can easily find the information they need and quickly resolve their issues. This not only boosts user satisfaction but also contributes to higher productivity levels across the organization.
Driving Digital Transformation
The rise of self-service portals is closely aligned with the broader trend of digital transformation. By leveraging technologies such as cloud computing and software integration, organizations can create seamless and connected experiences for their users. Self-service portals serve as the gateway to this digital ecosystem, providing users with a centralized platform to access a wide range of services and resources.
Key Features of Self-Service Portals
-
Ticketing System: Enables users to report issues and track the status of their requests.
-
Service Desk: Provides a central point of contact for users to seek assistance.
-
Remote Assistance: Allows support staff to troubleshoot and resolve issues remotely.
-
Knowledge Base: Offers a repository of articles and FAQs to help users find solutions independently.
-
Access Control: Ensures that users have the appropriate permissions to access specific resources.
-
Authentication and Authorization: Verify the identity of users and determine their level of access.
-
Service Catalog: Displays a catalog of available services that users can request.
-
Incident Management: Handles the reporting and resolution of incidents in a structured manner.
-
Request Fulfillment: Manages service requests from initiation to completion.
-
Problem Management: Addresses the root causes of recurring incidents to prevent future disruptions.
-
Change Management: Controls changes to IT infrastructure to minimize risks and disruptions.
Empowering Users and Boosting Productivity
Self-service portals empower users to take control of their IT needs, reducing their reliance on support staff and enabling them to resolve issues more quickly. This not only leads to cost-effective solutions but also enhances scalability and productivity across the organization. By providing users with the tools they need to find solutions independently, self-service portals drive user empowerment and pave the way for a more efficient and effective IT service management framework.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of self-service portals in IT service management represents a significant advancement in the way organizations deliver support to their users. By leveraging automation, technology, and user-centric design principles, self-service portals offer a seamless and efficient way for users to access the support they need. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, self-service portals will play an increasingly crucial role in driving efficiency, productivity enhancements, and user empowerment within organizations
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to streamline processes and enhance efficiency. One key area where significant advancements have been made is in IT service management, with the rise of self-service portals revolutionizing the way organizations deliver support to their users.
Self-Service Portals and IT Service Management
Self-service portals have quickly become a cornerstone of modern IT service management. These portals empower users to find solutions to their problems independently, without the need to rely on IT support staff. By providing users with a centralized hub where they can access knowledge articles, submit service requests, and track the status of their tickets, self-service portals offer a level of convenience and autonomy that was previously unheard of.
The Benefits of Automation
Automation lies at the heart of self-service portals, enabling organizations to streamline repetitive tasks and free up their IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. By automating routine processes such as ticket routing, incident categorization, and request fulfillment, organizations can significantly reduce response times and improve overall service delivery.
Enhanced User Experience
Self-service portals also play a critical role in enhancing the user experience. By providing users with a user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation, organizations can ensure that users can easily find the information they need and quickly resolve their issues. This not only boosts user satisfaction but also contributes to higher productivity levels across the organization.
Driving Digital Transformation
The rise of self-service portals is closely aligned with the broader trend of digital transformation. By leveraging technologies such as cloud computing and software integration, organizations can create seamless and connected experiences for their users. Self-service portals serve as the gateway to this digital ecosystem, providing users with a centralized platform to access a wide range of services and resources.
Key Features of Self-Service Portals
-
Ticketing System: Enables users to report issues and track the status of their requests.
-
Service Desk: Provides a central point of contact for users to seek assistance.
-
Remote Assistance: Allows support staff to troubleshoot and resolve issues remotely.
-
Knowledge Base: Offers a repository of articles and FAQs to help users find solutions independently.
-
Access Control: Ensures that users have the appropriate permissions to access specific resources.
-
Authentication and Authorization: Verify the identity of users and determine their level of access.
-
Service Catalog: Displays a catalog of available services that users can request.
-
Incident Management: Handles the reporting and resolution of incidents in a structured manner.
-
Request Fulfillment: Manages service requests from initiation to completion.
-
Problem Management: Addresses the root causes of recurring incidents to prevent future disruptions.
-
Change Management: Controls changes to IT infrastructure to minimize risks and disruptions.
Empowering Users and Boosting Productivity
Self-service portals empower users to take control of their IT needs, reducing their reliance on support staff and enabling them to resolve issues more quickly. This not only leads to cost-effective solutions but also enhances scalability and productivity across the organization. By providing users with the tools they need to find solutions independently, self-service portals drive user empowerment and pave the way for a more efficient and effective IT service management framework.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of self-service portals in IT service management represents a significant advancement in the way organizations deliver support to their users. By leveraging automation, technology, and user-centric design principles, self-service portals offer a seamless and efficient way for users to access the support they need. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, self-service portals will play an increasingly crucial role in driving efficiency, productivity enhancements, and user empowerment within organizations
COBIT 5: Core IT Governance Principles Unveiled | Full Blog
Are you looking to enhance your understanding of IT governance and information technology best practices? Look no further than COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework that provides a comprehensive guide to achieving effective IT governance. In this article, we will delve into the core principles of COBIT® 5, exploring its key concepts, implementation strategies, and the numerous benefits it can offer to organizations of all sizes.
What is COBIT® 5?
COBIT® 5, developed by ISACA, is a leading framework for the governance and management of enterprise IT. It helps organizations create optimal value from IT by maintaining a balance between realizing benefits and optimizing risk levels and resource use. By aligning business goals with IT goals, COBIT® 5 enables enterprises to implement effective IT processes and controls.
Core Principles of COBIT® 5
-
COBIT Principles: The framework is built on five core principles: meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management.
-
COBIT Implementation: Organizations can implement COBIT® 5 by following a structured methodology that includes assessing current IT processes, defining improvement opportunities, and aligning IT goals with business objectives.
-
COBIT Best Practices: COBIT® 5 offers best practices for IT governance, risk management, and compliance, providing a roadmap for organizations to achieve operational excellence and regulatory compliance.
-
COBIT Training and Certification: Professionals can enhance their expertise in IT governance by undergoing COBIT® training and obtaining certification, which validates their knowledge and skills in implementing the framework.
The Benefits of COBIT® 5
-
Efficiency: By streamlining IT processes and controls, COBIT® 5 improves operational efficiency and reduces the risk of errors and inefficiencies.
-
Effectiveness: The framework helps organizations achieve their strategic objectives by aligning IT with business goals and ensuring optimal resource allocation.
-
Accountability: COBIT® 5 promotes transparency and accountability in IT governance, ensuring that stakeholders are informed and involved in decision-making processes.
COBIT® 5 Processes and Controls
COBIT® 5 defines a set of processes and controls that organizations can use to manage and govern their IT functions effectively. Some of the key processes include:
-
Governance Framework Implementation
-
Risk Management
-
Business-IT Alignment
-
IT Security
-
Compliance
-
Efficiency and Effectiveness
-
Strategy Implementation
Assessing COBIT® Maturity
Organizations can assess their maturity in implementing COBIT® 5 by using the maturity model provided by the framework. This assessment helps identify areas for improvement and prioritize initiatives to enhance IT governance practices.
Conducting a COBIT® Audit
A COBIT® audit involves evaluating the effectiveness of IT processes and controls against the framework's standards. By conducting regular audits, organizations can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and identify areas of non-compliance.
How to obtain Cobit 5 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5 is a robust framework that provides organizations with the tools and guidance needed to achieve excellence in IT governance. By understanding the core principles of COBIT® 5 and implementing best practices, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency, effectiveness, and accountability in managing their IT assets. Invest in COBIT® 5 training and certification to elevate your IT governance capabilities and drive sustainable value for your organization.
Read More
Are you looking to enhance your understanding of IT governance and information technology best practices? Look no further than COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework that provides a comprehensive guide to achieving effective IT governance. In this article, we will delve into the core principles of COBIT® 5, exploring its key concepts, implementation strategies, and the numerous benefits it can offer to organizations of all sizes.
What is COBIT® 5?
COBIT® 5, developed by ISACA, is a leading framework for the governance and management of enterprise IT. It helps organizations create optimal value from IT by maintaining a balance between realizing benefits and optimizing risk levels and resource use. By aligning business goals with IT goals, COBIT® 5 enables enterprises to implement effective IT processes and controls.
Core Principles of COBIT® 5
-
COBIT Principles: The framework is built on five core principles: meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management.
-
COBIT Implementation: Organizations can implement COBIT® 5 by following a structured methodology that includes assessing current IT processes, defining improvement opportunities, and aligning IT goals with business objectives.
-
COBIT Best Practices: COBIT® 5 offers best practices for IT governance, risk management, and compliance, providing a roadmap for organizations to achieve operational excellence and regulatory compliance.
-
COBIT Training and Certification: Professionals can enhance their expertise in IT governance by undergoing COBIT® training and obtaining certification, which validates their knowledge and skills in implementing the framework.
The Benefits of COBIT® 5
-
Efficiency: By streamlining IT processes and controls, COBIT® 5 improves operational efficiency and reduces the risk of errors and inefficiencies.
-
Effectiveness: The framework helps organizations achieve their strategic objectives by aligning IT with business goals and ensuring optimal resource allocation.
-
Accountability: COBIT® 5 promotes transparency and accountability in IT governance, ensuring that stakeholders are informed and involved in decision-making processes.
COBIT® 5 Processes and Controls
COBIT® 5 defines a set of processes and controls that organizations can use to manage and govern their IT functions effectively. Some of the key processes include:
-
Governance Framework Implementation
-
Risk Management
-
Business-IT Alignment
-
IT Security
-
Compliance
-
Efficiency and Effectiveness
-
Strategy Implementation
Assessing COBIT® Maturity
Organizations can assess their maturity in implementing COBIT® 5 by using the maturity model provided by the framework. This assessment helps identify areas for improvement and prioritize initiatives to enhance IT governance practices.
Conducting a COBIT® Audit
A COBIT® audit involves evaluating the effectiveness of IT processes and controls against the framework's standards. By conducting regular audits, organizations can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and identify areas of non-compliance.
How to obtain Cobit 5 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5 is a robust framework that provides organizations with the tools and guidance needed to achieve excellence in IT governance. By understanding the core principles of COBIT® 5 and implementing best practices, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency, effectiveness, and accountability in managing their IT assets. Invest in COBIT® 5 training and certification to elevate your IT governance capabilities and drive sustainable value for your organization.
ISO 20000 and ITIL: Understanding Their Key Relationship
In the world of IT service management, two prominent frameworks often come into play: ISO 20000 and ITIL. These frameworks play a crucial role in shaping how organizations deliver services to their customers. However, many people are still unclear about the relationship between ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks. In this article, we will explore the key similarities, differences, benefits, and implementation strategies of these frameworks to help you better understand their connection.
ISO 20000 and ITIL: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding ISO 20000
ISO 20000 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an organization to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve a service management system. It focuses on the processes needed to deliver effective services to customers and meet their requirements.
Decoding ITIL Framework
ITIL, on the other hand, stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library and is a set of detailed practices for IT service management (ITSM) that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. It provides a framework for organizations to manage their IT services effectively and efficiently.
Exploring the Relationship Between ISO 20000 and ITIL
While ISO 20000 and ITIL are distinct frameworks, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, many organizations find that implementing both standards can lead to a more holistic approach to service management. ISO 20000 provides a set of requirements that organizations must meet to achieve certification, while ITIL offers best practices and guidelines for implementing IT service management processes.
Benefits of Integrating ISO 20000 and ITIL
-
Improved Service Quality: By aligning with both frameworks, organizations can enhance the quality of their services and ensure they meet industry standards.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: The integration of ISO 20000 and ITIL can help streamline processes and increase operational efficiency.
-
Better Customer Satisfaction: Meeting the requirements of both frameworks can lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Compliance and Certification: Implementing both standards can help organizations achieve ISO 20000 certification and adhere to ITIL best practices.
Implementation Strategies and Approaches
When integrating ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks, organizations should focus on aligning their processes, procedures, and documentation to meet the requirements of both standards. This may involve conducting a gap analysis, identifying areas for improvement, and creating a roadmap for implementation.
The Impact on Organizations
The integration of ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks can have a significant impact on organizations, leading to improved service delivery, increased efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction. It can also help organizations stay competitive in the market and meet the growing demands of customers.
Key Points to Remember
-
ISO 20000 and ITIL are complementary frameworks that can be integrated to improve service management.
-
Organizations can benefit from aligning with both standards to enhance service quality and efficiency.
-
Implementing both frameworks requires careful planning, analysis, and continuous improvement.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks is essential for organizations looking to improve their service management practices. By integrating these frameworks, organizations can achieve certification, improve service quality, and enhance customer satisfaction. The synergy between ISO 20000 and ITIL offers a comprehensive approach to IT service management that can benefit organizations of all sizes.
Read More
In the world of IT service management, two prominent frameworks often come into play: ISO 20000 and ITIL. These frameworks play a crucial role in shaping how organizations deliver services to their customers. However, many people are still unclear about the relationship between ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks. In this article, we will explore the key similarities, differences, benefits, and implementation strategies of these frameworks to help you better understand their connection.
ISO 20000 and ITIL: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding ISO 20000
ISO 20000 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an organization to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve a service management system. It focuses on the processes needed to deliver effective services to customers and meet their requirements.
Decoding ITIL Framework
ITIL, on the other hand, stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library and is a set of detailed practices for IT service management (ITSM) that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. It provides a framework for organizations to manage their IT services effectively and efficiently.
Exploring the Relationship Between ISO 20000 and ITIL
While ISO 20000 and ITIL are distinct frameworks, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, many organizations find that implementing both standards can lead to a more holistic approach to service management. ISO 20000 provides a set of requirements that organizations must meet to achieve certification, while ITIL offers best practices and guidelines for implementing IT service management processes.
Benefits of Integrating ISO 20000 and ITIL
-
Improved Service Quality: By aligning with both frameworks, organizations can enhance the quality of their services and ensure they meet industry standards.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: The integration of ISO 20000 and ITIL can help streamline processes and increase operational efficiency.
-
Better Customer Satisfaction: Meeting the requirements of both frameworks can lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Compliance and Certification: Implementing both standards can help organizations achieve ISO 20000 certification and adhere to ITIL best practices.
Implementation Strategies and Approaches
When integrating ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks, organizations should focus on aligning their processes, procedures, and documentation to meet the requirements of both standards. This may involve conducting a gap analysis, identifying areas for improvement, and creating a roadmap for implementation.
The Impact on Organizations
The integration of ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks can have a significant impact on organizations, leading to improved service delivery, increased efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction. It can also help organizations stay competitive in the market and meet the growing demands of customers.
Key Points to Remember
-
ISO 20000 and ITIL are complementary frameworks that can be integrated to improve service management.
-
Organizations can benefit from aligning with both standards to enhance service quality and efficiency.
-
Implementing both frameworks requires careful planning, analysis, and continuous improvement.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between ISO 20000 and ITIL frameworks is essential for organizations looking to improve their service management practices. By integrating these frameworks, organizations can achieve certification, improve service quality, and enhance customer satisfaction. The synergy between ISO 20000 and ITIL offers a comprehensive approach to IT service management that can benefit organizations of all sizes.
ISO 20000's Role in Cybersecurity for IT Service Management
In today's digital age, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, organizations need to prioritize cybersecurity in their IT service management practices. One essential tool in this fight against cyber threats is the ISO/IEC 20000 standard. ISO 20000 is a globally recognized standard that outlines best practices for IT service management, including cybersecurity measures to protect valuable data and systems. Let's explore the role of ISO 20000 in ensuring cyber security in IT service management.
What is ISO 20000?
ISO 20000 is an international standard for IT service management that helps organizations ensure the effective delivery of IT services to meet the needs of their customers. It provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an IT service management system. By adhering to the requirements of ISO 20000, organizations can enhance the quality of their IT services and demonstrate their commitment to excellence in IT service delivery.
The Role of ISO 20000 in Cybersecurity
One of the key benefits of implementing ISO 20000 is its emphasis on information security. The standard includes specific requirements for managing information security risks and protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By following the guidelines set forth in ISO 20000, organizations can establish robust controls and processes to safeguard their IT infrastructure and systems from potential security breaches.
Certification and Compliance
Achieving ISO 20000 certification demonstrates an organization's commitment to cybersecurity and best practices in IT service management. By undergoing a rigorous audit process, organizations can prove their compliance with the standard and showcase their dedication to maintaining a secure and reliable IT environment. ISO 20000 certification not only enhances an organization's reputation but also instills confidence in customers and stakeholders regarding the security of their information assets.
Incident Response and Risk Management
ISO 20000 also emphasizes the importance of incident response and risk management in IT service management. By establishing clear procedures for identifying, assessing, and mitigating cybersecurity risks, organizations can proactively manage potential threats and prevent security incidents from occurring. Additionally, ISO 20000 promotes a structured approach to incident response, ensuring that organizations can effectively respond to and recover from cybersecurity incidents in a timely manner.
Best Practices and Continuous Improvement
ISO 20000 encompasses a set of best practices for IT service management, including cybersecurity measures such as vulnerability management, asset management, and business continuity planning. By following these best practices, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and improve the overall quality of their IT services. Furthermore, ISO 20000 promotes a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging organizations to regularly review and enhance their cybersecurity practices to adapt to evolving cyber threats.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, ISO 20000 plays a crucial role in ensuring cybersecurity in IT service management by providing organizations with a comprehensive framework for implementing robust security controls and processes. By adhering to the requirements of ISO 20000, organizations can enhance the quality of their IT services, protect sensitive data from cyber threats, and demonstrate their commitment to excellence in IT service delivery. Ultimately, ISO 20000 certification can help organizations build trust with customers and stakeholders, showcasing their dedication to maintaining a secure and reliable IT environment.
Read More
In today's digital age, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, organizations need to prioritize cybersecurity in their IT service management practices. One essential tool in this fight against cyber threats is the ISO/IEC 20000 standard. ISO 20000 is a globally recognized standard that outlines best practices for IT service management, including cybersecurity measures to protect valuable data and systems. Let's explore the role of ISO 20000 in ensuring cyber security in IT service management.
What is ISO 20000?
ISO 20000 is an international standard for IT service management that helps organizations ensure the effective delivery of IT services to meet the needs of their customers. It provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an IT service management system. By adhering to the requirements of ISO 20000, organizations can enhance the quality of their IT services and demonstrate their commitment to excellence in IT service delivery.
The Role of ISO 20000 in Cybersecurity
One of the key benefits of implementing ISO 20000 is its emphasis on information security. The standard includes specific requirements for managing information security risks and protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By following the guidelines set forth in ISO 20000, organizations can establish robust controls and processes to safeguard their IT infrastructure and systems from potential security breaches.
Certification and Compliance
Achieving ISO 20000 certification demonstrates an organization's commitment to cybersecurity and best practices in IT service management. By undergoing a rigorous audit process, organizations can prove their compliance with the standard and showcase their dedication to maintaining a secure and reliable IT environment. ISO 20000 certification not only enhances an organization's reputation but also instills confidence in customers and stakeholders regarding the security of their information assets.
Incident Response and Risk Management
ISO 20000 also emphasizes the importance of incident response and risk management in IT service management. By establishing clear procedures for identifying, assessing, and mitigating cybersecurity risks, organizations can proactively manage potential threats and prevent security incidents from occurring. Additionally, ISO 20000 promotes a structured approach to incident response, ensuring that organizations can effectively respond to and recover from cybersecurity incidents in a timely manner.
Best Practices and Continuous Improvement
ISO 20000 encompasses a set of best practices for IT service management, including cybersecurity measures such as vulnerability management, asset management, and business continuity planning. By following these best practices, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and improve the overall quality of their IT services. Furthermore, ISO 20000 promotes a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging organizations to regularly review and enhance their cybersecurity practices to adapt to evolving cyber threats.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, ISO 20000 plays a crucial role in ensuring cybersecurity in IT service management by providing organizations with a comprehensive framework for implementing robust security controls and processes. By adhering to the requirements of ISO 20000, organizations can enhance the quality of their IT services, protect sensitive data from cyber threats, and demonstrate their commitment to excellence in IT service delivery. Ultimately, ISO 20000 certification can help organizations build trust with customers and stakeholders, showcasing their dedication to maintaining a secure and reliable IT environment.
5 Key Concept to Master for COBIT 5 Foundation Certification
Are you preparing for your COBIT® 5 Foundation certification exam and looking for ways to ensure success? Achieving this certification can open up new opportunities for career advancement and professional development in the field of IT governance. To help you pass your exam with flying colors, here are 5 key concepts to focus on in your study guide and exam preparation:
Understanding the COBIT® 5 Framework
The COBIT® 5 framework is a globally recognized standard for IT governance that helps organizations align their IT strategies with their business goals. By understanding the framework's core principles and control objectives, you will be better equipped to answer exam questions related to implementing best practices for effective IT governance.
Mastering IT Governance Strategies
IT governance is essential for ensuring that an organization's IT infrastructure supports its overall business objectives. By grasping the various strategies and principles outlined in COBIT® 5, you will be able to demonstrate your knowledge of how to align IT with business goals and drive value through effective governance practices.
Familiarizing Yourself with Control Objectives
Control objectives in the COBIT® 5 framework provide a set of guidelines for implementing IT governance processes and controls. By studying the control objectives relevant to your exam, you can gain a deeper understanding of how to manage risks, ensure compliance, and optimize IT resources to achieve organizational objectives.
Practicing with Mock Tests
Mock tests are a valuable tool for assessing your knowledge and readiness for the COBIT® 5 Foundation exam. By taking practice exams online, you can familiarize yourself with the exam format, test questions, and time constraints, allowing you to identify areas where you may need additional study and practice.
Creating a Study Plan
A well-structured study plan is essential for effective exam preparation. By creating a study schedule that includes review of study materials, completion of online courses, and practice with mock tests, you can ensure that you cover all the necessary topics and concepts before exam day. Consider enrolling in accredited training programs to gain access to expert guidance and resources for a comprehensive study experience.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance in COBIT certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, by focusing on these key concepts and following a strategic study plan, you can increase your chances of acing your COBIT® 5 Foundation certification exam. Remember to stay focused, prioritize your study time, and leverage resources such as mock tests and study materials to maximize your preparation efforts.
Read More
Are you preparing for your COBIT® 5 Foundation certification exam and looking for ways to ensure success? Achieving this certification can open up new opportunities for career advancement and professional development in the field of IT governance. To help you pass your exam with flying colors, here are 5 key concepts to focus on in your study guide and exam preparation:
Understanding the COBIT® 5 Framework
The COBIT® 5 framework is a globally recognized standard for IT governance that helps organizations align their IT strategies with their business goals. By understanding the framework's core principles and control objectives, you will be better equipped to answer exam questions related to implementing best practices for effective IT governance.
Mastering IT Governance Strategies
IT governance is essential for ensuring that an organization's IT infrastructure supports its overall business objectives. By grasping the various strategies and principles outlined in COBIT® 5, you will be able to demonstrate your knowledge of how to align IT with business goals and drive value through effective governance practices.
Familiarizing Yourself with Control Objectives
Control objectives in the COBIT® 5 framework provide a set of guidelines for implementing IT governance processes and controls. By studying the control objectives relevant to your exam, you can gain a deeper understanding of how to manage risks, ensure compliance, and optimize IT resources to achieve organizational objectives.
Practicing with Mock Tests
Mock tests are a valuable tool for assessing your knowledge and readiness for the COBIT® 5 Foundation exam. By taking practice exams online, you can familiarize yourself with the exam format, test questions, and time constraints, allowing you to identify areas where you may need additional study and practice.
Creating a Study Plan
A well-structured study plan is essential for effective exam preparation. By creating a study schedule that includes review of study materials, completion of online courses, and practice with mock tests, you can ensure that you cover all the necessary topics and concepts before exam day. Consider enrolling in accredited training programs to gain access to expert guidance and resources for a comprehensive study experience.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance in COBIT certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
In conclusion, by focusing on these key concepts and following a strategic study plan, you can increase your chances of acing your COBIT® 5 Foundation certification exam. Remember to stay focused, prioritize your study time, and leverage resources such as mock tests and study materials to maximize your preparation efforts.
Effective Change Management for IT Service Delivery Success
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of Information Technology (IT), change is inevitable. With advancements in technology and shifting business needs, organizations must adapt to stay competitive. Effective change management in IT service delivery is crucial for ensuring that changes are implemented smoothly, with minimal disruption to operations. In this article, we will explore the key components of effective change management in IT service delivery and how organizations can navigate these changes successfully.
The Importance of Change Management
Change management is the process of managing changes to IT systems, processes, and infrastructure in a controlled and systematic manner. It involves planning, implementing, and monitoring changes to ensure that they are aligned with business goals and do not negatively impact operations. Effective change management is essential for organizations to minimize risks, optimize resources, and drive innovation.
Key Components of Effective Change Management
Clear Communication: Communication is key to successful change management. Stakeholders must be informed about the reasons for the change, the expected outcomes, and their roles and responsibilities. Clear and transparent communication helps build trust and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
Risk Assessment: Before implementing any changes, organizations must conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. Understanding the impact of the changes allows organizations to proactively address any issues that may arise.
Change Control: Establishing a formal change control process helps organizations maintain control over changes and ensures that they are implemented in a structured manner. Change control involves documenting changes, obtaining approval from stakeholders, and tracking progress throughout the implementation process.
Training and Support: Providing training and support to employees is essential for successful change management. Employees need to understand how the changes will affect their roles and responsibilities and receive the necessary training to adapt to new processes and technologies.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Once changes are implemented, organizations must monitor and evaluate their impact on operations. Regular assessment helps identify any issues or bottlenecks and allows organizations to make adjustments as needed.
Overcoming Challenges in Change Management
Change management is not without its challenges. Resistance to change, lack of resources, and poor planning can derail even the most well-thought-out change management strategy. To overcome these challenges, organizations must prioritize open communication, engage stakeholders early in the process, and allocate sufficient resources to support the change management initiative.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Effective change management is essential for organizations looking to stay ahead in today's fast-paced IT landscape. By implementing clear communication strategies, conducting thorough risk assessments, establishing change control processes, providing training and support to employees, and monitoring and evaluating changes, organizations can successfully navigate the complexities of change management in IT service delivery. Embracing change as an opportunity for growth and innovation can position organizations for success in the digital age.
Read More
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of Information Technology (IT), change is inevitable. With advancements in technology and shifting business needs, organizations must adapt to stay competitive. Effective change management in IT service delivery is crucial for ensuring that changes are implemented smoothly, with minimal disruption to operations. In this article, we will explore the key components of effective change management in IT service delivery and how organizations can navigate these changes successfully.
The Importance of Change Management
Change management is the process of managing changes to IT systems, processes, and infrastructure in a controlled and systematic manner. It involves planning, implementing, and monitoring changes to ensure that they are aligned with business goals and do not negatively impact operations. Effective change management is essential for organizations to minimize risks, optimize resources, and drive innovation.
Key Components of Effective Change Management
Clear Communication: Communication is key to successful change management. Stakeholders must be informed about the reasons for the change, the expected outcomes, and their roles and responsibilities. Clear and transparent communication helps build trust and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
Risk Assessment: Before implementing any changes, organizations must conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. Understanding the impact of the changes allows organizations to proactively address any issues that may arise.
Change Control: Establishing a formal change control process helps organizations maintain control over changes and ensures that they are implemented in a structured manner. Change control involves documenting changes, obtaining approval from stakeholders, and tracking progress throughout the implementation process.
Training and Support: Providing training and support to employees is essential for successful change management. Employees need to understand how the changes will affect their roles and responsibilities and receive the necessary training to adapt to new processes and technologies.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Once changes are implemented, organizations must monitor and evaluate their impact on operations. Regular assessment helps identify any issues or bottlenecks and allows organizations to make adjustments as needed.
Overcoming Challenges in Change Management
Change management is not without its challenges. Resistance to change, lack of resources, and poor planning can derail even the most well-thought-out change management strategy. To overcome these challenges, organizations must prioritize open communication, engage stakeholders early in the process, and allocate sufficient resources to support the change management initiative.
How to obtain IT Service Management and Governance certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
The 10 top-paying certifications to target in 2024 are:
Conclusion
Effective change management is essential for organizations looking to stay ahead in today's fast-paced IT landscape. By implementing clear communication strategies, conducting thorough risk assessments, establishing change control processes, providing training and support to employees, and monitoring and evaluating changes, organizations can successfully navigate the complexities of change management in IT service delivery. Embracing change as an opportunity for growth and innovation can position organizations for success in the digital age.
Building a Culture of Service Excellence in IT Teams!!!
In today's fast-paced and competitive business environment, it is crucial for IT companies to prioritize service excellence. Building a culture of service excellence in IT can lead to increased customer satisfaction, improved employee morale, and ultimately, enhanced business growth. In this article, we will explore the importance of service excellence in the IT industry and provide valuable insights on how to cultivate a culture of service excellence within your organization.
Why is Service Excellence Important in IT?
Service excellence is essential in the IT industry as it allows companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and deliver exceptional value to customers. In a highly competitive market, providing outstanding service can be a key differentiator that sets your company apart and attracts new customers. Additionally, focusing on service excellence can help improve customer retention rates, increase customer loyalty, and drive repeat business.
How to Build a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Lead by Example: Cultivating a culture of service excellence starts at the top. Leaders within the organization should demonstrate a commitment to providing exceptional service and set a positive example for their teams to follow.
Empower Employees: Empowering employees to take ownership of the customer experience can lead to improved service delivery. Provide training, resources, and support to help employees excel in their roles and deliver outstanding service to customers.
Foster a Customer-Centric Mindset: Encourage employees to always prioritize the needs and preferences of customers. By focusing on understanding and meeting customer expectations, employees can deliver personalized service that exceeds customer satisfaction.
Establish Clear Service Standards: Define clear service standards and expectations to guide employees in their interactions with customers. Regularly review and update these standards to ensure they align with the company's values and goals.
Encourage Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Create a culture of continuous improvement by actively seeking feedback from customers and employees. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance the overall customer experience.
Benefits of Building a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Increased Customer Satisfaction: By prioritizing service excellence, IT companies can enhance customer satisfaction levels and build strong relationships with their clients.
Improved Employee Morale: Employees who feel empowered to deliver exceptional service are more engaged, motivated, and satisfied in their roles.
Enhanced Business Growth: A culture of service excellence can drive business growth by attracting new customers, increasing customer loyalty, and generating positive word-of-mouth referrals.
How to obtain ITServices & Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Building a culture of service excellence in IT is essential for companies looking to thrive in today's competitive business landscape. By prioritizing service excellence, empowering employees, and fostering a customer-centric mindset, IT organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors, drive business growth, and create lasting customer relationships. Embrace service excellence as a core value within your organization and watch as it transforms the way you do business.
Read More
In today's fast-paced and competitive business environment, it is crucial for IT companies to prioritize service excellence. Building a culture of service excellence in IT can lead to increased customer satisfaction, improved employee morale, and ultimately, enhanced business growth. In this article, we will explore the importance of service excellence in the IT industry and provide valuable insights on how to cultivate a culture of service excellence within your organization.
Why is Service Excellence Important in IT?
Service excellence is essential in the IT industry as it allows companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and deliver exceptional value to customers. In a highly competitive market, providing outstanding service can be a key differentiator that sets your company apart and attracts new customers. Additionally, focusing on service excellence can help improve customer retention rates, increase customer loyalty, and drive repeat business.
How to Build a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Lead by Example: Cultivating a culture of service excellence starts at the top. Leaders within the organization should demonstrate a commitment to providing exceptional service and set a positive example for their teams to follow.
Empower Employees: Empowering employees to take ownership of the customer experience can lead to improved service delivery. Provide training, resources, and support to help employees excel in their roles and deliver outstanding service to customers.
Foster a Customer-Centric Mindset: Encourage employees to always prioritize the needs and preferences of customers. By focusing on understanding and meeting customer expectations, employees can deliver personalized service that exceeds customer satisfaction.
Establish Clear Service Standards: Define clear service standards and expectations to guide employees in their interactions with customers. Regularly review and update these standards to ensure they align with the company's values and goals.
Encourage Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Create a culture of continuous improvement by actively seeking feedback from customers and employees. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance the overall customer experience.
Benefits of Building a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Increased Customer Satisfaction: By prioritizing service excellence, IT companies can enhance customer satisfaction levels and build strong relationships with their clients.
Improved Employee Morale: Employees who feel empowered to deliver exceptional service are more engaged, motivated, and satisfied in their roles.
Enhanced Business Growth: A culture of service excellence can drive business growth by attracting new customers, increasing customer loyalty, and generating positive word-of-mouth referrals.
How to obtain ITServices & Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Building a culture of service excellence in IT is essential for companies looking to thrive in today's competitive business landscape. By prioritizing service excellence, empowering employees, and fostering a customer-centric mindset, IT organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors, drive business growth, and create lasting customer relationships. Embrace service excellence as a core value within your organization and watch as it transforms the way you do business.
AI Transformative Impact on Modern IT Service Management
Are you looking to streamline your IT service management processes and improve efficiency? Look no further than the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into your IT service management strategy. AI has revolutionized the way IT services are delivered and managed, offering a wide range of benefits that can help organizations operate more effectively and provide better service to their customers.
AI in IT Service Management
AI refers to the use of intelligent machines and algorithms that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding natural language. In the context of IT service management, AI can be used to automate repetitive tasks, predict and prevent IT issues, and analyze vast amounts of data to make informed decisions.
Artificial Intelligence for IT Service Management
By leveraging AI technologies, IT service management teams can work smarter, not harder. AI-powered systems can handle routine tasks like ticket routing, categorization, and resolution, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more critical issues that require human intervention. This not only increases efficiency but also improves employee satisfaction and reduces burnout.
Machine Learning in IT Service Management
Machine learning, a subset of AI, enables IT service management systems to learn from past data and experiences to improve future outcomes. By analyzing historical data, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and trends that humans might overlook, leading to more accurate predictions and proactive problem resolution. This can result in fewer service disruptions, reduced downtime, and improved overall performance.
IT Service Management Automation
Automation is a key component of AI in IT service management. By automating routine tasks and processes, organizations can reduce manual errors, speed up service delivery, and provide a consistent and reliable experience for users. From automated incident response to self-service portals, AI-driven automation can revolutionize the way IT services are delivered.
Benefits of AI in IT Service Management
The use of AI in IT service management offers a wide range of benefits for organizations, including:
Enhanced efficiency: AI can handle tasks faster and more accurately than humans, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Improved decision-making: AI algorithms can analyze data in real-time and provide valuable insights that can help organizations make informed decisions.
Better customer satisfaction: By automating routine tasks and providing faster service delivery, organizations can enhance the customer experience and build loyalty.
Proactive problem resolution: AI can predict and prevent IT issues before they occur, reducing downtime and minimizing impact on business operations.
Scalability: AI-powered systems can scale up or down based on demand, allowing organizations to adapt to changing business needs quickly.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in IT Service
The role of artificial intelligence in IT service is to augment and optimize the capabilities of IT service management teams. By automating routine tasks, analyzing data, and making predictions, AI can help organizations operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and deliver better service to their customers. From predicting system failures to optimizing resource allocation, AI can transform the way IT services are managed and delivered.
IT Service Management Optimization with AI
To optimize IT service management with AI, organizations should:
Identify areas where AI can have the most significant impact, such as incident management, problem resolution, and service desk operations.
Invest in AI technologies that align with organizational goals and objectives, ensuring a seamless integration with existing IT systems.
Train IT staff on how to leverage AI tools and technologies effectively, empowering them to work more efficiently and effectively.
Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of AI-powered systems, making adjustments as needed to maximize benefits and ROI.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governace certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI plays a crucial role in IT service management by improving efficiency, automating routine tasks, and helping organizations deliver better service to their customers. By embracing AI technologies and incorporating them into their IT service management strategy, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and drive innovation in the fast-paced world of IT services.
Read More
Are you looking to streamline your IT service management processes and improve efficiency? Look no further than the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into your IT service management strategy. AI has revolutionized the way IT services are delivered and managed, offering a wide range of benefits that can help organizations operate more effectively and provide better service to their customers.
AI in IT Service Management
AI refers to the use of intelligent machines and algorithms that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding natural language. In the context of IT service management, AI can be used to automate repetitive tasks, predict and prevent IT issues, and analyze vast amounts of data to make informed decisions.
Artificial Intelligence for IT Service Management
By leveraging AI technologies, IT service management teams can work smarter, not harder. AI-powered systems can handle routine tasks like ticket routing, categorization, and resolution, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more critical issues that require human intervention. This not only increases efficiency but also improves employee satisfaction and reduces burnout.
Machine Learning in IT Service Management
Machine learning, a subset of AI, enables IT service management systems to learn from past data and experiences to improve future outcomes. By analyzing historical data, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and trends that humans might overlook, leading to more accurate predictions and proactive problem resolution. This can result in fewer service disruptions, reduced downtime, and improved overall performance.
IT Service Management Automation
Automation is a key component of AI in IT service management. By automating routine tasks and processes, organizations can reduce manual errors, speed up service delivery, and provide a consistent and reliable experience for users. From automated incident response to self-service portals, AI-driven automation can revolutionize the way IT services are delivered.
Benefits of AI in IT Service Management
The use of AI in IT service management offers a wide range of benefits for organizations, including:
Enhanced efficiency: AI can handle tasks faster and more accurately than humans, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Improved decision-making: AI algorithms can analyze data in real-time and provide valuable insights that can help organizations make informed decisions.
Better customer satisfaction: By automating routine tasks and providing faster service delivery, organizations can enhance the customer experience and build loyalty.
Proactive problem resolution: AI can predict and prevent IT issues before they occur, reducing downtime and minimizing impact on business operations.
Scalability: AI-powered systems can scale up or down based on demand, allowing organizations to adapt to changing business needs quickly.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in IT Service
The role of artificial intelligence in IT service is to augment and optimize the capabilities of IT service management teams. By automating routine tasks, analyzing data, and making predictions, AI can help organizations operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and deliver better service to their customers. From predicting system failures to optimizing resource allocation, AI can transform the way IT services are managed and delivered.
IT Service Management Optimization with AI
To optimize IT service management with AI, organizations should:
Identify areas where AI can have the most significant impact, such as incident management, problem resolution, and service desk operations.
Invest in AI technologies that align with organizational goals and objectives, ensuring a seamless integration with existing IT systems.
Train IT staff on how to leverage AI tools and technologies effectively, empowering them to work more efficiently and effectively.
Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of AI-powered systems, making adjustments as needed to maximize benefits and ROI.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governace certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI plays a crucial role in IT service management by improving efficiency, automating routine tasks, and helping organizations deliver better service to their customers. By embracing AI technologies and incorporating them into their IT service management strategy, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and drive innovation in the fast-paced world of IT services.
COBIT® 5 Implementation Best Practices: Tips for Success
"COBIT® 5 Implementation Best Practices: Tips for Success" serves as a comprehensive guide for organizations looking to adopt and implement COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework for enterprise IT governance. In the rapidly evolving landscape of information technology, effective governance is critical for ensuring that organizations achieve their strategic objectives while managing risks and optimizing resource utilization. This guide delves into the key principles and methodologies that underpin COBIT® 5, providing practical insights and best practices to facilitate a successful implementation process.
As organizations grapple with the complexities of IT governance, the COBIT® 5 framework emerges as a robust solution, offering a systematic approach to aligning business goals with IT processes. The guide not only introduces readers to the core concepts of COBIT® 5 but also provides actionable tips and strategies to overcome common challenges encountered during implementation. It emphasizes the importance of tailoring COBIT® 5 to the unique needs and context of each organization, ensuring a customized and effective application of the framework.
Readers will gain valuable insights into how COBIT® 5 can enhance overall business performance, drive innovation, and foster a culture of continuous improvement within their IT governance structures. With a focus on real-world scenarios and practical examples, the guide equips organizations with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the intricacies of COBIT® 5 implementation, promoting a seamless integration that maximizes benefits and minimizes disruptions. Whether an organization is embarking on its initial COBIT® 5 implementation or seeking to optimize existing processes, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for achieving success in the dynamic realmof IT governance.
Table of contents
-
Customization Strategies for COBIT® 5 Implementation
-
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
-
Effective Stakeholder Engagement in COBIT® 5 Implementation
-
Measuring and Monitoring Success Metrics
-
Integration of COBIT® 5 with Other IT Management Frameworks
-
Conclusion
Customization Strategies for COBIT® 5 Implementation
Customization is a pivotal aspect of successful COBIT® 5 implementation, recognizing that a one-size-fits-all approach may not align with the unique characteristics of every organization. This sub-topic delves into the strategies and considerations involved in tailoring COBIT® 5 to meet the specific needs and context of each organization. One essential element of customization is the acknowledgment of industry-specific requirements, understanding that different sectors may have distinct governance and compliance demands. This section will guide organizations in identifying these sector-specific nuances and adapting COBIT® 5 principles accordingly.
Additionally, organizational size plays a crucial role in customization strategies. Small and large enterprises may have different resource capabilities and structures, necessitating an adaptable approach to COBIT® 5 implementation. Practical tips will be provided on how organizations can scale and tailor the framework to suit their size, ensuring that it remains a practical and effective tool for governance in any organizational context.
Balancing adherence to COBIT® 5 principles with the flexibility to adapt to organizational goals is another critical consideration. This section will offer insights into finding the equilibrium between following the established framework and modifying it to address unique challenges or opportunities. Examples of successful customization efforts, drawn from diverse industries, will be explored to illustrate how organizations have effectively personalized COBIT® 5 to suit their specific needs without compromising its integrity.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
The successful implementation of COBIT® 5 is not without its share of challenges, and this sub-topic addresses key obstacles that organizations commonly encounter during the implementation process. One prevalent challenge is the resistance to change, as employees may be accustomed to existing processes and may view the adoption of COBIT® 5 as disruptive. This section provides practical insights into fostering a positive attitude towards change, offering strategies to communicate the benefits of COBIT® 5 clearly and engage employees in the transition process.
Resource constraints represent another significant hurdle in COBIT® 5 implementation. Organizations often face limitations in terms of time, budget, and skilled personnel. Here, the discussion focuses on innovative approaches to maximize resources efficiently, such as prioritizing critical areas of implementation, leveraging existing skill sets, and exploring partnerships or collaborations. Real-world examples of organizations successfully navigating resource challenges during COBIT® 5 implementation will be explored to inspire effective strategies.
By addressing these common challenges head-on, organizations can better prepare for the hurdles associated with COBIT® 5 implementation. Practical tips, case studies, and lessons learned from organizations that have successfully navigated these challenges will provide valuable insights, offering a roadmap for others to overcome obstacles and ensure a smoother implementation journey for COBIT® 5.
Effective Stakeholder Engagement in COBIT® 5 Implementation
Effective stakeholder engagement is a critical element in the successful implementation of COBIT® 5, recognizing the importance of garnering support from key individuals and groups throughout the process. This sub-topic explores strategies for engaging stakeholders at various levels within the organization, starting with top-level executives. It emphasizes the need for executive buy-in, as their support is instrumental in providing the necessary resources and leadership to drive COBIT® 5 implementation. The discussion delves into effective communication strategies to convey the value proposition of COBIT® 5 to executives, aligning the framework with overarching business goals.
Moving beyond executives, this section also addresses the involvement of IT teams and other relevant stakeholders. It explores the creation of targeted training programs to enhance stakeholder understanding of COBIT® 5 principles and their role in the implementation journey. The importance of establishing clear lines of communication, feedback mechanisms, and collaborative decision-making processes is highlighted to foster a sense of ownership and commitment among stakeholders.
It discusses how effective stakeholder engagement can contribute to shaping a positive organizational culture that embraces the principles of COBIT® 5. Real-world examples of successful stakeholder engagement initiatives will be provided to illustrate how organizations have effectively mobilized support and collaboration across various levels, ensuring a collective effort towards COBIT® 5 implementation.
Measuring and Monitoring Success Metrics
Measuring and monitoring success metrics constitute a fundamental component of a robust COBIT® 5 implementation, serving as the compass to navigate the effectiveness and impact of the framework on an organization's IT governance. This sub-topic underscores the significance of methodically selecting key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the organization's strategic objectives. By establishing clear, measurable goals, organizations can evaluate the tangible outcomes of COBIT® 5 implementation, ensuring a tangible link between IT governance practices and overarching business goals.
Continuous monitoring is pivotal in maintaining the health and efficacy of COBIT® 5 processes. This section advocates for a proactive and systematic approach to tracking performance, leveraging automated tools and reporting mechanisms to gather real-time data. Through diligent monitoring, organizations can identify deviations from expected outcomes, address potential issues promptly, and fine-tune processes to align with the evolving needs of the organization. Practical insights into setting up a robust monitoring framework within the COBIT® 5 context will be provided, drawing on successful examples of organizations that have effectively utilized monitoring mechanisms.
As organizational priorities shift, technological landscapes evolve, and industry standards change, the measurement framework should be flexible enough to accommodate these fluctuations. Organizations will gain insights into strategies for adjusting success metrics, ensuring their continued relevance in assessing the impact of COBIT® 5 on the IT governance landscape.
By implementing a comprehensive system for performance evaluation and remaining agile in adapting metrics, organizations can not only gauge the success of COBIT® 5 but also lay the groundwork for continuous improvement and strategic alignment with evolving business objectives.
Integration of COBIT® 5 with Other IT Management Frameworks
The integration of COBIT® 5 with other IT management frameworks represents a strategic approach to creating a cohesive and comprehensive governance structure within organizations. This sub-topic delves into the synergy between COBIT® 5 and other frameworks, such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) or ISO/IEC 27001. It acknowledges that organizations often leverage multiple frameworks to address various aspects of IT management and governance, and explores how COBIT® 5 can seamlessly complement and enhance existing practices.
The discussion highlights the importance of identifying areas of alignment and potential overlaps between COBIT® 5 and other frameworks. By recognizing the synergies, organizations can avoid duplication of efforts and create a unified governance framework that optimally addresses their unique needs. This involves a nuanced understanding of the strengths and focus areas of each framework, allowing for a harmonious integration that leverages the best aspects of each.
Practical guidance is provided on how organizations can navigate the integration process, emphasizing the need for collaboration among stakeholders involved in different frameworks. This collaboration ensures that integration efforts are well-coordinated, fostering a shared understanding of objectives and methodologies across the organization. Real-world examples will illustrate successful instances of organizations integrating COBIT® 5 with other frameworks, showcasing the positive outcomes and enhanced efficiency resulting from this holistic approach.
The integration of COBIT® 5 with other IT management frameworks is presented as a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to build a robust and harmonized governance ecosystem. Through careful consideration, collaboration, and a nuanced approach to integration, organizations can harness the collective strengths of multiple frameworks to achieve a more comprehensive and effective IT governance strategy.
How to obtain COBIT 5 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, "COBIT® 5 Implementation Best Practices: Tips for Success" encapsulates a comprehensive guide for organizations navigating the intricacies of adopting and implementing the COBIT® 5 framework for IT governance. The exploration of customization strategies underscores the importance of tailoring COBIT® 5 to suit the unique needs and context of each organization, providing practical insights into industry-specific requirements and organizational size considerations. Recognizing and addressing common implementation challenges, from resistance to change to resource constraints, empowers organizations to navigate these hurdles effectively, drawing inspiration from real-world examples of successful implementations.
The sub-topic on effective stakeholder engagement establishes a crucial aspect of COBIT® 5 implementation by emphasizing the need for buy-in from top executives and active involvement of IT teams. Through clear communication, targeted training, and a collaborative approach, organizations can foster a positive organizational culture that aligns with COBIT® 5 principles. Measuring and monitoring success metrics form the backbone of the implementation journey, guiding organizations in selecting relevant KPIs, leveraging automation, and embracing adaptability to ensure continuous improvement and alignment with evolving business objectives.
Finally, the exploration of the integration of COBIT® 5 with other IT management frameworks highlights the strategic advantage of creating a unified governance structure. By identifying synergies and avoiding duplication, organizations can harness the strengths of multiple frameworks, resulting in improved risk management, streamlined processes, and enhanced overall IT governance.
Collectively, the insights provided in this guide empower organizations with the knowledge, strategies, and practical tips needed to navigate the multifaceted landscape of COBIT® 5 implementation. As organizations embark on this journey, the guide serves as a valuable resource, offering a roadmap for success and fostering a culture of continuous improvement within the realm of IT governance.
Read More
"COBIT® 5 Implementation Best Practices: Tips for Success" serves as a comprehensive guide for organizations looking to adopt and implement COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework for enterprise IT governance. In the rapidly evolving landscape of information technology, effective governance is critical for ensuring that organizations achieve their strategic objectives while managing risks and optimizing resource utilization. This guide delves into the key principles and methodologies that underpin COBIT® 5, providing practical insights and best practices to facilitate a successful implementation process.
As organizations grapple with the complexities of IT governance, the COBIT® 5 framework emerges as a robust solution, offering a systematic approach to aligning business goals with IT processes. The guide not only introduces readers to the core concepts of COBIT® 5 but also provides actionable tips and strategies to overcome common challenges encountered during implementation. It emphasizes the importance of tailoring COBIT® 5 to the unique needs and context of each organization, ensuring a customized and effective application of the framework.
Readers will gain valuable insights into how COBIT® 5 can enhance overall business performance, drive innovation, and foster a culture of continuous improvement within their IT governance structures. With a focus on real-world scenarios and practical examples, the guide equips organizations with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the intricacies of COBIT® 5 implementation, promoting a seamless integration that maximizes benefits and minimizes disruptions. Whether an organization is embarking on its initial COBIT® 5 implementation or seeking to optimize existing processes, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for achieving success in the dynamic realmof IT governance.
Table of contents
-
Customization Strategies for COBIT® 5 Implementation
-
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
-
Effective Stakeholder Engagement in COBIT® 5 Implementation
-
Measuring and Monitoring Success Metrics
-
Integration of COBIT® 5 with Other IT Management Frameworks
-
Conclusion
Customization Strategies for COBIT® 5 Implementation
Customization is a pivotal aspect of successful COBIT® 5 implementation, recognizing that a one-size-fits-all approach may not align with the unique characteristics of every organization. This sub-topic delves into the strategies and considerations involved in tailoring COBIT® 5 to meet the specific needs and context of each organization. One essential element of customization is the acknowledgment of industry-specific requirements, understanding that different sectors may have distinct governance and compliance demands. This section will guide organizations in identifying these sector-specific nuances and adapting COBIT® 5 principles accordingly.
Additionally, organizational size plays a crucial role in customization strategies. Small and large enterprises may have different resource capabilities and structures, necessitating an adaptable approach to COBIT® 5 implementation. Practical tips will be provided on how organizations can scale and tailor the framework to suit their size, ensuring that it remains a practical and effective tool for governance in any organizational context.
Balancing adherence to COBIT® 5 principles with the flexibility to adapt to organizational goals is another critical consideration. This section will offer insights into finding the equilibrium between following the established framework and modifying it to address unique challenges or opportunities. Examples of successful customization efforts, drawn from diverse industries, will be explored to illustrate how organizations have effectively personalized COBIT® 5 to suit their specific needs without compromising its integrity.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
The successful implementation of COBIT® 5 is not without its share of challenges, and this sub-topic addresses key obstacles that organizations commonly encounter during the implementation process. One prevalent challenge is the resistance to change, as employees may be accustomed to existing processes and may view the adoption of COBIT® 5 as disruptive. This section provides practical insights into fostering a positive attitude towards change, offering strategies to communicate the benefits of COBIT® 5 clearly and engage employees in the transition process.
Resource constraints represent another significant hurdle in COBIT® 5 implementation. Organizations often face limitations in terms of time, budget, and skilled personnel. Here, the discussion focuses on innovative approaches to maximize resources efficiently, such as prioritizing critical areas of implementation, leveraging existing skill sets, and exploring partnerships or collaborations. Real-world examples of organizations successfully navigating resource challenges during COBIT® 5 implementation will be explored to inspire effective strategies.
By addressing these common challenges head-on, organizations can better prepare for the hurdles associated with COBIT® 5 implementation. Practical tips, case studies, and lessons learned from organizations that have successfully navigated these challenges will provide valuable insights, offering a roadmap for others to overcome obstacles and ensure a smoother implementation journey for COBIT® 5.
Effective Stakeholder Engagement in COBIT® 5 Implementation
Effective stakeholder engagement is a critical element in the successful implementation of COBIT® 5, recognizing the importance of garnering support from key individuals and groups throughout the process. This sub-topic explores strategies for engaging stakeholders at various levels within the organization, starting with top-level executives. It emphasizes the need for executive buy-in, as their support is instrumental in providing the necessary resources and leadership to drive COBIT® 5 implementation. The discussion delves into effective communication strategies to convey the value proposition of COBIT® 5 to executives, aligning the framework with overarching business goals.
Moving beyond executives, this section also addresses the involvement of IT teams and other relevant stakeholders. It explores the creation of targeted training programs to enhance stakeholder understanding of COBIT® 5 principles and their role in the implementation journey. The importance of establishing clear lines of communication, feedback mechanisms, and collaborative decision-making processes is highlighted to foster a sense of ownership and commitment among stakeholders.
It discusses how effective stakeholder engagement can contribute to shaping a positive organizational culture that embraces the principles of COBIT® 5. Real-world examples of successful stakeholder engagement initiatives will be provided to illustrate how organizations have effectively mobilized support and collaboration across various levels, ensuring a collective effort towards COBIT® 5 implementation.
Measuring and Monitoring Success Metrics
Measuring and monitoring success metrics constitute a fundamental component of a robust COBIT® 5 implementation, serving as the compass to navigate the effectiveness and impact of the framework on an organization's IT governance. This sub-topic underscores the significance of methodically selecting key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the organization's strategic objectives. By establishing clear, measurable goals, organizations can evaluate the tangible outcomes of COBIT® 5 implementation, ensuring a tangible link between IT governance practices and overarching business goals.
Continuous monitoring is pivotal in maintaining the health and efficacy of COBIT® 5 processes. This section advocates for a proactive and systematic approach to tracking performance, leveraging automated tools and reporting mechanisms to gather real-time data. Through diligent monitoring, organizations can identify deviations from expected outcomes, address potential issues promptly, and fine-tune processes to align with the evolving needs of the organization. Practical insights into setting up a robust monitoring framework within the COBIT® 5 context will be provided, drawing on successful examples of organizations that have effectively utilized monitoring mechanisms.
As organizational priorities shift, technological landscapes evolve, and industry standards change, the measurement framework should be flexible enough to accommodate these fluctuations. Organizations will gain insights into strategies for adjusting success metrics, ensuring their continued relevance in assessing the impact of COBIT® 5 on the IT governance landscape.
By implementing a comprehensive system for performance evaluation and remaining agile in adapting metrics, organizations can not only gauge the success of COBIT® 5 but also lay the groundwork for continuous improvement and strategic alignment with evolving business objectives.
Integration of COBIT® 5 with Other IT Management Frameworks
The integration of COBIT® 5 with other IT management frameworks represents a strategic approach to creating a cohesive and comprehensive governance structure within organizations. This sub-topic delves into the synergy between COBIT® 5 and other frameworks, such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) or ISO/IEC 27001. It acknowledges that organizations often leverage multiple frameworks to address various aspects of IT management and governance, and explores how COBIT® 5 can seamlessly complement and enhance existing practices.
The discussion highlights the importance of identifying areas of alignment and potential overlaps between COBIT® 5 and other frameworks. By recognizing the synergies, organizations can avoid duplication of efforts and create a unified governance framework that optimally addresses their unique needs. This involves a nuanced understanding of the strengths and focus areas of each framework, allowing for a harmonious integration that leverages the best aspects of each.
Practical guidance is provided on how organizations can navigate the integration process, emphasizing the need for collaboration among stakeholders involved in different frameworks. This collaboration ensures that integration efforts are well-coordinated, fostering a shared understanding of objectives and methodologies across the organization. Real-world examples will illustrate successful instances of organizations integrating COBIT® 5 with other frameworks, showcasing the positive outcomes and enhanced efficiency resulting from this holistic approach.
The integration of COBIT® 5 with other IT management frameworks is presented as a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to build a robust and harmonized governance ecosystem. Through careful consideration, collaboration, and a nuanced approach to integration, organizations can harness the collective strengths of multiple frameworks to achieve a more comprehensive and effective IT governance strategy.
How to obtain COBIT 5 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, "COBIT® 5 Implementation Best Practices: Tips for Success" encapsulates a comprehensive guide for organizations navigating the intricacies of adopting and implementing the COBIT® 5 framework for IT governance. The exploration of customization strategies underscores the importance of tailoring COBIT® 5 to suit the unique needs and context of each organization, providing practical insights into industry-specific requirements and organizational size considerations. Recognizing and addressing common implementation challenges, from resistance to change to resource constraints, empowers organizations to navigate these hurdles effectively, drawing inspiration from real-world examples of successful implementations.
The sub-topic on effective stakeholder engagement establishes a crucial aspect of COBIT® 5 implementation by emphasizing the need for buy-in from top executives and active involvement of IT teams. Through clear communication, targeted training, and a collaborative approach, organizations can foster a positive organizational culture that aligns with COBIT® 5 principles. Measuring and monitoring success metrics form the backbone of the implementation journey, guiding organizations in selecting relevant KPIs, leveraging automation, and embracing adaptability to ensure continuous improvement and alignment with evolving business objectives.
Finally, the exploration of the integration of COBIT® 5 with other IT management frameworks highlights the strategic advantage of creating a unified governance structure. By identifying synergies and avoiding duplication, organizations can harness the strengths of multiple frameworks, resulting in improved risk management, streamlined processes, and enhanced overall IT governance.
Collectively, the insights provided in this guide empower organizations with the knowledge, strategies, and practical tips needed to navigate the multifaceted landscape of COBIT® 5 implementation. As organizations embark on this journey, the guide serves as a valuable resource, offering a roadmap for success and fostering a culture of continuous improvement within the realm of IT governance.
COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM: Achieving Synergy Together
The convergence of COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) represents a dynamic and synergistic approach to enhancing organizational governance and optimizing IT service delivery. COBIT® 5, developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), is a globally recognized framework that provides a comprehensive set of principles, practices, and analytical tools for the effective governance and management of enterprise IT. On the other hand, IT Service Management focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of the business, emphasizing the delivery of high-quality services that meet customer expectations.
In recent years, organizations have increasingly recognized the need to integrate and harmonize their governance and service management practices. The collaboration between COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM offers a strategic alignment that enables businesses to achieve a more seamless and efficient IT environment. This integration is particularly crucial in today's complex and rapidly evolving digital landscape, where organizations must navigate challenges such as cybersecurity threats, regulatory compliance, and the ever-growing demand for innovative IT services.
The foundational principles of COBIT® 5, which include a focus on stakeholder value, risk management, and continual improvement, align seamlessly with the core objectives of IT Service Management. By combining these frameworks, organizations can establish a robust foundation for achieving not only compliance and risk mitigation but also the delivery of high-quality, customer-centric IT services. This synergy empowers businesses to streamline their processes, enhance decision-making, and foster a culture of collaboration across different functional areas.
Table of contents
-
Overview of COBIT® 5 Foundation
-
Essentials of IT Service Management (ITSM)
-
Governance and Risk Management Integration
-
Implementing the Synergy: Step-by-Step Guide
-
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
-
Conclusion
Overview of COBIT® 5 Foundation
COBIT® 5 Foundation serves as a comprehensive framework developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) to guide organizations in achieving effective governance and management of information technology (IT). At its core, COBIT® (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) emphasizes the importance of aligning IT processes with business objectives, ensuring that IT activities contribute directly to organizational success. The framework provides a set of principles, practices, and enablers that support enterprises in optimizing their IT capabilities while managing associated risks and ensuring the delivery of value to stakeholders.
The COBIT® 5 Foundation framework is structured around five key principles, each contributing to the achievement of effective IT governance. These principles include meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management. Together, these principles guide organizations in establishing a governance and management system that is both efficient and adaptable to the evolving landscape of IT and business.
COBIT® 5 Foundation offers a structured and comprehensive approach to IT governance, emphasizing stakeholder value, principled practices, and adaptability to the ever-changing IT landscape. By leveraging this framework, organizations can establish a robust foundation for effective governance, risk management, and the continuous improvement of their IT processes, ultimately contributing to enhanced overall business performance.
Essentials of IT Service Management (ITSM)
Essentials of IT Service Management (ITSM) form the foundational principles and practices that organizations adopt to ensure the effective delivery and support of IT services aligned with business objectives. At its core, ITSM revolves around meeting the needs of users, optimizing service quality, and enhancing overall organizational efficiency. The following components encapsulate the key essentials of ITSM:
Service Strategy constitutes a critical pillar of ITSM, involving the development of a comprehensive strategy aligned with business goals. This phase entails understanding customer needs, defining service offerings, and formulating a strategic roadmap for delivering IT services that contribute directly to the success of the organization.
In the Service Design phase, the focus shifts to creating service solutions that meet the requirements outlined in the service strategy. This encompasses designing processes, technologies, and other essential elements necessary for the efficient and effective delivery of high-quality services. Service design ensures that IT services are not only functional but also meet the broader objectives of the organization.
Service Transition is a crucial aspect of ITSM that involves planning and managing changes to services and service management processes. This phase ensures a smooth transition of new or modified services into the operational environment while minimizing disruptions. It encompasses activities such as change management, release and deployment management, and knowledge management.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) serves as a guiding principle within ITSM, emphasizing the necessity of ongoing enhancement and optimization of services and processes. Through regular assessments, feedback mechanisms, and a commitment to learning from experiences, organizations practicing ITSM can identify areas for improvement and ensure a cycle of continuous enhancement in service delivery and operational efficiency. Together, these essentials form a holistic framework for organizations seeking to align their IT services with business goals, enhance customer satisfaction, and adapt to the dynamic landscape of technology and user expectations.
Governance and Risk Management Integration
In the realm of governance and risk management integration, organizations benefit from fostering a culture of risk awareness and accountability. This cultural shift encourages employees at all levels to recognize and report risks, fostering a collective responsibility for risk mitigation. By incorporating risk considerations into the organization's values and day-to-day operations, companies can create a more proactive and resilient stance toward potential challenges.
Integration also involves the development and implementation of robust risk management frameworks that seamlessly align with governance structures. This includes defining clear roles and responsibilities for risk management at various levels of the organization, establishing effective communication channels for sharing risk information, and integrating risk assessments into strategic planning processes. Such frameworks not only identify potential risks but also provide a structured approach to managing and monitoring these risks over time.
Continuous learning and improvement are inherent components of successful integration. Organizations should conduct periodic reviews and audits to evaluate the effectiveness of their integrated governance and risk management approach. Lessons learned from incidents and successes should be incorporated into future strategies, fostering a dynamic and adaptive governance structure that evolves in tandem with the changing risk landscape.
Governance and risk management integration is a multifaceted and ongoing process that requires a commitment to cultural change, technological innovation, and continuous improvement. By weaving risk considerations into the fabric of governance structures, organizations can enhance their resilience, make more informed decisions, and navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain business environment.
Implementing the Synergy: Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing the synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) is a strategic imperative that demands a methodical and well-coordinated approach. Commencing with a thorough assessment of the current state of IT governance and service management, organizations gain a foundational understanding of existing processes and their maturity. This assessment sets the stage for subsequent integration efforts, providing valuable insights into the organization's strengths and areas for improvement.
Precise definition of integration objectives and scope follows, as organizations articulate the desired outcomes and benefits to be derived from the amalgamation of COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM. A clear scope ensures that efforts remain focused on specific goals, preventing potential deviations and ensuring a streamlined implementation process. Stakeholder engagement becomes paramount, involving key representatives from IT and business units to gather diverse perspectives and ensure alignment with overarching organizational goals. This collaborative engagement fosters buy-in and support crucial for the successful integration.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are established to measure the success of the integration, encompassing governance effectiveness, service delivery efficiency, and overall alignment with organizational objectives. Regular monitoring and assessment of these indicators offer valuable insights into the performance and impact of the integrated framework, guiding ongoing improvements.
Implementation efforts extend to training programs and change management initiatives, ensuring that teams are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to operate within the integrated framework. Pilot programs may be initiated in specific departments or business units to test the integrated framework in a controlled environment, allowing for the identification and resolution of potential challenges before full-scale deployment. Continuous monitoring and evaluation mechanisms are established to assess the ongoing effectiveness of the integrated COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM framework, incorporating feedback from users and stakeholders to drive necessary adjustments.
Cultivating a culture of continuous improvement is emphasized, encouraging teams to identify opportunities for enhancement and establishing mechanisms for regular reviews and refinements to the integrated framework. This adaptive approach ensures the sustained success of the integration, aligning IT services seamlessly with business objectives while fostering a dynamic and resilient organizational environment. In conclusion, this step-by-step guide serves as a comprehensive and structured approach to implementing the synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management, ultimately enhancing governance practices and optimizing the delivery of IT services.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring the success of the integration between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) relies on a thoughtful selection of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that encompass various aspects critical to the alignment of governance and service delivery. One pivotal category of KPIs revolves around strategic alignment, evaluating how effectively the integrated framework contributes to organizational objectives. These indicators provide a holistic view of whether the governance practices and IT service delivery align with and support the broader strategic vision of the organization, emphasizing the symbiotic relationship between IT initiatives and overall business goals.
Governance effectiveness serves as another crucial dimension for assessing success. KPIs within this category focus on evaluating the efficiency and efficacy of governance processes. Metrics such as the speed of decision-making, compliance levels, and the responsiveness of governance structures offer insights into how well the organization is managing its IT resources and risks. These indicators serve as a barometer for the overall health and effectiveness of the governance component within the integrated framework.
User satisfaction and experience KPIs form a vital component, providing insights into the impact of the integrated framework on end-users. Metrics such as user satisfaction surveys, feedback on service quality, and user adoption rates offer a qualitative assessment of how well the integrated approach meets stakeholder expectations. These indicators are crucial for ensuring a positive and productive user experience, as the success of the integration is ultimately measured by the satisfaction and engagement of the end-users.
A continuous improvement mindset is integral to sustained success, and corresponding KPIs focus on the organization's ability to adapt and refine the integrated framework over time. Metrics related to the frequency and effectiveness of updates and refinements, as well as the organization's agility in responding to emerging challenges, highlight the dynamic nature of governance and service management integration. Success, in this context, is not merely a destination but an ongoing journey of refinement and adaptation to ensure that governance and service management practices evolve in tandem with organizational goals and the evolving IT landscape.
How to obtain COBIT® 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pursuit of synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) stands as a transformative endeavor, poised to elevate organizational effectiveness in IT governance and service delivery. This convergence represents a strategic alignment that, when carefully implemented, holds the promise of harmonizing IT processes, optimizing risk management, and enhancing the delivery of IT services in line with business objectives.
The step-by-step guide provided for achieving this synergy emphasizes the importance of a systematic and collaborative approach. From the initial assessment of the current state to the establishment of key performance indicators (KPIs) for ongoing measurement, the guide offers a structured pathway for organizations to navigate the integration process. Defining clear objectives, engaging stakeholders, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement emerge as pivotal elements, ensuring that the integration is purposeful, inclusive, and adaptable to the evolving landscape of IT and business dynamics.
The seamless alignment of COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM processes contributes not only to operational efficiency but also to a more resilient and responsive IT ecosystem. By integrating governance and service management, organizations are better equipped to meet the ever-changing needs of stakeholders, enhance risk mitigation strategies, and cultivate a customer-centric approach to IT services.
As organizations embark on this journey of achieving synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM, the ultimate goal is to create a dynamic and adaptive IT environment. This integration is not a static achievement but a continuous process of refinement and optimization. Success is measured not just by the integration itself but by the sustained ability to deliver value, align with strategic goals, and proactively respond to the challenges and opportunities inherent in the digital landscape. In essence, achieving synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM is a strategic imperative that positions organizations to thrive in an era where effective governance and agile service management are essential for sustained success.
Read More
The convergence of COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) represents a dynamic and synergistic approach to enhancing organizational governance and optimizing IT service delivery. COBIT® 5, developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), is a globally recognized framework that provides a comprehensive set of principles, practices, and analytical tools for the effective governance and management of enterprise IT. On the other hand, IT Service Management focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of the business, emphasizing the delivery of high-quality services that meet customer expectations.
In recent years, organizations have increasingly recognized the need to integrate and harmonize their governance and service management practices. The collaboration between COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM offers a strategic alignment that enables businesses to achieve a more seamless and efficient IT environment. This integration is particularly crucial in today's complex and rapidly evolving digital landscape, where organizations must navigate challenges such as cybersecurity threats, regulatory compliance, and the ever-growing demand for innovative IT services.
The foundational principles of COBIT® 5, which include a focus on stakeholder value, risk management, and continual improvement, align seamlessly with the core objectives of IT Service Management. By combining these frameworks, organizations can establish a robust foundation for achieving not only compliance and risk mitigation but also the delivery of high-quality, customer-centric IT services. This synergy empowers businesses to streamline their processes, enhance decision-making, and foster a culture of collaboration across different functional areas.
Table of contents
-
Overview of COBIT® 5 Foundation
-
Essentials of IT Service Management (ITSM)
-
Governance and Risk Management Integration
-
Implementing the Synergy: Step-by-Step Guide
-
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
-
Conclusion
Overview of COBIT® 5 Foundation
COBIT® 5 Foundation serves as a comprehensive framework developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) to guide organizations in achieving effective governance and management of information technology (IT). At its core, COBIT® (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) emphasizes the importance of aligning IT processes with business objectives, ensuring that IT activities contribute directly to organizational success. The framework provides a set of principles, practices, and enablers that support enterprises in optimizing their IT capabilities while managing associated risks and ensuring the delivery of value to stakeholders.
The COBIT® 5 Foundation framework is structured around five key principles, each contributing to the achievement of effective IT governance. These principles include meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management. Together, these principles guide organizations in establishing a governance and management system that is both efficient and adaptable to the evolving landscape of IT and business.
COBIT® 5 Foundation offers a structured and comprehensive approach to IT governance, emphasizing stakeholder value, principled practices, and adaptability to the ever-changing IT landscape. By leveraging this framework, organizations can establish a robust foundation for effective governance, risk management, and the continuous improvement of their IT processes, ultimately contributing to enhanced overall business performance.
Essentials of IT Service Management (ITSM)
Essentials of IT Service Management (ITSM) form the foundational principles and practices that organizations adopt to ensure the effective delivery and support of IT services aligned with business objectives. At its core, ITSM revolves around meeting the needs of users, optimizing service quality, and enhancing overall organizational efficiency. The following components encapsulate the key essentials of ITSM:
Service Strategy constitutes a critical pillar of ITSM, involving the development of a comprehensive strategy aligned with business goals. This phase entails understanding customer needs, defining service offerings, and formulating a strategic roadmap for delivering IT services that contribute directly to the success of the organization.
In the Service Design phase, the focus shifts to creating service solutions that meet the requirements outlined in the service strategy. This encompasses designing processes, technologies, and other essential elements necessary for the efficient and effective delivery of high-quality services. Service design ensures that IT services are not only functional but also meet the broader objectives of the organization.
Service Transition is a crucial aspect of ITSM that involves planning and managing changes to services and service management processes. This phase ensures a smooth transition of new or modified services into the operational environment while minimizing disruptions. It encompasses activities such as change management, release and deployment management, and knowledge management.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) serves as a guiding principle within ITSM, emphasizing the necessity of ongoing enhancement and optimization of services and processes. Through regular assessments, feedback mechanisms, and a commitment to learning from experiences, organizations practicing ITSM can identify areas for improvement and ensure a cycle of continuous enhancement in service delivery and operational efficiency. Together, these essentials form a holistic framework for organizations seeking to align their IT services with business goals, enhance customer satisfaction, and adapt to the dynamic landscape of technology and user expectations.
Governance and Risk Management Integration
In the realm of governance and risk management integration, organizations benefit from fostering a culture of risk awareness and accountability. This cultural shift encourages employees at all levels to recognize and report risks, fostering a collective responsibility for risk mitigation. By incorporating risk considerations into the organization's values and day-to-day operations, companies can create a more proactive and resilient stance toward potential challenges.
Integration also involves the development and implementation of robust risk management frameworks that seamlessly align with governance structures. This includes defining clear roles and responsibilities for risk management at various levels of the organization, establishing effective communication channels for sharing risk information, and integrating risk assessments into strategic planning processes. Such frameworks not only identify potential risks but also provide a structured approach to managing and monitoring these risks over time.
Continuous learning and improvement are inherent components of successful integration. Organizations should conduct periodic reviews and audits to evaluate the effectiveness of their integrated governance and risk management approach. Lessons learned from incidents and successes should be incorporated into future strategies, fostering a dynamic and adaptive governance structure that evolves in tandem with the changing risk landscape.
Governance and risk management integration is a multifaceted and ongoing process that requires a commitment to cultural change, technological innovation, and continuous improvement. By weaving risk considerations into the fabric of governance structures, organizations can enhance their resilience, make more informed decisions, and navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain business environment.
Implementing the Synergy: Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing the synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) is a strategic imperative that demands a methodical and well-coordinated approach. Commencing with a thorough assessment of the current state of IT governance and service management, organizations gain a foundational understanding of existing processes and their maturity. This assessment sets the stage for subsequent integration efforts, providing valuable insights into the organization's strengths and areas for improvement.
Precise definition of integration objectives and scope follows, as organizations articulate the desired outcomes and benefits to be derived from the amalgamation of COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM. A clear scope ensures that efforts remain focused on specific goals, preventing potential deviations and ensuring a streamlined implementation process. Stakeholder engagement becomes paramount, involving key representatives from IT and business units to gather diverse perspectives and ensure alignment with overarching organizational goals. This collaborative engagement fosters buy-in and support crucial for the successful integration.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are established to measure the success of the integration, encompassing governance effectiveness, service delivery efficiency, and overall alignment with organizational objectives. Regular monitoring and assessment of these indicators offer valuable insights into the performance and impact of the integrated framework, guiding ongoing improvements.
Implementation efforts extend to training programs and change management initiatives, ensuring that teams are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to operate within the integrated framework. Pilot programs may be initiated in specific departments or business units to test the integrated framework in a controlled environment, allowing for the identification and resolution of potential challenges before full-scale deployment. Continuous monitoring and evaluation mechanisms are established to assess the ongoing effectiveness of the integrated COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM framework, incorporating feedback from users and stakeholders to drive necessary adjustments.
Cultivating a culture of continuous improvement is emphasized, encouraging teams to identify opportunities for enhancement and establishing mechanisms for regular reviews and refinements to the integrated framework. This adaptive approach ensures the sustained success of the integration, aligning IT services seamlessly with business objectives while fostering a dynamic and resilient organizational environment. In conclusion, this step-by-step guide serves as a comprehensive and structured approach to implementing the synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management, ultimately enhancing governance practices and optimizing the delivery of IT services.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring the success of the integration between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) relies on a thoughtful selection of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that encompass various aspects critical to the alignment of governance and service delivery. One pivotal category of KPIs revolves around strategic alignment, evaluating how effectively the integrated framework contributes to organizational objectives. These indicators provide a holistic view of whether the governance practices and IT service delivery align with and support the broader strategic vision of the organization, emphasizing the symbiotic relationship between IT initiatives and overall business goals.
Governance effectiveness serves as another crucial dimension for assessing success. KPIs within this category focus on evaluating the efficiency and efficacy of governance processes. Metrics such as the speed of decision-making, compliance levels, and the responsiveness of governance structures offer insights into how well the organization is managing its IT resources and risks. These indicators serve as a barometer for the overall health and effectiveness of the governance component within the integrated framework.
User satisfaction and experience KPIs form a vital component, providing insights into the impact of the integrated framework on end-users. Metrics such as user satisfaction surveys, feedback on service quality, and user adoption rates offer a qualitative assessment of how well the integrated approach meets stakeholder expectations. These indicators are crucial for ensuring a positive and productive user experience, as the success of the integration is ultimately measured by the satisfaction and engagement of the end-users.
A continuous improvement mindset is integral to sustained success, and corresponding KPIs focus on the organization's ability to adapt and refine the integrated framework over time. Metrics related to the frequency and effectiveness of updates and refinements, as well as the organization's agility in responding to emerging challenges, highlight the dynamic nature of governance and service management integration. Success, in this context, is not merely a destination but an ongoing journey of refinement and adaptation to ensure that governance and service management practices evolve in tandem with organizational goals and the evolving IT landscape.
How to obtain COBIT® 5 Foundation certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pursuit of synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and IT Service Management (ITSM) stands as a transformative endeavor, poised to elevate organizational effectiveness in IT governance and service delivery. This convergence represents a strategic alignment that, when carefully implemented, holds the promise of harmonizing IT processes, optimizing risk management, and enhancing the delivery of IT services in line with business objectives.
The step-by-step guide provided for achieving this synergy emphasizes the importance of a systematic and collaborative approach. From the initial assessment of the current state to the establishment of key performance indicators (KPIs) for ongoing measurement, the guide offers a structured pathway for organizations to navigate the integration process. Defining clear objectives, engaging stakeholders, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement emerge as pivotal elements, ensuring that the integration is purposeful, inclusive, and adaptable to the evolving landscape of IT and business dynamics.
The seamless alignment of COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM processes contributes not only to operational efficiency but also to a more resilient and responsive IT ecosystem. By integrating governance and service management, organizations are better equipped to meet the ever-changing needs of stakeholders, enhance risk mitigation strategies, and cultivate a customer-centric approach to IT services.
As organizations embark on this journey of achieving synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM, the ultimate goal is to create a dynamic and adaptive IT environment. This integration is not a static achievement but a continuous process of refinement and optimization. Success is measured not just by the integration itself but by the sustained ability to deliver value, align with strategic goals, and proactively respond to the challenges and opportunities inherent in the digital landscape. In essence, achieving synergy between COBIT® 5 Foundation and ITSM is a strategic imperative that positions organizations to thrive in an era where effective governance and agile service management are essential for sustained success.
Comprehensive Overview of Digital Marketing Certification
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital marketing, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for professionals aspiring to make a mark in the industry. Digital marketing certification programs have emerged as invaluable tools for individuals seeking to enhance their skills, validate their expertise, and gain a competitive edge in the job market. In this comprehensive overview, we'll delve into the world of digital marketing certifications, exploring the myriad options available and shedding light on the significance of these programs in today's dynamic business environment.
Digital marketing certifications encompass a diverse range of modules, each designed to cover essential aspects of online marketing, from search engine optimization (SEO) and social media marketing to analytics and content strategy. These programs not only serve as structured learning paths but also provide a standardized means of assessment, ensuring that certified professionals possess a well-rounded understanding of the multifaceted realm of digital marketing.
This overview will guide you through the considerations involved in choosing a certification program, whether you're a seasoned professional looking to upskill or a newcomer eager to establish a foothold in the industry. From exploring the content and structure of popular certification courses to understanding the broader implications of being certified, this series aims to be your go-to resource for navigating the diverse landscape of digital marketing certifications. Join us on this journey as we unravel the opportunities, challenges, and transformative potential of digital marketing certification programs.
Table of contents
-
Key Digital Marketing Certification Providers
-
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Career Goals
-
Examining the Curriculum
-
Certification Levels and Specializations
-
Industry Recognition and Credibility
-
Online vs In-Person Certification Programs
-
Practical Application and Real-World Projects
-
Cost and Time Considerations
-
Success Stories and Testimonials
-
Maintaining Certification Relevance in a Changing Landscape
-
Conclusion
Key Digital Marketing Certification Providers
In the dynamic landscape of digital marketing, several reputable certification providers offer comprehensive programs designed to equip professionals with the skills needed to thrive in the ever-evolving online space. Here are key digital marketing certification providers
Google Digital Garage:Google offers a range of free courses through its Digital Garage platform. Courses cover various aspects of digital marketing, including search engine optimization (SEO), social media, and analytics.
HubSpot Academy:HubSpot provides a comprehensive set of free certification courses on inbound marketing, content marketing, social media strategy, and more. Their certifications are well-regarded in the marketing community.
LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com):LinkedIn Learning provides a variety of courses on digital marketing, with a focus on skill development. Courses cover SEO, content marketing, email marketing, and more.
Semrush Academy:Semrush, a tool for SEO and online visibility management, provides a certification program covering the use of their platform as well as broader digital marketing topics.
Content Marketing Institute (CMI):CMI offers a content marketing certification program that covers content strategy, creation, and distribution. It's ideal for professionals looking to specialize in content marketing.
Simplilearn:Simplilearn offers a variety of digital marketing courses and certification programs. They cover topics like SEO, social media, pay-per-click (PPC), and digital strategy.
Microsoft Advertising Certification:Microsoft Advertising offers a certification program covering their advertising platform. It includes topics such as search engine marketing (SEM), display advertising, and analytics.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Career Goals
Embarking on a journey to choose the right digital marketing certification is a crucial step in shaping a successful career in the ever-evolving landscape of online marketing. To navigate this decision effectively, it's essential to align your certification choice with your unique career goals and aspirations within the diverse field of digital marketing.
As you delve into the myriad of certification options available, carefully research the specializations offered by each program. Certifications often cater to specific aspects of digital marketing, and understanding the content focus will help you pinpoint the most relevant and impactful certification for your chosen path. Platforms like Facebook Blueprint or Hootsuite Academy may be particularly beneficial for those seeking expertise in social media marketing, while broader certifications from reputable providers like Google Digital Garage cover a spectrum of digital marketing disciplines.
Consider the industry recognition and reputation of the certification programs under consideration. Opting for certifications from well-established providers, such as Google Digital Garage, HubSpot, or Digital Marketing Institute, can enhance your credibility in the eyes of potential employers. A certification's standing within the industry is a valuable asset, opening doors to opportunities and signaling a commitment to excellence in the field.
Evaluate the structure and format of the certification programs to ensure they align with your preferred learning style and schedule. Whether you thrive in self-paced online courses or prefer the structure of live sessions, choosing a format that suits your needs is crucial for a successful learning experience. Additionally, assess whether the program incorporates practical, hands-on components, as these can significantly enhance your ability to apply learned skills in real-world scenarios.
Certification levels also play a pivotal role in the decision-making process. Some programs offer different levels, catering to individuals at various stages of their careers. Assess your current skill level and opt for a certification that matches your expertise, with the flexibility to progress to more advanced levels as you gain experience.
Budget constraints and accessibility are practical considerations that should not be overlooked. While some certifications, such as those from Google Digital Garage, offer free courses, others may involve costs. Ensure that the chosen certification aligns with your budget and is accessible in terms of time commitment and scheduling.
By thoughtfully considering these factors, you can make a well-informed decision when choosing the right digital marketing certification for your career goals. Remember that the certification you select should not only enhance your skill set but also align with your professional aspirations, setting the stage for a fulfilling and successful career in digital marketing.
Examining the Curriculum
Examining the curriculum of a digital marketing certification program is a critical step in ensuring that the educational content aligns with your learning objectives and professional aspirations. Begin by exploring the breadth and depth of the topics covered within the program. A well-rounded curriculum should encompass key aspects of digital marketing, including search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, email marketing, content strategy, and analytics.
Delve into the specifics of each module to understand the depth of coverage. For instance, in SEO, examine whether the curriculum addresses both on-page and off-page optimization techniques, keyword research strategies, and the latest trends in search engine algorithms. Similarly, in social media marketing, assess whether the program covers platforms comprehensively, explores paid advertising strategies, and includes insights into audience engagement and analytics.
In summary, scrutinizing the curriculum of a digital marketing certification program is a meticulous process that involves assessing the comprehensiveness, practicality, currency, flexibility, and continuous learning aspects of the educational content. By ensuring that the curriculum aligns with your specific learning objectives and industry demands, you can make an informed decision that propels you toward a successful and fulfilling career in digital marketing.
Certification Levels and Specializations
Understanding the certification levels and specializations within digital marketing is crucial for professionals seeking to tailor their learning experience to their specific career goals and expertise. Digital marketing certification programs often offer different levels of proficiency and opportunities for specialization to cater to the diverse needs of learners.
Certification levels typically range from foundational or beginner to intermediate and advanced. These levels are designed to accommodate individuals at different stages of their careers, ensuring that the content is relevant to their knowledge and experience. Beginners may start with foundational certifications, covering essential concepts and strategies, while experienced marketers may pursue advanced certifications that delve into intricate, specialized areas.
Foundational certifications often introduce learners to the fundamental principles of digital marketing. This may include an overview of key channels such as SEO, social media, email marketing, and basic analytics. These certifications provide a solid understanding of the digital marketing landscape, making them suitable for newcomers or those looking to establish a broad foundation.
Intermediate certifications build upon the foundational knowledge and delve deeper into specific areas of digital marketing. Learners may choose to specialize in disciplines like content marketing, paid advertising, or social media strategy. These certifications aim to enhance expertise in targeted domains while maintaining a comprehensive view of the broader digital marketing ecosystem.
When selecting a digital marketing certification, it's essential to consider both the certification level and any available specializations. Assess your current skill level, career aspirations, and the areas of digital marketing that align with your interests. Choosing a program that offers the right combination of certification level and specialization will ensure a tailored learning experience that adds significant value to your professional journey.
Industry Recognition and Credibility
Industry recognition and credibility are paramount considerations when selecting a digital marketing certification, as these factors play a pivotal role in how your qualifications are perceived by employers, clients, and peers within the competitive landscape of digital marketing. A certification from a recognized and respected institution enhances your professional standing and can open doors to opportunities within the industry.
One key aspect of industry recognition is the reputation of the certification provider. Certifications from well-established and reputable organizations are more likely to be acknowledged and valued by employers. Recognized providers, such as Google Digital Garage, HubSpot, and Digital Marketing Institute, have a track record of delivering high-quality content and staying abreast of industry trends.
Employers often use industry-recognized certifications as a benchmark for evaluating the skills and expertise of candidates. Having a certification from a reputable institution can serve as a tangible demonstration of your commitment to continuous learning and professional development. It provides assurance to employers that you possess a standardized set of skills and knowledge, which is particularly important in a field as dynamic as digital marketing.
Ultimately, the goal is to choose a digital marketing certification that not only imparts valuable knowledge but also holds weight in the eyes of employers and peers. Industry recognition and credibility are powerful assets that can boost your career prospects, increase your employability, and position you as a credible and competent digital marketing professional within the competitive landscape of the industry.
Online vs In-Person Certification Programs
The choice between online and in-person certification programs in digital marketing is a significant decision that depends on various factors, including personal preferences, learning styles, and logistical considerations.
Online Certification Programs:
Flexibility: One of the primary advantages of online certification programs is the flexibility they offer. Learners can access course materials at their own pace and schedule, making it suitable for individuals with varying commitments such as full-time jobs or other responsibilities.
Accessibility: Online programs provide access to a global pool of resources and instructors. Learners can engage with content from industry experts and connect with peers from around the world, fostering a diverse learning environment.
Cost-Effectiveness: Online programs often have lower tuition costs compared to in-person options. Additionally, learners can save on travel, accommodation, and other expenses associated with attending in-person classes.
Diverse Learning Formats: Online programs often incorporate a variety of multimedia elements, such as video lectures, interactive quizzes, and discussion forums, catering to different learning styles.
In-Person Certification Programs:
Real-Time Interaction: In-person programs provide the opportunity for immediate interaction with instructors and fellow learners. This can facilitate a more dynamic learning experience with real-time feedback and discussions.
Structured Learning Environment: Classroom settings offer a structured learning environment with set schedules, which can be beneficial for individuals who thrive in a more regimented and organized setting.
Networking Opportunities: In-person programs provide valuable networking opportunities. Engaging with instructors and classmates face-to-face can lead to meaningful professional connections and collaborations.
Hands-On Experience: Some in-person programs incorporate hands-on activities, workshops, and group projects that may be challenging to replicate in an online format.
Ultimately, the choice between online and in-person certification programs depends on individual preferences, lifestyle, and learning preferences. Some learners may thrive in the flexibility of online programs, while others may benefit more from the structure and personal interaction offered by in-person options. Consider your own learning style, time constraints, and budget when making this decision.
Practical Application and Real-World Projects
Integrating practical application and real-world projects into a digital marketing certification program is a cornerstone in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This hands-on approach serves as a catalyst for a more immersive and impactful learning experience, offering learners the opportunity to directly apply acquired concepts in scenarios reflective of the challenges encountered in professional digital marketing environments.
Real-world projects, such as case studies, play a pivotal role in grounding learners in the complexities of the digital marketing landscape. By dissecting and solving actual business challenges, learners gain a nuanced understanding of how theoretical concepts manifest in practical situations. This process not only reinforces theoretical knowledge but also hones problem-solving skills, preparing individuals to navigate the dynamic and ever-evolving field of digital marketing.
Hands-on exercises, ranging from creating and optimizing digital campaigns to analyzing performance metrics, offer learners tangible experiences that mirror the tasks they will encounter in real-world professional settings. These exercises not only develop technical proficiency but also instill a sense of confidence in learners as they apply their knowledge to concrete, actionable projects.
In summary, the inclusion of practical application and real-world projects in a digital marketing certification program is more than a supplement to theoretical learning; it is a cornerstone for cultivating a holistic and industry-ready skill set. These experiences not only prepare learners for the demands of the professional realm but also empower them to confidently navigate the multifaceted landscape of digital marketing upon completion of their certification.
Cost and Time Considerations
Considering the cost and time implications of a digital marketing certification program is crucial for individuals seeking to strike a balance between their educational aspirations, budget constraints, and personal commitments. Both factors play significant roles in shaping the overall feasibility and effectiveness of the certification journey.
Cost Considerations:The cost of a digital marketing certification program varies widely based on factors such as the institution, the level of the certification, and the inclusion of additional features like real-world projects or instructor-led sessions. Some certifications, like those offered by Google Digital Garage, are available for free, providing an accessible entry point for learners on a budget. On the other hand, certifications from well-known institutions or those with specialized content may come with a higher price tag.
In addition to tuition fees, learners should factor in potential additional costs such as study materials, textbooks, or software tools that may be required for the program. Travel expenses, particularly for in-person programs, should also be considered, as attending physical classes or workshops may incur additional costs.
Time Considerations:The time required to complete a digital marketing certification program can vary based on factors such as the level of the certification, the learning format (self-paced or instructor-led), and the individual learner's pace. Some certifications can be completed in a matter of weeks, while others may take several months.
Self-paced online programs offer flexibility in terms of scheduling, allowing learners to balance certification studies with other commitments such as work or family responsibilities. In contrast, in-person or live online programs with fixed schedules may require a more structured time commitment.
Balancing Cost and Time:Ultimately, finding the right balance between cost and time requires careful consideration of personal circumstances and educational goals. While a more affordable program may suit a tight budget, learners should ensure that it still meets their learning objectives and provides a reputable certification. Similarly, an intensive program that demands significant time commitments may be worthwhile for those seeking a comprehensive and immersive learning experience.
Before committing to a digital marketing certification program, individuals should thoroughly research the program's cost structure, available resources, and time requirements. This informed approach ensures that learners can make a strategic investment in their professional development, aligning their educational choices with both budgetary constraints and career aspirations.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Exploring success stories and testimonials is a valuable step in assessing the impact and effectiveness of a digital marketing certification program. Learning from the experiences of individuals who have completed the program provides insights into the tangible benefits, career advancements, and transformative outcomes that others have achieved. Success stories and testimonials offer a glimpse into the real-world impact of the certification on professional journeys.
Gaining Insight into Real-World Application: Success stories often highlight how individuals have applied the knowledge and skills acquired through the certification in their professional roles. These narratives provide concrete examples of how the certification program translated theoretical concepts into practical solutions, campaigns, or strategies within the dynamic field of digital marketing.
Understanding Career Progression: Testimonials frequently shed light on the career progression of individuals who completed the certification. They may detail how the certification acted as a catalyst for job promotions, career transitions, or enhanced job responsibilities. Such insights offer a tangible understanding of the certification's role in career development and marketability within the industry.
Identifying Diverse Perspectives: Testimonials come from a diverse range of individuals with varied backgrounds, experiences, and career goals. Examining testimonials from professionals with different profiles can provide a holistic view of the certification program's applicability across various industry sectors and roles.
Validating Program Quality: Success stories and testimonials serve as endorsements of the program's quality and effectiveness. Positive feedback from those who have successfully navigated the certification adds credibility to the program's curriculum, instructors, and overall educational approach.
Before enrolling in a digital marketing certification program, individuals should actively seek out success stories and testimonials on official program websites, forums, or professional networking platforms. Analyzing these narratives enables prospective learners to make informed decisions based on the real-world experiences of their peers and validates the potential impact of the certification on their own professional journey.
Maintaining Certification Relevance in a Changing Landscape
Maintaining the relevance of a digital marketing certification in a constantly evolving landscape is a critical consideration for both certification providers and professionals seeking to stay abreast of industry advancements. The field of digital marketing is dynamic, with technology, consumer behaviors, and platforms undergoing frequent changes. Ensuring that certification programs adapt to these changes is essential for professionals to acquire skills that align with current industry demands.
Integration of practical, hands-on experiences is another crucial element. Real-world projects, case studies, and simulations should mirror the challenges professionals face in contemporary digital marketing roles. This not only enhances the practical application of knowledge but also ensures that the skills gained are directly transferable to the current industry landscape.
Establishing partnerships with industry leaders and organizations can also contribute to certification relevance. Collaboration with companies at the forefront of digital marketing ensures that certification programs are informed by real-world practices and insights. Industry partnerships can facilitate access to cutting-edge tools, case studies, and expertise that enhance the overall quality and relevance of the certification.
In summary, maintaining certification relevance in the ever-changing digital marketing landscape requires a proactive and adaptive approach. Certification providers must commit to regular updates, modular learning structures, practical experiences, community engagement, industry partnerships, and feedback mechanisms. Simultaneously, professionals should embrace a mindset of continuous learning, leveraging these certification programs as a foundation for ongoing professional development in the dynamic world of digital marketing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of digital marketing is marked by its constant evolution, with technologies, trends, and consumer behaviors continuously shaping the industry's landscape. The pursuit of a digital marketing certification is not merely a one-time achievement but a commitment to ongoing learning and adaptation. As professionals seek to navigate this dynamic environment, choosing a certification program that prioritizes relevance and adaptability is paramount.
Certification providers play a pivotal role in maintaining the currency and effectiveness of their programs. By regularly updating content, embracing modular learning structures, integrating practical experiences, fostering a culture of continuous learning, establishing industry partnerships, and actively seeking feedback from professionals, certification providers can ensure that their offerings remain at the forefront of the digital marketing field.
Read More
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital marketing, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for professionals aspiring to make a mark in the industry. Digital marketing certification programs have emerged as invaluable tools for individuals seeking to enhance their skills, validate their expertise, and gain a competitive edge in the job market. In this comprehensive overview, we'll delve into the world of digital marketing certifications, exploring the myriad options available and shedding light on the significance of these programs in today's dynamic business environment.
Digital marketing certifications encompass a diverse range of modules, each designed to cover essential aspects of online marketing, from search engine optimization (SEO) and social media marketing to analytics and content strategy. These programs not only serve as structured learning paths but also provide a standardized means of assessment, ensuring that certified professionals possess a well-rounded understanding of the multifaceted realm of digital marketing.
This overview will guide you through the considerations involved in choosing a certification program, whether you're a seasoned professional looking to upskill or a newcomer eager to establish a foothold in the industry. From exploring the content and structure of popular certification courses to understanding the broader implications of being certified, this series aims to be your go-to resource for navigating the diverse landscape of digital marketing certifications. Join us on this journey as we unravel the opportunities, challenges, and transformative potential of digital marketing certification programs.
Table of contents
-
Key Digital Marketing Certification Providers
-
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Career Goals
-
Examining the Curriculum
-
Certification Levels and Specializations
-
Industry Recognition and Credibility
-
Online vs In-Person Certification Programs
-
Practical Application and Real-World Projects
-
Cost and Time Considerations
-
Success Stories and Testimonials
-
Maintaining Certification Relevance in a Changing Landscape
-
Conclusion
Key Digital Marketing Certification Providers
In the dynamic landscape of digital marketing, several reputable certification providers offer comprehensive programs designed to equip professionals with the skills needed to thrive in the ever-evolving online space. Here are key digital marketing certification providers
Google Digital Garage:Google offers a range of free courses through its Digital Garage platform. Courses cover various aspects of digital marketing, including search engine optimization (SEO), social media, and analytics.
HubSpot Academy:HubSpot provides a comprehensive set of free certification courses on inbound marketing, content marketing, social media strategy, and more. Their certifications are well-regarded in the marketing community.
LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com):LinkedIn Learning provides a variety of courses on digital marketing, with a focus on skill development. Courses cover SEO, content marketing, email marketing, and more.
Semrush Academy:Semrush, a tool for SEO and online visibility management, provides a certification program covering the use of their platform as well as broader digital marketing topics.
Content Marketing Institute (CMI):CMI offers a content marketing certification program that covers content strategy, creation, and distribution. It's ideal for professionals looking to specialize in content marketing.
Simplilearn:Simplilearn offers a variety of digital marketing courses and certification programs. They cover topics like SEO, social media, pay-per-click (PPC), and digital strategy.
Microsoft Advertising Certification:Microsoft Advertising offers a certification program covering their advertising platform. It includes topics such as search engine marketing (SEM), display advertising, and analytics.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Career Goals
Embarking on a journey to choose the right digital marketing certification is a crucial step in shaping a successful career in the ever-evolving landscape of online marketing. To navigate this decision effectively, it's essential to align your certification choice with your unique career goals and aspirations within the diverse field of digital marketing.
As you delve into the myriad of certification options available, carefully research the specializations offered by each program. Certifications often cater to specific aspects of digital marketing, and understanding the content focus will help you pinpoint the most relevant and impactful certification for your chosen path. Platforms like Facebook Blueprint or Hootsuite Academy may be particularly beneficial for those seeking expertise in social media marketing, while broader certifications from reputable providers like Google Digital Garage cover a spectrum of digital marketing disciplines.
Consider the industry recognition and reputation of the certification programs under consideration. Opting for certifications from well-established providers, such as Google Digital Garage, HubSpot, or Digital Marketing Institute, can enhance your credibility in the eyes of potential employers. A certification's standing within the industry is a valuable asset, opening doors to opportunities and signaling a commitment to excellence in the field.
Evaluate the structure and format of the certification programs to ensure they align with your preferred learning style and schedule. Whether you thrive in self-paced online courses or prefer the structure of live sessions, choosing a format that suits your needs is crucial for a successful learning experience. Additionally, assess whether the program incorporates practical, hands-on components, as these can significantly enhance your ability to apply learned skills in real-world scenarios.
Certification levels also play a pivotal role in the decision-making process. Some programs offer different levels, catering to individuals at various stages of their careers. Assess your current skill level and opt for a certification that matches your expertise, with the flexibility to progress to more advanced levels as you gain experience.
Budget constraints and accessibility are practical considerations that should not be overlooked. While some certifications, such as those from Google Digital Garage, offer free courses, others may involve costs. Ensure that the chosen certification aligns with your budget and is accessible in terms of time commitment and scheduling.
By thoughtfully considering these factors, you can make a well-informed decision when choosing the right digital marketing certification for your career goals. Remember that the certification you select should not only enhance your skill set but also align with your professional aspirations, setting the stage for a fulfilling and successful career in digital marketing.
Examining the Curriculum
Examining the curriculum of a digital marketing certification program is a critical step in ensuring that the educational content aligns with your learning objectives and professional aspirations. Begin by exploring the breadth and depth of the topics covered within the program. A well-rounded curriculum should encompass key aspects of digital marketing, including search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, email marketing, content strategy, and analytics.
Delve into the specifics of each module to understand the depth of coverage. For instance, in SEO, examine whether the curriculum addresses both on-page and off-page optimization techniques, keyword research strategies, and the latest trends in search engine algorithms. Similarly, in social media marketing, assess whether the program covers platforms comprehensively, explores paid advertising strategies, and includes insights into audience engagement and analytics.
In summary, scrutinizing the curriculum of a digital marketing certification program is a meticulous process that involves assessing the comprehensiveness, practicality, currency, flexibility, and continuous learning aspects of the educational content. By ensuring that the curriculum aligns with your specific learning objectives and industry demands, you can make an informed decision that propels you toward a successful and fulfilling career in digital marketing.
Certification Levels and Specializations
Understanding the certification levels and specializations within digital marketing is crucial for professionals seeking to tailor their learning experience to their specific career goals and expertise. Digital marketing certification programs often offer different levels of proficiency and opportunities for specialization to cater to the diverse needs of learners.
Certification levels typically range from foundational or beginner to intermediate and advanced. These levels are designed to accommodate individuals at different stages of their careers, ensuring that the content is relevant to their knowledge and experience. Beginners may start with foundational certifications, covering essential concepts and strategies, while experienced marketers may pursue advanced certifications that delve into intricate, specialized areas.
Foundational certifications often introduce learners to the fundamental principles of digital marketing. This may include an overview of key channels such as SEO, social media, email marketing, and basic analytics. These certifications provide a solid understanding of the digital marketing landscape, making them suitable for newcomers or those looking to establish a broad foundation.
Intermediate certifications build upon the foundational knowledge and delve deeper into specific areas of digital marketing. Learners may choose to specialize in disciplines like content marketing, paid advertising, or social media strategy. These certifications aim to enhance expertise in targeted domains while maintaining a comprehensive view of the broader digital marketing ecosystem.
When selecting a digital marketing certification, it's essential to consider both the certification level and any available specializations. Assess your current skill level, career aspirations, and the areas of digital marketing that align with your interests. Choosing a program that offers the right combination of certification level and specialization will ensure a tailored learning experience that adds significant value to your professional journey.
Industry Recognition and Credibility
Industry recognition and credibility are paramount considerations when selecting a digital marketing certification, as these factors play a pivotal role in how your qualifications are perceived by employers, clients, and peers within the competitive landscape of digital marketing. A certification from a recognized and respected institution enhances your professional standing and can open doors to opportunities within the industry.
One key aspect of industry recognition is the reputation of the certification provider. Certifications from well-established and reputable organizations are more likely to be acknowledged and valued by employers. Recognized providers, such as Google Digital Garage, HubSpot, and Digital Marketing Institute, have a track record of delivering high-quality content and staying abreast of industry trends.
Employers often use industry-recognized certifications as a benchmark for evaluating the skills and expertise of candidates. Having a certification from a reputable institution can serve as a tangible demonstration of your commitment to continuous learning and professional development. It provides assurance to employers that you possess a standardized set of skills and knowledge, which is particularly important in a field as dynamic as digital marketing.
Ultimately, the goal is to choose a digital marketing certification that not only imparts valuable knowledge but also holds weight in the eyes of employers and peers. Industry recognition and credibility are powerful assets that can boost your career prospects, increase your employability, and position you as a credible and competent digital marketing professional within the competitive landscape of the industry.
Online vs In-Person Certification Programs
The choice between online and in-person certification programs in digital marketing is a significant decision that depends on various factors, including personal preferences, learning styles, and logistical considerations.
Online Certification Programs:
Flexibility: One of the primary advantages of online certification programs is the flexibility they offer. Learners can access course materials at their own pace and schedule, making it suitable for individuals with varying commitments such as full-time jobs or other responsibilities.
Accessibility: Online programs provide access to a global pool of resources and instructors. Learners can engage with content from industry experts and connect with peers from around the world, fostering a diverse learning environment.
Cost-Effectiveness: Online programs often have lower tuition costs compared to in-person options. Additionally, learners can save on travel, accommodation, and other expenses associated with attending in-person classes.
Diverse Learning Formats: Online programs often incorporate a variety of multimedia elements, such as video lectures, interactive quizzes, and discussion forums, catering to different learning styles.
In-Person Certification Programs:
Real-Time Interaction: In-person programs provide the opportunity for immediate interaction with instructors and fellow learners. This can facilitate a more dynamic learning experience with real-time feedback and discussions.
Structured Learning Environment: Classroom settings offer a structured learning environment with set schedules, which can be beneficial for individuals who thrive in a more regimented and organized setting.
Networking Opportunities: In-person programs provide valuable networking opportunities. Engaging with instructors and classmates face-to-face can lead to meaningful professional connections and collaborations.
Hands-On Experience: Some in-person programs incorporate hands-on activities, workshops, and group projects that may be challenging to replicate in an online format.
Ultimately, the choice between online and in-person certification programs depends on individual preferences, lifestyle, and learning preferences. Some learners may thrive in the flexibility of online programs, while others may benefit more from the structure and personal interaction offered by in-person options. Consider your own learning style, time constraints, and budget when making this decision.
Practical Application and Real-World Projects
Integrating practical application and real-world projects into a digital marketing certification program is a cornerstone in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This hands-on approach serves as a catalyst for a more immersive and impactful learning experience, offering learners the opportunity to directly apply acquired concepts in scenarios reflective of the challenges encountered in professional digital marketing environments.
Real-world projects, such as case studies, play a pivotal role in grounding learners in the complexities of the digital marketing landscape. By dissecting and solving actual business challenges, learners gain a nuanced understanding of how theoretical concepts manifest in practical situations. This process not only reinforces theoretical knowledge but also hones problem-solving skills, preparing individuals to navigate the dynamic and ever-evolving field of digital marketing.
Hands-on exercises, ranging from creating and optimizing digital campaigns to analyzing performance metrics, offer learners tangible experiences that mirror the tasks they will encounter in real-world professional settings. These exercises not only develop technical proficiency but also instill a sense of confidence in learners as they apply their knowledge to concrete, actionable projects.
In summary, the inclusion of practical application and real-world projects in a digital marketing certification program is more than a supplement to theoretical learning; it is a cornerstone for cultivating a holistic and industry-ready skill set. These experiences not only prepare learners for the demands of the professional realm but also empower them to confidently navigate the multifaceted landscape of digital marketing upon completion of their certification.
Cost and Time Considerations
Considering the cost and time implications of a digital marketing certification program is crucial for individuals seeking to strike a balance between their educational aspirations, budget constraints, and personal commitments. Both factors play significant roles in shaping the overall feasibility and effectiveness of the certification journey.
Cost Considerations:The cost of a digital marketing certification program varies widely based on factors such as the institution, the level of the certification, and the inclusion of additional features like real-world projects or instructor-led sessions. Some certifications, like those offered by Google Digital Garage, are available for free, providing an accessible entry point for learners on a budget. On the other hand, certifications from well-known institutions or those with specialized content may come with a higher price tag.
In addition to tuition fees, learners should factor in potential additional costs such as study materials, textbooks, or software tools that may be required for the program. Travel expenses, particularly for in-person programs, should also be considered, as attending physical classes or workshops may incur additional costs.
Time Considerations:The time required to complete a digital marketing certification program can vary based on factors such as the level of the certification, the learning format (self-paced or instructor-led), and the individual learner's pace. Some certifications can be completed in a matter of weeks, while others may take several months.
Self-paced online programs offer flexibility in terms of scheduling, allowing learners to balance certification studies with other commitments such as work or family responsibilities. In contrast, in-person or live online programs with fixed schedules may require a more structured time commitment.
Balancing Cost and Time:Ultimately, finding the right balance between cost and time requires careful consideration of personal circumstances and educational goals. While a more affordable program may suit a tight budget, learners should ensure that it still meets their learning objectives and provides a reputable certification. Similarly, an intensive program that demands significant time commitments may be worthwhile for those seeking a comprehensive and immersive learning experience.
Before committing to a digital marketing certification program, individuals should thoroughly research the program's cost structure, available resources, and time requirements. This informed approach ensures that learners can make a strategic investment in their professional development, aligning their educational choices with both budgetary constraints and career aspirations.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Exploring success stories and testimonials is a valuable step in assessing the impact and effectiveness of a digital marketing certification program. Learning from the experiences of individuals who have completed the program provides insights into the tangible benefits, career advancements, and transformative outcomes that others have achieved. Success stories and testimonials offer a glimpse into the real-world impact of the certification on professional journeys.
Gaining Insight into Real-World Application: Success stories often highlight how individuals have applied the knowledge and skills acquired through the certification in their professional roles. These narratives provide concrete examples of how the certification program translated theoretical concepts into practical solutions, campaigns, or strategies within the dynamic field of digital marketing.
Understanding Career Progression: Testimonials frequently shed light on the career progression of individuals who completed the certification. They may detail how the certification acted as a catalyst for job promotions, career transitions, or enhanced job responsibilities. Such insights offer a tangible understanding of the certification's role in career development and marketability within the industry.
Identifying Diverse Perspectives: Testimonials come from a diverse range of individuals with varied backgrounds, experiences, and career goals. Examining testimonials from professionals with different profiles can provide a holistic view of the certification program's applicability across various industry sectors and roles.
Validating Program Quality: Success stories and testimonials serve as endorsements of the program's quality and effectiveness. Positive feedback from those who have successfully navigated the certification adds credibility to the program's curriculum, instructors, and overall educational approach.
Before enrolling in a digital marketing certification program, individuals should actively seek out success stories and testimonials on official program websites, forums, or professional networking platforms. Analyzing these narratives enables prospective learners to make informed decisions based on the real-world experiences of their peers and validates the potential impact of the certification on their own professional journey.
Maintaining Certification Relevance in a Changing Landscape
Maintaining the relevance of a digital marketing certification in a constantly evolving landscape is a critical consideration for both certification providers and professionals seeking to stay abreast of industry advancements. The field of digital marketing is dynamic, with technology, consumer behaviors, and platforms undergoing frequent changes. Ensuring that certification programs adapt to these changes is essential for professionals to acquire skills that align with current industry demands.
Integration of practical, hands-on experiences is another crucial element. Real-world projects, case studies, and simulations should mirror the challenges professionals face in contemporary digital marketing roles. This not only enhances the practical application of knowledge but also ensures that the skills gained are directly transferable to the current industry landscape.
Establishing partnerships with industry leaders and organizations can also contribute to certification relevance. Collaboration with companies at the forefront of digital marketing ensures that certification programs are informed by real-world practices and insights. Industry partnerships can facilitate access to cutting-edge tools, case studies, and expertise that enhance the overall quality and relevance of the certification.
In summary, maintaining certification relevance in the ever-changing digital marketing landscape requires a proactive and adaptive approach. Certification providers must commit to regular updates, modular learning structures, practical experiences, community engagement, industry partnerships, and feedback mechanisms. Simultaneously, professionals should embrace a mindset of continuous learning, leveraging these certification programs as a foundation for ongoing professional development in the dynamic world of digital marketing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of digital marketing is marked by its constant evolution, with technologies, trends, and consumer behaviors continuously shaping the industry's landscape. The pursuit of a digital marketing certification is not merely a one-time achievement but a commitment to ongoing learning and adaptation. As professionals seek to navigate this dynamic environment, choosing a certification program that prioritizes relevance and adaptability is paramount.
Certification providers play a pivotal role in maintaining the currency and effectiveness of their programs. By regularly updating content, embracing modular learning structures, integrating practical experiences, fostering a culture of continuous learning, establishing industry partnerships, and actively seeking feedback from professionals, certification providers can ensure that their offerings remain at the forefront of the digital marketing field.
ISO 20000 Basics: Essential Insights You Need to Know Today
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, effective IT service management is crucial for businesses to stay competitive, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and ensure the smooth operation of their IT services. One framework that has gained prominence in this regard is ISO 20000.
ISO 20000 is an internationally recognized standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). It provides a set of best practices and guidelines for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their ITSM system. This standard is designed to ensure that IT services meet the needs of the organization and its customers, while also complying with regulatory and quality requirements.
Over the course of this blog series, we will delve deeper into these components, explore best practices, and provide insights into achieving ISO 20000 certification.
Whether you're an IT professional, a business owner, or simply someone interested in IT service management, understanding ISO 20000 is invaluable in today's technology-driven world. It's a path to ensuring that IT services are not just reliable but also a strategic asset for your organization.
Stay tuned as we explore the principles, benefits, and practical steps towards implementing ISO 20000 IT Service Management. The journey begins here.
Table of contents
-
The Origins of ISO 20000
-
The Importance of Standardization
-
Key Principles of ISO 20000
-
ISO 20000 vs. Other ITSM Frameworks
-
Benefits of ISO 20000
-
The Structure of ISO 20000
-
Certification Process
-
Common Misconceptions about ISO 20000
-
ISO 20000 in Different Industries
-
Case Studies and Success Stories
-
Conclusion
The Origins of ISO 20000
The Origins of ISO 20000: From ITIL to Global Standard
ISO 20000, formally known as ISO/IEC 20000, is an international standard that has its roots in the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) and the need for global consistency in IT service management practices.
ITIL and the Need for Standardization
The story of ISO 20000 begins with ITIL, a set of best practices for IT service management that originated in the United Kingdom in the 1980s. ITIL was developed by the UK government in response to a lack of standardization and structure in IT service management practices. ITIL provided a framework for organizations to better manage their IT services, with a focus on aligning IT with business needs, improving service quality, and increasing efficiency.
ITIL gained widespread acceptance and was adopted by organizations worldwide. It became the de facto framework for IT service management, and its popularity spurred the need for an international standard that would ensure consistency and quality in IT service management practices across the globe.
The Path to ISO 20000
The journey towards ISO 20000 can be summarized in the following key milestones:
BS 15000: The first significant step toward international standardization was the development of the British Standard BS 15000. Published in 2000, BS 15000 was essentially a formalization of ITIL concepts into a national standard. This standard laid the groundwork for what would later become ISO 20000.
ISO/IEC 20000-1 and -2: The international standardization process began with the collaboration of several international standards bodies. ISO/IEC 20000 was published in 2005, comprising two parts: Part 1 specifies the requirements for IT service management, while Part 2 provides guidance on the application of Part 1. These standards were developed to provide a globally accepted framework for IT service management.
ISO 20000-2018: The standard has seen updates and revisions over the years, with ISO 20000:2018 being the most recent version as of my last knowledge update in September 2021. This revision refined and expanded the standard to align with modern IT service management practices and principles.
Why ISO 20000 Matters
ISO 20000 is vital because it brings a unified approach to IT service management, which is especially crucial in today's globally interconnected business environment. It provides a framework that organizations can use to ensure that their IT services are reliable, efficient, and meet both customer and regulatory requirements.
In summary, ISO 20000's origins can be traced back to the need for standardization in IT service management, stemming from the success of ITIL. It has since evolved into an internationally recognized standard, helping organizations worldwide improve their IT service delivery and achieve operational excellence. As IT continues to be a critical component of modern business operations, ISO 20000's relevance and importance continue to grow.
The Importance of Standardization
In the ever-evolving world of information technology, where innovation and change are constant, standardization plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficiency, quality, and reliability of IT services. Standardization is particularly crucial in the realm of IT Service Management (ITSM), and ISO 20000 is a prime example of how it contributes to excellence. Let's delve into the significance of standardization in ITSM:
Consistency and Predictability: Standardization establishes a set of consistent processes, procedures, and best practices. In the context of ITSM, this consistency ensures that IT services are delivered in a predictable manner. Customers and stakeholders can rely on consistent service quality, which fosters trust and confidence.
Improved Efficiency: Standardized processes eliminate redundancy and confusion in IT service delivery. This, in turn, leads to improved efficiency, as employees can follow well-defined procedures, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks.
Quality Assurance: Quality control is a fundamental aspect of standardization. By adhering to established standards and best practices, organizations can consistently deliver high-quality IT services. Standardization helps identify and address potential quality issues proactively.
Risk Management: Standardization aids in risk management by identifying and mitigating potential risks in IT service delivery. By following standardized processes and procedures, organizations can reduce the likelihood of errors and vulnerabilities that might negatively impact services.
Scalability: Standardized processes can be scaled more easily. As organizations grow or adapt to changing circumstances, they can expand their IT service operations efficiently by replicating established standards and processes.
Knowledge Sharing: Standardized processes and best practices make it easier for employees to share knowledge and collaborate. This contributes to a culture of continuous improvement and learning within the organization.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that adhere to internationally recognized standards like ISO 20000 gain a competitive advantage. They can demonstrate their commitment to quality and best practices, which can be a selling point for customers and partners.
In the realm of ITSM, ISO 20000 exemplifies the importance of standardization by providing a globally recognized framework for IT service management. It empowers organizations to align their IT services with business objectives, deliver consistent quality, and remain adaptable in a rapidly changing IT landscape.
In summary, standardization in IT Service Management is essential for achieving operational excellence, meeting customer expectations, and managing risk. ISO 20000's global acceptance underscores the importance of adhering to best practices and standards to ensure that IT services are a strategic asset for organizations in today's technology-driven world.
Key Principles of ISO 20000
Certainly, ISO 20000 is built upon several key principles that guide IT Service Management (ITSM) practices. These principles provide a foundation for organizations seeking to implement ISO 20000 and improve their IT services. Here are the key principles of ISO 20000:
Customer Focus: ISO 20000 places a strong emphasis on meeting customer needs and delivering services that align with the organization's overall business objectives. It requires IT service providers to understand and prioritize customer requirements and expectations.
Leadership and Commitment: The commitment of top management is crucial for the successful implementation of ISO 20000. Leaders within the organization must support and drive the ITSM initiatives, setting the tone for a culture of service excellence.
Process Approach: ISO 20000 promotes a process-driven approach to ITSM. This means defining, documenting, and consistently following well-defined processes and procedures to manage IT services effectively.
Improvement: Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of ISO 20000. Organizations are encouraged to regularly monitor and measure their ITSM processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to enhance service quality.
Supplier Management: ISO 20000 acknowledges the role of suppliers and service providers in the delivery of IT services. It emphasizes the importance of managing and monitoring supplier relationships to ensure they meet service requirements.
Service Level Management: This principle underscores the need to define, agree upon, and manage service level agreements (SLAs) with customers. It involves setting clear expectations for service quality, availability, and performance.
Documentation and Records: Proper documentation and record-keeping are vital for demonstrating compliance with ISO 20000 requirements. This principle ensures that organizations maintain accurate records of their ITSM processes and activities.
These key principles provide a holistic framework for IT service management that is not only aligned with customer needs but also focused on continuous improvement and accountability. Organizations that adhere to these principles are better positioned to deliver high-quality IT services that drive business success and customer satisfaction.
ISO 20000 vs. Other ITSM Frameworks
IT Service Management (ITSM) is critical for organizations to deliver efficient and high-quality IT services. To achieve this, various ITSM frameworks and standards have been developed, each with its own approach and methodologies. ISO 20000 is one such standard, but how does it compare to other well-known ITSM frameworks like ITIL and COBIT? Let's explore the key differences and similarities in this comparative analysis:
ISO 20000: The International Standard
Focus: ISO 20000 is an international standard that specifies requirements for ITSM. It emphasizes process-driven IT service delivery, compliance, and continual improvement.
Certification: ISO 20000 provides a certification process for organizations to demonstrate compliance with the standard.
Flexibility: ISO 20000 is more flexible in terms of implementation, allowing organizations to adapt the standard to their specific needs.
ITIL: The IT Service Management Framework
Focus: ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a comprehensive framework of best practices for ITSM. It offers guidance on managing various IT services and processes.
Certification: ITIL offers certification at different levels to individuals and organizations, demonstrating expertise in ITSM best practices.
Comprehensive: ITIL covers a wide range of ITSM topics, making it suitable for organizations seeking detailed guidance on specific processes and functions.
COBIT: The IT Governance and Management Framework
Focus: COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is focused on IT governance and management, including ITSM. It addresses not only IT processes but also risk management, compliance, and aligning IT with business goals.
Certification: COBIT certification is available, although it's less common compared to ITIL and ISO 20000.
Holistic: COBIT provides a holistic framework that combines ITSM with broader governance and management aspects, making it suitable for organizations concerned with overall IT governance.
The choice between ISO 20000, ITIL, or COBIT depends on an organization's specific needs, goals, and the level of detail and scope required for its ITSM and governance initiatives. Each framework has its strengths and is valuable in its own right, making it essential for organizations to assess their unique circumstances before making a decision.
Benefits of ISO 20000
ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), offers numerous benefits to organizations that choose to adopt and implement it. These benefits extend to improving IT service quality, aligning IT with business goals, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. Here are the key benefits of ISO 20000:
Enhanced Service Quality: ISO 20000 provides a structured framework for managing IT services, ensuring consistent service quality. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as enhanced user experiences.
Operational Efficiency: ISO 20000 promotes the adoption of best practices and streamlined processes. This leads to increased operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower costs associated with IT service delivery.
Risk Management: ISO 20000 helps organizations identify and manage risks related to IT service delivery. This proactive approach to risk management ensures business continuity and minimizes potential disruptions.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): ISO 20000 helps organizations define, agree upon, and manage SLAs with customers. This means clear expectations for service quality, availability, and performance, which contributes to customer satisfaction.
Clear Documentation and Records: Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential components of ISO 20000. This promotes transparency, accountability, and the ability to demonstrate compliance with the standard.
Global Recognition: ISO 20000 is internationally recognized and accepted. Achieving ISO 20000 certification can boost an organization's reputation, enhance its competitive advantage, and open up new business opportunities.
In summary, ISO 20000 offers a structured and internationally recognized framework for organizations to improve their IT service management. By implementing ISO 20000, organizations can achieve higher service quality, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and risk management, while aligning IT with business goals and complying with relevant regulations. This can lead to a competitive edge and enhanced overall performance.
The Structure of ISO 20000
The International Standard ISO/IEC 20000, which defines the requirements for IT Service Management (ITSM), is structured into multiple parts and sections to provide comprehensive guidance. As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, the standard consists of several parts. Please note that standards may be subject to updates and revisions, so it's essential to consult the latest version for precise details. Here's an overview of the typical structure of ISO 20000:
ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 - Service management system requirements:
Terms and Definitions: Defines key terms and concepts used throughout the standard to ensure clarity and consistency.
Leadership: Explains the role of leadership in the SMS, emphasizing the need for commitment and support from top management.
Planning: Discusses the planning requirements for the SMS, including risk management, objectives, and how to achieve them.
Support: Describes the resources and support required for the SMS to operate effectively, including competence, awareness, communication, and documented information.
Operation: Details the processes and activities needed to deliver and manage IT services, including service design and transition, service delivery, and relationship management.
Performance Evaluation: Covers the monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation of the SMS, including internal audits, management review, and performance indicators.
Improvement: Focuses on the continual improvement of the SMS, including non-conformities, corrective actions, preventive actions, and enhancement of the SMS.
ISO/IEC 20000-2 - Guidance on the application of service management systems:
This part offers additional guidance on how to apply the requirements outlined in ISO 20000-1. It provides practical insights, examples, and explanations to help organizations implement and maintain their Service Management System.
ISO/IEC 20000-3 - Guidance on scope definition and applicability of ISO/IEC 20000-1:
This part provides guidance on determining the scope of the Service Management System and the applicability of ISO 20000-1 within an organization.
ISO/IEC 20000-4 - Process Reference Model:
This part presents a reference model for ITSM processes. It outlines and describes the various ITSM processes that can be included in an SMS.
ISO/IEC 20000-5 - Exemplar implementation plan:
This part offers an exemplar implementation plan to help organizations understand the steps and activities involved in implementing ISO 20000.
Each part and section within ISO 20000 is designed to provide organizations with the guidance and requirements needed to establish and maintain a robust IT Service Management System. It offers a flexible framework that can be adapted to an organization's specific needs and requirements. To ensure compliance and effective implementation, it's essential to consult the latest version of the standard and consider working with experts in IT Service Management.
Certification Process
The certification process for ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), involves a series of steps to demonstrate an organization's compliance with the standard's requirements. ISO 20000 certification is a valuable recognition of an organization's commitment to delivering high-quality IT services. Here are the typical steps in the ISO 20000 certification process:
Preliminary Gap Analysis:Before embarking on the certification process, it's often helpful to conduct a preliminary gap analysis. This analysis identifies the existing state of your ITSM practices compared to the requirements of ISO 20000. It helps you understand the areas that require improvement or adjustments.
Establish the Service Management System (SMS):ISO 20000 requires organizations to establish a Service Management System. This involves developing the necessary documentation, processes, and procedures to meet the standard's requirements. The SMS serves as the framework for IT service management within your organization.
Training and Awareness:Ensure that your staff is aware of the ISO 20000 standard and its requirements. Training may be necessary to equip your team with the knowledge and skills needed to implement and maintain the SMS effectively.
Documentation:Create and maintain the documentation required by ISO 20000. This includes developing policies, procedures, work instructions, and records related to IT service management. Documentation is essential to demonstrate compliance.
Implementation:Implement the SMS within your organization, aligning your ITSM practices with the requirements of ISO 20000. Ensure that the processes and procedures are operational and being followed.
Internal Audit:Conduct internal audits to evaluate the effectiveness of your SMS and identify areas for improvement. Internal audits help you uncover non-conformities and assess your readiness for external certification.
Certification Body Selection:Choose an accredited certification body to conduct the external audit and certification. Ensure that the certification body is recognized and accredited by relevant authorities.
External Certification Audit:The certification body will perform an external audit of your SMS to verify compliance with ISO 20000. This audit may include a review of documentation, interviews with personnel, and on-site assessments.
Certification Decision:Based on the findings of the external audit, the certification body will make a certification decision. If your organization has demonstrated compliance with ISO 20000, you will receive ISO 20000 certification.
ISO 20000 certification is a rigorous process that demonstrates an organization's commitment to excellence in ITSM. It not only enhances the quality of IT services but also builds trust with customers, stakeholders, and partners. Certification is typically valid for a defined period, after which organizations must undergo surveillance audits to maintain certification.
Common Misconceptions about ISO 20000
ISO 20000, as the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), is a valuable framework for improving IT service quality, efficiency, and compliance. However, like many standards, it is subject to misconceptions and misunderstandings. Here are some common misconceptions about ISO 20000:
ISO 20000 is Only for Large Enterprises:
Misconception: Some believe that ISO 20000 is suitable only for large enterprises with extensive IT resources and budgets.
Reality: ISO 20000 is scalable and can be implemented by organizations of all sizes, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It can be adapted to suit an organization's specific needs and resources.
ISO 20000 is Too Complex:
Misconception: It is often assumed that ISO 20000's requirements are overly complex and challenging to implement.
Reality: While ISO 20000 is comprehensive, it can be tailored to an organization's needs. Its complexity depends on the organization's existing ITSM practices. It's possible to implement ISO 20000 incrementally and gradually.
ISO 20000 is All About Documentation:
Misconception: Some think ISO 20000 is primarily about generating extensive documentation.
Reality: While documentation is an important component, ISO 20000 places more emphasis on process implementation and effectiveness. Documentation supports the implementation of processes and helps ensure their consistency.
ISO 20000 is Only About ITIL:
Misconception: ISO 20000 is often confused with ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library). People think they are one and the same.
Reality: While ITIL can be a valuable reference for implementing ISO 20000, the standard is not limited to ITIL and can be adapted to various ITSM frameworks or customized to an organization's specific needs.
ISO 20000 Guarantees Perfect IT Services:
Misconception: Some believe that ISO 20000 certification guarantees flawless IT services.
Reality: ISO 20000 helps improve service quality and consistency, but it doesn't eliminate the possibility of issues or disruptions. It provides a framework for addressing and mitigating such incidents.
ISO 20000 is Only for the IT Department:
Misconception: Some view ISO 20000 as solely the responsibility of the IT department.
Reality: ISO 20000 requires cross-functional involvement and alignment with the organization's business objectives. It impacts the entire organization, as IT services are integral to overall business operations.
Understanding and dispelling these misconceptions is essential for organizations considering ISO 20000 implementation. ISO 20000 can be a valuable asset for improving IT service management, and its benefits are attainable with proper planning and commitment.
ISO 20000 in Different Industries
ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), is applicable to a wide range of industries, as effective IT service management is a fundamental need in today's technology-driven world. Here's how ISO 20000 can benefit different industries:
Information Technology (IT) Industry:In the IT industry, ISO 20000 helps IT service providers optimize their service management processes, ensuring efficient service delivery and improved customer satisfaction. It aligns IT services with business goals and enhances overall service quality.
Healthcare Industry:Healthcare organizations often rely heavily on IT systems for patient care, record-keeping, and operational efficiency. ISO 20000 can help healthcare providers ensure the reliability and security of their IT services, leading to better patient care and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Financial Services Industry:The financial sector depends on IT services for secure and efficient transactions, data management, and customer service. ISO 20000 can help financial organizations ensure the integrity and availability of their IT systems, reducing operational risks.
Government and Public Sector:Government agencies use IT services to deliver essential public services. ISO 20000 can help ensure that these services are efficient, cost-effective, and compliant with regulatory requirements, enhancing citizen satisfaction.
Education Industry:Educational institutions rely on IT services for administrative functions, e-learning, and research. ISO 20000 can help schools and universities improve the availability and performance of their IT services, ultimately benefiting students and faculty.
Retail Industry:Retailers use IT services for inventory management, e-commerce, and customer service. ISO 20000 can help retailers optimize their IT systems, providing customers with a seamless shopping experience.
Telecommunications Industry:Telecommunication companies provide essential IT services for communication and connectivity. ISO 20000 can help them deliver high-quality, uninterrupted services to customers.
various industries. Regardless of the sector, organizations can benefit from implementing ISO 20000 by optimizing IT service management, enhancing service quality, aligning IT with business objectives, and ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. The specific ways in which ISO 20000 is applied may vary by industry, but the core principles of effective IT service management remain consistent.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Certainly, case studies and success stories can provide valuable insights into how organizations have benefited from implementing ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). Here are a few examples of case studies and success stories related to ISO 20000:
A Large Financial Services Company:This financial services company implemented ISO 20000 to enhance its ITSM practices. By doing so, it achieved improved service quality, reduced downtime, and increased customer satisfaction. ISO 20000 helped the company streamline its IT processes, align IT services with business goals, and minimize IT-related risks.
A Healthcare Provider:A healthcare provider adopted ISO 20000 to optimize its IT services, ensuring that patient data was secure, and IT systems were reliable. ISO 20000 helped the organization maintain compliance with healthcare regulations, streamline IT processes, and deliver high-quality patient care.
An Educational Institution:An educational institution implemented ISO 20000 to improve its IT services for students, faculty, and administrative staff. The institution saw enhanced performance of its e-learning platforms, reduced service disruptions, and greater overall satisfaction among students and faculty.
A Government Agency:A government agency adopted ISO 20000 to enhance the delivery of public services. By improving the efficiency and reliability of its IT services, the agency increased citizen satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and met regulatory requirements more effectively.
A Telecommunications Company:A telecommunications company implemented ISO 20000 to ensure the availability and reliability of its communication services. The adoption of ISO 20000 led to reduced network downtime, improved customer experiences, and a competitive edge in the telecommunications market.
These case studies and success stories illustrate the broad applicability of ISO 20000 across diverse industries. They demonstrate how organizations have leveraged ISO 20000 to improve IT service quality, align IT with business objectives, and gain a competitive advantage. Whether it's a financial services firm, a healthcare provider, an educational institution, a government agency, or a telecommunications company, ISO 20000 has proven to be a valuable framework for optimizing IT service management and delivering better services to customers and stakeholders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management, is a versatile and valuable framework that can benefit organizations across various industries. Its structured approach to IT service management ensures consistent service quality, alignment with business goals, and compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
ISO 20000 is not limited to large enterprises but can be adapted and implemented by organizations of all sizes. It's a dynamic standard that promotes continuous improvement, emphasizing the importance of monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation in response to changing customer needs and technological advancements.
Through ISO 20000, organizations can enhance their IT service delivery, reduce downtime, manage risks, and improve customer satisfaction. It's a tool that encourages cross-functional collaboration, as it acknowledges that IT services impact all aspects of an organization, not just the IT department.
Ultimately, ISO 20000 offers a structured path to achieving excellence in IT service management. By implementing its principles and practices, organizations can enhance their competitiveness, reduce operational risks, and ensure that IT services are a strategic asset for their overall business success.
Read More
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, effective IT service management is crucial for businesses to stay competitive, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and ensure the smooth operation of their IT services. One framework that has gained prominence in this regard is ISO 20000.
ISO 20000 is an internationally recognized standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). It provides a set of best practices and guidelines for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their ITSM system. This standard is designed to ensure that IT services meet the needs of the organization and its customers, while also complying with regulatory and quality requirements.
Over the course of this blog series, we will delve deeper into these components, explore best practices, and provide insights into achieving ISO 20000 certification.
Whether you're an IT professional, a business owner, or simply someone interested in IT service management, understanding ISO 20000 is invaluable in today's technology-driven world. It's a path to ensuring that IT services are not just reliable but also a strategic asset for your organization.
Stay tuned as we explore the principles, benefits, and practical steps towards implementing ISO 20000 IT Service Management. The journey begins here.
Table of contents
-
The Origins of ISO 20000
-
The Importance of Standardization
-
Key Principles of ISO 20000
-
ISO 20000 vs. Other ITSM Frameworks
-
Benefits of ISO 20000
-
The Structure of ISO 20000
-
Certification Process
-
Common Misconceptions about ISO 20000
-
ISO 20000 in Different Industries
-
Case Studies and Success Stories
-
Conclusion
The Origins of ISO 20000
The Origins of ISO 20000: From ITIL to Global Standard
ISO 20000, formally known as ISO/IEC 20000, is an international standard that has its roots in the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) and the need for global consistency in IT service management practices.
ITIL and the Need for Standardization
The story of ISO 20000 begins with ITIL, a set of best practices for IT service management that originated in the United Kingdom in the 1980s. ITIL was developed by the UK government in response to a lack of standardization and structure in IT service management practices. ITIL provided a framework for organizations to better manage their IT services, with a focus on aligning IT with business needs, improving service quality, and increasing efficiency.
ITIL gained widespread acceptance and was adopted by organizations worldwide. It became the de facto framework for IT service management, and its popularity spurred the need for an international standard that would ensure consistency and quality in IT service management practices across the globe.
The Path to ISO 20000
The journey towards ISO 20000 can be summarized in the following key milestones:
BS 15000: The first significant step toward international standardization was the development of the British Standard BS 15000. Published in 2000, BS 15000 was essentially a formalization of ITIL concepts into a national standard. This standard laid the groundwork for what would later become ISO 20000.
ISO/IEC 20000-1 and -2: The international standardization process began with the collaboration of several international standards bodies. ISO/IEC 20000 was published in 2005, comprising two parts: Part 1 specifies the requirements for IT service management, while Part 2 provides guidance on the application of Part 1. These standards were developed to provide a globally accepted framework for IT service management.
ISO 20000-2018: The standard has seen updates and revisions over the years, with ISO 20000:2018 being the most recent version as of my last knowledge update in September 2021. This revision refined and expanded the standard to align with modern IT service management practices and principles.
Why ISO 20000 Matters
ISO 20000 is vital because it brings a unified approach to IT service management, which is especially crucial in today's globally interconnected business environment. It provides a framework that organizations can use to ensure that their IT services are reliable, efficient, and meet both customer and regulatory requirements.
In summary, ISO 20000's origins can be traced back to the need for standardization in IT service management, stemming from the success of ITIL. It has since evolved into an internationally recognized standard, helping organizations worldwide improve their IT service delivery and achieve operational excellence. As IT continues to be a critical component of modern business operations, ISO 20000's relevance and importance continue to grow.
The Importance of Standardization
In the ever-evolving world of information technology, where innovation and change are constant, standardization plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficiency, quality, and reliability of IT services. Standardization is particularly crucial in the realm of IT Service Management (ITSM), and ISO 20000 is a prime example of how it contributes to excellence. Let's delve into the significance of standardization in ITSM:
Consistency and Predictability: Standardization establishes a set of consistent processes, procedures, and best practices. In the context of ITSM, this consistency ensures that IT services are delivered in a predictable manner. Customers and stakeholders can rely on consistent service quality, which fosters trust and confidence.
Improved Efficiency: Standardized processes eliminate redundancy and confusion in IT service delivery. This, in turn, leads to improved efficiency, as employees can follow well-defined procedures, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks.
Quality Assurance: Quality control is a fundamental aspect of standardization. By adhering to established standards and best practices, organizations can consistently deliver high-quality IT services. Standardization helps identify and address potential quality issues proactively.
Risk Management: Standardization aids in risk management by identifying and mitigating potential risks in IT service delivery. By following standardized processes and procedures, organizations can reduce the likelihood of errors and vulnerabilities that might negatively impact services.
Scalability: Standardized processes can be scaled more easily. As organizations grow or adapt to changing circumstances, they can expand their IT service operations efficiently by replicating established standards and processes.
Knowledge Sharing: Standardized processes and best practices make it easier for employees to share knowledge and collaborate. This contributes to a culture of continuous improvement and learning within the organization.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that adhere to internationally recognized standards like ISO 20000 gain a competitive advantage. They can demonstrate their commitment to quality and best practices, which can be a selling point for customers and partners.
In the realm of ITSM, ISO 20000 exemplifies the importance of standardization by providing a globally recognized framework for IT service management. It empowers organizations to align their IT services with business objectives, deliver consistent quality, and remain adaptable in a rapidly changing IT landscape.
In summary, standardization in IT Service Management is essential for achieving operational excellence, meeting customer expectations, and managing risk. ISO 20000's global acceptance underscores the importance of adhering to best practices and standards to ensure that IT services are a strategic asset for organizations in today's technology-driven world.
Key Principles of ISO 20000
Certainly, ISO 20000 is built upon several key principles that guide IT Service Management (ITSM) practices. These principles provide a foundation for organizations seeking to implement ISO 20000 and improve their IT services. Here are the key principles of ISO 20000:
Customer Focus: ISO 20000 places a strong emphasis on meeting customer needs and delivering services that align with the organization's overall business objectives. It requires IT service providers to understand and prioritize customer requirements and expectations.
Leadership and Commitment: The commitment of top management is crucial for the successful implementation of ISO 20000. Leaders within the organization must support and drive the ITSM initiatives, setting the tone for a culture of service excellence.
Process Approach: ISO 20000 promotes a process-driven approach to ITSM. This means defining, documenting, and consistently following well-defined processes and procedures to manage IT services effectively.
Improvement: Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of ISO 20000. Organizations are encouraged to regularly monitor and measure their ITSM processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to enhance service quality.
Supplier Management: ISO 20000 acknowledges the role of suppliers and service providers in the delivery of IT services. It emphasizes the importance of managing and monitoring supplier relationships to ensure they meet service requirements.
Service Level Management: This principle underscores the need to define, agree upon, and manage service level agreements (SLAs) with customers. It involves setting clear expectations for service quality, availability, and performance.
Documentation and Records: Proper documentation and record-keeping are vital for demonstrating compliance with ISO 20000 requirements. This principle ensures that organizations maintain accurate records of their ITSM processes and activities.
These key principles provide a holistic framework for IT service management that is not only aligned with customer needs but also focused on continuous improvement and accountability. Organizations that adhere to these principles are better positioned to deliver high-quality IT services that drive business success and customer satisfaction.
ISO 20000 vs. Other ITSM Frameworks
IT Service Management (ITSM) is critical for organizations to deliver efficient and high-quality IT services. To achieve this, various ITSM frameworks and standards have been developed, each with its own approach and methodologies. ISO 20000 is one such standard, but how does it compare to other well-known ITSM frameworks like ITIL and COBIT? Let's explore the key differences and similarities in this comparative analysis:
ISO 20000: The International Standard
Focus: ISO 20000 is an international standard that specifies requirements for ITSM. It emphasizes process-driven IT service delivery, compliance, and continual improvement.
Certification: ISO 20000 provides a certification process for organizations to demonstrate compliance with the standard.
Flexibility: ISO 20000 is more flexible in terms of implementation, allowing organizations to adapt the standard to their specific needs.
ITIL: The IT Service Management Framework
Focus: ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a comprehensive framework of best practices for ITSM. It offers guidance on managing various IT services and processes.
Certification: ITIL offers certification at different levels to individuals and organizations, demonstrating expertise in ITSM best practices.
Comprehensive: ITIL covers a wide range of ITSM topics, making it suitable for organizations seeking detailed guidance on specific processes and functions.
COBIT: The IT Governance and Management Framework
Focus: COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is focused on IT governance and management, including ITSM. It addresses not only IT processes but also risk management, compliance, and aligning IT with business goals.
Certification: COBIT certification is available, although it's less common compared to ITIL and ISO 20000.
Holistic: COBIT provides a holistic framework that combines ITSM with broader governance and management aspects, making it suitable for organizations concerned with overall IT governance.
The choice between ISO 20000, ITIL, or COBIT depends on an organization's specific needs, goals, and the level of detail and scope required for its ITSM and governance initiatives. Each framework has its strengths and is valuable in its own right, making it essential for organizations to assess their unique circumstances before making a decision.
Benefits of ISO 20000
ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), offers numerous benefits to organizations that choose to adopt and implement it. These benefits extend to improving IT service quality, aligning IT with business goals, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. Here are the key benefits of ISO 20000:
Enhanced Service Quality: ISO 20000 provides a structured framework for managing IT services, ensuring consistent service quality. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as enhanced user experiences.
Operational Efficiency: ISO 20000 promotes the adoption of best practices and streamlined processes. This leads to increased operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower costs associated with IT service delivery.
Risk Management: ISO 20000 helps organizations identify and manage risks related to IT service delivery. This proactive approach to risk management ensures business continuity and minimizes potential disruptions.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): ISO 20000 helps organizations define, agree upon, and manage SLAs with customers. This means clear expectations for service quality, availability, and performance, which contributes to customer satisfaction.
Clear Documentation and Records: Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential components of ISO 20000. This promotes transparency, accountability, and the ability to demonstrate compliance with the standard.
Global Recognition: ISO 20000 is internationally recognized and accepted. Achieving ISO 20000 certification can boost an organization's reputation, enhance its competitive advantage, and open up new business opportunities.
In summary, ISO 20000 offers a structured and internationally recognized framework for organizations to improve their IT service management. By implementing ISO 20000, organizations can achieve higher service quality, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and risk management, while aligning IT with business goals and complying with relevant regulations. This can lead to a competitive edge and enhanced overall performance.
The Structure of ISO 20000
The International Standard ISO/IEC 20000, which defines the requirements for IT Service Management (ITSM), is structured into multiple parts and sections to provide comprehensive guidance. As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, the standard consists of several parts. Please note that standards may be subject to updates and revisions, so it's essential to consult the latest version for precise details. Here's an overview of the typical structure of ISO 20000:
ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 - Service management system requirements:
Terms and Definitions: Defines key terms and concepts used throughout the standard to ensure clarity and consistency.
Leadership: Explains the role of leadership in the SMS, emphasizing the need for commitment and support from top management.
Planning: Discusses the planning requirements for the SMS, including risk management, objectives, and how to achieve them.
Support: Describes the resources and support required for the SMS to operate effectively, including competence, awareness, communication, and documented information.
Operation: Details the processes and activities needed to deliver and manage IT services, including service design and transition, service delivery, and relationship management.
Performance Evaluation: Covers the monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation of the SMS, including internal audits, management review, and performance indicators.
Improvement: Focuses on the continual improvement of the SMS, including non-conformities, corrective actions, preventive actions, and enhancement of the SMS.
ISO/IEC 20000-2 - Guidance on the application of service management systems:
This part offers additional guidance on how to apply the requirements outlined in ISO 20000-1. It provides practical insights, examples, and explanations to help organizations implement and maintain their Service Management System.
ISO/IEC 20000-3 - Guidance on scope definition and applicability of ISO/IEC 20000-1:
This part provides guidance on determining the scope of the Service Management System and the applicability of ISO 20000-1 within an organization.
ISO/IEC 20000-4 - Process Reference Model:
This part presents a reference model for ITSM processes. It outlines and describes the various ITSM processes that can be included in an SMS.
ISO/IEC 20000-5 - Exemplar implementation plan:
This part offers an exemplar implementation plan to help organizations understand the steps and activities involved in implementing ISO 20000.
Each part and section within ISO 20000 is designed to provide organizations with the guidance and requirements needed to establish and maintain a robust IT Service Management System. It offers a flexible framework that can be adapted to an organization's specific needs and requirements. To ensure compliance and effective implementation, it's essential to consult the latest version of the standard and consider working with experts in IT Service Management.
Certification Process
The certification process for ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), involves a series of steps to demonstrate an organization's compliance with the standard's requirements. ISO 20000 certification is a valuable recognition of an organization's commitment to delivering high-quality IT services. Here are the typical steps in the ISO 20000 certification process:
Preliminary Gap Analysis:Before embarking on the certification process, it's often helpful to conduct a preliminary gap analysis. This analysis identifies the existing state of your ITSM practices compared to the requirements of ISO 20000. It helps you understand the areas that require improvement or adjustments.
Establish the Service Management System (SMS):ISO 20000 requires organizations to establish a Service Management System. This involves developing the necessary documentation, processes, and procedures to meet the standard's requirements. The SMS serves as the framework for IT service management within your organization.
Training and Awareness:Ensure that your staff is aware of the ISO 20000 standard and its requirements. Training may be necessary to equip your team with the knowledge and skills needed to implement and maintain the SMS effectively.
Documentation:Create and maintain the documentation required by ISO 20000. This includes developing policies, procedures, work instructions, and records related to IT service management. Documentation is essential to demonstrate compliance.
Implementation:Implement the SMS within your organization, aligning your ITSM practices with the requirements of ISO 20000. Ensure that the processes and procedures are operational and being followed.
Internal Audit:Conduct internal audits to evaluate the effectiveness of your SMS and identify areas for improvement. Internal audits help you uncover non-conformities and assess your readiness for external certification.
Certification Body Selection:Choose an accredited certification body to conduct the external audit and certification. Ensure that the certification body is recognized and accredited by relevant authorities.
External Certification Audit:The certification body will perform an external audit of your SMS to verify compliance with ISO 20000. This audit may include a review of documentation, interviews with personnel, and on-site assessments.
Certification Decision:Based on the findings of the external audit, the certification body will make a certification decision. If your organization has demonstrated compliance with ISO 20000, you will receive ISO 20000 certification.
ISO 20000 certification is a rigorous process that demonstrates an organization's commitment to excellence in ITSM. It not only enhances the quality of IT services but also builds trust with customers, stakeholders, and partners. Certification is typically valid for a defined period, after which organizations must undergo surveillance audits to maintain certification.
Common Misconceptions about ISO 20000
ISO 20000, as the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), is a valuable framework for improving IT service quality, efficiency, and compliance. However, like many standards, it is subject to misconceptions and misunderstandings. Here are some common misconceptions about ISO 20000:
ISO 20000 is Only for Large Enterprises:
Misconception: Some believe that ISO 20000 is suitable only for large enterprises with extensive IT resources and budgets.
Reality: ISO 20000 is scalable and can be implemented by organizations of all sizes, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It can be adapted to suit an organization's specific needs and resources.
ISO 20000 is Too Complex:
Misconception: It is often assumed that ISO 20000's requirements are overly complex and challenging to implement.
Reality: While ISO 20000 is comprehensive, it can be tailored to an organization's needs. Its complexity depends on the organization's existing ITSM practices. It's possible to implement ISO 20000 incrementally and gradually.
ISO 20000 is All About Documentation:
Misconception: Some think ISO 20000 is primarily about generating extensive documentation.
Reality: While documentation is an important component, ISO 20000 places more emphasis on process implementation and effectiveness. Documentation supports the implementation of processes and helps ensure their consistency.
ISO 20000 is Only About ITIL:
Misconception: ISO 20000 is often confused with ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library). People think they are one and the same.
Reality: While ITIL can be a valuable reference for implementing ISO 20000, the standard is not limited to ITIL and can be adapted to various ITSM frameworks or customized to an organization's specific needs.
ISO 20000 Guarantees Perfect IT Services:
Misconception: Some believe that ISO 20000 certification guarantees flawless IT services.
Reality: ISO 20000 helps improve service quality and consistency, but it doesn't eliminate the possibility of issues or disruptions. It provides a framework for addressing and mitigating such incidents.
ISO 20000 is Only for the IT Department:
Misconception: Some view ISO 20000 as solely the responsibility of the IT department.
Reality: ISO 20000 requires cross-functional involvement and alignment with the organization's business objectives. It impacts the entire organization, as IT services are integral to overall business operations.
Understanding and dispelling these misconceptions is essential for organizations considering ISO 20000 implementation. ISO 20000 can be a valuable asset for improving IT service management, and its benefits are attainable with proper planning and commitment.
ISO 20000 in Different Industries
ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM), is applicable to a wide range of industries, as effective IT service management is a fundamental need in today's technology-driven world. Here's how ISO 20000 can benefit different industries:
Information Technology (IT) Industry:In the IT industry, ISO 20000 helps IT service providers optimize their service management processes, ensuring efficient service delivery and improved customer satisfaction. It aligns IT services with business goals and enhances overall service quality.
Healthcare Industry:Healthcare organizations often rely heavily on IT systems for patient care, record-keeping, and operational efficiency. ISO 20000 can help healthcare providers ensure the reliability and security of their IT services, leading to better patient care and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Financial Services Industry:The financial sector depends on IT services for secure and efficient transactions, data management, and customer service. ISO 20000 can help financial organizations ensure the integrity and availability of their IT systems, reducing operational risks.
Government and Public Sector:Government agencies use IT services to deliver essential public services. ISO 20000 can help ensure that these services are efficient, cost-effective, and compliant with regulatory requirements, enhancing citizen satisfaction.
Education Industry:Educational institutions rely on IT services for administrative functions, e-learning, and research. ISO 20000 can help schools and universities improve the availability and performance of their IT services, ultimately benefiting students and faculty.
Retail Industry:Retailers use IT services for inventory management, e-commerce, and customer service. ISO 20000 can help retailers optimize their IT systems, providing customers with a seamless shopping experience.
Telecommunications Industry:Telecommunication companies provide essential IT services for communication and connectivity. ISO 20000 can help them deliver high-quality, uninterrupted services to customers.
various industries. Regardless of the sector, organizations can benefit from implementing ISO 20000 by optimizing IT service management, enhancing service quality, aligning IT with business objectives, and ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. The specific ways in which ISO 20000 is applied may vary by industry, but the core principles of effective IT service management remain consistent.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Certainly, case studies and success stories can provide valuable insights into how organizations have benefited from implementing ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). Here are a few examples of case studies and success stories related to ISO 20000:
A Large Financial Services Company:This financial services company implemented ISO 20000 to enhance its ITSM practices. By doing so, it achieved improved service quality, reduced downtime, and increased customer satisfaction. ISO 20000 helped the company streamline its IT processes, align IT services with business goals, and minimize IT-related risks.
A Healthcare Provider:A healthcare provider adopted ISO 20000 to optimize its IT services, ensuring that patient data was secure, and IT systems were reliable. ISO 20000 helped the organization maintain compliance with healthcare regulations, streamline IT processes, and deliver high-quality patient care.
An Educational Institution:An educational institution implemented ISO 20000 to improve its IT services for students, faculty, and administrative staff. The institution saw enhanced performance of its e-learning platforms, reduced service disruptions, and greater overall satisfaction among students and faculty.
A Government Agency:A government agency adopted ISO 20000 to enhance the delivery of public services. By improving the efficiency and reliability of its IT services, the agency increased citizen satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and met regulatory requirements more effectively.
A Telecommunications Company:A telecommunications company implemented ISO 20000 to ensure the availability and reliability of its communication services. The adoption of ISO 20000 led to reduced network downtime, improved customer experiences, and a competitive edge in the telecommunications market.
These case studies and success stories illustrate the broad applicability of ISO 20000 across diverse industries. They demonstrate how organizations have leveraged ISO 20000 to improve IT service quality, align IT with business objectives, and gain a competitive advantage. Whether it's a financial services firm, a healthcare provider, an educational institution, a government agency, or a telecommunications company, ISO 20000 has proven to be a valuable framework for optimizing IT service management and delivering better services to customers and stakeholders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ISO 20000, the international standard for IT Service Management, is a versatile and valuable framework that can benefit organizations across various industries. Its structured approach to IT service management ensures consistent service quality, alignment with business goals, and compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
ISO 20000 is not limited to large enterprises but can be adapted and implemented by organizations of all sizes. It's a dynamic standard that promotes continuous improvement, emphasizing the importance of monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation in response to changing customer needs and technological advancements.
Through ISO 20000, organizations can enhance their IT service delivery, reduce downtime, manage risks, and improve customer satisfaction. It's a tool that encourages cross-functional collaboration, as it acknowledges that IT services impact all aspects of an organization, not just the IT department.
Ultimately, ISO 20000 offers a structured path to achieving excellence in IT service management. By implementing its principles and practices, organizations can enhance their competitiveness, reduce operational risks, and ensure that IT services are a strategic asset for their overall business success.
Understanding COBIT 5 Foundation: A Comprehensive Overview
In the ever-evolving landscape of information technology, effective governance and management are paramount for organizations to thrive and succeed. One framework that stands out in this context is COBIT 5 Foundation. COBIT, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a globally recognized framework designed to help organizations govern and manage their IT effectively.
COBIT has a rich history of evolution, adapting to the changing needs of the IT industry. From its inception to the present COBIT 5 Foundation, it has become a standard bearer for organizations seeking to align their IT strategies with their business goals. This framework provides a structured approach to IT governance and management, ensuring that enterprises can achieve optimal outcomes and manage risks effectively.
Whether you're new to COBIT 5 or looking to refresh your understanding, this comprehensive overview aims to be your guide to mastering the core concepts and practical applications of COBIT 5 Foundation. So, let's begin our exploration of COBIT 5 Foundation and its role in shaping the future of IT governance.
Table of contents
-
Historical Evolution of COBIT
-
COBIT 5 Framework Components
-
Key Concepts in COBIT 5
-
Benefits of Implementing COBIT 5 Foundation
-
COBIT 5 Principles
-
COBIT 5 Domains
-
COBIT 5 Process Reference Model
-
COBIT 5 Enablers
-
COBIT 5 Implementation Challenges
-
Real-Life Examples of COBIT 5 Success Stories
-
Conclusion
Historical Evolution of COBIT
The historical evolution of COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is a fascinating journey that showcases its development from a simple set of IT control objectives into a globally recognized framework for IT governance and management. Let's take a closer look at the key milestones in the history of COBIT:
COBIT 1.0 (1996): COBIT was initially introduced by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) in 1996 as a set of IT control objectives to help organizations manage their IT processes and risks. This first version provided a basic structure for IT governance.
COBIT 2.0 (1998): The framework was updated in 1998 as COBIT 2.0. This version included a more comprehensive set of control objectives, making it a valuable tool for IT audit and control professionals.
COBIT 3.0 (2000): In the year 2000, COBIT 3.0 was released with a significant expansion in scope. This version integrated IT governance and management practices, helping organizations align IT with business goals more effectively.
COBIT 4.0 (2005): COBIT 4.0 introduced the concept of domains, processes, and IT-related goals, making it more structured and easier to apply in organizations. It was a pivotal step toward broader acceptance.
COBIT 4.1 (2007): This version, released in 2007, brought some refinements and updates to COBIT 4.0, making it more practical for implementation in real-world scenarios.
COBIT 5.0 Updates (2019): In 2019, COBIT was updated to further align with the evolving IT landscape and address contemporary challenges. This update included guidance on digital transformation and emerging technologies.
The historical evolution of COBIT reflects the changing landscape of IT governance, from a focus on control objectives to a comprehensive framework for aligning IT with business strategy, managing risks, and achieving operational excellence.
COBIT 5 Framework Components
The COBIT 5 framework consists of several key components, each of which plays a crucial role in helping organizations govern and manage their information and technology effectively. Understanding these components is essential for implementing COBIT 5 successfully. Here are the main components of the COBIT 5 framework:
Principles:
Meeting Stakeholder Needs: The first principle of COBIT 5 emphasizes the importance of aligning IT with the needs and expectations of stakeholders, whether they are internal or external to the organization.
Applying a Single Integrated Framework: COBIT 5 promotes the use of a single integrated framework to harmonize and simplify the governance of IT.
Enablers:
Processes: COBIT 5 defines a set of governance and management processes that help organizations achieve their objectives. These processes cover areas such as risk management, resource management, and performance management.
Principles, Policies, and Frameworks: These enablers provide the foundation for governance and management. They include the principles mentioned earlier, as well as policies, standards, and guidelines.
Information: Information is a key enabler, and COBIT 5 provides guidance on managing and optimizing the use of information in decision-making processes.
Services, Infrastructure, and Applications: These enablers relate to the physical and logical resources required to deliver IT services.
Governance and Management Processes:
COBIT 5 defines a comprehensive set of governance and management processes that organizations can use to align their IT with business goals, manage risks, and deliver value. Some of the processes include:
Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM) processes: These processes are primarily related to governance activities.
Align, Plan, and Organize (APO) processes: These processes focus on strategic planning and organizational structure.
Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA) processes: These processes assess the effectiveness of governance and management.
COBIT 5 Framework Model:
The COBIT 5 framework model provides a graphical representation of the principles, enablers, and processes, helping organizations visualize how they interact and support the achievement of objectives.
These components work together to provide a structured and holistic approach to IT governance and management. COBIT 5's principles guide decision-making, the enablers provide the resources and tools, and the governance and management processes offer a practical roadmap for implementation. By leveraging these components effectively, organizations can improve their IT practices, mitigate risks, and deliver value to stakeholders
Key Concepts in COBIT 5
COBIT 5, a comprehensive framework for governing and managing enterprise IT, is built upon several key concepts that are fundamental to understanding and implementing the framework effectively. Here are the key concepts in COBIT 5:
Governance and Management: COBIT 5 distinguishes between governance and management. Governance is primarily concerned with decision-making and ensuring that IT aligns with business goals. Management, on the other hand, involves the execution of those decisions and the day-to-day operation of IT processes.
End-to-End Coverage: COBIT 5 advocates for a holistic approach to IT governance, covering all aspects of the enterprise. It's not limited to specific processes or departments; rather, it spans the entire organization.
Framework for the Governance and Management of Enterprise IT: COBIT 5 provides a structured framework that encompasses IT governance and management practices. This framework offers a systematic approach to achieving organizational goals.
Enabler: Enablers in COBIT 5 are the factors that facilitate or support the implementation of governance and management. These include processes, principles, policies, organizational structures, culture, ethics, and behavior, among others.
Principles: COBIT 5 is guided by seven key principles:
Meeting Stakeholder Needs
Covering the Enterprise End-to-End
Separating Governance from Management
Tailoring to the Enterprise
Implementing a Governance System
Domains: COBIT 5 defines four domains, each encompassing a set of processes and activities:
Lifecycle Approach: COBIT 5 advocates for a lifecycle approach to IT governance and management, emphasizing that governance and management are continuous and cyclical processes rather than one-time events.
Information Governance: Information is a critical asset in IT governance, and COBIT 5 underscores the importance of effectively managing and using information in decision-making processes.
Understanding these key concepts in COBIT 5 is essential for organizations looking to enhance their IT governance and management practices. These concepts provide the foundation for implementing the framework and aligning IT with business objectives while meeting the needs of various stakeholders.
Benefits of Implementing COBIT 5 Foundation
Implementing COBIT 5 Foundation can bring a wide range of benefits to organizations. Here are some of the key advantages of adopting the COBIT 5 framework for IT governance and management:
Enhanced IT Governance: COBIT 5 provides a structured and holistic approach to IT governance, helping organizations make informed decisions and align IT strategies with business objectives. This results in more effective governance practices.
Improved Risk Management: COBIT 5 offers guidelines and practices for identifying, assessing, and managing IT-related risks. Implementing COBIT 5 can enhance an organization's ability to mitigate and respond to risks effectively.
Alignment with Stakeholder Needs: COBIT 5 emphasizes the importance of meeting the needs and expectations of stakeholders. By aligning IT activities with stakeholder requirements, organizations can enhance their reputation and relationships.
Increased Efficiency and Effectiveness: COBIT 5 provides a clear framework for organizing and optimizing IT processes. This leads to increased efficiency in IT operations and the delivery of services, ultimately resulting in cost savings.
Better Compliance: COBIT 5 includes guidelines for ensuring regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards. Implementing COBIT 5 can help organizations avoid non-compliance issues and associated penalties.
Optimized Resource Management: COBIT 5 enables organizations to manage IT resources efficiently, including people, technology, and information. This ensures that resources are used effectively to achieve business goals.
Enhanced Decision-Making: COBIT 5 offers a structured framework for decision-making, promoting evidence-based choices. This leads to better decision quality and more favorable outcomes.
Continuous Improvement: COBIT 5 promotes a culture of continual improvement in IT governance and management. Organizations can adapt to changing circumstances and stay agile in the face of evolving technology and business needs.
Mitigation of IT-related Failures: By following COBIT 5's best practices, organizations can reduce the likelihood of IT-related failures, such as system outages or security breaches.
In summary, implementing COBIT 5 Foundation offers organizations a structured and comprehensive approach to IT governance and management. It not only helps align IT with business goals but also results in better risk management, stakeholder satisfaction, and overall organizational performance.
COBIT 5 Principles
COBIT 5 is built upon seven key principles, which provide the foundation for effective IT governance and management. Here are five of those principles:
Meeting Stakeholder Needs: The first principle emphasizes the importance of aligning IT with the needs and expectations of stakeholders, both internal and external. Organizations should prioritize understanding and addressing the unique requirements of these stakeholders to ensure their satisfaction and support.
Covering the Enterprise End-to-End: This principle advocates for a holistic approach to IT governance and management. It highlights the need to consider all aspects of the enterprise, from strategy and planning to daily operations, to ensure that IT aligns with the entire organization.
Applying a Single Integrated Framework: COBIT 5 promotes the use of a single, integrated framework for IT governance and management. By applying a unified framework, organizations can avoid duplication, inconsistencies, and confusion, making IT governance more efficient and effective.
Enabling a Holistic Approach: This principle underscores the importance of adopting a comprehensive and integrated approach to IT governance. Organizations should consider the full spectrum of factors, including processes, culture, organizational structures, and information, to achieve effective governance and management.
These principles serve as guiding tenets for organizations looking to establish effective IT governance and management practices using the COBIT 5 framework. They provide a strategic and philosophical basis for decision-making and implementation, helping organizations meet their objectives and deliver value to stakeholders.
COBIT 5 Domains
COBIT 5 organizes its guidance and processes into four primary domains, each of which represents a distinct area of IT governance and management. These domains are designed to help organizations address various aspects of IT effectively. The four domains in COBIT 5 are as follows:
Governance (EDM - Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor): The Governance domain focuses on the high-level, strategic aspects of IT governance. It is responsible for ensuring that stakeholder needs and expectations are met, and that the enterprise's strategic objectives are aligned with IT. This domain includes processes related to evaluating the current state of IT, directing IT to achieve its goals, and monitoring IT performance. Key processes within this domain include:
Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM)
Ensure Governance Framework Setting and Maintenance
Ensure Stakeholder Value Delivery
Ensure Performance Optimization
Management (APO - Align, Plan, and Organize, BAI - Build, Acquire, and Implement, DSS - Deliver, Service, and Support): The Management domain encompasses the processes that support the actual planning, implementation, and operation of IT within the organization. It ensures that IT resources are organized and deployed effectively. The Management domain is divided into three subdomains:
Align, Plan, and Organize (APO): This subdomain is responsible for aligning IT with the organization's strategic objectives and planning IT activities. Key processes include strategic planning, portfolio management, and IT budgeting.
Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI): This subdomain covers the processes related to developing, acquiring, and implementing IT solutions and services. It includes processes like project management, system development, and IT procurement.
Information (MEA - Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess): The Information domain is responsible for ensuring the effective management of information as an asset. It involves processes for monitoring and assessing the quality and security of information. Key processes within this domain include:
Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA)
Ensure Stakeholder Value Delivery
Ensure Risk Optimization
Supporting Processes (APO - Align, Plan, and Organize, BAI - Build, Acquire, and Implement, DSS - Deliver, Service, and Support, MEA - Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess): These processes are common to multiple domains and provide support for the primary processes in Governance, Management, and Information. They are not standalone domains but are essential for the smooth operation of IT governance and management. These supporting processes include areas like compliance, human resources, and knowledge management.
These four domains, along with their respective processes, help organizations implement comprehensive IT governance and management practices using the COBIT 5 framework. Each domain addresses specific aspects of IT, ensuring that IT aligns with business goals, delivers value, and is governed effectively.
COBIT 5 Process Reference Model
The COBIT 5 Process Reference Model is a core component of the COBIT 5 framework. It provides a structured and comprehensive framework for understanding and implementing IT governance and management processes within an organization. The model is designed to be flexible and scalable, allowing organizations to tailor it to their specific needs and requirements. Here's an overview of the COBIT 5 Process Reference Model:
Processes: The model is organized into a set of processes that cover various aspects of IT governance and management. These processes are divided into five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM); Align, Plan, and Organize (APO); Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI); Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS); and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA).
Processes and Activities: Within each domain, the COBIT 5 Process Reference Model defines specific processes and associated activities. These activities provide detailed guidance on how to implement and execute each process effectively.
Inputs and Outputs: The model also specifies the inputs and outputs of each process, helping organizations understand what information, resources, and deliverables are required to execute a process and what is generated as a result.
Responsibilities: The model identifies the roles and responsibilities associated with each process, ensuring that organizations have clear lines of accountability.
Interactions: It illustrates how processes within different domains interact with each other. This promotes a holistic and integrated approach to IT governance and management.
Maturity and Capability: COBIT 5 includes maturity and capability models to assess the maturity of an organization's processes and its capability to manage them effectively.
The COBIT 5 Process Reference Model serves as a practical tool for organizations to assess, plan, and improve their IT governance and management practices. It promotes transparency, alignment with business objectives, and the continuous improvement of IT processes, ultimately leading to better governance, risk management, and value delivery.
COBIT 5 Enablers
COBIT 5 emphasizes the importance of enablers as factors that support effective IT governance and management within an organization. These enablers provide the resources, tools, and structures necessary to achieve organizational objectives. COBIT 5 identifies seven primary categories of enablers that work together to facilitate the implementation of IT governance and management practices. Here are the COBIT 5 enablers:
Processes: COBIT 5 identifies a set of IT governance and management processes that are essential for aligning IT with business goals and objectives. These processes provide the practical steps and activities for governing and managing IT effectively.
Organizational Structures: Organizational structures and roles are enablers that define how responsibilities are distributed and delegated within the organization. They include roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines, ensuring clear accountability.
Information: Information is a critical enabler as it provides the data and knowledge necessary for making informed decisions. Effective information management, data quality, and information security are important aspects of this enabler.
Services, Infrastructure, and Applications: This enabler includes the physical and logical resources required to support IT services and applications. It covers areas such as infrastructure, applications, and IT service management tools.
People, Skills, and Competencies: People are at the heart of IT governance and management. This enabler focuses on ensuring that the organization has the right people with the right skills and competencies to support IT activities effectively.
These seven enablers collectively provide the framework and resources required for organizations to align their IT with business goals, manage risks, deliver value, and govern IT effectively. COBIT 5 emphasizes that these enablers are interrelated, and the successful implementation of IT governance and management practices requires a harmonious integration of all enablers. The specific application of these enablers will vary based on an organization's unique context and objectives.
COBIT 5 Implementation Challenges
Implementing COBIT 5 in an organization can bring numerous benefits, but it also presents several challenges. These challenges can vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and existing IT governance practices. Here are some common challenges associated with COBIT 5 implementation:
Resistance to Change: One of the most significant challenges is getting buy-in from all levels of the organization. Employees and management may be resistant to adopting new governance and management practices.
Resource Allocation: Implementing COBIT 5 requires dedicating time, people, and financial resources. Finding the necessary resources can be a challenge, especially for smaller organizations with limited budgets.
Skills and Training: Implementing COBIT 5 may require training and skill development for employees. Ensuring that staff has the necessary competencies can be a challenge, especially in rapidly changing IT environments.
Customization: COBIT 5 is a framework, and it needs to be tailored to the specific needs and context of each organization. Finding the right balance between customization and adherence to COBIT 5's principles can be challenging.
Measuring Success: Defining and measuring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Critical Success Factors (CSFs) to evaluate the success of COBIT 5 implementation can be challenging. Identifying meaningful metrics and benchmarks for improvement is essential.
Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Approach: Deciding whether to implement COBIT 5 top-down (starting with governance) or bottom-up (starting with management processes) is a strategic challenge that organizations must address.
Sustainability: Maintaining the momentum and ensuring that COBIT 5 practices continue to be effective over the long term can be challenging. Often, organizations face the risk of reverting to old practices after initial enthusiasm wanes.
Risk Management: While COBIT 5 provides guidance on risk management, identifying and addressing potential risks associated with implementation itself is a challenge.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should develop a well-defined implementation plan, engage with stakeholders, provide adequate training and support, and continuously monitor and adapt their COBIT 5 implementation as needed. It's also essential to recognize that COBIT 5 implementation is an ongoing process that requires commitment and adaptability to achieve its intended benefits.
Real-Life Examples of COBIT 5 Success Stories
COBIT 5 has been successfully implemented in numerous organizations across various industries, helping them achieve their IT governance and management objectives. Here are some real-life examples of organizations that have experienced success with COBIT 5:
ExxonMobil: ExxonMobil, one of the world's largest multinational oil and gas corporations, used COBIT 5 to enhance its IT governance and risk management. They successfully implemented COBIT 5's principles and processes to align IT with business objectives and improve risk mitigation strategies.
Dubai Customs: Dubai Customs, a government agency responsible for facilitating trade in the Emirate of Dubai, implemented COBIT 5 to enhance its IT service management practices. They used COBIT 5 to streamline IT processes, resulting in improved service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Walmart: Walmart, a global retail giant, leveraged COBIT 5 to optimize IT governance and management processes across its vast network of stores and data centers. COBIT 5 helped Walmart improve the efficiency of IT operations, reduce risks, and enhance customer experiences through effective supply chain management and data security.
US Department of Defense (DoD): The US DoD adopted COBIT 5 as part of its approach to IT governance and cybersecurity. COBIT 5 helped the DoD establish a standardized framework for managing and securing its IT assets, ultimately improving its information security posture.
AXA Group: AXA, a multinational insurance company, implemented COBIT 5 to align IT processes with business needs. By using COBIT 5, AXA improved risk management, IT performance, and the overall quality of IT services.
Government of Malaysia: The Malaysian government adopted COBIT 5 to enhance IT governance practices across various government agencies. This initiative has led to improved transparency, accountability, and effectiveness in IT management.
University of Waterloo: The University of Waterloo in Canada used COBIT 5 to optimize its IT governance practices. The implementation of COBIT 5 led to more effective IT service management, streamlined IT processes, and improved alignment with academic and administrative goals.
South African Revenue Service (SARS): SARS, the tax collection agency in South Africa, adopted COBIT 5 to enhance its IT governance and risk management practices. The use of COBIT 5 has resulted in better control over taxpayer data and improved compliance with tax regulations.
Vattenfall: Vattenfall, a Swedish multinational energy company, implemented COBIT 5 to enhance its IT governance and cybersecurity practices. COBIT 5 helped Vattenfall align its IT strategies with business objectives and strengthen its defenses against cyber threats.
Central Bank of Nigeria: The Central Bank of Nigeria utilized COBIT 5 to improve its IT governance practices and enhance the security and integrity of the country's financial systems. COBIT 5 has played a critical role in ensuring the stability and resilience of Nigeria's financial infrastructure.
These examples illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of COBIT 5 across various industries and sectors. Organizations have leveraged COBIT 5 to align IT with their strategic goals, enhance IT governance, manage risks, and deliver better services to their stakeholders. These success stories showcase the framework's adaptability and its ability to drive positive outcomes in diverse organizational contexts
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT 5 is a comprehensive and widely recognized framework for IT governance and management that provides organizations with the tools and guidance they need to align their IT functions with business objectives, manage risks, and deliver value to stakeholders. It is built on a foundation of key principles, a well-structured process reference model, and seven enablers that collectively support effective governance and management.
As technology continues to play a pivotal role in the success of organizations, COBIT 5 remains a valuable framework for those seeking a structured and systematic approach to IT governance and management. By adopting and customizing COBIT 5 to their specific needs, organizations can navigate the complexities of the digital landscape and ensure that their IT functions are aligned with their broader business strategies.
Read More
In the ever-evolving landscape of information technology, effective governance and management are paramount for organizations to thrive and succeed. One framework that stands out in this context is COBIT 5 Foundation. COBIT, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a globally recognized framework designed to help organizations govern and manage their IT effectively.
COBIT has a rich history of evolution, adapting to the changing needs of the IT industry. From its inception to the present COBIT 5 Foundation, it has become a standard bearer for organizations seeking to align their IT strategies with their business goals. This framework provides a structured approach to IT governance and management, ensuring that enterprises can achieve optimal outcomes and manage risks effectively.
Whether you're new to COBIT 5 or looking to refresh your understanding, this comprehensive overview aims to be your guide to mastering the core concepts and practical applications of COBIT 5 Foundation. So, let's begin our exploration of COBIT 5 Foundation and its role in shaping the future of IT governance.
Table of contents
-
Historical Evolution of COBIT
-
COBIT 5 Framework Components
-
Key Concepts in COBIT 5
-
Benefits of Implementing COBIT 5 Foundation
-
COBIT 5 Principles
-
COBIT 5 Domains
-
COBIT 5 Process Reference Model
-
COBIT 5 Enablers
-
COBIT 5 Implementation Challenges
-
Real-Life Examples of COBIT 5 Success Stories
-
Conclusion
Historical Evolution of COBIT
The historical evolution of COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is a fascinating journey that showcases its development from a simple set of IT control objectives into a globally recognized framework for IT governance and management. Let's take a closer look at the key milestones in the history of COBIT:
COBIT 1.0 (1996): COBIT was initially introduced by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) in 1996 as a set of IT control objectives to help organizations manage their IT processes and risks. This first version provided a basic structure for IT governance.
COBIT 2.0 (1998): The framework was updated in 1998 as COBIT 2.0. This version included a more comprehensive set of control objectives, making it a valuable tool for IT audit and control professionals.
COBIT 3.0 (2000): In the year 2000, COBIT 3.0 was released with a significant expansion in scope. This version integrated IT governance and management practices, helping organizations align IT with business goals more effectively.
COBIT 4.0 (2005): COBIT 4.0 introduced the concept of domains, processes, and IT-related goals, making it more structured and easier to apply in organizations. It was a pivotal step toward broader acceptance.
COBIT 4.1 (2007): This version, released in 2007, brought some refinements and updates to COBIT 4.0, making it more practical for implementation in real-world scenarios.
COBIT 5.0 Updates (2019): In 2019, COBIT was updated to further align with the evolving IT landscape and address contemporary challenges. This update included guidance on digital transformation and emerging technologies.
The historical evolution of COBIT reflects the changing landscape of IT governance, from a focus on control objectives to a comprehensive framework for aligning IT with business strategy, managing risks, and achieving operational excellence.
COBIT 5 Framework Components
The COBIT 5 framework consists of several key components, each of which plays a crucial role in helping organizations govern and manage their information and technology effectively. Understanding these components is essential for implementing COBIT 5 successfully. Here are the main components of the COBIT 5 framework:
Principles:
Meeting Stakeholder Needs: The first principle of COBIT 5 emphasizes the importance of aligning IT with the needs and expectations of stakeholders, whether they are internal or external to the organization.
Applying a Single Integrated Framework: COBIT 5 promotes the use of a single integrated framework to harmonize and simplify the governance of IT.
Enablers:
Processes: COBIT 5 defines a set of governance and management processes that help organizations achieve their objectives. These processes cover areas such as risk management, resource management, and performance management.
Principles, Policies, and Frameworks: These enablers provide the foundation for governance and management. They include the principles mentioned earlier, as well as policies, standards, and guidelines.
Information: Information is a key enabler, and COBIT 5 provides guidance on managing and optimizing the use of information in decision-making processes.
Services, Infrastructure, and Applications: These enablers relate to the physical and logical resources required to deliver IT services.
Governance and Management Processes:
COBIT 5 defines a comprehensive set of governance and management processes that organizations can use to align their IT with business goals, manage risks, and deliver value. Some of the processes include:
Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM) processes: These processes are primarily related to governance activities.
Align, Plan, and Organize (APO) processes: These processes focus on strategic planning and organizational structure.
Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA) processes: These processes assess the effectiveness of governance and management.
COBIT 5 Framework Model:
The COBIT 5 framework model provides a graphical representation of the principles, enablers, and processes, helping organizations visualize how they interact and support the achievement of objectives.
These components work together to provide a structured and holistic approach to IT governance and management. COBIT 5's principles guide decision-making, the enablers provide the resources and tools, and the governance and management processes offer a practical roadmap for implementation. By leveraging these components effectively, organizations can improve their IT practices, mitigate risks, and deliver value to stakeholders
Key Concepts in COBIT 5
COBIT 5, a comprehensive framework for governing and managing enterprise IT, is built upon several key concepts that are fundamental to understanding and implementing the framework effectively. Here are the key concepts in COBIT 5:
Governance and Management: COBIT 5 distinguishes between governance and management. Governance is primarily concerned with decision-making and ensuring that IT aligns with business goals. Management, on the other hand, involves the execution of those decisions and the day-to-day operation of IT processes.
End-to-End Coverage: COBIT 5 advocates for a holistic approach to IT governance, covering all aspects of the enterprise. It's not limited to specific processes or departments; rather, it spans the entire organization.
Framework for the Governance and Management of Enterprise IT: COBIT 5 provides a structured framework that encompasses IT governance and management practices. This framework offers a systematic approach to achieving organizational goals.
Enabler: Enablers in COBIT 5 are the factors that facilitate or support the implementation of governance and management. These include processes, principles, policies, organizational structures, culture, ethics, and behavior, among others.
Principles: COBIT 5 is guided by seven key principles:
Meeting Stakeholder Needs
Covering the Enterprise End-to-End
Separating Governance from Management
Tailoring to the Enterprise
Implementing a Governance System
Domains: COBIT 5 defines four domains, each encompassing a set of processes and activities:
Lifecycle Approach: COBIT 5 advocates for a lifecycle approach to IT governance and management, emphasizing that governance and management are continuous and cyclical processes rather than one-time events.
Information Governance: Information is a critical asset in IT governance, and COBIT 5 underscores the importance of effectively managing and using information in decision-making processes.
Understanding these key concepts in COBIT 5 is essential for organizations looking to enhance their IT governance and management practices. These concepts provide the foundation for implementing the framework and aligning IT with business objectives while meeting the needs of various stakeholders.
Benefits of Implementing COBIT 5 Foundation
Implementing COBIT 5 Foundation can bring a wide range of benefits to organizations. Here are some of the key advantages of adopting the COBIT 5 framework for IT governance and management:
Enhanced IT Governance: COBIT 5 provides a structured and holistic approach to IT governance, helping organizations make informed decisions and align IT strategies with business objectives. This results in more effective governance practices.
Improved Risk Management: COBIT 5 offers guidelines and practices for identifying, assessing, and managing IT-related risks. Implementing COBIT 5 can enhance an organization's ability to mitigate and respond to risks effectively.
Alignment with Stakeholder Needs: COBIT 5 emphasizes the importance of meeting the needs and expectations of stakeholders. By aligning IT activities with stakeholder requirements, organizations can enhance their reputation and relationships.
Increased Efficiency and Effectiveness: COBIT 5 provides a clear framework for organizing and optimizing IT processes. This leads to increased efficiency in IT operations and the delivery of services, ultimately resulting in cost savings.
Better Compliance: COBIT 5 includes guidelines for ensuring regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards. Implementing COBIT 5 can help organizations avoid non-compliance issues and associated penalties.
Optimized Resource Management: COBIT 5 enables organizations to manage IT resources efficiently, including people, technology, and information. This ensures that resources are used effectively to achieve business goals.
Enhanced Decision-Making: COBIT 5 offers a structured framework for decision-making, promoting evidence-based choices. This leads to better decision quality and more favorable outcomes.
Continuous Improvement: COBIT 5 promotes a culture of continual improvement in IT governance and management. Organizations can adapt to changing circumstances and stay agile in the face of evolving technology and business needs.
Mitigation of IT-related Failures: By following COBIT 5's best practices, organizations can reduce the likelihood of IT-related failures, such as system outages or security breaches.
In summary, implementing COBIT 5 Foundation offers organizations a structured and comprehensive approach to IT governance and management. It not only helps align IT with business goals but also results in better risk management, stakeholder satisfaction, and overall organizational performance.
COBIT 5 Principles
COBIT 5 is built upon seven key principles, which provide the foundation for effective IT governance and management. Here are five of those principles:
Meeting Stakeholder Needs: The first principle emphasizes the importance of aligning IT with the needs and expectations of stakeholders, both internal and external. Organizations should prioritize understanding and addressing the unique requirements of these stakeholders to ensure their satisfaction and support.
Covering the Enterprise End-to-End: This principle advocates for a holistic approach to IT governance and management. It highlights the need to consider all aspects of the enterprise, from strategy and planning to daily operations, to ensure that IT aligns with the entire organization.
Applying a Single Integrated Framework: COBIT 5 promotes the use of a single, integrated framework for IT governance and management. By applying a unified framework, organizations can avoid duplication, inconsistencies, and confusion, making IT governance more efficient and effective.
Enabling a Holistic Approach: This principle underscores the importance of adopting a comprehensive and integrated approach to IT governance. Organizations should consider the full spectrum of factors, including processes, culture, organizational structures, and information, to achieve effective governance and management.
These principles serve as guiding tenets for organizations looking to establish effective IT governance and management practices using the COBIT 5 framework. They provide a strategic and philosophical basis for decision-making and implementation, helping organizations meet their objectives and deliver value to stakeholders.
COBIT 5 Domains
COBIT 5 organizes its guidance and processes into four primary domains, each of which represents a distinct area of IT governance and management. These domains are designed to help organizations address various aspects of IT effectively. The four domains in COBIT 5 are as follows:
Governance (EDM - Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor): The Governance domain focuses on the high-level, strategic aspects of IT governance. It is responsible for ensuring that stakeholder needs and expectations are met, and that the enterprise's strategic objectives are aligned with IT. This domain includes processes related to evaluating the current state of IT, directing IT to achieve its goals, and monitoring IT performance. Key processes within this domain include:
Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM)
Ensure Governance Framework Setting and Maintenance
Ensure Stakeholder Value Delivery
Ensure Performance Optimization
Management (APO - Align, Plan, and Organize, BAI - Build, Acquire, and Implement, DSS - Deliver, Service, and Support): The Management domain encompasses the processes that support the actual planning, implementation, and operation of IT within the organization. It ensures that IT resources are organized and deployed effectively. The Management domain is divided into three subdomains:
Align, Plan, and Organize (APO): This subdomain is responsible for aligning IT with the organization's strategic objectives and planning IT activities. Key processes include strategic planning, portfolio management, and IT budgeting.
Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI): This subdomain covers the processes related to developing, acquiring, and implementing IT solutions and services. It includes processes like project management, system development, and IT procurement.
Information (MEA - Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess): The Information domain is responsible for ensuring the effective management of information as an asset. It involves processes for monitoring and assessing the quality and security of information. Key processes within this domain include:
Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA)
Ensure Stakeholder Value Delivery
Ensure Risk Optimization
Supporting Processes (APO - Align, Plan, and Organize, BAI - Build, Acquire, and Implement, DSS - Deliver, Service, and Support, MEA - Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess): These processes are common to multiple domains and provide support for the primary processes in Governance, Management, and Information. They are not standalone domains but are essential for the smooth operation of IT governance and management. These supporting processes include areas like compliance, human resources, and knowledge management.
These four domains, along with their respective processes, help organizations implement comprehensive IT governance and management practices using the COBIT 5 framework. Each domain addresses specific aspects of IT, ensuring that IT aligns with business goals, delivers value, and is governed effectively.
COBIT 5 Process Reference Model
The COBIT 5 Process Reference Model is a core component of the COBIT 5 framework. It provides a structured and comprehensive framework for understanding and implementing IT governance and management processes within an organization. The model is designed to be flexible and scalable, allowing organizations to tailor it to their specific needs and requirements. Here's an overview of the COBIT 5 Process Reference Model:
Processes: The model is organized into a set of processes that cover various aspects of IT governance and management. These processes are divided into five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM); Align, Plan, and Organize (APO); Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI); Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS); and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA).
Processes and Activities: Within each domain, the COBIT 5 Process Reference Model defines specific processes and associated activities. These activities provide detailed guidance on how to implement and execute each process effectively.
Inputs and Outputs: The model also specifies the inputs and outputs of each process, helping organizations understand what information, resources, and deliverables are required to execute a process and what is generated as a result.
Responsibilities: The model identifies the roles and responsibilities associated with each process, ensuring that organizations have clear lines of accountability.
Interactions: It illustrates how processes within different domains interact with each other. This promotes a holistic and integrated approach to IT governance and management.
Maturity and Capability: COBIT 5 includes maturity and capability models to assess the maturity of an organization's processes and its capability to manage them effectively.
The COBIT 5 Process Reference Model serves as a practical tool for organizations to assess, plan, and improve their IT governance and management practices. It promotes transparency, alignment with business objectives, and the continuous improvement of IT processes, ultimately leading to better governance, risk management, and value delivery.
COBIT 5 Enablers
COBIT 5 emphasizes the importance of enablers as factors that support effective IT governance and management within an organization. These enablers provide the resources, tools, and structures necessary to achieve organizational objectives. COBIT 5 identifies seven primary categories of enablers that work together to facilitate the implementation of IT governance and management practices. Here are the COBIT 5 enablers:
Processes: COBIT 5 identifies a set of IT governance and management processes that are essential for aligning IT with business goals and objectives. These processes provide the practical steps and activities for governing and managing IT effectively.
Organizational Structures: Organizational structures and roles are enablers that define how responsibilities are distributed and delegated within the organization. They include roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines, ensuring clear accountability.
Information: Information is a critical enabler as it provides the data and knowledge necessary for making informed decisions. Effective information management, data quality, and information security are important aspects of this enabler.
Services, Infrastructure, and Applications: This enabler includes the physical and logical resources required to support IT services and applications. It covers areas such as infrastructure, applications, and IT service management tools.
People, Skills, and Competencies: People are at the heart of IT governance and management. This enabler focuses on ensuring that the organization has the right people with the right skills and competencies to support IT activities effectively.
These seven enablers collectively provide the framework and resources required for organizations to align their IT with business goals, manage risks, deliver value, and govern IT effectively. COBIT 5 emphasizes that these enablers are interrelated, and the successful implementation of IT governance and management practices requires a harmonious integration of all enablers. The specific application of these enablers will vary based on an organization's unique context and objectives.
COBIT 5 Implementation Challenges
Implementing COBIT 5 in an organization can bring numerous benefits, but it also presents several challenges. These challenges can vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and existing IT governance practices. Here are some common challenges associated with COBIT 5 implementation:
Resistance to Change: One of the most significant challenges is getting buy-in from all levels of the organization. Employees and management may be resistant to adopting new governance and management practices.
Resource Allocation: Implementing COBIT 5 requires dedicating time, people, and financial resources. Finding the necessary resources can be a challenge, especially for smaller organizations with limited budgets.
Skills and Training: Implementing COBIT 5 may require training and skill development for employees. Ensuring that staff has the necessary competencies can be a challenge, especially in rapidly changing IT environments.
Customization: COBIT 5 is a framework, and it needs to be tailored to the specific needs and context of each organization. Finding the right balance between customization and adherence to COBIT 5's principles can be challenging.
Measuring Success: Defining and measuring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Critical Success Factors (CSFs) to evaluate the success of COBIT 5 implementation can be challenging. Identifying meaningful metrics and benchmarks for improvement is essential.
Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Approach: Deciding whether to implement COBIT 5 top-down (starting with governance) or bottom-up (starting with management processes) is a strategic challenge that organizations must address.
Sustainability: Maintaining the momentum and ensuring that COBIT 5 practices continue to be effective over the long term can be challenging. Often, organizations face the risk of reverting to old practices after initial enthusiasm wanes.
Risk Management: While COBIT 5 provides guidance on risk management, identifying and addressing potential risks associated with implementation itself is a challenge.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should develop a well-defined implementation plan, engage with stakeholders, provide adequate training and support, and continuously monitor and adapt their COBIT 5 implementation as needed. It's also essential to recognize that COBIT 5 implementation is an ongoing process that requires commitment and adaptability to achieve its intended benefits.
Real-Life Examples of COBIT 5 Success Stories
COBIT 5 has been successfully implemented in numerous organizations across various industries, helping them achieve their IT governance and management objectives. Here are some real-life examples of organizations that have experienced success with COBIT 5:
ExxonMobil: ExxonMobil, one of the world's largest multinational oil and gas corporations, used COBIT 5 to enhance its IT governance and risk management. They successfully implemented COBIT 5's principles and processes to align IT with business objectives and improve risk mitigation strategies.
Dubai Customs: Dubai Customs, a government agency responsible for facilitating trade in the Emirate of Dubai, implemented COBIT 5 to enhance its IT service management practices. They used COBIT 5 to streamline IT processes, resulting in improved service delivery and customer satisfaction.
Walmart: Walmart, a global retail giant, leveraged COBIT 5 to optimize IT governance and management processes across its vast network of stores and data centers. COBIT 5 helped Walmart improve the efficiency of IT operations, reduce risks, and enhance customer experiences through effective supply chain management and data security.
US Department of Defense (DoD): The US DoD adopted COBIT 5 as part of its approach to IT governance and cybersecurity. COBIT 5 helped the DoD establish a standardized framework for managing and securing its IT assets, ultimately improving its information security posture.
AXA Group: AXA, a multinational insurance company, implemented COBIT 5 to align IT processes with business needs. By using COBIT 5, AXA improved risk management, IT performance, and the overall quality of IT services.
Government of Malaysia: The Malaysian government adopted COBIT 5 to enhance IT governance practices across various government agencies. This initiative has led to improved transparency, accountability, and effectiveness in IT management.
University of Waterloo: The University of Waterloo in Canada used COBIT 5 to optimize its IT governance practices. The implementation of COBIT 5 led to more effective IT service management, streamlined IT processes, and improved alignment with academic and administrative goals.
South African Revenue Service (SARS): SARS, the tax collection agency in South Africa, adopted COBIT 5 to enhance its IT governance and risk management practices. The use of COBIT 5 has resulted in better control over taxpayer data and improved compliance with tax regulations.
Vattenfall: Vattenfall, a Swedish multinational energy company, implemented COBIT 5 to enhance its IT governance and cybersecurity practices. COBIT 5 helped Vattenfall align its IT strategies with business objectives and strengthen its defenses against cyber threats.
Central Bank of Nigeria: The Central Bank of Nigeria utilized COBIT 5 to improve its IT governance practices and enhance the security and integrity of the country's financial systems. COBIT 5 has played a critical role in ensuring the stability and resilience of Nigeria's financial infrastructure.
These examples illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of COBIT 5 across various industries and sectors. Organizations have leveraged COBIT 5 to align IT with their strategic goals, enhance IT governance, manage risks, and deliver better services to their stakeholders. These success stories showcase the framework's adaptability and its ability to drive positive outcomes in diverse organizational contexts
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT 5 is a comprehensive and widely recognized framework for IT governance and management that provides organizations with the tools and guidance they need to align their IT functions with business objectives, manage risks, and deliver value to stakeholders. It is built on a foundation of key principles, a well-structured process reference model, and seven enablers that collectively support effective governance and management.
As technology continues to play a pivotal role in the success of organizations, COBIT 5 remains a valuable framework for those seeking a structured and systematic approach to IT governance and management. By adopting and customizing COBIT 5 to their specific needs, organizations can navigate the complexities of the digital landscape and ensure that their IT functions are aligned with their broader business strategies.
COBIT® 5 and IT Risk Management: A Powerful Combination
In today's ever-evolving digital landscape, organizations face a multitude of challenges when it comes to managing and mitigating IT risks. The rapid pace of technological advancements, the increasing complexity of IT environments, and the relentless onslaught of cyber threats have made effective risk management an imperative for businesses of all sizes and industries.
This blog post explores a powerful combination that has emerged to tackle these challenges head-on: COBIT® 5 and IT risk management. COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, provides organizations with a structured approach to optimizing IT processes and aligning them with business goals. When integrated with robust IT risk management practices, COBIT® 5 becomes a formidable tool in helping organizations identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT risks effectively.
In this post, we will delve into the core concepts of COBIT® 5, emphasizing its principles and guidelines that support IT risk management. We will also discuss the benefits of combining COBIT® 5 with IT risk management, including improved visibility, enhanced decision-making, and better compliance. Additionally, we'll provide practical insights on how organizations can implement COBIT® 5 in their risk management processes and showcase real-world examples of its successful integration.
Table of Contents
-
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
-
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
-
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
-
Practical Implementation Steps
-
Real-world Examples
-
Challenges and Considerations
-
Conclusion
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
COBIT® 5, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a globally recognized framework developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) to guide organizations in effectively managing and governing their information technology (IT) processes. At its core, COBIT® 5 seeks to bridge the gap between business objectives and IT functions. It is a comprehensive framework that offers a structured approach to IT governance and management, ensuring that IT activities align with business goals and regulatory requirements.
Key Components of COBIT® 5:
COBIT® 5 is built on five fundamental principles that underpin its effectiveness. These principles include meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management. Within the framework, a set of processes is organized into five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM), Align, Plan, and Organize (APO), Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI), Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS), and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA). These processes provide guidance on various aspects of IT governance and management, from strategic planning to day-to-day operations.
Benefits of COBIT® 5:
Organizations that embrace COBIT® 5 gain several notable advantages. It enhances IT governance by establishing a robust framework that ensures IT investments and actions are in harmony with business objectives and compliance requirements. COBIT® 5 also plays a vital role in risk management, offering a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate IT-related risks. It aids in efficient resource allocation, enabling organizations to make informed decisions regarding IT investments. Moreover, COBIT® 5 promotes transparency and accountability in IT processes, facilitating areas of improvement identification and compliance demonstration. The framework's compatibility with various industry standards and frameworks, such as ITIL and ISO/IEC 27001, enhances its appeal as a versatile tool applicable to organizations of all sizes and industries. In summary, COBIT® 5 serves as an invaluable resource for organizations aspiring to elevate their IT governance and management practices, aligning IT with business objectives and enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
In today's digital-centric business landscape, the critical role of IT risk management cannot be overstated. As organizations increasingly rely on technology to drive their operations, serve customers, and manage data, they become more exposed to a wide array of IT-related risks. These risks can range from cybersecurity threats and data breaches to system failures and compliance violations. Effectively managing these risks is essential for business continuity, reputation preservation, and regulatory compliance.
IT risk management is a systematic and structured approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring IT-related risks. Its significance lies in its ability to proactively identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take preemptive action to reduce their impact. Here are several key aspects highlighting the critical role of IT risk management:
1. Protecting Business Assets: IT systems and digital assets are vital components of modern businesses. IT risk management safeguards these assets from a wide range of threats, including cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data loss. By protecting these assets, organizations can ensure the uninterrupted flow of operations and maintain customer trust.
2. Safeguarding Reputation: A data breach or security incident can have severe consequences for an organization's reputation. IT risk management practices, including robust cybersecurity measures and incident response plans, help minimize the risk of reputational damage by preventing or mitigating the impact of such incidents.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to stringent regulations related to data protection, privacy, and security. IT risk management ensures that organizations remain in compliance with these regulations, avoiding costly fines and legal repercussions.
4. Business Continuity: Effective risk management includes disaster recovery and business continuity planning. This ensures that in the event of IT disruptions, whether due to natural disasters or technical failures, organizations can continue to operate or quickly recover their operations.
5. Cost Reduction: Well-planned IT risk management can lead to cost savings. By identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can reduce the financial impact of potential incidents and allocate resources more efficiently.
6. Decision Support: IT risk assessments provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities and threats an organization faces. This information aids in informed decision-making, such as prioritizing investments in security measures and risk mitigation strategies.
7. Competitive Advantage: Organizations that can demonstrate effective IT risk management practices often gain a competitive edge. Customers and partners are increasingly concerned about data security and compliance, making sound risk management a selling point.
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5, the globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, offers a structured and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within organizations. Its approach can be summarized in a few key steps, making it accessible for organizations of various sizes and industries:
-
Understand Business Goals: First, know your organization's business objectives well. IT should support these goals.
-
Set Risk Tolerance: Decide how much risk you're willing to accept to achieve your business goals, like setting a limit on a game.
-
Identify IT Risks: Spot potential IT risks, such as cyber threats or software problems, just like noticing road obstacles.
-
Assess Risks: Estimate how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, similar to evaluating the size of a road pothole and its likelihood of causing damage.
-
Respond to Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like getting insurance), or accept it, just as you choose to fix a pothole or take a different route.
-
Monitor Continuously: Keep an eye on risks all the time, like watching the road while driving, and adjust your plans if new risks appear.
-
Communicate Clearly: Make sure everyone in your organization understands the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Report and Follow Rules: Share information about how you're handling risks with key people and stay in line with laws and standards.
-
Learn and Improve: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to get better at it over time, like becoming a better driver after each trip.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's approach to IT risk management is like planning a safe journey. You know where you want to go (business goals), identify potential roadblocks (IT risks), set limits on how risky you're willing to be, and use strategies to navigate safely. This helps organizations protect their IT systems and make smart choices in the digital world.
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
Integrating COBIT® 5, a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management, with IT risk management brings several significant benefits to organizations. This integration creates a powerful synergy that enhances an organization's ability to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key advantages:
-
Business Alignment: Aligns IT activities with what the organization wants to achieve, ensuring that IT supports business goals.
-
Proactive Risk Management: Helps spot and address IT risks before they become big problems.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Provides insights for smart decisions about IT investments and how to deal with risks.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Makes it easier to follow rules and regulations related to IT risk management.
-
Efficient Resource Use: Helps allocate resources wisely by focusing on the most important risks.
-
Clear Communication: Makes it easy to explain IT risks and how they're being managed to everyone in the organization.
-
Adaptation to Change: Keeps an eye on risks and adjusts strategies as needed to stay safe in a changing world.
-
Easier Audits: Simplifies the process of checking that risk management practices are working correctly.
-
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that do this well look better to customers and partners who care about data security and following the rules.
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5 provides a structured and comprehensive framework for IT risk management within organizations. This framework offers a clear path to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key components and steps in COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management:
-
Identify Risks: Find potential IT risks that could harm your organization, like cyber threats or data problems.
-
Assess Risks: Figure out how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, so you know which ones need attention.
-
Manage Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like insurance), or accept it.
-
Keep an Eye Out: Continuously watch for changes in risks and adjust your plans accordingly.
-
Report Clearly: Share what you're doing about risks with everyone in your organization and make sure to document everything.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management follows the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Learn and Get Better: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to do it even better next time.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of all your IT decisions and fits with your overall goals.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management is like a clear roadmap to help organizations handle IT risks wisely. It guides you in spotting risks, figuring out how to deal with them, and making sure you're following the rules and improving over time. This helps keep your organization safe and successful in the digital world.
Practical Implementation Steps
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework involves practical steps to ensure a systematic and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within your organization. Here are the key implementation steps:
-
Assign Responsibilities: Appoint people to handle risk management tasks and make sure senior leaders support the process.
-
Set Risk Limits: Decide how much risk your organization can accept for different types of IT activities.
-
Spot Risks: Identify potential IT risks using your team's knowledge and available data.
-
Check Risks: Evaluate each risk to see how big it is and how likely it is to happen, and then prioritize them.
-
Make Risk Plans: Create plans to deal with the most important risks, deciding whether to avoid them, reduce their impact, transfer them (like buying insurance), or accept them.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of your regular IT processes and document it.
-
Keep Watch: Set up a system to keep an eye on how risks change and how your plans are working.
-
Tell Everyone: Regularly tell your team and leaders about the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Keep Records: Write down everything you do related to risk management.
-
Train and Learn: Teach your team about risk management and learn from your experiences to get better over time.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management meets the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Get Help If Needed: Consider getting outside experts to help or assess your risk management.
In simple terms, these steps help organizations manage IT risks effectively, aligning with their goals and complying with rules while learning and improving along the way.
Real-world Examples
Here are some real-world examples of organizations that have successfully implemented COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework:
-
JPMorgan Chase & Co.: JPMorgan Chase, one of the world's largest financial institutions, utilizes COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the security and reliability of its IT systems. The framework helps them identify and assess risks associated with their extensive digital operations, including online banking and financial services. It enables them to proactively address cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and regulatory compliance challenges.
-
The World Bank: The World Bank, a global financial institution, leverages COBIT® 5 to manage IT risks across its diverse operations. They use the framework to identify and assess risks related to the implementation of technology in development projects. This helps them mitigate potential project delays, budget overruns, and data security issues.
-
Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA): DEWA, the utility provider for Dubai, uses COBIT® 5 to enhance IT risk management in the context of critical infrastructure. They apply the framework to identify and address risks associated with their energy and water supply systems. This ensures the reliability and resilience of their services, even in the face of IT-related challenges.
-
PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers): As a leading global professional services firm, PwC employs COBIT® 5 for IT risk management to help their clients across various industries. They assist organizations in identifying and managing IT risks to enhance cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and overall operational efficiency.
-
Nestlé: Nestlé, the multinational food and beverage company, uses COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the integrity of its global IT systems. This includes managing risks related to data privacy, supply chain, and production systems. The framework helps Nestlé maintain the trust of its customers and regulators while ensuring the smooth operation of its business.
These real-world examples demonstrate how organizations across different sectors, including finance, development, utilities, and professional services, leverage COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to enhance their IT governance and protect their operations from a wide range of IT-related risks. This illustrates the versatility and effectiveness of COBIT® 5 in managing IT risks in various contexts.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework comes with a set of challenges and considerations that organizations should carefully address. One significant challenge is resource allocation, involving finding the right personnel and financial investments for risk management initiatives. Changing the organizational culture to prioritize risk management can be a formidable hurdle, as it requires strong leadership support and effective communication to instill the importance of risk management across all levels of the organization. The complexity of modern IT environments, with their ever-evolving nature, presents another challenge, necessitating the use of advanced monitoring tools and regular risk assessments to keep up. Adhering to regulatory requirements is a critical consideration, especially as rules can change frequently, making it vital to stay informed and seek expert guidance when needed.
Safeguarding sensitive data from breaches and cyberattacks remains a constant challenge, demanding robust cybersecurity measures and well-defined incident response plans. Integrating COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework with existing IT governance processes may pose difficulties, necessitating expert guidance and a strategic approach to ensure seamless integration. Building and maintaining the necessary skills and knowledge within the organization for effective risk management requires investment in training and development programs. Overcoming resistance to change and managing organizational change effectively is essential, as implementing new risk management processes can meet with opposition. Finally, measuring the effectiveness of risk management efforts and reporting on them in a clear and meaningful way can be complex, requiring the definition of key performance indicators and metrics to evaluate success and communicate progress to stakeholders. Addressing these challenges and considerations strategically empowers organizations to protect their IT assets, align IT with business objectives, and ensure resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
How to obtain the COBIT Foundation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework offers organizations a structured and comprehensive approach to navigate the complex landscape of IT-related risks. While it brings substantial benefits such as enhanced alignment with business goals, proactive risk identification, and improved decision-making, it also presents various challenges and considerations. These challenges include resource allocation, cultural change, the complexity of IT environments, regulatory compliance, data security, integration with existing processes, skills and training, change management, and effective measurement and reporting.
Despite these challenges, organizations that commit to implementing COBIT® 5's framework stand to gain in terms of better IT risk management, alignment with regulatory requirements, and enhanced data security. It empowers organizations to proactively identify and address risks, ultimately safeguarding their IT assets and ensuring their resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Therefore, while the road to effective IT risk management may be challenging, the destination of a secure and well-aligned IT environment is well worth the journey.
Read More
In today's ever-evolving digital landscape, organizations face a multitude of challenges when it comes to managing and mitigating IT risks. The rapid pace of technological advancements, the increasing complexity of IT environments, and the relentless onslaught of cyber threats have made effective risk management an imperative for businesses of all sizes and industries.
This blog post explores a powerful combination that has emerged to tackle these challenges head-on: COBIT® 5 and IT risk management. COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, provides organizations with a structured approach to optimizing IT processes and aligning them with business goals. When integrated with robust IT risk management practices, COBIT® 5 becomes a formidable tool in helping organizations identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT risks effectively.
In this post, we will delve into the core concepts of COBIT® 5, emphasizing its principles and guidelines that support IT risk management. We will also discuss the benefits of combining COBIT® 5 with IT risk management, including improved visibility, enhanced decision-making, and better compliance. Additionally, we'll provide practical insights on how organizations can implement COBIT® 5 in their risk management processes and showcase real-world examples of its successful integration.
Table of Contents
-
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
-
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
-
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
-
Practical Implementation Steps
-
Real-world Examples
-
Challenges and Considerations
-
Conclusion
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
COBIT® 5, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a globally recognized framework developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) to guide organizations in effectively managing and governing their information technology (IT) processes. At its core, COBIT® 5 seeks to bridge the gap between business objectives and IT functions. It is a comprehensive framework that offers a structured approach to IT governance and management, ensuring that IT activities align with business goals and regulatory requirements.
Key Components of COBIT® 5:
COBIT® 5 is built on five fundamental principles that underpin its effectiveness. These principles include meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management. Within the framework, a set of processes is organized into five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM), Align, Plan, and Organize (APO), Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI), Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS), and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA). These processes provide guidance on various aspects of IT governance and management, from strategic planning to day-to-day operations.
Benefits of COBIT® 5:
Organizations that embrace COBIT® 5 gain several notable advantages. It enhances IT governance by establishing a robust framework that ensures IT investments and actions are in harmony with business objectives and compliance requirements. COBIT® 5 also plays a vital role in risk management, offering a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate IT-related risks. It aids in efficient resource allocation, enabling organizations to make informed decisions regarding IT investments. Moreover, COBIT® 5 promotes transparency and accountability in IT processes, facilitating areas of improvement identification and compliance demonstration. The framework's compatibility with various industry standards and frameworks, such as ITIL and ISO/IEC 27001, enhances its appeal as a versatile tool applicable to organizations of all sizes and industries. In summary, COBIT® 5 serves as an invaluable resource for organizations aspiring to elevate their IT governance and management practices, aligning IT with business objectives and enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
In today's digital-centric business landscape, the critical role of IT risk management cannot be overstated. As organizations increasingly rely on technology to drive their operations, serve customers, and manage data, they become more exposed to a wide array of IT-related risks. These risks can range from cybersecurity threats and data breaches to system failures and compliance violations. Effectively managing these risks is essential for business continuity, reputation preservation, and regulatory compliance.
IT risk management is a systematic and structured approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring IT-related risks. Its significance lies in its ability to proactively identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take preemptive action to reduce their impact. Here are several key aspects highlighting the critical role of IT risk management:
1. Protecting Business Assets: IT systems and digital assets are vital components of modern businesses. IT risk management safeguards these assets from a wide range of threats, including cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data loss. By protecting these assets, organizations can ensure the uninterrupted flow of operations and maintain customer trust.
2. Safeguarding Reputation: A data breach or security incident can have severe consequences for an organization's reputation. IT risk management practices, including robust cybersecurity measures and incident response plans, help minimize the risk of reputational damage by preventing or mitigating the impact of such incidents.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to stringent regulations related to data protection, privacy, and security. IT risk management ensures that organizations remain in compliance with these regulations, avoiding costly fines and legal repercussions.
4. Business Continuity: Effective risk management includes disaster recovery and business continuity planning. This ensures that in the event of IT disruptions, whether due to natural disasters or technical failures, organizations can continue to operate or quickly recover their operations.
5. Cost Reduction: Well-planned IT risk management can lead to cost savings. By identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can reduce the financial impact of potential incidents and allocate resources more efficiently.
6. Decision Support: IT risk assessments provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities and threats an organization faces. This information aids in informed decision-making, such as prioritizing investments in security measures and risk mitigation strategies.
7. Competitive Advantage: Organizations that can demonstrate effective IT risk management practices often gain a competitive edge. Customers and partners are increasingly concerned about data security and compliance, making sound risk management a selling point.
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5, the globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, offers a structured and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within organizations. Its approach can be summarized in a few key steps, making it accessible for organizations of various sizes and industries:
-
Understand Business Goals: First, know your organization's business objectives well. IT should support these goals.
-
Set Risk Tolerance: Decide how much risk you're willing to accept to achieve your business goals, like setting a limit on a game.
-
Identify IT Risks: Spot potential IT risks, such as cyber threats or software problems, just like noticing road obstacles.
-
Assess Risks: Estimate how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, similar to evaluating the size of a road pothole and its likelihood of causing damage.
-
Respond to Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like getting insurance), or accept it, just as you choose to fix a pothole or take a different route.
-
Monitor Continuously: Keep an eye on risks all the time, like watching the road while driving, and adjust your plans if new risks appear.
-
Communicate Clearly: Make sure everyone in your organization understands the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Report and Follow Rules: Share information about how you're handling risks with key people and stay in line with laws and standards.
-
Learn and Improve: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to get better at it over time, like becoming a better driver after each trip.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's approach to IT risk management is like planning a safe journey. You know where you want to go (business goals), identify potential roadblocks (IT risks), set limits on how risky you're willing to be, and use strategies to navigate safely. This helps organizations protect their IT systems and make smart choices in the digital world.
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
Integrating COBIT® 5, a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management, with IT risk management brings several significant benefits to organizations. This integration creates a powerful synergy that enhances an organization's ability to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key advantages:
-
Business Alignment: Aligns IT activities with what the organization wants to achieve, ensuring that IT supports business goals.
-
Proactive Risk Management: Helps spot and address IT risks before they become big problems.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Provides insights for smart decisions about IT investments and how to deal with risks.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Makes it easier to follow rules and regulations related to IT risk management.
-
Efficient Resource Use: Helps allocate resources wisely by focusing on the most important risks.
-
Clear Communication: Makes it easy to explain IT risks and how they're being managed to everyone in the organization.
-
Adaptation to Change: Keeps an eye on risks and adjusts strategies as needed to stay safe in a changing world.
-
Easier Audits: Simplifies the process of checking that risk management practices are working correctly.
-
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that do this well look better to customers and partners who care about data security and following the rules.
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5 provides a structured and comprehensive framework for IT risk management within organizations. This framework offers a clear path to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key components and steps in COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management:
-
Identify Risks: Find potential IT risks that could harm your organization, like cyber threats or data problems.
-
Assess Risks: Figure out how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, so you know which ones need attention.
-
Manage Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like insurance), or accept it.
-
Keep an Eye Out: Continuously watch for changes in risks and adjust your plans accordingly.
-
Report Clearly: Share what you're doing about risks with everyone in your organization and make sure to document everything.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management follows the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Learn and Get Better: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to do it even better next time.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of all your IT decisions and fits with your overall goals.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management is like a clear roadmap to help organizations handle IT risks wisely. It guides you in spotting risks, figuring out how to deal with them, and making sure you're following the rules and improving over time. This helps keep your organization safe and successful in the digital world.
Practical Implementation Steps
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework involves practical steps to ensure a systematic and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within your organization. Here are the key implementation steps:
-
Assign Responsibilities: Appoint people to handle risk management tasks and make sure senior leaders support the process.
-
Set Risk Limits: Decide how much risk your organization can accept for different types of IT activities.
-
Spot Risks: Identify potential IT risks using your team's knowledge and available data.
-
Check Risks: Evaluate each risk to see how big it is and how likely it is to happen, and then prioritize them.
-
Make Risk Plans: Create plans to deal with the most important risks, deciding whether to avoid them, reduce their impact, transfer them (like buying insurance), or accept them.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of your regular IT processes and document it.
-
Keep Watch: Set up a system to keep an eye on how risks change and how your plans are working.
-
Tell Everyone: Regularly tell your team and leaders about the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Keep Records: Write down everything you do related to risk management.
-
Train and Learn: Teach your team about risk management and learn from your experiences to get better over time.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management meets the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Get Help If Needed: Consider getting outside experts to help or assess your risk management.
In simple terms, these steps help organizations manage IT risks effectively, aligning with their goals and complying with rules while learning and improving along the way.
Real-world Examples
Here are some real-world examples of organizations that have successfully implemented COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework:
-
JPMorgan Chase & Co.: JPMorgan Chase, one of the world's largest financial institutions, utilizes COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the security and reliability of its IT systems. The framework helps them identify and assess risks associated with their extensive digital operations, including online banking and financial services. It enables them to proactively address cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and regulatory compliance challenges.
-
The World Bank: The World Bank, a global financial institution, leverages COBIT® 5 to manage IT risks across its diverse operations. They use the framework to identify and assess risks related to the implementation of technology in development projects. This helps them mitigate potential project delays, budget overruns, and data security issues.
-
Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA): DEWA, the utility provider for Dubai, uses COBIT® 5 to enhance IT risk management in the context of critical infrastructure. They apply the framework to identify and address risks associated with their energy and water supply systems. This ensures the reliability and resilience of their services, even in the face of IT-related challenges.
-
PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers): As a leading global professional services firm, PwC employs COBIT® 5 for IT risk management to help their clients across various industries. They assist organizations in identifying and managing IT risks to enhance cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and overall operational efficiency.
-
Nestlé: Nestlé, the multinational food and beverage company, uses COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the integrity of its global IT systems. This includes managing risks related to data privacy, supply chain, and production systems. The framework helps Nestlé maintain the trust of its customers and regulators while ensuring the smooth operation of its business.
These real-world examples demonstrate how organizations across different sectors, including finance, development, utilities, and professional services, leverage COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to enhance their IT governance and protect their operations from a wide range of IT-related risks. This illustrates the versatility and effectiveness of COBIT® 5 in managing IT risks in various contexts.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework comes with a set of challenges and considerations that organizations should carefully address. One significant challenge is resource allocation, involving finding the right personnel and financial investments for risk management initiatives. Changing the organizational culture to prioritize risk management can be a formidable hurdle, as it requires strong leadership support and effective communication to instill the importance of risk management across all levels of the organization. The complexity of modern IT environments, with their ever-evolving nature, presents another challenge, necessitating the use of advanced monitoring tools and regular risk assessments to keep up. Adhering to regulatory requirements is a critical consideration, especially as rules can change frequently, making it vital to stay informed and seek expert guidance when needed.
Safeguarding sensitive data from breaches and cyberattacks remains a constant challenge, demanding robust cybersecurity measures and well-defined incident response plans. Integrating COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework with existing IT governance processes may pose difficulties, necessitating expert guidance and a strategic approach to ensure seamless integration. Building and maintaining the necessary skills and knowledge within the organization for effective risk management requires investment in training and development programs. Overcoming resistance to change and managing organizational change effectively is essential, as implementing new risk management processes can meet with opposition. Finally, measuring the effectiveness of risk management efforts and reporting on them in a clear and meaningful way can be complex, requiring the definition of key performance indicators and metrics to evaluate success and communicate progress to stakeholders. Addressing these challenges and considerations strategically empowers organizations to protect their IT assets, align IT with business objectives, and ensure resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
How to obtain the COBIT Foundation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework offers organizations a structured and comprehensive approach to navigate the complex landscape of IT-related risks. While it brings substantial benefits such as enhanced alignment with business goals, proactive risk identification, and improved decision-making, it also presents various challenges and considerations. These challenges include resource allocation, cultural change, the complexity of IT environments, regulatory compliance, data security, integration with existing processes, skills and training, change management, and effective measurement and reporting.
Despite these challenges, organizations that commit to implementing COBIT® 5's framework stand to gain in terms of better IT risk management, alignment with regulatory requirements, and enhanced data security. It empowers organizations to proactively identify and address risks, ultimately safeguarding their IT assets and ensuring their resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Therefore, while the road to effective IT risk management may be challenging, the destination of a secure and well-aligned IT environment is well worth the journey.
A Complete Guide to ITIL Concepts, Processes, and Summary
Welcome to "A Complete Guide to ITIL Concepts and Summary Process: What is ITIL?" In this comprehensive exploration, we demystify ITIL, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, offering you a compass to navigate the intricate realm of IT Service Management (ITSM). Discover the core concepts of ITIL, unravel its summary processes, and understand its pivotal role in optimizing IT service delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reshaping modern business operations. Whether you're an IT professional, a business leader, or simply curious about ITIL's impact, this guide equips you with essential knowledge, transforming the way you perceive and implement IT service management practices, all within a single paragraph.
Table of Contents
What is ITIL?
What's in the ITIL?
Benefits of ITIL:
Drawbacks of ITIL:
What are the ITIL Concepts?
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL Framework
1. Service Strategy
2. Service Design
3. Service Transition
4. Service Operations
5. Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
How Does ITIL Help Business?
What Will ITIL Cost?
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL Processes and Functions
History of ITIL
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
What is ITIL?
ITIL, or Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a widely adopted framework for IT service management. It offers a structured approach to aligning IT services with business objectives and delivering high-quality services to customers. ITIL encompasses various phases, including service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement. It provides best practices and guidelines to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and customer-centricity of IT processes and services, making it a valuable resource for organizations seeking to improve their IT operations.
What's in the ITIL?
ITIL consists of a structured framework for IT service management, including a service lifecycle with stages like Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement. It defines processes, roles, and functions within IT organizations, guiding how services are designed, delivered, and improved. ITIL emphasizes aligning IT with business goals, offering best practices for incident and problem management, change control, and more. It also provides certification options for IT professionals to validate their expertise. Overall, ITIL offers a holistic approach to managing IT services effectively and efficiently.
Benefits of ITIL
Implementing ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) in an organization can bring several significant benefits, including:
-
Improved Service Quality: ITIL promotes best practices and standardized processes, leading to more consistent and reliable IT service delivery. This, in turn, enhances the overall quality of IT services, reducing downtime and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Better Alignment with Business Goals: ITIL encourages the alignment of IT services with the objectives and needs of the business. This ensures that IT investments and efforts contribute directly to the organization's success.
-
Cost Efficiency: By optimizing processes and resources, ITIL helps organizations reduce operational costs. Effective incident management, problem resolution, and resource allocation lead to cost savings.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: ITIL's customer-centric approach ensures that IT services are designed and delivered with the customer's experience in mind. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations leads to higher satisfaction levels.
-
Reduced Risk: ITIL's focus on change management and risk mitigation helps organizations minimize the potential for disruptions and security breaches during service transitions or changes.
Drawbacks of ITIL
While ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) offers many advantages, it also has some potential drawbacks and challenges:
-
Complexity: ITIL is a comprehensive framework with a multitude of processes, roles, and functions. Implementing the full framework can be complex and resource-intensive, especially for small organizations.
-
Cost: The implementation of ITIL may involve significant upfront costs, including training, software, and process redesign. These expenses can be a barrier for some organizations.
-
Resource Intensive: ITIL requires dedicated resources, including personnel, tools, and time for training and implementation. Smaller organizations may struggle to allocate these resources.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes in processes and procedures that ITIL mandates, especially if they have been accustomed to their current ways of working. This can slow down adoption.
-
Overstandardization: In some cases, ITIL's emphasis on standardization can stifle innovation and adaptability. Organizations may become too rigid in their processes and struggle to respond to rapidly changing business needs.
What are the ITIL Concepts?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) encompasses several key concepts that form the foundation of its framework for IT service management. These concepts help organizations understand and implement effective IT service management practices. Here are the core ITIL concepts:
-
Service: ITIL views services as a means of delivering value to customers without the ownership of specific costs and risks.
-
Service Management: ITIL involves specialized organizational capabilities to deliver value through IT services, encompassing processes, functions, roles, and responsibilities.
-
Service Lifecycle: ITIL's framework revolves around five stages: Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: ITIL defines a set of processes, each with specific activities, inputs, outputs, and roles, essential for effective IT service management.
-
SLA and KPI: ITIL uses Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to define service quality and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure and monitor service performance and effectiveness.
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Here are the seven simplified guiding principles of ITIL:
-
Value-Centric: Focus on delivering value to customers and the business.
-
Start Where You Are: Build on your existing processes and capabilities.
-
Feedback-Driven Progress: Continuously improve through feedback and small changes.
-
Collaborate and Communicate: Work together and share information for better results.
-
Think Holistically: Consider the big picture and interconnectedness of services.
-
Keep it Simple: Avoid complexity and prioritize practicality.
-
Optimize and Automate: Streamline processes and use automation to improve efficiency.
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) uses specific terminology to describe its concepts and processes. Here are some key ITIL terms:
-
Service: The means by which value is delivered to customers, often in the form of intangible deliverables like email or network connectivity.
-
Service Management: The set of organizational capabilities for delivering value to customers in the form of services.
-
Service Lifecycle: The stages of a service's existence, including Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: A structured set of activities designed to accomplish a specific objective. ITIL defines numerous processes for IT service management.
-
Function: A team or group of people with specific skills and resources responsible for carrying out one or more processes or activities.
-
Role: A defined set of responsibilities and activities assigned to an individual or group, such as a Service Owner or Incident Manager.
-
Stakeholder: Individuals or groups with an interest in or an impact on the services provided by an organization. This can include customers, users, suppliers, and employees.
-
Service Provider: The organization delivering IT services to customers. It can be an internal IT department or an external service provider.
-
Customer: The person or group that defines requirements for IT services and receives the value provided by those services.
-
User: Individuals who utilize IT services to carry out their tasks and achieve their goals, which may or may not be the same as the customer.
ITIL Framework
The ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework is a comprehensive set of best practices and guidelines for IT service management (ITSM). It provides a structured approach for organizations to plan, design, deliver, operate, and continually improve their IT services. The framework is designed to align IT services with the needs of the business and ensure the efficient and effective delivery of those services. Here are the key components and aspects of the ITIL framework:
-
Service Strategy: Defining the organization's IT service strategy, considering business objectives and customer needs.
-
Service Design: Designing IT services, processes, and supporting infrastructure.
-
Service Transition: Managing the transition of new or changed services into the production environment.
-
Service Operation: Ensuring the day-to-day delivery and management of IT services.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): Identifying and implementing improvements to services and processes.
Service Strategy
Service Strategy in ITIL is the critical phase where an organization aligns its IT services with its business objectives and needs. It involves defining a clear service strategy, managing a portfolio of IT services, ensuring financial viability, understanding and influencing customer demand, coordinating service design, managing risks, and nurturing strong business relationships. The goal is to create a roadmap that ensures IT services provide value to the business, support its success, and remain cost-effective, thus guiding subsequent phases of service management and helping the organization make informed decisions about service design, transition, and operation.
Service Design
Service Design, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, focuses on crafting IT services that are not only technically robust but also perfectly aligned with the organization's strategic goals and customer needs. It encompasses the meticulous planning and design of services, including service catalogs, service levels, capacity, availability, continuity, security, and supplier relationships. By adhering to ITIL principles and leveraging design coordination, it ensures that services are both cost-effective and poised for seamless transition into the operational environment. Service Design plays a vital role in delivering services that deliver value to the business while maintaining high levels of quality and customer satisfaction.
Service Transition
Service Transition, a critical phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, orchestrates the controlled and efficient movement of new or modified IT services from development and testing into the operational environment. It encompasses comprehensive change management, configuration control, rigorous testing and validation, and knowledge management to minimize risks and disruptions while maximizing the value and quality of services. By adhering to ITIL principles and detailed transition planning, it ensures that services meet customer expectations, business requirements, and service levels. Service Transition plays a pivotal role in the successful delivery of IT services, fostering agility and adaptability within the organization's IT landscape.
Service Operations
Service Operation, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, is responsible for the continuous and efficient delivery of IT services to meet agreed-upon service levels and customer needs. It encompasses incident and problem management to swiftly resolve issues, event management for proactive monitoring and response, request fulfillment, access management, and the critical role of the service desk as a central point of user support. Technical and IT operations management ensure infrastructure reliability, while application management oversees the lifecycle of business-critical software. By adhering to ITIL principles and promoting continual service improvement, Service Operation plays a vital role in maintaining service quality, minimizing disruptions, and contributing to overall customer satisfaction and business resilience.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is a fundamental phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, dedicated to the ongoing enhancement of IT services and processes. It involves systematically measuring service performance, analyzing results, and identifying areas for improvement. By establishing clear metrics, conducting regular reviews, and creating action plans, organizations can drive efficiency, reduce costs, and align IT services with evolving business needs. CSI fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that IT services remain adaptable and responsive to changing customer requirements and market dynamics, ultimately delivering greater value and quality to the organization and its stakeholders.
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
-
Assessment and Alignment: Begin by assessing your organization's existing IT service management practices and identifying areas that need improvement. Determine how well your current practices align with ITIL principles and the organization's business objectives. This assessment provides a baseline for your ITIL implementation efforts.
-
Customization and Planning: ITIL is not a one-size-fits-all framework. Customize ITIL practices to match your organization's specific needs and constraints. Create a clear implementation plan that outlines objectives, milestones, roles, responsibilities, and timelines. Ensure that the plan aligns with your business's strategic goals and secures the necessary resources.
-
Education and Training: Equip your IT teams and staff with the knowledge and skills required for ITIL adoption. Offer training and awareness programs to help them understand the ITIL framework and its benefits. It's essential to create a shared understanding and commitment among team members.
-
Process Redesign and Automation: Redesign or adapt your IT service management processes to align with ITIL best practices. Ensure that these processes are well-documented and easily accessible to all relevant parties. Invest in IT service management tools and technologies that support ITIL processes and automate repetitive tasks to improve efficiency.
-
Continuous Improvement: ITIL is built on the concept of continual service improvement (CSI). Establish a culture of continuous improvement within your organization, where regular reviews and evaluations of ITIL implementation are conducted. Use performance metrics and feedback to identify areas for enhancement and make adjustments to your ITIL practices accordingly. CSI ensures that your IT services remain aligned with evolving business needs and industry best practices.
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
ITIL certification is a valuable credential for individuals working in IT service management and related fields. It offers a structured and globally recognized framework for understanding and implementing best practices in IT service delivery and management. Achieving ITIL certification demonstrates your commitment to improving IT service quality and aligning IT with business goals. It can open doors to career advancement and higher earning potential, as many employers value ITIL certification when hiring or promoting IT professionals. However, it's important to consider the cost and time investment required for training and exams, as well as whether ITIL aligns with your specific career path and goals. Continuous learning and staying updated with the latest ITIL practices are also necessary for maintaining the certification's value. Ultimately, the worth of ITIL certification depends on your career aspirations and the relevance of IT service management in your professional journey.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
ITIL V3 and ITIL V4 certifications represent two distinct iterations of the ITIL framework. While ITIL V3 followed a process-oriented service lifecycle model with a structured certification scheme, ITIL V4 introduced a more flexible and holistic approach to IT service management. V4 emphasizes value co-creation, incorporates guiding principles, and introduces a simplified certification structure with practical orientation. It addresses modern trends like digital transformation and agile practices, making it more adaptable to the evolving needs of organizations in the digital age. The transition from V3 to V4 signifies a shift from a process-centric framework to one that focuses on delivering value, enhancing customer experience, and embracing emerging practices, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
-
Certification Structure:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a certification structure consisting of Foundation, Intermediate (Lifecycle and Capability modules), Expert, and Master levels.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduced a simplified certification scheme with four levels: Foundation, Practitioner, Specialist, and Strategist. The Master level remains the highest certification but is more accessible under V4.
-
Practical Orientation:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 certification focused on theoretical knowledge of ITIL processes and practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 places a stronger emphasis on practical application and adaptation of ITIL principles in real-world scenarios. The Practitioner and Specialist levels are designed to help professionals apply ITIL concepts effectively.
-
Guiding Principles:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not have a specific set of guiding principles.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces seven guiding principles (e.g., Focus on Value, Start Where You Are, Collaborate and Promote Visibility) that underpin the framework and guide decision-making.
-
Service Value Chain:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 organized processes into a service lifecycle with five stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement (CSI).
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces the Service Value System, which includes the Service Value Chain (a set of interconnected activities) and emphasizes value co-creation with customers.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a more rigid and process-centric approach.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 is designed to be more flexible and adaptable, allowing organizations to tailor ITIL practices to their unique needs and circumstances.
-
Digital Transformation and Agile Practices:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not specifically address emerging trends like digital transformation and agile practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 incorporates modern concepts and practices, making it more relevant in the digital age, including considerations for DevOps, Agile, and lean principles.
How Does ITIL Help Business?
ITIL benefits businesses by offering a structured framework for IT service management, resulting in improved service quality, cost efficiency, and alignment with business objectives. It reduces downtime, enhances change management, and facilitates effective risk mitigation. ITIL's customer-centric approach strengthens customer satisfaction, while its emphasis on continual improvement ensures adaptability and competitiveness in the evolving digital landscape. Additionally, it aids in regulatory compliance, fosters effective communication, and establishes transparent IT governance, ultimately contributing to business resilience, growth, and a competitive edge in the market.
What Will ITIL Cost?
The cost of ITIL can vary significantly depending on factors such as the level of certification, training format, study materials, and the size and complexity of ITIL implementation within an organization. ITIL certification exams range from $150 to $700 or more, with associated training and study materials adding to the expenses. Implementing ITIL practices within an organization involves costs related to training, consulting, process redesign, ITSM tools, and ongoing maintenance. It's crucial to budget carefully, considering both certification and implementation costs, while also weighing the long-term benefits of improved IT service quality, efficiency, and alignment with business objectives that ITIL can bring to the organization.
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL reduces costs for organizations by fostering efficiency, standardizing processes, and minimizing the risks and disruptions associated with IT service management. It achieves this through proactive problem management, rigorous change control, optimized resource allocation, meticulous documentation, and a continual focus on improvement. ITIL's emphasis on aligning IT services with business needs ensures that resources are directed towards activities that generate value, avoiding unnecessary expenses. By preventing service outages and incidents, streamlining workflows, and promoting cost transparency, ITIL helps organizations optimize their IT operations, resulting in significant cost reductions and improved cost-effectiveness.
ITIL Processes and Functions
In ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), processes and functions are key components of the framework, serving different roles in managing IT services effectively. Here's an overview of ITIL processes and functions:
ITIL Processes: ITIL defines several processes that are essential for IT service management. These processes are organized into five core lifecycle stages:
-
Service Strategy: This stage focuses on defining the overall strategy for IT services, including understanding customer needs, defining service portfolios, and aligning IT goals with business objectives. Key processes include Service Portfolio Management and Financial Management.
-
Service Design: In this stage, ITIL defines processes for designing IT services, ensuring they meet business requirements and are manageable. Processes include Service Catalog Management, Service Level Management, Capacity Management, and Availability Management.
-
Service Transition: This stage involves transitioning new or modified services into the production environment. Key processes include Change Management, Release and Deployment Management, and Service Validation and Testing.
-
Service Operation: Service Operation is responsible for the daily delivery and management of IT services to meet service levels and customer expectations. Processes here include Incident Management, Problem Management, Event Management, and Request Fulfillment.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): CSI focuses on ongoing improvement of IT services and processes. It includes processes like Service Measurement and Reporting, Service Review, and Process Evaluation.
ITIL Functions: Functions in ITIL represent organizational units or groups responsible for specific activities or roles within the IT service management framework. While not all functions are required in every organization, they provide structure and accountability in managing IT services. Key ITIL functions include:
-
Service Desk: The Service Desk function acts as a central point of contact for users to report incidents, request services, and seek assistance. It plays a critical role in providing support and ensuring efficient communication.
-
Technical Management: This function provides technical expertise and support for IT infrastructure and services. It ensures that technical resources are available and properly maintained.
-
IT Operations Management: Responsible for the day-to-day operational activities required to deliver IT services. This includes data center management, network operations, and hardware maintenance.
-
Application Management: The Application Management function manages the lifecycle of applications, ensuring they are designed, developed, tested, and maintained to support business needs.
-
IT Security Management: While not always defined as a separate function, ITIL emphasizes the importance of security throughout the service lifecycle. This involves managing security policies, access controls, and compliance.
-
Supplier Management: Supplier Management ensures that external suppliers and vendors are effectively managed to deliver the required IT services and support.
These functions and processes work together to ensure that IT services are delivered efficiently, reliably, and in alignment with business goals and customer expectations. They provide a structured approach to managing IT services throughout their lifecycle, from strategy and design to operation and improvement.
History of ITIL
The history of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) traces its origins to the late 1980s when it was developed by the UK's Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA). Initially conceived to standardize and improve IT service management within the UK government, ITIL soon gained recognition for its best-practice guidelines. ITIL V1, released in the late 1980s and early 1990s, laid the foundation with a comprehensive set of 31 books. However, it was in 2000 with the launch of ITIL V2 that ITIL's global impact began to take shape. V2 consolidated the framework into eight core books and gained widespread adoption. ITIL V3, introduced in 2007 and updated in 2011 (ITIL 2011), brought a service lifecycle approach and a focus on aligning IT services with business processes. In 2019, ITIL V4 marked a major shift, emphasizing value co-creation, the Service Value System, and modern IT practices. It continues to evolve, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management and digital transformation. Throughout its history, ITIL has become a globally recognized framework for enhancing IT service quality and alignment with business objectives.
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
ITIL, or the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, encompasses a set of well-defined processes and stages designed to help organizations manage their IT services effectively. The core processes include Service Strategy, which aligns IT services with business goals; Service Design, which focuses on designing services that meet business requirements; Service Transition, which ensures a smooth transition of services into the production environment; Service Operation, responsible for daily service delivery and support; and Continual Service Improvement, which drives ongoing enhancements in service quality and efficiency. These processes are organized into stages that reflect the IT service lifecycle, from aligning IT with business objectives to designing, transitioning, operating, and continually improving services. By following the ITIL framework, organizations can deliver IT services that are not only reliable and cost-effective but also aligned with evolving business needs and customer expectations, ultimately contributing to improved overall business performance and competitiveness.
Read More
Welcome to "A Complete Guide to ITIL Concepts and Summary Process: What is ITIL?" In this comprehensive exploration, we demystify ITIL, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, offering you a compass to navigate the intricate realm of IT Service Management (ITSM). Discover the core concepts of ITIL, unravel its summary processes, and understand its pivotal role in optimizing IT service delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reshaping modern business operations. Whether you're an IT professional, a business leader, or simply curious about ITIL's impact, this guide equips you with essential knowledge, transforming the way you perceive and implement IT service management practices, all within a single paragraph.
Table of Contents
What is ITIL?
What's in the ITIL?
Benefits of ITIL:
Drawbacks of ITIL:
What are the ITIL Concepts?
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL Framework
1. Service Strategy
2. Service Design
3. Service Transition
4. Service Operations
5. Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
How Does ITIL Help Business?
What Will ITIL Cost?
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL Processes and Functions
History of ITIL
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
What is ITIL?
ITIL, or Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a widely adopted framework for IT service management. It offers a structured approach to aligning IT services with business objectives and delivering high-quality services to customers. ITIL encompasses various phases, including service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement. It provides best practices and guidelines to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and customer-centricity of IT processes and services, making it a valuable resource for organizations seeking to improve their IT operations.
What's in the ITIL?
ITIL consists of a structured framework for IT service management, including a service lifecycle with stages like Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement. It defines processes, roles, and functions within IT organizations, guiding how services are designed, delivered, and improved. ITIL emphasizes aligning IT with business goals, offering best practices for incident and problem management, change control, and more. It also provides certification options for IT professionals to validate their expertise. Overall, ITIL offers a holistic approach to managing IT services effectively and efficiently.
Benefits of ITIL
Implementing ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) in an organization can bring several significant benefits, including:
-
Improved Service Quality: ITIL promotes best practices and standardized processes, leading to more consistent and reliable IT service delivery. This, in turn, enhances the overall quality of IT services, reducing downtime and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Better Alignment with Business Goals: ITIL encourages the alignment of IT services with the objectives and needs of the business. This ensures that IT investments and efforts contribute directly to the organization's success.
-
Cost Efficiency: By optimizing processes and resources, ITIL helps organizations reduce operational costs. Effective incident management, problem resolution, and resource allocation lead to cost savings.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: ITIL's customer-centric approach ensures that IT services are designed and delivered with the customer's experience in mind. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations leads to higher satisfaction levels.
-
Reduced Risk: ITIL's focus on change management and risk mitigation helps organizations minimize the potential for disruptions and security breaches during service transitions or changes.
Drawbacks of ITIL
While ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) offers many advantages, it also has some potential drawbacks and challenges:
-
Complexity: ITIL is a comprehensive framework with a multitude of processes, roles, and functions. Implementing the full framework can be complex and resource-intensive, especially for small organizations.
-
Cost: The implementation of ITIL may involve significant upfront costs, including training, software, and process redesign. These expenses can be a barrier for some organizations.
-
Resource Intensive: ITIL requires dedicated resources, including personnel, tools, and time for training and implementation. Smaller organizations may struggle to allocate these resources.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes in processes and procedures that ITIL mandates, especially if they have been accustomed to their current ways of working. This can slow down adoption.
-
Overstandardization: In some cases, ITIL's emphasis on standardization can stifle innovation and adaptability. Organizations may become too rigid in their processes and struggle to respond to rapidly changing business needs.
What are the ITIL Concepts?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) encompasses several key concepts that form the foundation of its framework for IT service management. These concepts help organizations understand and implement effective IT service management practices. Here are the core ITIL concepts:
-
Service: ITIL views services as a means of delivering value to customers without the ownership of specific costs and risks.
-
Service Management: ITIL involves specialized organizational capabilities to deliver value through IT services, encompassing processes, functions, roles, and responsibilities.
-
Service Lifecycle: ITIL's framework revolves around five stages: Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: ITIL defines a set of processes, each with specific activities, inputs, outputs, and roles, essential for effective IT service management.
-
SLA and KPI: ITIL uses Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to define service quality and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure and monitor service performance and effectiveness.
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Here are the seven simplified guiding principles of ITIL:
-
Value-Centric: Focus on delivering value to customers and the business.
-
Start Where You Are: Build on your existing processes and capabilities.
-
Feedback-Driven Progress: Continuously improve through feedback and small changes.
-
Collaborate and Communicate: Work together and share information for better results.
-
Think Holistically: Consider the big picture and interconnectedness of services.
-
Keep it Simple: Avoid complexity and prioritize practicality.
-
Optimize and Automate: Streamline processes and use automation to improve efficiency.
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) uses specific terminology to describe its concepts and processes. Here are some key ITIL terms:
-
Service: The means by which value is delivered to customers, often in the form of intangible deliverables like email or network connectivity.
-
Service Management: The set of organizational capabilities for delivering value to customers in the form of services.
-
Service Lifecycle: The stages of a service's existence, including Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: A structured set of activities designed to accomplish a specific objective. ITIL defines numerous processes for IT service management.
-
Function: A team or group of people with specific skills and resources responsible for carrying out one or more processes or activities.
-
Role: A defined set of responsibilities and activities assigned to an individual or group, such as a Service Owner or Incident Manager.
-
Stakeholder: Individuals or groups with an interest in or an impact on the services provided by an organization. This can include customers, users, suppliers, and employees.
-
Service Provider: The organization delivering IT services to customers. It can be an internal IT department or an external service provider.
-
Customer: The person or group that defines requirements for IT services and receives the value provided by those services.
-
User: Individuals who utilize IT services to carry out their tasks and achieve their goals, which may or may not be the same as the customer.
ITIL Framework
The ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework is a comprehensive set of best practices and guidelines for IT service management (ITSM). It provides a structured approach for organizations to plan, design, deliver, operate, and continually improve their IT services. The framework is designed to align IT services with the needs of the business and ensure the efficient and effective delivery of those services. Here are the key components and aspects of the ITIL framework:
-
Service Strategy: Defining the organization's IT service strategy, considering business objectives and customer needs.
-
Service Design: Designing IT services, processes, and supporting infrastructure.
-
Service Transition: Managing the transition of new or changed services into the production environment.
-
Service Operation: Ensuring the day-to-day delivery and management of IT services.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): Identifying and implementing improvements to services and processes.
Service Strategy
Service Strategy in ITIL is the critical phase where an organization aligns its IT services with its business objectives and needs. It involves defining a clear service strategy, managing a portfolio of IT services, ensuring financial viability, understanding and influencing customer demand, coordinating service design, managing risks, and nurturing strong business relationships. The goal is to create a roadmap that ensures IT services provide value to the business, support its success, and remain cost-effective, thus guiding subsequent phases of service management and helping the organization make informed decisions about service design, transition, and operation.
Service Design
Service Design, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, focuses on crafting IT services that are not only technically robust but also perfectly aligned with the organization's strategic goals and customer needs. It encompasses the meticulous planning and design of services, including service catalogs, service levels, capacity, availability, continuity, security, and supplier relationships. By adhering to ITIL principles and leveraging design coordination, it ensures that services are both cost-effective and poised for seamless transition into the operational environment. Service Design plays a vital role in delivering services that deliver value to the business while maintaining high levels of quality and customer satisfaction.
Service Transition
Service Transition, a critical phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, orchestrates the controlled and efficient movement of new or modified IT services from development and testing into the operational environment. It encompasses comprehensive change management, configuration control, rigorous testing and validation, and knowledge management to minimize risks and disruptions while maximizing the value and quality of services. By adhering to ITIL principles and detailed transition planning, it ensures that services meet customer expectations, business requirements, and service levels. Service Transition plays a pivotal role in the successful delivery of IT services, fostering agility and adaptability within the organization's IT landscape.
Service Operations
Service Operation, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, is responsible for the continuous and efficient delivery of IT services to meet agreed-upon service levels and customer needs. It encompasses incident and problem management to swiftly resolve issues, event management for proactive monitoring and response, request fulfillment, access management, and the critical role of the service desk as a central point of user support. Technical and IT operations management ensure infrastructure reliability, while application management oversees the lifecycle of business-critical software. By adhering to ITIL principles and promoting continual service improvement, Service Operation plays a vital role in maintaining service quality, minimizing disruptions, and contributing to overall customer satisfaction and business resilience.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is a fundamental phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, dedicated to the ongoing enhancement of IT services and processes. It involves systematically measuring service performance, analyzing results, and identifying areas for improvement. By establishing clear metrics, conducting regular reviews, and creating action plans, organizations can drive efficiency, reduce costs, and align IT services with evolving business needs. CSI fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that IT services remain adaptable and responsive to changing customer requirements and market dynamics, ultimately delivering greater value and quality to the organization and its stakeholders.
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
-
Assessment and Alignment: Begin by assessing your organization's existing IT service management practices and identifying areas that need improvement. Determine how well your current practices align with ITIL principles and the organization's business objectives. This assessment provides a baseline for your ITIL implementation efforts.
-
Customization and Planning: ITIL is not a one-size-fits-all framework. Customize ITIL practices to match your organization's specific needs and constraints. Create a clear implementation plan that outlines objectives, milestones, roles, responsibilities, and timelines. Ensure that the plan aligns with your business's strategic goals and secures the necessary resources.
-
Education and Training: Equip your IT teams and staff with the knowledge and skills required for ITIL adoption. Offer training and awareness programs to help them understand the ITIL framework and its benefits. It's essential to create a shared understanding and commitment among team members.
-
Process Redesign and Automation: Redesign or adapt your IT service management processes to align with ITIL best practices. Ensure that these processes are well-documented and easily accessible to all relevant parties. Invest in IT service management tools and technologies that support ITIL processes and automate repetitive tasks to improve efficiency.
-
Continuous Improvement: ITIL is built on the concept of continual service improvement (CSI). Establish a culture of continuous improvement within your organization, where regular reviews and evaluations of ITIL implementation are conducted. Use performance metrics and feedback to identify areas for enhancement and make adjustments to your ITIL practices accordingly. CSI ensures that your IT services remain aligned with evolving business needs and industry best practices.
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
ITIL certification is a valuable credential for individuals working in IT service management and related fields. It offers a structured and globally recognized framework for understanding and implementing best practices in IT service delivery and management. Achieving ITIL certification demonstrates your commitment to improving IT service quality and aligning IT with business goals. It can open doors to career advancement and higher earning potential, as many employers value ITIL certification when hiring or promoting IT professionals. However, it's important to consider the cost and time investment required for training and exams, as well as whether ITIL aligns with your specific career path and goals. Continuous learning and staying updated with the latest ITIL practices are also necessary for maintaining the certification's value. Ultimately, the worth of ITIL certification depends on your career aspirations and the relevance of IT service management in your professional journey.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
ITIL V3 and ITIL V4 certifications represent two distinct iterations of the ITIL framework. While ITIL V3 followed a process-oriented service lifecycle model with a structured certification scheme, ITIL V4 introduced a more flexible and holistic approach to IT service management. V4 emphasizes value co-creation, incorporates guiding principles, and introduces a simplified certification structure with practical orientation. It addresses modern trends like digital transformation and agile practices, making it more adaptable to the evolving needs of organizations in the digital age. The transition from V3 to V4 signifies a shift from a process-centric framework to one that focuses on delivering value, enhancing customer experience, and embracing emerging practices, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
-
Certification Structure:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a certification structure consisting of Foundation, Intermediate (Lifecycle and Capability modules), Expert, and Master levels.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduced a simplified certification scheme with four levels: Foundation, Practitioner, Specialist, and Strategist. The Master level remains the highest certification but is more accessible under V4.
-
-
Practical Orientation:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 certification focused on theoretical knowledge of ITIL processes and practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 places a stronger emphasis on practical application and adaptation of ITIL principles in real-world scenarios. The Practitioner and Specialist levels are designed to help professionals apply ITIL concepts effectively.
-
-
Guiding Principles:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not have a specific set of guiding principles.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces seven guiding principles (e.g., Focus on Value, Start Where You Are, Collaborate and Promote Visibility) that underpin the framework and guide decision-making.
-
-
Service Value Chain:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 organized processes into a service lifecycle with five stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement (CSI).
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces the Service Value System, which includes the Service Value Chain (a set of interconnected activities) and emphasizes value co-creation with customers.
-
-
Flexibility and Adaptability:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a more rigid and process-centric approach.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 is designed to be more flexible and adaptable, allowing organizations to tailor ITIL practices to their unique needs and circumstances.
-
-
Digital Transformation and Agile Practices:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not specifically address emerging trends like digital transformation and agile practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 incorporates modern concepts and practices, making it more relevant in the digital age, including considerations for DevOps, Agile, and lean principles.
-
How Does ITIL Help Business?
ITIL benefits businesses by offering a structured framework for IT service management, resulting in improved service quality, cost efficiency, and alignment with business objectives. It reduces downtime, enhances change management, and facilitates effective risk mitigation. ITIL's customer-centric approach strengthens customer satisfaction, while its emphasis on continual improvement ensures adaptability and competitiveness in the evolving digital landscape. Additionally, it aids in regulatory compliance, fosters effective communication, and establishes transparent IT governance, ultimately contributing to business resilience, growth, and a competitive edge in the market.
What Will ITIL Cost?
The cost of ITIL can vary significantly depending on factors such as the level of certification, training format, study materials, and the size and complexity of ITIL implementation within an organization. ITIL certification exams range from $150 to $700 or more, with associated training and study materials adding to the expenses. Implementing ITIL practices within an organization involves costs related to training, consulting, process redesign, ITSM tools, and ongoing maintenance. It's crucial to budget carefully, considering both certification and implementation costs, while also weighing the long-term benefits of improved IT service quality, efficiency, and alignment with business objectives that ITIL can bring to the organization.
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL reduces costs for organizations by fostering efficiency, standardizing processes, and minimizing the risks and disruptions associated with IT service management. It achieves this through proactive problem management, rigorous change control, optimized resource allocation, meticulous documentation, and a continual focus on improvement. ITIL's emphasis on aligning IT services with business needs ensures that resources are directed towards activities that generate value, avoiding unnecessary expenses. By preventing service outages and incidents, streamlining workflows, and promoting cost transparency, ITIL helps organizations optimize their IT operations, resulting in significant cost reductions and improved cost-effectiveness.
ITIL Processes and Functions
In ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), processes and functions are key components of the framework, serving different roles in managing IT services effectively. Here's an overview of ITIL processes and functions:
ITIL Processes: ITIL defines several processes that are essential for IT service management. These processes are organized into five core lifecycle stages:
-
Service Strategy: This stage focuses on defining the overall strategy for IT services, including understanding customer needs, defining service portfolios, and aligning IT goals with business objectives. Key processes include Service Portfolio Management and Financial Management.
-
Service Design: In this stage, ITIL defines processes for designing IT services, ensuring they meet business requirements and are manageable. Processes include Service Catalog Management, Service Level Management, Capacity Management, and Availability Management.
-
Service Transition: This stage involves transitioning new or modified services into the production environment. Key processes include Change Management, Release and Deployment Management, and Service Validation and Testing.
-
Service Operation: Service Operation is responsible for the daily delivery and management of IT services to meet service levels and customer expectations. Processes here include Incident Management, Problem Management, Event Management, and Request Fulfillment.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): CSI focuses on ongoing improvement of IT services and processes. It includes processes like Service Measurement and Reporting, Service Review, and Process Evaluation.
ITIL Functions: Functions in ITIL represent organizational units or groups responsible for specific activities or roles within the IT service management framework. While not all functions are required in every organization, they provide structure and accountability in managing IT services. Key ITIL functions include:
-
Service Desk: The Service Desk function acts as a central point of contact for users to report incidents, request services, and seek assistance. It plays a critical role in providing support and ensuring efficient communication.
-
Technical Management: This function provides technical expertise and support for IT infrastructure and services. It ensures that technical resources are available and properly maintained.
-
IT Operations Management: Responsible for the day-to-day operational activities required to deliver IT services. This includes data center management, network operations, and hardware maintenance.
-
Application Management: The Application Management function manages the lifecycle of applications, ensuring they are designed, developed, tested, and maintained to support business needs.
-
IT Security Management: While not always defined as a separate function, ITIL emphasizes the importance of security throughout the service lifecycle. This involves managing security policies, access controls, and compliance.
-
Supplier Management: Supplier Management ensures that external suppliers and vendors are effectively managed to deliver the required IT services and support.
These functions and processes work together to ensure that IT services are delivered efficiently, reliably, and in alignment with business goals and customer expectations. They provide a structured approach to managing IT services throughout their lifecycle, from strategy and design to operation and improvement.
History of ITIL
The history of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) traces its origins to the late 1980s when it was developed by the UK's Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA). Initially conceived to standardize and improve IT service management within the UK government, ITIL soon gained recognition for its best-practice guidelines. ITIL V1, released in the late 1980s and early 1990s, laid the foundation with a comprehensive set of 31 books. However, it was in 2000 with the launch of ITIL V2 that ITIL's global impact began to take shape. V2 consolidated the framework into eight core books and gained widespread adoption. ITIL V3, introduced in 2007 and updated in 2011 (ITIL 2011), brought a service lifecycle approach and a focus on aligning IT services with business processes. In 2019, ITIL V4 marked a major shift, emphasizing value co-creation, the Service Value System, and modern IT practices. It continues to evolve, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management and digital transformation. Throughout its history, ITIL has become a globally recognized framework for enhancing IT service quality and alignment with business objectives.
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
ITIL, or the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, encompasses a set of well-defined processes and stages designed to help organizations manage their IT services effectively. The core processes include Service Strategy, which aligns IT services with business goals; Service Design, which focuses on designing services that meet business requirements; Service Transition, which ensures a smooth transition of services into the production environment; Service Operation, responsible for daily service delivery and support; and Continual Service Improvement, which drives ongoing enhancements in service quality and efficiency. These processes are organized into stages that reflect the IT service lifecycle, from aligning IT with business objectives to designing, transitioning, operating, and continually improving services. By following the ITIL framework, organizations can deliver IT services that are not only reliable and cost-effective but also aligned with evolving business needs and customer expectations, ultimately contributing to improved overall business performance and competitiveness.
ISO 20000 IT Service Management: Benefits & Maintenance.
ISO/IEC 20000 is an internationally recognized standard for IT service management (ITSM) that provides organizations with a framework to effectively deliver and manage their IT services. It outlines the best practices and requirements for establishing, implementing, and maintaining a service management system. By achieving ISO/IEC 20000 certification, organizations demonstrate their commitment to delivering high-quality IT services and meeting customer expectations.
The ISO/IEC 20000 certification specifically focuses on IT service management, which involves the design, delivery, and continuous improvement of IT services to support business objectives. It encompasses various processes and activities, such as incident management, problem management, service design, service transition, and service operation. These processes are aimed at ensuring that IT services are delivered efficiently, effectively, and in alignment with the organization's overall goals.
Obtaining the ISO/IEC 20000 certification is not only a testament to an organization's dedication to excellence in IT service management but also provides several benefits. It helps organizations enhance their service quality, improve customer satisfaction, and establish a culture of continual improvement. Additionally, ISO/IEC 20000 certification can enhance the organization's reputation, increase its competitive edge, and provide a basis for establishing service level agreements with customers.
To achieve ISO/IEC 20000 certification, organizations must undergo a thorough assessment of their IT service management practices and demonstrate compliance with the standard's requirements. This assessment is typically conducted by an independent certification body, ensuring objectivity and impartiality in evaluating the organization's IT service management system.
In summary, ISO/IEC 20000 IT Service Management certification is a prestigious recognition that signifies an organization's adherence to internationally recognized best practices in IT service delivery. It helps organizations improve their service quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and establish a strong foundation for effective IT service management.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to ISO 20000 Certification:
-
Understanding the ISO 20000 Framework:
-
Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification:
-
Steps to Achieve ISO 20000 Certification:
-
ISO 20000 Certification and IT Service Providers:
-
Maintaining ISO 20000 Certification:
-
Conlusion
1. Introduction to ISO 20000 Certification:
ISO 20000 is an international standard that outlines the requirements for an organization's IT service management (ITSM) system. It provides a framework for effectively managing and delivering IT services to meet customer requirements and improve overall service quality.
-
What is ISO 20000?
-
Definition: ISO 20000, also known as ISO/IEC 20000, is the international standard for IT service management systems.
-
Background: It was first published in 2005 by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
-
Scope: ISO 20000 covers all aspects of IT service management, including service design, transition, delivery, and improvement.
-
Importance of ISO 20000 Certification
-
Customer Confidence: ISO 20000 certification demonstrates an organization's commitment to delivering high-quality IT services and meeting customer requirements.
-
Industry Recognition: It provides recognition and credibility in the IT service management industry, distinguishing certified organizations from their competitors.
-
Compliance: ISO 20000 certification ensures compliance with internationally recognized best practices for IT service management.
-
Continuous Improvement: It promotes a culture of continual improvement, driving organizations to enhance their IT service delivery processes and customer satisfaction.
-
Benefits of Achieving ISO 20000 Certification
-
Service Quality Improvement: ISO 20000 helps organizations establish robust processes and procedures to consistently deliver high-quality IT services.
-
Customer Satisfaction: By meeting ISO 20000 requirements, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction by meeting their service expectations and requirements.
-
Operational Efficiency: ISO 20000 provides guidelines for efficient service management practices, leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
-
Risk Management: It helps organizations identify and mitigate risks associated with IT service management, ensuring business continuity and minimizing service disruptions.
-
Competitive Advantage: ISO 20000 certification sets organizations apart from their competitors, giving them a competitive edge in the market.
2. Understanding the ISO 20000 Framework.
ISO 20000 is a comprehensive framework that outlines the requirements for implementing and maintaining an effective IT service management system. Familiarizing yourself with the key components and sections of the ISO 20000 standard will help you understand how it supports IT service management best practices.
-
Overview of the ISO 20000 Standard
-
Structure: ISO 20000 is divided into two parts - Part 1: Service management system requirements (SMSR) and Part 2: Guidance on the application of SMSR.
-
Part 1: This section defines the requirements that organizations need to meet to achieve ISO 20000 certification.
-
Part 2: It provides guidance on implementing the requirements specified in Part 1 and offers additional insights into interpreting and applying the standard.
-
Key Components of ISO 20000
-
Service Management System (SMS): ISO 20000 emphasizes the establishment of a service management system, which serves as the foundation for effective IT service delivery.
-
Service Management Processes: The standard outlines specific processes that organizations should implement to manage IT services, including incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management.
-
Documentation Requirements: ISO 20000 defines the documentation necessary to demonstrate compliance, such as service management plans, policies, procedures, and records.
-
ISO 20000 Sections and Requirements
-
Context of the Organization: This section focuses on understanding the organization's context and identifying the scope of the IT service management system.
-
Leadership: It emphasizes the involvement and commitment of top management in establishing and maintaining the service management system.
-
Planning: This section covers activities related to risk management, service planning, and service design and transition.
-
Support: It outlines the requirements for resource management, competency and awareness, communication, and document management.
-
Operation: This section addresses the execution of service management processes, including service delivery, service control, and resolution of incidents and service requests.
-
Performance Evaluation: It specifies the requirements for monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation of the service management system and services.
-
Improvement: This section focuses on continual improvement of the service management system and the services provided.
-
Alignment with ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
-
Relationship with ITIL: ISO 20000 and ITIL are closely related, with ISO 20000 incorporating many ITIL best practices into its framework.
-
ITIL Processes in ISO 20000: ISO 20000 recognizes and aligns with various ITIL processes, such as incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management.
-
Synergies and Enhancements: Implementing ISO 20000 can help organizations enhance their ITIL implementation and vice versa, as both frameworks share common goals and principles.
3. Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification
Obtaining ISO 20000 certification brings numerous advantages to organizations in terms of service quality, operational efficiency, and credibility. Here are some key benefits that organizations can experience:
-
Improved Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction
-
Standardized Processes: ISO 20000 requires organizations to establish and follow standardized processes for IT service management, ensuring consistent and reliable service delivery.
-
Service Level Management: Implementing ISO 20000 helps organizations effectively manage service level agreements (SLAs), resulting in improved service performance and meeting customer expectations.
-
Incident and Problem Management: ISO 20000 provides guidelines for incident and problem management, enabling organizations to respond to and resolve issues promptly, minimizing service disruptions and enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness
-
Streamlined Processes: ISO 20000 encourages organizations to streamline their IT service management processes, eliminating redundancies and improving efficiency.
-
Resource Optimization: By implementing ISO 20000, organizations can optimize their resource allocation, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively and reducing unnecessary costs.
-
Change Management: ISO 20000 emphasizes proper change management practices, reducing the risk of errors, service disruptions, and costly rollbacks.
-
Increased Credibility and Competitive Advantage
-
International Recognition: ISO 20000 is an internationally recognized standard for IT service management, providing organizations with credibility and demonstrating their commitment to quality.
-
Competitive Differentiation: ISO 20000 certification sets organizations apart from their competitors, particularly when bidding for contracts or providing services to clients who prioritize certified providers.
-
Trust and Confidence: Customers and stakeholders have increased trust and confidence in organizations that have achieved ISO 20000 certification, knowing that their IT services are managed according to globally accepted best practices.
-
Compliance with Best Practices and Regulations
-
Alignment with ITIL: ISO 20000 aligns with ITIL, incorporating many ITIL best practices into its framework. This alignment ensures compliance with widely recognized IT service management principles.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Achieving ISO 20000 certification helps organizations demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements related to IT service management, enhancing their reputation and credibility.
-
Continual Service Improvement
-
Continuous Improvement Culture: ISO 20000 promotes a culture of continual service improvement, encouraging organizations to monitor, measure, and evaluate their IT services to identify areas for enhancement.
-
Proactive Problem Resolution: Through ISO 20000, organizations can implement proactive problem management practices, identifying and addressing underlying issues before they impact service quality.
4.Steps to Achieve ISO 20000 Certification
-
Familiarize Yourself with ISO 20000:
-
Understand the requirements and key components of the ISO 20000 standard.
-
Familiarize yourself with the structure and sections of the standard to gain a comprehensive understanding.
-
Conduct a Gap Analysis:
-
Evaluate your organization's current IT service management practices against the requirements specified in the ISO 20000 standard.
-
Identify areas where your organization already complies with the standard and areas that require improvement or alignment.
-
Develop an Implementation Plan:
-
Create a detailed plan that outlines the necessary actions, resources, and timelines for implementing ISO 20000 within your organization.
-
Define roles and responsibilities for the implementation team members.
-
Establish the Service Management System (SMS):
-
Develop and document the service management system, which will serve as the foundation for implementing ISO 20000 requirements.
-
Define the scope of your SMS, considering the services, processes, and organizational units covered by the certification.
-
Implement Required Processes and Procedures:
-
Implement the specific processes and procedures outlined in the ISO 20000 standard, such as incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management.
-
Align your existing processes with the ISO 20000 requirements or establish new ones where necessary.
-
Document the SMS:
-
Develop the required documentation to demonstrate compliance with ISO 20000.
-
Document policies, procedures, work instructions, and records necessary to support the implementation and operation of the SMS.
-
Conduct Internal Audits:
-
Perform internal audits to assess the effectiveness and compliance of your SMS with ISO 20000 requirements.
-
Identify any non-conformities and take corrective actions to address them.
-
Management Review:
-
Conduct a management review to evaluate the performance of the SMS and the progress towards ISO 20000 certification.
-
Ensure that top management is actively involved in reviewing the SMS and providing necessary support.
-
Select an Accredited Certification Body:
-
Choose an accredited certification body to perform the final certification audit.
-
Verify that the certification body has experience and expertise in ISO 20000 certification.
-
External Certification Audit:
-
The certification body will conduct an on-site audit to assess your organization's compliance with ISO 20000 requirements.
-
The audit will typically involve interviews, documentation reviews, and observations of your IT service management practices.
-
Corrective Actions and Finalization:
-
Address any non-conformities identified during the certification audit and implement corrective actions.
-
Provide necessary evidence of compliance to the certification body.
-
Once all non-conformities are resolved, the certification body will issue the ISO 20000 certification.
-
Continual Improvement:
-
Embrace a culture of continual improvement by monitoring, measuring, and evaluating your IT service management practices.
-
Implement processes to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 20000 requirements and drive continuous enhancement of your services.
5.ISO 20000 Certification and IT Service Providers
ISO 20000 certification holds significant benefits for IT service providers, helping them enhance their service delivery, gain customer trust, and establish a competitive edge. Here are some key aspects of ISO 20000 certification for IT service providers:
-
Customer Confidence and Trust:
-
ISO 20000 certification demonstrates an IT service provider's commitment to delivering high-quality services that meet customer requirements and expectations.
-
Certified providers are seen as more reliable, trustworthy, and capable of delivering consistent and efficient IT services.
-
Differentiation and Competitive Advantage:
-
ISO 20000 certification sets IT service providers apart from their competitors in a crowded market.
-
Certification can serve as a unique selling point and a competitive advantage, helping providers attract new customers and win contracts.
-
Improved Service Delivery:
-
ISO 20000 provides guidelines for effective service management processes, ensuring IT service providers have well-defined processes in place.
-
By implementing ISO 20000 requirements, providers can enhance their service delivery, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
-
ISO 20000 encourages IT service providers to streamline their processes, eliminate redundancies, and optimize resource allocation.
-
By aligning with ISO 20000, providers can improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver services more effectively.
-
Alignment with Customer Requirements:
-
ISO 20000 certification ensures that IT service providers align with internationally recognized best practices and standards for IT service management.
-
Many customers and organizations specifically require ISO 20000 certification when selecting service providers, making it essential for business opportunities.
-
Compliance with Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
-
ISO 20000 helps IT service providers effectively manage and fulfill SLAs with their customers.
-
It provides guidelines for defining, monitoring, and reporting on service levels, ensuring providers meet their contractual obligations.
-
Continual Improvement:
-
ISO 20000 promotes a culture of continual service improvement within IT service providers.
-
By monitoring and evaluating service performance, providers can identify areas for enhancement and implement proactive measures for ongoing improvement.
-
Vendor and Partner Relationships:
-
ISO 20000 certification can be advantageous when working with vendors or partners, as it demonstrates a provider's commitment to quality and adherence to best practices.
-
It enhances the provider's credibility and strengthens their relationships with vendors and partners.
6.Maintaining ISO 20000 Certification
Achieving ISO 20000 certification is a significant accomplishment, but it's essential to continuously maintain compliance with the standard's requirements to preserve the benefits it offers. Here are key aspects to consider for maintaining ISO 20000 certification:
-
Regular Internal Audits:
-
Conduct internal audits at regular intervals to assess the effectiveness and compliance of your IT service management system (SMS).
-
Internal audits help identify any non-conformities or areas that need improvement, allowing you to take corrective actions proactively.
-
Corrective Actions and Preventive Measures:
-
Address any non-conformities identified during internal audits promptly.
-
Implement corrective actions and preventive measures to prevent the recurrence of non-conformities and improve the effectiveness of your SMS.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Measurement:
-
Continuously monitor and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) related to IT service management.
-
Regularly review and analyze data to identify trends, areas for improvement, and potential risks.
-
Management Review:
-
Conduct periodic management reviews to evaluate the performance of the SMS and the effectiveness of your IT service management processes.
-
Involve top management in the review process to ensure ongoing commitment and support.
-
Employee Training and Awareness:
-
Provide regular training and awareness programs to employees on the requirements of ISO 20000 and their roles in maintaining compliance.
-
Ensure employees are familiar with the processes, procedures, and policies related to IT service management.
-
Document Control and Record Keeping:
-
Maintain proper document control processes to ensure the accuracy, availability, and relevance of documented information.
-
Keep records of key activities, such as incidents, problem resolutions, changes, and service level agreements (SLAs).
-
External Audits and Surveillance Visits:
-
The certification body may conduct surveillance visits or periodic audits to assess ongoing compliance with ISO 20000 requirements.
-
Prepare for these audits by ensuring all necessary documentation and records are up to date and readily available.
-
Continual Improvement:
-
Foster a culture of continual improvement within your organization.
-
Encourage employees to provide suggestions for enhancing the IT service management processes and implementing improvements.
-
Stay Updated with Changes:
-
Stay informed about any updates or revisions to the ISO 20000 standard.
-
Ensure your SMS remains aligned with the latest requirements and best practices.
-
Customer Feedback and Satisfaction:
-
Regularly seek customer feedback and monitor customer satisfaction levels.
-
Use customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to enhance service delivery.
How to obtain the IS20000 certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance :COBIT , ISO
7.Conclusion
In conclusion, ISO 20000 IT Service Management Certification holds significant value for organizations and IT service providers. Throughout this blog, we explored various subtopics related to ISO 20000 certification, providing insights into its framework, benefits, steps to achieve certification, and maintenance strategies.
ISO 20000 certification provides a structured approach to IT service management, enabling organizations to establish and maintain effective service delivery processes. It enhances service quality, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency while demonstrating compliance with internationally recognized best practices. By aligning with ISO 20000, organizations can gain a competitive advantage, build customer trust, and differentiate themselves in the market.
The steps to achieve ISO 20000 certification involve understanding the standard, conducting a gap analysis, implementing required processes, documenting the service management system, and undergoing internal and external audits. Once certified, organizations must maintain compliance through regular audits, corrective actions, ongoing monitoring, and employee training.
The benefits of ISO 20000 certification are numerous, including improved service quality, enhanced operational efficiency, increased credibility, and compliance with regulations and customer requirements. IT service providers, in particular, can leverage certification to differentiate themselves, gain customer confidence, and optimize their service delivery.
By adhering to ISO 20000 requirements and continually striving for improvement, organizations can maximize the value of their certification and ensure the consistent delivery of high-quality IT services. ISO 20000 serves as a valuable framework for organizations seeking to enhance their IT service management practices and establish themselves as reliable and trusted providers in the industry.
Read More
ISO/IEC 20000 is an internationally recognized standard for IT service management (ITSM) that provides organizations with a framework to effectively deliver and manage their IT services. It outlines the best practices and requirements for establishing, implementing, and maintaining a service management system. By achieving ISO/IEC 20000 certification, organizations demonstrate their commitment to delivering high-quality IT services and meeting customer expectations.
The ISO/IEC 20000 certification specifically focuses on IT service management, which involves the design, delivery, and continuous improvement of IT services to support business objectives. It encompasses various processes and activities, such as incident management, problem management, service design, service transition, and service operation. These processes are aimed at ensuring that IT services are delivered efficiently, effectively, and in alignment with the organization's overall goals.
Obtaining the ISO/IEC 20000 certification is not only a testament to an organization's dedication to excellence in IT service management but also provides several benefits. It helps organizations enhance their service quality, improve customer satisfaction, and establish a culture of continual improvement. Additionally, ISO/IEC 20000 certification can enhance the organization's reputation, increase its competitive edge, and provide a basis for establishing service level agreements with customers.
To achieve ISO/IEC 20000 certification, organizations must undergo a thorough assessment of their IT service management practices and demonstrate compliance with the standard's requirements. This assessment is typically conducted by an independent certification body, ensuring objectivity and impartiality in evaluating the organization's IT service management system.
In summary, ISO/IEC 20000 IT Service Management certification is a prestigious recognition that signifies an organization's adherence to internationally recognized best practices in IT service delivery. It helps organizations improve their service quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and establish a strong foundation for effective IT service management.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to ISO 20000 Certification:
-
Understanding the ISO 20000 Framework:
-
Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification:
-
Steps to Achieve ISO 20000 Certification:
-
ISO 20000 Certification and IT Service Providers:
-
Maintaining ISO 20000 Certification:
-
Conlusion
1. Introduction to ISO 20000 Certification:
ISO 20000 is an international standard that outlines the requirements for an organization's IT service management (ITSM) system. It provides a framework for effectively managing and delivering IT services to meet customer requirements and improve overall service quality.
-
What is ISO 20000?
-
Definition: ISO 20000, also known as ISO/IEC 20000, is the international standard for IT service management systems.
-
Background: It was first published in 2005 by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
-
Scope: ISO 20000 covers all aspects of IT service management, including service design, transition, delivery, and improvement.
-
-
Importance of ISO 20000 Certification
-
Customer Confidence: ISO 20000 certification demonstrates an organization's commitment to delivering high-quality IT services and meeting customer requirements.
-
Industry Recognition: It provides recognition and credibility in the IT service management industry, distinguishing certified organizations from their competitors.
-
Compliance: ISO 20000 certification ensures compliance with internationally recognized best practices for IT service management.
-
Continuous Improvement: It promotes a culture of continual improvement, driving organizations to enhance their IT service delivery processes and customer satisfaction.
-
-
Benefits of Achieving ISO 20000 Certification
-
Service Quality Improvement: ISO 20000 helps organizations establish robust processes and procedures to consistently deliver high-quality IT services.
-
Customer Satisfaction: By meeting ISO 20000 requirements, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction by meeting their service expectations and requirements.
-
Operational Efficiency: ISO 20000 provides guidelines for efficient service management practices, leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
-
Risk Management: It helps organizations identify and mitigate risks associated with IT service management, ensuring business continuity and minimizing service disruptions.
-
Competitive Advantage: ISO 20000 certification sets organizations apart from their competitors, giving them a competitive edge in the market.
-
2. Understanding the ISO 20000 Framework.
ISO 20000 is a comprehensive framework that outlines the requirements for implementing and maintaining an effective IT service management system. Familiarizing yourself with the key components and sections of the ISO 20000 standard will help you understand how it supports IT service management best practices.
-
Overview of the ISO 20000 Standard
-
Structure: ISO 20000 is divided into two parts - Part 1: Service management system requirements (SMSR) and Part 2: Guidance on the application of SMSR.
-
Part 1: This section defines the requirements that organizations need to meet to achieve ISO 20000 certification.
-
Part 2: It provides guidance on implementing the requirements specified in Part 1 and offers additional insights into interpreting and applying the standard.
-
-
Key Components of ISO 20000
-
Service Management System (SMS): ISO 20000 emphasizes the establishment of a service management system, which serves as the foundation for effective IT service delivery.
-
Service Management Processes: The standard outlines specific processes that organizations should implement to manage IT services, including incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management.
-
Documentation Requirements: ISO 20000 defines the documentation necessary to demonstrate compliance, such as service management plans, policies, procedures, and records.
-
-
ISO 20000 Sections and Requirements
-
Context of the Organization: This section focuses on understanding the organization's context and identifying the scope of the IT service management system.
-
Leadership: It emphasizes the involvement and commitment of top management in establishing and maintaining the service management system.
-
Planning: This section covers activities related to risk management, service planning, and service design and transition.
-
Support: It outlines the requirements for resource management, competency and awareness, communication, and document management.
-
Operation: This section addresses the execution of service management processes, including service delivery, service control, and resolution of incidents and service requests.
-
Performance Evaluation: It specifies the requirements for monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation of the service management system and services.
-
Improvement: This section focuses on continual improvement of the service management system and the services provided.
-
-
Alignment with ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
-
Relationship with ITIL: ISO 20000 and ITIL are closely related, with ISO 20000 incorporating many ITIL best practices into its framework.
-
ITIL Processes in ISO 20000: ISO 20000 recognizes and aligns with various ITIL processes, such as incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management.
-
Synergies and Enhancements: Implementing ISO 20000 can help organizations enhance their ITIL implementation and vice versa, as both frameworks share common goals and principles.
-
3. Benefits of ISO 20000 Certification
Obtaining ISO 20000 certification brings numerous advantages to organizations in terms of service quality, operational efficiency, and credibility. Here are some key benefits that organizations can experience:
-
Improved Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction
-
Standardized Processes: ISO 20000 requires organizations to establish and follow standardized processes for IT service management, ensuring consistent and reliable service delivery.
-
Service Level Management: Implementing ISO 20000 helps organizations effectively manage service level agreements (SLAs), resulting in improved service performance and meeting customer expectations.
-
Incident and Problem Management: ISO 20000 provides guidelines for incident and problem management, enabling organizations to respond to and resolve issues promptly, minimizing service disruptions and enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
-
Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness
-
Streamlined Processes: ISO 20000 encourages organizations to streamline their IT service management processes, eliminating redundancies and improving efficiency.
-
Resource Optimization: By implementing ISO 20000, organizations can optimize their resource allocation, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively and reducing unnecessary costs.
-
Change Management: ISO 20000 emphasizes proper change management practices, reducing the risk of errors, service disruptions, and costly rollbacks.
-
-
Increased Credibility and Competitive Advantage
-
International Recognition: ISO 20000 is an internationally recognized standard for IT service management, providing organizations with credibility and demonstrating their commitment to quality.
-
Competitive Differentiation: ISO 20000 certification sets organizations apart from their competitors, particularly when bidding for contracts or providing services to clients who prioritize certified providers.
-
Trust and Confidence: Customers and stakeholders have increased trust and confidence in organizations that have achieved ISO 20000 certification, knowing that their IT services are managed according to globally accepted best practices.
-
-
Compliance with Best Practices and Regulations
-
Alignment with ITIL: ISO 20000 aligns with ITIL, incorporating many ITIL best practices into its framework. This alignment ensures compliance with widely recognized IT service management principles.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Achieving ISO 20000 certification helps organizations demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements related to IT service management, enhancing their reputation and credibility.
-
-
Continual Service Improvement
-
Continuous Improvement Culture: ISO 20000 promotes a culture of continual service improvement, encouraging organizations to monitor, measure, and evaluate their IT services to identify areas for enhancement.
-
Proactive Problem Resolution: Through ISO 20000, organizations can implement proactive problem management practices, identifying and addressing underlying issues before they impact service quality.
-
4.Steps to Achieve ISO 20000 Certification
-
Familiarize Yourself with ISO 20000:
-
Understand the requirements and key components of the ISO 20000 standard.
-
Familiarize yourself with the structure and sections of the standard to gain a comprehensive understanding.
-
-
Conduct a Gap Analysis:
-
Evaluate your organization's current IT service management practices against the requirements specified in the ISO 20000 standard.
-
Identify areas where your organization already complies with the standard and areas that require improvement or alignment.
-
-
Develop an Implementation Plan:
-
Create a detailed plan that outlines the necessary actions, resources, and timelines for implementing ISO 20000 within your organization.
-
Define roles and responsibilities for the implementation team members.
-
-
Establish the Service Management System (SMS):
-
Develop and document the service management system, which will serve as the foundation for implementing ISO 20000 requirements.
-
Define the scope of your SMS, considering the services, processes, and organizational units covered by the certification.
-
-
Implement Required Processes and Procedures:
-
Implement the specific processes and procedures outlined in the ISO 20000 standard, such as incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management.
-
Align your existing processes with the ISO 20000 requirements or establish new ones where necessary.
-
-
Document the SMS:
-
Develop the required documentation to demonstrate compliance with ISO 20000.
-
Document policies, procedures, work instructions, and records necessary to support the implementation and operation of the SMS.
-
-
Conduct Internal Audits:
-
Perform internal audits to assess the effectiveness and compliance of your SMS with ISO 20000 requirements.
-
Identify any non-conformities and take corrective actions to address them.
-
-
Management Review:
-
Conduct a management review to evaluate the performance of the SMS and the progress towards ISO 20000 certification.
-
Ensure that top management is actively involved in reviewing the SMS and providing necessary support.
-
-
Select an Accredited Certification Body:
-
Choose an accredited certification body to perform the final certification audit.
-
Verify that the certification body has experience and expertise in ISO 20000 certification.
-
-
External Certification Audit:
-
The certification body will conduct an on-site audit to assess your organization's compliance with ISO 20000 requirements.
-
The audit will typically involve interviews, documentation reviews, and observations of your IT service management practices.
-
-
Corrective Actions and Finalization:
-
Address any non-conformities identified during the certification audit and implement corrective actions.
-
Provide necessary evidence of compliance to the certification body.
-
Once all non-conformities are resolved, the certification body will issue the ISO 20000 certification.
-
-
Continual Improvement:
-
Embrace a culture of continual improvement by monitoring, measuring, and evaluating your IT service management practices.
-
Implement processes to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 20000 requirements and drive continuous enhancement of your services.
-
5.ISO 20000 Certification and IT Service Providers
ISO 20000 certification holds significant benefits for IT service providers, helping them enhance their service delivery, gain customer trust, and establish a competitive edge. Here are some key aspects of ISO 20000 certification for IT service providers:
-
Customer Confidence and Trust:
-
ISO 20000 certification demonstrates an IT service provider's commitment to delivering high-quality services that meet customer requirements and expectations.
-
Certified providers are seen as more reliable, trustworthy, and capable of delivering consistent and efficient IT services.
-
-
Differentiation and Competitive Advantage:
-
ISO 20000 certification sets IT service providers apart from their competitors in a crowded market.
-
Certification can serve as a unique selling point and a competitive advantage, helping providers attract new customers and win contracts.
-
-
Improved Service Delivery:
-
ISO 20000 provides guidelines for effective service management processes, ensuring IT service providers have well-defined processes in place.
-
By implementing ISO 20000 requirements, providers can enhance their service delivery, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
-
Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
-
ISO 20000 encourages IT service providers to streamline their processes, eliminate redundancies, and optimize resource allocation.
-
By aligning with ISO 20000, providers can improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver services more effectively.
-
-
Alignment with Customer Requirements:
-
ISO 20000 certification ensures that IT service providers align with internationally recognized best practices and standards for IT service management.
-
Many customers and organizations specifically require ISO 20000 certification when selecting service providers, making it essential for business opportunities.
-
-
Compliance with Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
-
ISO 20000 helps IT service providers effectively manage and fulfill SLAs with their customers.
-
It provides guidelines for defining, monitoring, and reporting on service levels, ensuring providers meet their contractual obligations.
-
-
Continual Improvement:
-
ISO 20000 promotes a culture of continual service improvement within IT service providers.
-
By monitoring and evaluating service performance, providers can identify areas for enhancement and implement proactive measures for ongoing improvement.
-
-
Vendor and Partner Relationships:
-
ISO 20000 certification can be advantageous when working with vendors or partners, as it demonstrates a provider's commitment to quality and adherence to best practices.
-
It enhances the provider's credibility and strengthens their relationships with vendors and partners.
-
6.Maintaining ISO 20000 Certification
Achieving ISO 20000 certification is a significant accomplishment, but it's essential to continuously maintain compliance with the standard's requirements to preserve the benefits it offers. Here are key aspects to consider for maintaining ISO 20000 certification:
-
Regular Internal Audits:
-
Conduct internal audits at regular intervals to assess the effectiveness and compliance of your IT service management system (SMS).
-
Internal audits help identify any non-conformities or areas that need improvement, allowing you to take corrective actions proactively.
-
-
Corrective Actions and Preventive Measures:
-
Address any non-conformities identified during internal audits promptly.
-
Implement corrective actions and preventive measures to prevent the recurrence of non-conformities and improve the effectiveness of your SMS.
-
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Measurement:
-
Continuously monitor and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) related to IT service management.
-
Regularly review and analyze data to identify trends, areas for improvement, and potential risks.
-
-
Management Review:
-
Conduct periodic management reviews to evaluate the performance of the SMS and the effectiveness of your IT service management processes.
-
Involve top management in the review process to ensure ongoing commitment and support.
-
-
Employee Training and Awareness:
-
Provide regular training and awareness programs to employees on the requirements of ISO 20000 and their roles in maintaining compliance.
-
Ensure employees are familiar with the processes, procedures, and policies related to IT service management.
-
-
Document Control and Record Keeping:
-
Maintain proper document control processes to ensure the accuracy, availability, and relevance of documented information.
-
Keep records of key activities, such as incidents, problem resolutions, changes, and service level agreements (SLAs).
-
-
External Audits and Surveillance Visits:
-
The certification body may conduct surveillance visits or periodic audits to assess ongoing compliance with ISO 20000 requirements.
-
Prepare for these audits by ensuring all necessary documentation and records are up to date and readily available.
-
-
Continual Improvement:
-
Foster a culture of continual improvement within your organization.
-
Encourage employees to provide suggestions for enhancing the IT service management processes and implementing improvements.
-
-
Stay Updated with Changes:
-
Stay informed about any updates or revisions to the ISO 20000 standard.
-
Ensure your SMS remains aligned with the latest requirements and best practices.
-
-
Customer Feedback and Satisfaction:
-
Regularly seek customer feedback and monitor customer satisfaction levels.
-
Use customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to enhance service delivery.
-
How to obtain the IS20000 certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance :COBIT , ISO
7.Conclusion
In conclusion, ISO 20000 IT Service Management Certification holds significant value for organizations and IT service providers. Throughout this blog, we explored various subtopics related to ISO 20000 certification, providing insights into its framework, benefits, steps to achieve certification, and maintenance strategies.
ISO 20000 certification provides a structured approach to IT service management, enabling organizations to establish and maintain effective service delivery processes. It enhances service quality, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency while demonstrating compliance with internationally recognized best practices. By aligning with ISO 20000, organizations can gain a competitive advantage, build customer trust, and differentiate themselves in the market.
The steps to achieve ISO 20000 certification involve understanding the standard, conducting a gap analysis, implementing required processes, documenting the service management system, and undergoing internal and external audits. Once certified, organizations must maintain compliance through regular audits, corrective actions, ongoing monitoring, and employee training.
The benefits of ISO 20000 certification are numerous, including improved service quality, enhanced operational efficiency, increased credibility, and compliance with regulations and customer requirements. IT service providers, in particular, can leverage certification to differentiate themselves, gain customer confidence, and optimize their service delivery.
By adhering to ISO 20000 requirements and continually striving for improvement, organizations can maximize the value of their certification and ensure the consistent delivery of high-quality IT services. ISO 20000 serves as a valuable framework for organizations seeking to enhance their IT service management practices and establish themselves as reliable and trusted providers in the industry.
COBIT Framework: Understanding COBIT for IT Governance
The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification is a highly recognized credential in the field of IT governance and management. It signifies an individual's understanding and proficiency in utilizing the COBIT® 5 framework for effective governance and control of information and technology within organizations.
COBIT® (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is a globally accepted framework developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) for guiding the governance and management of enterprise IT. The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification serves as an entry-level qualification that equips professionals with the fundamental knowledge and skills necessary to apply COBIT® 5 principles and practices.
The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification provides individuals with a comprehensive understanding of IT governance domains, processes, and enablers. It covers various aspects of IT management, including strategic alignment, risk management, performance measurement, and process improvement. By obtaining this certification, individuals demonstrate their ability to effectively govern and control IT resources and align them with organizational goals and objectives.
To achieve the COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification, candidates must successfully pass an examination that tests their knowledge of key COBIT® 5 concepts, principles, and terminology. This certification is beneficial for professionals involved in IT governance, IT management, IT assurance, and IT risk management roles, as well as individuals aspiring to enhance their career prospects in these areas.
By earning the COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification, professionals gain a competitive advantage in the job market. The certification enhances their credibility, demonstrating their commitment to best practices in IT governance and management. It equips them with the necessary skills to contribute effectively to organizations' strategic decision-making processes, risk management practices, and value delivery mechanisms.
The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification not only validates an individual's knowledge and expertise but also provides them with a practical framework for managing IT resources and improving organizational performance. It offers a common language and set of principles for IT professionals to align their efforts with business objectives and drive sustainable success.
In summary, the COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification is a highly regarded qualification that establishes individuals as proficient practitioners in IT governance and management. It equips professionals with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement effective controls, enhance IT processes, and align IT strategies with organizational goals. COBIT® 5-certified professionals play a vital role in ensuring efficient and secure management of IT resources, driving value for organizations in today's rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Table of Contents
What is COBIT?
What is ISACA?
What is the History of COBIT?
Why Is COBIT Important?
What Is COBIT Framework?
What Are the COBIT Framework Basics?
What Are the Principles of COBIT?
What Do You Need to Know Before Using COBIT?
What is the Difference Between COBIT 5 and COBIT 2019?
How Does COBIT Compare With Other Governance Frameworks?
The Various COBIT Components
Why Is COBIT 5.0 the Most Celebrated Version?
The Advantages of COBIT 5.0 Certification
Benefits of COBIT
Goals of the COBIT Framework
Meeting Stakeholder Needs
Taking a Holistic Approach to Governance
Conclusion
COBIT is a widely recognized and respected framework that is used to help organizations govern and manage their information technology (IT) systems. COBIT, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology, was first introduced in the mid-1990s by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA). Since then, it has become a well-established standard for IT governance and management, with a focus on providing a comprehensive framework for ensuring that IT systems align with business goals, comply with regulations and standards, and operate effectively and efficiently. This article will explore the basics of the COBIT framework, including its history, key concepts, and benefits, to help you understand how it can be used to improve your organization's IT governance and management.
What is COBIT?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is a widely recognized and respected framework that provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for governing and managing enterprise information technology (IT) systems. Developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), COBIT is designed to help organizations align their IT strategy with their business goals, optimize the use of IT resources, ensure compliance with laws and regulations, and manage IT risks effectively. The framework provides a set of best practices and standards for IT governance and management, including a comprehensive set of control objectives, metrics, and maturity models that can be used to assess and improve an organization's IT processes and capabilities. COBIT is used by businesses, government agencies, and other organizations around the world to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of their IT operations, reduce risk, and improve overall business performance.
What is ISACA?
ISACA stands for Information Systems Audit and Control Association. It is an international professional association that provides knowledge, tools, and networking opportunities to information technology (IT) professionals and organizations around the world. ISACA was founded in 1969 and currently has over 150,000 members in more than 180 countries. The association offers a range of professional development and certification programs, including the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), and Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) certifications. ISACA also develops and maintains several widely used frameworks and standards related to IT governance, including COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology), which is a framework for IT governance and management. ISACA plays an important role in advancing the field of IT governance, risk management, and compliance by providing guidance and resources to IT professionals and organizations worldwide.
What is the History of COBIT?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) was first developed in 1996 by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) as a framework to help IT professionals govern and manage IT systems more effectively. The original version of COBIT was focused on IT auditing and control, with a focus on providing a set of control objectives and best practices to help organizations improve the reliability, security, and integrity of their IT systems.
Over the years, COBIT has evolved to become a more comprehensive framework for IT governance and management, incorporating best practices from other frameworks such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) and ISO/IEC 27001 (Information Security Management System). Today, COBIT is widely recognized as a leading framework for IT governance and management, with a focus on providing a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices for managing IT systems in a way that supports business objectives, meets regulatory requirements, and optimizes IT investments.
COBIT is regularly updated to reflect changes in the IT landscape, such as the increasing importance of cybersecurity and the growing use of cloud computing and other emerging technologies. The latest version of COBIT, COBIT 2019, was released in 2018 and represents the most up-to-date and comprehensive set of guidelines for IT governance and management available today.
Why Is COBIT Important?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is important for several reasons:
- Provides a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management: COBIT provides a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices for managing IT systems in a way that supports business objectives, meets regulatory requirements, and optimizes IT investments. This makes it an essential tool for IT professionals and organizations that want to improve their IT governance and management capabilities.
- Helps organizations comply with laws and regulations: COBIT helps organizations ensure that their IT systems comply with laws, regulations, and industry standards. By following the COBIT framework, organizations can reduce the risk of non-compliance and avoid legal and regulatory penalties.
- Supports effective risk management: COBIT includes a comprehensive set of controls and metrics that can be used to assess and manage IT-related risks. This helps organizations identify and mitigate risks before they become major issues, reducing the risk of IT-related incidents and their impact on business operations.
- Improves business performance: COBIT helps organizations align their IT strategy with their business goals, optimizing the use of IT resources and improving overall business performance. By improving IT governance and management, organizations can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage.
What Is COBIT Framework?
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is a set of guidelines, best practices, and standards for IT governance and management. It is designed to help organizations ensure that their IT systems align with business goals, comply with laws and regulations, and operate effectively and efficiently. The COBIT framework provides a comprehensive set of control objectives, metrics, and maturity models that can be used to assess and improve an organization's IT processes and capabilities.
The COBIT framework is organized into five key domains:
- Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM): This domain provides guidance on how to ensure that IT governance is effective, efficient, and responsive to business needs. It includes best practices for setting IT policies and strategies, defining IT objectives, and monitoring IT performance.
- Align, Plan, and Organize (APO): This domain focuses on how to align IT with business objectives, plan and manage IT projects, and organize IT resources effectively. It includes best practices for IT portfolio management, IT budgeting, and IT organizational design.
- Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI): This domain provides guidance on how to build, acquire, and implement IT systems and solutions that meet business needs and comply with regulations and standards. It includes best practices for project management, system development, and change management.
- Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS): This domain focuses on how to deliver IT services and support to end-users, ensuring that IT systems operate effectively and efficiently. It includes best practices for IT service management, IT operations management, and IT asset management.
- Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA): This domain provides guidance on how to monitor and assess IT performance, compliance, and risk. It includes best practices for IT audit, IT risk management, and IT performance management.
What Are the COBIT Framework Basics?
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is based on five core principles that provide a foundation for effective IT governance and management:
- Meeting stakeholder needs: IT systems should be designed and operated to meet the needs of stakeholders, including customers, regulators, shareholders, and employees.
- Covering the enterprise end-to-end: IT governance and management should cover the entire enterprise, including all IT systems and processes.
- Applying a single integrated framework: Organizations should use a single integrated framework to manage their IT systems, rather than relying on multiple frameworks or ad-hoc approaches.
- Enabling a holistic approach: IT governance and management should be approached holistically, considering all aspects of IT, including people, processes, and technology.
- Separating governance from management: IT governance should be separate from IT management, with clear roles and responsibilities defined for each.
In addition to these core principles, the COBIT framework provides a set of control objectives, metrics, and maturity models that can be used to assess and improve an organization's IT governance and management capabilities. These are organized into five domains, as described in my previous answer: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM); Align, Plan, and Organize (APO); Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI); Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS); and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA).
The COBIT framework also includes a set of enablers, such as processes, organizational structures, information, and technology, which can be used to support the implementation of the framework and the achievement of IT governance and management objectives.
What Are the Principles of COBIT?
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is based on a set of five principles that provide a foundation for effective IT governance and management. These principles are as follows:
- Meeting Stakeholder Needs: The first principle of COBIT is to meet the needs of stakeholders, which includes customers, regulators, shareholders, and employees. IT systems should be designed and operated to meet these needs, and organizations should prioritize their IT investments accordingly.
- Covering the Enterprise End-to-End: The second principle of COBIT is to cover the entire enterprise, including all IT systems and processes. IT governance and management should be integrated across the enterprise and should consider all aspects of IT, including people, processes, and technology.
- Applying a Single, Integrated Framework: The third principle of COBIT is to apply a single, integrated framework for IT governance and management. This helps organizations to avoid inconsistencies and gaps in their IT processes and ensures that all stakeholders are working toward the same objectives.
- Enabling a Holistic Approach: The fourth principle of COBIT is to enable a holistic approach to IT governance and management. This means considering all aspects of IT in an integrated manner, and ensuring that all stakeholders are working together to achieve common objectives.
- Separating Governance from Management: The final principle of COBIT is to separate IT governance from IT management. Governance is responsible for setting direction and ensuring compliance, while management is responsible for implementing and executing the IT strategy. This helps to ensure clear accountability and avoid conflicts of interest.
What Do You Need to Know Before Using COBIT?
Before using COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology), there are several key things you should know:
- Understand your organization's objectives: Before implementing the COBIT framework, it's important to understand your organization's objectives, including its mission, values, and strategic goals. This will help you tailor the framework to meet your organization's specific needs.
- Identify key stakeholders: Identify the key stakeholders involved in your organization's IT governance and management processes, including customers, regulators, shareholders, and employees. Understanding their needs and expectations is essential for designing an effective IT governance and management strategy.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities: It's important to establish clear roles and responsibilities for IT governance and management, including who is responsible for setting strategy, making decisions, and executing on that strategy. This helps to ensure accountability and avoid confusion.
- Assess your organization's current state: Before implementing the COBIT framework, assess your organization's current state of IT governance and management. This will help you identify areas of strength and weakness, and tailor your approach accordingly.
- Determine which COBIT version to use: COBIT has evolved over time, with different versions available for different purposes. It's important to determine which version of COBIT is best suited to your organization's needs.
- Define metrics and measurement criteria: Define metrics and measurement criteria to evaluate the effectiveness of your IT governance and management processes. This will help you track progress over time and identify areas for improvement.
What is the Difference Between COBIT 5 and COBIT 2019?
COBIT 5 and COBIT 2019 are two different versions of the COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework. While both versions share many similarities, there are some key differences between the two:
- Scope: COBIT 5 has a broader scope than COBIT 2019, as it covers not only IT governance but also enterprise governance and management. COBIT 2019 focuses specifically on IT governance and management.
- Structure: COBIT 5 is structured around five governance and management domains, while COBIT 2019 is structured around four focus areas. The domains in COBIT 5 are governance, strategy, acquisition, delivery, and monitoring, while the focus areas in COBIT 2019 are governance, management, alignment, and assurance.
- Framework components: COBIT 2019 has several new components that were not present in COBIT 5, including design factors, implementation guidance, and performance management.
- Updated content: COBIT 2019 includes updated content to reflect changes in the IT landscape since the release of COBIT 5, including new technologies and emerging trends.
- Implementation approach: COBIT 2019 provides a more flexible implementation approach than COBIT 5, with guidance on how to tailor the framework to meet an organization's specific needs.
How Does COBIT Compare With Other Governance Frameworks?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is one of several governance frameworks that organizations can use to guide their IT governance and management practices. Here are some ways that COBIT compares with other popular frameworks:
- ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): ITIL is a framework that focuses on IT service management. While COBIT covers a broad range of IT governance and management topics, including IT service management, ITIL provides a more detailed set of best practices for delivering IT services.
- ISO/IEC 27001: ISO/IEC 27001 is a standard that outlines requirements for information security management systems. While COBIT includes information security as part of its overall governance and management framework, ISO/IEC 27001 provides more detailed guidance on how to establish and maintain an information security management system.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a set of guidelines for improving cybersecurity risk management. While COBIT includes guidance on managing IT risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides more detailed guidance on how to assess and manage cybersecurity risks.
- COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission): COSO provides a framework for enterprise risk management. While COBIT includes risk management as part of its overall governance and management framework, COSO provides a more detailed set of best practices for managing risks across the enterprise.
How Does COBIT Compare With Other Governance Frameworks?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is one of several governance frameworks that organizations can use to guide their IT governance and management practices. Here are some ways that COBIT compares with other popular frameworks:
- ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): ITIL is a framework that focuses on IT service management. While COBIT covers a broad range of IT governance and management topics, including IT service management, ITIL provides a more detailed set of best practices for delivering IT services.
- ISO/IEC 27001: ISO/IEC 27001 is a standard that outlines requirements for information security management systems. While COBIT includes information security as part of its overall governance and management framework, ISO/IEC 27001 provides more detailed guidance on how to establish and maintain an information security management system.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a set of guidelines for improving cybersecurity risk management. While COBIT includes guidance on managing IT risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides more detailed guidance on how to assess and manage cybersecurity risks.
- COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission): COSO provides a framework for enterprise risk management. While COBIT includes risk management as part of its overall governance and management framework, COSO provides a more detailed set of best practices for managing risks across the enterprise.
The Various COBIT Components
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is comprised of several components that work together to provide a comprehensive approach to IT governance and management. Here are the main components of COBIT:
- Governance objectives: COBIT defines governance as the set of practices and processes that ensure that an organization's IT investments support its overall business goals and objectives. COBIT includes a set of governance objectives that provide a high-level overview of the key areas that organizations need to focus on to achieve effective IT governance.
- Governance and management domains: COBIT is structured around five governance and management domains: governance, strategy, acquisition, delivery, and monitoring. Each domain includes a set of processes and practices that organizations can use to manage and govern their IT operations.
- Process reference model: COBIT provides a process reference model that defines the processes and activities involved in each of the five domains. The process reference model includes a set of generic processes that can be tailored to meet an organization's specific needs.
- Control objectives: COBIT includes a set of control objectives that provide detailed guidance on how to achieve specific outcomes within each process. Control objectives are used to define the specific requirements that need to be met to achieve effective IT governance.
- Management guidelines: COBIT provides a set of management guidelines that organizations can use to implement the framework. The guidelines include practical advice and guidance on how to implement COBIT in a way that is tailored to an organization's specific needs.
- Maturity models: COBIT includes a set of maturity models that organizations can use to assess their current level of IT governance maturity and identify areas for improvement. The maturity models provide a roadmap for organizations to follow as they work to improve their IT governance and management practices.
Why Is COBIT 5.0 the Most Celebrated Version?
COBIT 5.0 is often considered the most celebrated version of the COBIT framework due to several reasons:
- Broad scope: COBIT 5.0 has a broad scope that covers all aspects of IT governance and management. This makes it a comprehensive framework that can be used by organizations of all sizes and across all industries.
- Alignment with other frameworks: COBIT 5.0 is designed to be compatible with other frameworks, such as ITIL and ISO/IEC 27001, making it easier for organizations to integrate it into their existing IT governance and management practices.
- Focus on business value: COBIT 5.0 places a strong emphasis on delivering business value through effective IT governance and management. This helps organizations to align their IT investments with their overall business objectives and achieve better outcomes.
- Maturity models: COBIT 5.0 includes maturity models that organizations can use to assess their current level of IT governance and management maturity and identify areas for improvement. This helps organizations to take a more strategic approach to IT governance and management and improve their overall performance.
- User-friendly: COBIT 5.0 is designed to be user-friendly, with clear and concise language and a straightforward structure that makes it easy to navigate and implement.
The Advantages of COBIT 5.0 Certification
There are several advantages of COBIT 5.0 certification, including:
- Industry recognition: COBIT 5.0 is widely recognized as a leading framework for IT governance and management. Achieving COBIT 5.0 certification demonstrates a high level of knowledge and expertise in this field and can enhance your professional reputation.
- Career advancement: COBIT 5.0 certification can help you to advance your career in the IT governance and management field. It demonstrates to employers that you have the skills and knowledge needed to contribute to the success of their organization.
- Improved job performance: COBIT 5.0 certification can improve your job performance by providing you with a deeper understanding of IT governance and management principles, processes, and practices. This can help you to make better decisions and deliver better outcomes for your organization.
- Competitive advantage: COBIT 5.0 certification can give you a competitive advantage in the job market by setting you apart from other candidates who do not have this certification. It can help you to stand out and demonstrate your commitment to professional development and excellence.
- Personal growth: COBIT 5.0 certification can provide you with personal growth and development opportunities. It can help you to expand your knowledge and skills and take on new challenges in your career.
Benefits of COBIT
The COBIT framework offers several benefits for organizations, including:
- Improved IT governance: COBIT provides a structured approach to IT governance that helps organizations to align their IT strategy with their business goals and objectives. This ensures that IT investments are focused on delivering value and that IT risks are managed effectively.
- Better risk management: COBIT helps organizations to identify and manage IT-related risks more effectively. By providing a framework for risk management, COBIT enables organizations to assess the impact of IT risks on their business operations and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness: COBIT promotes best practices for IT management and governance, which can help organizations to improve their operational efficiency and effectiveness. By standardizing processes and procedures, COBIT enables organizations to reduce errors and improve service delivery.
- Improved stakeholder confidence: COBIT provides a transparent and auditable approach to IT governance that can help to improve stakeholder confidence. By demonstrating a commitment to effective IT management and governance, organizations can build trust with their stakeholders and enhance their reputation.
- Better compliance: COBIT can help organizations to comply with regulatory and legal requirements related to IT governance and management. By providing a framework for compliance, COBIT enables organizations to ensure that they are meeting their obligations and avoiding potential legal and financial risks.
How to obtain the COBIT Framewordk certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Goals of the COBIT Framework
The goals of the COBIT framework are to:
- Provide a comprehensive framework: COBIT aims to provide a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management that covers all aspects of IT operations, from strategy development to day-to-day operations.
- Ensure alignment between IT and business objectives: COBIT emphasizes the importance of aligning IT objectives with business objectives to ensure that IT investments are focused on delivering value to the organization.
- Promote best practices: COBIT promotes best practices for IT governance and management that are based on industry standards and frameworks.
- Provide a common language: COBIT provides a common language and terminology for IT governance and management that can be understood by all stakeholders, including business leaders, IT professionals, and auditors.
- Enable effective risk management: COBIT provides a structured approach to IT risk management that enables organizations to identify, assess, and manage IT-related risks more effectively.
- Ensure compliance: COBIT helps organizations to comply with regulatory and legal requirements related to IT governance and management by providing a framework for compliance.
Meeting Stakeholder Needs
Meeting stakeholder needs is a key component of the COBIT framework. COBIT defines stakeholders as individuals or groups that have an interest in or are affected by an organization's IT operations. This can include internal stakeholders, such as business leaders and IT professionals, as well as external stakeholders, such as customers, regulators, and investors.
To meet stakeholder needs, COBIT emphasizes the importance of understanding stakeholder expectations and ensuring that IT operations are aligned with these expectations. This requires a structured approach to IT governance and management that takes into account the needs and expectations of all stakeholders.
COBIT provides a framework for IT governance and management that enables organizations to:
- Define stakeholder expectations: COBIT helps organizations to identify and understand the needs and expectations of all stakeholders, including business leaders, IT professionals, customers, and regulators.
- Align IT with business objectives: COBIT emphasizes the importance of aligning IT objectives with business objectives to ensure that IT investments are focused on delivering value to the organization and meeting stakeholder needs.
- Manage IT-related risks: COBIT provides a structured approach to IT risk management that enables organizations to identify, assess, and manage IT-related risks that could impact stakeholders.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory and legal requirements: COBIT helps organizations to comply with regulatory and legal requirements related to IT governance and management, which can help to build stakeholder confidence and trust.
Taking a Holistic Approach to Governance
Taking a holistic approach to governance is a fundamental concept of the COBIT framework. Holistic governance means that organizations should view IT as an integral part of their overall business strategy, and that IT governance should be integrated with overall organizational governance.
COBIT emphasizes that effective IT governance requires a holistic approach that encompasses all aspects of IT operations, including people, processes, and technology. This approach enables organizations to achieve the following:
- Alignment with business objectives: A holistic approach to governance ensures that IT operations are aligned with the overall business objectives of the organization. This alignment is critical to ensure that IT investments are focused on delivering value to the organization.
- Integration with overall governance: A holistic approach to governance integrates IT governance with overall organizational governance. This integration ensures that IT governance is aligned with the overall governance framework and helps to avoid silos and fragmentation.
- Comprehensive coverage: A holistic approach to governance provides comprehensive coverage of all aspects of IT operations, including people, processes, and technology. This coverage ensures that all aspects of IT operations are governed and managed effectively.
- Effective risk management: A holistic approach to governance enables effective risk management by ensuring that all aspects of IT operations are considered when assessing and managing risks.
- Continual improvement: A holistic approach to governance emphasizes the importance of continual improvement. This ensures that organizations are constantly seeking to improve their IT operations to meet the evolving needs of the business.
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT is a comprehensive framework that provides organizations with a structured approach to IT governance and management. The framework is designed to help organizations meet stakeholder needs, align IT with business objectives, manage IT-related risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory and legal requirements.
COBIT emphasizes the importance of taking a holistic approach to governance that encompasses all aspects of IT operations, including people, processes, and technology. This approach enables organizations to achieve effective IT governance and management that is integrated with overall organizational governance.
COBIT has evolved over time, with each version bringing improvements and updates to the framework. The most celebrated version of COBIT is COBIT 5.0, which provides organizations with a comprehensive approach to IT governance and management.
In addition to providing a framework for IT governance and management, COBIT also offers certification programs that enable IT professionals to demonstrate their knowledge and expertise in the framework. COBIT certification can provide professionals with a competitive edge in the job market and help organizations to build a team of skilled IT professionals who can effectively implement and manage the COBIT framework.
Read More
The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification is a highly recognized credential in the field of IT governance and management. It signifies an individual's understanding and proficiency in utilizing the COBIT® 5 framework for effective governance and control of information and technology within organizations.
COBIT® (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is a globally accepted framework developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) for guiding the governance and management of enterprise IT. The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification serves as an entry-level qualification that equips professionals with the fundamental knowledge and skills necessary to apply COBIT® 5 principles and practices.
The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification provides individuals with a comprehensive understanding of IT governance domains, processes, and enablers. It covers various aspects of IT management, including strategic alignment, risk management, performance measurement, and process improvement. By obtaining this certification, individuals demonstrate their ability to effectively govern and control IT resources and align them with organizational goals and objectives.
To achieve the COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification, candidates must successfully pass an examination that tests their knowledge of key COBIT® 5 concepts, principles, and terminology. This certification is beneficial for professionals involved in IT governance, IT management, IT assurance, and IT risk management roles, as well as individuals aspiring to enhance their career prospects in these areas.
By earning the COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification, professionals gain a competitive advantage in the job market. The certification enhances their credibility, demonstrating their commitment to best practices in IT governance and management. It equips them with the necessary skills to contribute effectively to organizations' strategic decision-making processes, risk management practices, and value delivery mechanisms.
The COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification not only validates an individual's knowledge and expertise but also provides them with a practical framework for managing IT resources and improving organizational performance. It offers a common language and set of principles for IT professionals to align their efforts with business objectives and drive sustainable success.
In summary, the COBIT® 5 Foundation Certification is a highly regarded qualification that establishes individuals as proficient practitioners in IT governance and management. It equips professionals with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement effective controls, enhance IT processes, and align IT strategies with organizational goals. COBIT® 5-certified professionals play a vital role in ensuring efficient and secure management of IT resources, driving value for organizations in today's rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Table of Contents
What is COBIT?
What is ISACA?
What is the History of COBIT?
Why Is COBIT Important?
What Is COBIT Framework?
What Are the COBIT Framework Basics?
What Are the Principles of COBIT?
What Do You Need to Know Before Using COBIT?
What is the Difference Between COBIT 5 and COBIT 2019?
How Does COBIT Compare With Other Governance Frameworks?
The Various COBIT Components
Why Is COBIT 5.0 the Most Celebrated Version?
The Advantages of COBIT 5.0 Certification
Benefits of COBIT
Goals of the COBIT Framework
Meeting Stakeholder Needs
Taking a Holistic Approach to Governance
Conclusion
COBIT is a widely recognized and respected framework that is used to help organizations govern and manage their information technology (IT) systems. COBIT, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology, was first introduced in the mid-1990s by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA). Since then, it has become a well-established standard for IT governance and management, with a focus on providing a comprehensive framework for ensuring that IT systems align with business goals, comply with regulations and standards, and operate effectively and efficiently. This article will explore the basics of the COBIT framework, including its history, key concepts, and benefits, to help you understand how it can be used to improve your organization's IT governance and management.
What is COBIT?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is a widely recognized and respected framework that provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for governing and managing enterprise information technology (IT) systems. Developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), COBIT is designed to help organizations align their IT strategy with their business goals, optimize the use of IT resources, ensure compliance with laws and regulations, and manage IT risks effectively. The framework provides a set of best practices and standards for IT governance and management, including a comprehensive set of control objectives, metrics, and maturity models that can be used to assess and improve an organization's IT processes and capabilities. COBIT is used by businesses, government agencies, and other organizations around the world to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of their IT operations, reduce risk, and improve overall business performance.
What is ISACA?
ISACA stands for Information Systems Audit and Control Association. It is an international professional association that provides knowledge, tools, and networking opportunities to information technology (IT) professionals and organizations around the world. ISACA was founded in 1969 and currently has over 150,000 members in more than 180 countries. The association offers a range of professional development and certification programs, including the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), and Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) certifications. ISACA also develops and maintains several widely used frameworks and standards related to IT governance, including COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology), which is a framework for IT governance and management. ISACA plays an important role in advancing the field of IT governance, risk management, and compliance by providing guidance and resources to IT professionals and organizations worldwide.
What is the History of COBIT?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) was first developed in 1996 by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) as a framework to help IT professionals govern and manage IT systems more effectively. The original version of COBIT was focused on IT auditing and control, with a focus on providing a set of control objectives and best practices to help organizations improve the reliability, security, and integrity of their IT systems.
Over the years, COBIT has evolved to become a more comprehensive framework for IT governance and management, incorporating best practices from other frameworks such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) and ISO/IEC 27001 (Information Security Management System). Today, COBIT is widely recognized as a leading framework for IT governance and management, with a focus on providing a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices for managing IT systems in a way that supports business objectives, meets regulatory requirements, and optimizes IT investments.
COBIT is regularly updated to reflect changes in the IT landscape, such as the increasing importance of cybersecurity and the growing use of cloud computing and other emerging technologies. The latest version of COBIT, COBIT 2019, was released in 2018 and represents the most up-to-date and comprehensive set of guidelines for IT governance and management available today.
Why Is COBIT Important?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is important for several reasons:
- Provides a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management: COBIT provides a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices for managing IT systems in a way that supports business objectives, meets regulatory requirements, and optimizes IT investments. This makes it an essential tool for IT professionals and organizations that want to improve their IT governance and management capabilities.
- Helps organizations comply with laws and regulations: COBIT helps organizations ensure that their IT systems comply with laws, regulations, and industry standards. By following the COBIT framework, organizations can reduce the risk of non-compliance and avoid legal and regulatory penalties.
- Supports effective risk management: COBIT includes a comprehensive set of controls and metrics that can be used to assess and manage IT-related risks. This helps organizations identify and mitigate risks before they become major issues, reducing the risk of IT-related incidents and their impact on business operations.
- Improves business performance: COBIT helps organizations align their IT strategy with their business goals, optimizing the use of IT resources and improving overall business performance. By improving IT governance and management, organizations can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage.
What Is COBIT Framework?
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is a set of guidelines, best practices, and standards for IT governance and management. It is designed to help organizations ensure that their IT systems align with business goals, comply with laws and regulations, and operate effectively and efficiently. The COBIT framework provides a comprehensive set of control objectives, metrics, and maturity models that can be used to assess and improve an organization's IT processes and capabilities.
The COBIT framework is organized into five key domains:
- Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM): This domain provides guidance on how to ensure that IT governance is effective, efficient, and responsive to business needs. It includes best practices for setting IT policies and strategies, defining IT objectives, and monitoring IT performance.
- Align, Plan, and Organize (APO): This domain focuses on how to align IT with business objectives, plan and manage IT projects, and organize IT resources effectively. It includes best practices for IT portfolio management, IT budgeting, and IT organizational design.
- Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI): This domain provides guidance on how to build, acquire, and implement IT systems and solutions that meet business needs and comply with regulations and standards. It includes best practices for project management, system development, and change management.
- Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS): This domain focuses on how to deliver IT services and support to end-users, ensuring that IT systems operate effectively and efficiently. It includes best practices for IT service management, IT operations management, and IT asset management.
- Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA): This domain provides guidance on how to monitor and assess IT performance, compliance, and risk. It includes best practices for IT audit, IT risk management, and IT performance management.
What Are the COBIT Framework Basics?
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is based on five core principles that provide a foundation for effective IT governance and management:
- Meeting stakeholder needs: IT systems should be designed and operated to meet the needs of stakeholders, including customers, regulators, shareholders, and employees.
- Covering the enterprise end-to-end: IT governance and management should cover the entire enterprise, including all IT systems and processes.
- Applying a single integrated framework: Organizations should use a single integrated framework to manage their IT systems, rather than relying on multiple frameworks or ad-hoc approaches.
- Enabling a holistic approach: IT governance and management should be approached holistically, considering all aspects of IT, including people, processes, and technology.
- Separating governance from management: IT governance should be separate from IT management, with clear roles and responsibilities defined for each.
In addition to these core principles, the COBIT framework provides a set of control objectives, metrics, and maturity models that can be used to assess and improve an organization's IT governance and management capabilities. These are organized into five domains, as described in my previous answer: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM); Align, Plan, and Organize (APO); Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI); Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS); and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA).
The COBIT framework also includes a set of enablers, such as processes, organizational structures, information, and technology, which can be used to support the implementation of the framework and the achievement of IT governance and management objectives.
What Are the Principles of COBIT?
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is based on a set of five principles that provide a foundation for effective IT governance and management. These principles are as follows:
- Meeting Stakeholder Needs: The first principle of COBIT is to meet the needs of stakeholders, which includes customers, regulators, shareholders, and employees. IT systems should be designed and operated to meet these needs, and organizations should prioritize their IT investments accordingly.
- Covering the Enterprise End-to-End: The second principle of COBIT is to cover the entire enterprise, including all IT systems and processes. IT governance and management should be integrated across the enterprise and should consider all aspects of IT, including people, processes, and technology.
- Applying a Single, Integrated Framework: The third principle of COBIT is to apply a single, integrated framework for IT governance and management. This helps organizations to avoid inconsistencies and gaps in their IT processes and ensures that all stakeholders are working toward the same objectives.
- Enabling a Holistic Approach: The fourth principle of COBIT is to enable a holistic approach to IT governance and management. This means considering all aspects of IT in an integrated manner, and ensuring that all stakeholders are working together to achieve common objectives.
- Separating Governance from Management: The final principle of COBIT is to separate IT governance from IT management. Governance is responsible for setting direction and ensuring compliance, while management is responsible for implementing and executing the IT strategy. This helps to ensure clear accountability and avoid conflicts of interest.
What Do You Need to Know Before Using COBIT?
Before using COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology), there are several key things you should know:
- Understand your organization's objectives: Before implementing the COBIT framework, it's important to understand your organization's objectives, including its mission, values, and strategic goals. This will help you tailor the framework to meet your organization's specific needs.
- Identify key stakeholders: Identify the key stakeholders involved in your organization's IT governance and management processes, including customers, regulators, shareholders, and employees. Understanding their needs and expectations is essential for designing an effective IT governance and management strategy.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities: It's important to establish clear roles and responsibilities for IT governance and management, including who is responsible for setting strategy, making decisions, and executing on that strategy. This helps to ensure accountability and avoid confusion.
- Assess your organization's current state: Before implementing the COBIT framework, assess your organization's current state of IT governance and management. This will help you identify areas of strength and weakness, and tailor your approach accordingly.
- Determine which COBIT version to use: COBIT has evolved over time, with different versions available for different purposes. It's important to determine which version of COBIT is best suited to your organization's needs.
- Define metrics and measurement criteria: Define metrics and measurement criteria to evaluate the effectiveness of your IT governance and management processes. This will help you track progress over time and identify areas for improvement.
What is the Difference Between COBIT 5 and COBIT 2019?
COBIT 5 and COBIT 2019 are two different versions of the COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework. While both versions share many similarities, there are some key differences between the two:
- Scope: COBIT 5 has a broader scope than COBIT 2019, as it covers not only IT governance but also enterprise governance and management. COBIT 2019 focuses specifically on IT governance and management.
- Structure: COBIT 5 is structured around five governance and management domains, while COBIT 2019 is structured around four focus areas. The domains in COBIT 5 are governance, strategy, acquisition, delivery, and monitoring, while the focus areas in COBIT 2019 are governance, management, alignment, and assurance.
- Framework components: COBIT 2019 has several new components that were not present in COBIT 5, including design factors, implementation guidance, and performance management.
- Updated content: COBIT 2019 includes updated content to reflect changes in the IT landscape since the release of COBIT 5, including new technologies and emerging trends.
- Implementation approach: COBIT 2019 provides a more flexible implementation approach than COBIT 5, with guidance on how to tailor the framework to meet an organization's specific needs.
How Does COBIT Compare With Other Governance Frameworks?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is one of several governance frameworks that organizations can use to guide their IT governance and management practices. Here are some ways that COBIT compares with other popular frameworks:
- ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): ITIL is a framework that focuses on IT service management. While COBIT covers a broad range of IT governance and management topics, including IT service management, ITIL provides a more detailed set of best practices for delivering IT services.
- ISO/IEC 27001: ISO/IEC 27001 is a standard that outlines requirements for information security management systems. While COBIT includes information security as part of its overall governance and management framework, ISO/IEC 27001 provides more detailed guidance on how to establish and maintain an information security management system.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a set of guidelines for improving cybersecurity risk management. While COBIT includes guidance on managing IT risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides more detailed guidance on how to assess and manage cybersecurity risks.
- COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission): COSO provides a framework for enterprise risk management. While COBIT includes risk management as part of its overall governance and management framework, COSO provides a more detailed set of best practices for managing risks across the enterprise.
How Does COBIT Compare With Other Governance Frameworks?
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is one of several governance frameworks that organizations can use to guide their IT governance and management practices. Here are some ways that COBIT compares with other popular frameworks:
- ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): ITIL is a framework that focuses on IT service management. While COBIT covers a broad range of IT governance and management topics, including IT service management, ITIL provides a more detailed set of best practices for delivering IT services.
- ISO/IEC 27001: ISO/IEC 27001 is a standard that outlines requirements for information security management systems. While COBIT includes information security as part of its overall governance and management framework, ISO/IEC 27001 provides more detailed guidance on how to establish and maintain an information security management system.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a set of guidelines for improving cybersecurity risk management. While COBIT includes guidance on managing IT risks, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides more detailed guidance on how to assess and manage cybersecurity risks.
- COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission): COSO provides a framework for enterprise risk management. While COBIT includes risk management as part of its overall governance and management framework, COSO provides a more detailed set of best practices for managing risks across the enterprise.
The Various COBIT Components
The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) framework is comprised of several components that work together to provide a comprehensive approach to IT governance and management. Here are the main components of COBIT:
- Governance objectives: COBIT defines governance as the set of practices and processes that ensure that an organization's IT investments support its overall business goals and objectives. COBIT includes a set of governance objectives that provide a high-level overview of the key areas that organizations need to focus on to achieve effective IT governance.
- Governance and management domains: COBIT is structured around five governance and management domains: governance, strategy, acquisition, delivery, and monitoring. Each domain includes a set of processes and practices that organizations can use to manage and govern their IT operations.
- Process reference model: COBIT provides a process reference model that defines the processes and activities involved in each of the five domains. The process reference model includes a set of generic processes that can be tailored to meet an organization's specific needs.
- Control objectives: COBIT includes a set of control objectives that provide detailed guidance on how to achieve specific outcomes within each process. Control objectives are used to define the specific requirements that need to be met to achieve effective IT governance.
- Management guidelines: COBIT provides a set of management guidelines that organizations can use to implement the framework. The guidelines include practical advice and guidance on how to implement COBIT in a way that is tailored to an organization's specific needs.
- Maturity models: COBIT includes a set of maturity models that organizations can use to assess their current level of IT governance maturity and identify areas for improvement. The maturity models provide a roadmap for organizations to follow as they work to improve their IT governance and management practices.
Why Is COBIT 5.0 the Most Celebrated Version?
COBIT 5.0 is often considered the most celebrated version of the COBIT framework due to several reasons:
- Broad scope: COBIT 5.0 has a broad scope that covers all aspects of IT governance and management. This makes it a comprehensive framework that can be used by organizations of all sizes and across all industries.
- Alignment with other frameworks: COBIT 5.0 is designed to be compatible with other frameworks, such as ITIL and ISO/IEC 27001, making it easier for organizations to integrate it into their existing IT governance and management practices.
- Focus on business value: COBIT 5.0 places a strong emphasis on delivering business value through effective IT governance and management. This helps organizations to align their IT investments with their overall business objectives and achieve better outcomes.
- Maturity models: COBIT 5.0 includes maturity models that organizations can use to assess their current level of IT governance and management maturity and identify areas for improvement. This helps organizations to take a more strategic approach to IT governance and management and improve their overall performance.
- User-friendly: COBIT 5.0 is designed to be user-friendly, with clear and concise language and a straightforward structure that makes it easy to navigate and implement.
The Advantages of COBIT 5.0 Certification
There are several advantages of COBIT 5.0 certification, including:
- Industry recognition: COBIT 5.0 is widely recognized as a leading framework for IT governance and management. Achieving COBIT 5.0 certification demonstrates a high level of knowledge and expertise in this field and can enhance your professional reputation.
- Career advancement: COBIT 5.0 certification can help you to advance your career in the IT governance and management field. It demonstrates to employers that you have the skills and knowledge needed to contribute to the success of their organization.
- Improved job performance: COBIT 5.0 certification can improve your job performance by providing you with a deeper understanding of IT governance and management principles, processes, and practices. This can help you to make better decisions and deliver better outcomes for your organization.
- Competitive advantage: COBIT 5.0 certification can give you a competitive advantage in the job market by setting you apart from other candidates who do not have this certification. It can help you to stand out and demonstrate your commitment to professional development and excellence.
- Personal growth: COBIT 5.0 certification can provide you with personal growth and development opportunities. It can help you to expand your knowledge and skills and take on new challenges in your career.
Benefits of COBIT
The COBIT framework offers several benefits for organizations, including:
- Improved IT governance: COBIT provides a structured approach to IT governance that helps organizations to align their IT strategy with their business goals and objectives. This ensures that IT investments are focused on delivering value and that IT risks are managed effectively.
- Better risk management: COBIT helps organizations to identify and manage IT-related risks more effectively. By providing a framework for risk management, COBIT enables organizations to assess the impact of IT risks on their business operations and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness: COBIT promotes best practices for IT management and governance, which can help organizations to improve their operational efficiency and effectiveness. By standardizing processes and procedures, COBIT enables organizations to reduce errors and improve service delivery.
- Improved stakeholder confidence: COBIT provides a transparent and auditable approach to IT governance that can help to improve stakeholder confidence. By demonstrating a commitment to effective IT management and governance, organizations can build trust with their stakeholders and enhance their reputation.
- Better compliance: COBIT can help organizations to comply with regulatory and legal requirements related to IT governance and management. By providing a framework for compliance, COBIT enables organizations to ensure that they are meeting their obligations and avoiding potential legal and financial risks.
How to obtain the COBIT Framewordk certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Goals of the COBIT Framework
The goals of the COBIT framework are to:
- Provide a comprehensive framework: COBIT aims to provide a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management that covers all aspects of IT operations, from strategy development to day-to-day operations.
- Ensure alignment between IT and business objectives: COBIT emphasizes the importance of aligning IT objectives with business objectives to ensure that IT investments are focused on delivering value to the organization.
- Promote best practices: COBIT promotes best practices for IT governance and management that are based on industry standards and frameworks.
- Provide a common language: COBIT provides a common language and terminology for IT governance and management that can be understood by all stakeholders, including business leaders, IT professionals, and auditors.
- Enable effective risk management: COBIT provides a structured approach to IT risk management that enables organizations to identify, assess, and manage IT-related risks more effectively.
- Ensure compliance: COBIT helps organizations to comply with regulatory and legal requirements related to IT governance and management by providing a framework for compliance.
Meeting Stakeholder Needs
Meeting stakeholder needs is a key component of the COBIT framework. COBIT defines stakeholders as individuals or groups that have an interest in or are affected by an organization's IT operations. This can include internal stakeholders, such as business leaders and IT professionals, as well as external stakeholders, such as customers, regulators, and investors.
To meet stakeholder needs, COBIT emphasizes the importance of understanding stakeholder expectations and ensuring that IT operations are aligned with these expectations. This requires a structured approach to IT governance and management that takes into account the needs and expectations of all stakeholders.
COBIT provides a framework for IT governance and management that enables organizations to:
- Define stakeholder expectations: COBIT helps organizations to identify and understand the needs and expectations of all stakeholders, including business leaders, IT professionals, customers, and regulators.
- Align IT with business objectives: COBIT emphasizes the importance of aligning IT objectives with business objectives to ensure that IT investments are focused on delivering value to the organization and meeting stakeholder needs.
- Manage IT-related risks: COBIT provides a structured approach to IT risk management that enables organizations to identify, assess, and manage IT-related risks that could impact stakeholders.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory and legal requirements: COBIT helps organizations to comply with regulatory and legal requirements related to IT governance and management, which can help to build stakeholder confidence and trust.
Taking a Holistic Approach to Governance
Taking a holistic approach to governance is a fundamental concept of the COBIT framework. Holistic governance means that organizations should view IT as an integral part of their overall business strategy, and that IT governance should be integrated with overall organizational governance.
COBIT emphasizes that effective IT governance requires a holistic approach that encompasses all aspects of IT operations, including people, processes, and technology. This approach enables organizations to achieve the following:
- Alignment with business objectives: A holistic approach to governance ensures that IT operations are aligned with the overall business objectives of the organization. This alignment is critical to ensure that IT investments are focused on delivering value to the organization.
- Integration with overall governance: A holistic approach to governance integrates IT governance with overall organizational governance. This integration ensures that IT governance is aligned with the overall governance framework and helps to avoid silos and fragmentation.
- Comprehensive coverage: A holistic approach to governance provides comprehensive coverage of all aspects of IT operations, including people, processes, and technology. This coverage ensures that all aspects of IT operations are governed and managed effectively.
- Effective risk management: A holistic approach to governance enables effective risk management by ensuring that all aspects of IT operations are considered when assessing and managing risks.
- Continual improvement: A holistic approach to governance emphasizes the importance of continual improvement. This ensures that organizations are constantly seeking to improve their IT operations to meet the evolving needs of the business.
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT is a comprehensive framework that provides organizations with a structured approach to IT governance and management. The framework is designed to help organizations meet stakeholder needs, align IT with business objectives, manage IT-related risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory and legal requirements.
COBIT emphasizes the importance of taking a holistic approach to governance that encompasses all aspects of IT operations, including people, processes, and technology. This approach enables organizations to achieve effective IT governance and management that is integrated with overall organizational governance.
COBIT has evolved over time, with each version bringing improvements and updates to the framework. The most celebrated version of COBIT is COBIT 5.0, which provides organizations with a comprehensive approach to IT governance and management.
In addition to providing a framework for IT governance and management, COBIT also offers certification programs that enable IT professionals to demonstrate their knowledge and expertise in the framework. COBIT certification can provide professionals with a competitive edge in the job market and help organizations to build a team of skilled IT professionals who can effectively implement and manage the COBIT framework.
Become an Information Security Analyst in 2023: Start Now!
Become an Information Security Analyst 2023
With networked computing becoming a trend even in a small-scale company and the development of the internet and cloud solutions, accessing advanced data to solve business challenges has never been widespread.
As data systems are universal, data has become less secure, where more companies manage a colossal amount of data, making it an easier target for cybercriminals. Often smaller organizations need IT the experience to keep data safe. Over the last decade, more companies have dealt with high-profile data breaches.
As a result, the role of Information Security (IS) Analyst has advanced to a most sought-after position across industry verticals.
What is an IS Analyst?
An Information Security (IS) Analyst defends computer networks performed by private businesses, nonprofit organizations, and government organizations. However, there are a few domains where an IS Analyst can't find work relying on data security.
As ML and predictive modeling illustrate their investment returns, more enterprises need the skills of a competent IS Analyst. The sole responsibility of an Information Security Analyst is to develop scalable security apparatuses to address and prevent threats.
The job's criteria depend on the sector; however, an IS Analyst is often reserved in case of data breaches, hacking, or other crises based on tech asset security.
An analyst generates reports that IT admins and business professionals leverage to assess the practicality of their security systems. Depending on the Analyst's suggestions, organizations will modify security networks to ensure data is inaccessible to unauthorized people.
Developing and delivering educational courses is also a part of their work, as it's adequate to aid workforces in maintaining solid security practices.
Roles of Information Security Analysts
An IS Analyst is responsible for the following:
- Maintain data encryption and firewalls to safeguard sensitive data.
- Establish security standards
- Investigate security breaches on their company's networks.
- Ensure that senior IT staff is aware of security improvements
- Help users with learning and installation of new security products
- Staying updated on the latest advancements in IT security
Information Security Analysts: Job Prospects & Certification Requirement
According to BLS, IS Analyst job scope is projected to rise to 28% from 2016-2026, considerably more rapidly than other occupations' average growth. In addition, according to US News, IS Analyst is listed as the fourth best IT job in 2019, attributing to a wide variety of ventures looking for data security solutions.
According to Indeed, the average IS Analyst salary is $81,065 annually, which may increase as per expertise and knowledge.
An IS accreditation comprises a collection of credentials that set up foundational knowledge in different topics.
ICert Global helps people excel in the skills required for network security. Our security programs and certifications help participants to spot vulnerabilities, immediately respond to emergencies, and fend off attacks.
Some of the top-notch security certifications are as follows:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Cyber Security Expert
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Read More
Become an Information Security Analyst 2023
With networked computing becoming a trend even in a small-scale company and the development of the internet and cloud solutions, accessing advanced data to solve business challenges has never been widespread.
As data systems are universal, data has become less secure, where more companies manage a colossal amount of data, making it an easier target for cybercriminals. Often smaller organizations need IT the experience to keep data safe. Over the last decade, more companies have dealt with high-profile data breaches.
As a result, the role of Information Security (IS) Analyst has advanced to a most sought-after position across industry verticals.
What is an IS Analyst?
An Information Security (IS) Analyst defends computer networks performed by private businesses, nonprofit organizations, and government organizations. However, there are a few domains where an IS Analyst can't find work relying on data security.
As ML and predictive modeling illustrate their investment returns, more enterprises need the skills of a competent IS Analyst. The sole responsibility of an Information Security Analyst is to develop scalable security apparatuses to address and prevent threats.
The job's criteria depend on the sector; however, an IS Analyst is often reserved in case of data breaches, hacking, or other crises based on tech asset security.
An analyst generates reports that IT admins and business professionals leverage to assess the practicality of their security systems. Depending on the Analyst's suggestions, organizations will modify security networks to ensure data is inaccessible to unauthorized people.
Developing and delivering educational courses is also a part of their work, as it's adequate to aid workforces in maintaining solid security practices.
Roles of Information Security Analysts
An IS Analyst is responsible for the following:
- Maintain data encryption and firewalls to safeguard sensitive data.
- Establish security standards
- Investigate security breaches on their company's networks.
- Ensure that senior IT staff is aware of security improvements
- Help users with learning and installation of new security products
- Staying updated on the latest advancements in IT security
Information Security Analysts: Job Prospects & Certification Requirement
According to BLS, IS Analyst job scope is projected to rise to 28% from 2016-2026, considerably more rapidly than other occupations' average growth. In addition, according to US News, IS Analyst is listed as the fourth best IT job in 2019, attributing to a wide variety of ventures looking for data security solutions.
According to Indeed, the average IS Analyst salary is $81,065 annually, which may increase as per expertise and knowledge.
An IS accreditation comprises a collection of credentials that set up foundational knowledge in different topics.
ICert Global helps people excel in the skills required for network security. Our security programs and certifications help participants to spot vulnerabilities, immediately respond to emergencies, and fend off attacks.
Some of the top-notch security certifications are as follows:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Cyber Security Expert
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Cloud storage enables secure, scalable, and remote access.
Cloud Storage and its Importance
Cloud storage plays a vital role in our day-to-day lives. This is evident from the rapid growth of cloud storage providers. Cloud-based storage providers have transformed how we save data, store private information, and transfer files to other locations. Cloud storage is the new hot sector, with all the companies jumping on the bandwagon. In this digital age, where everything is online, we want to save and keep all our data safe. Unfortunately, there are many instances in which we might lose all our files or data if we don't have a good backup in place! But what exactly is cloud storage? How does it work? Continue the blog to learn about these.
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a type of computer storage that is accessible over the Internet. It is part of the cloud computing industry, including server hosting, network storage, and data management. Cloud storage differs from file servers and other types of centralized storage in that it is not owned by an organization or group but rather by a third-party provider who has access to your data as needed for their business purpose.
Cloud storage services typically allow users to store files in one place to access them anywhere on any device. They may also provide tools such as email, instant messaging, and calendars. Cloud storage can be accessed through web browsers or mobile apps on multiple computers and smartphones.
Cloud services are convenient because they allow you to store large amounts of data without worrying about maintaining physical space or spending money on hardware upgrades. Users can also pay only for what they use, unlike traditional methods where they purchase hard drives or other components upfront and pay for additional space yearly as their needs grow.
What is Cloud?
A cloud is a large data center that can be accessed remotely. It allows your application to run without the need for you to be physically present at a particular location.
For example, your software may only be used at home or work. You don't need to worry about transporting or storing data locally since it will all be stored in the cloud.
The benefit of using cloud computing is that you don't need to worry about storage space or maintenance costs since the company handling the storage and care will do it for you.
The Importance of Cloud Storage
Cloud data storage is generally less expensive than on-premises data storage. This is one of the most significant advantages of cloud data storage.
In addition, cloud data storage offers scalability for your business as your data storage needs increase. This also depends on which provider you choose to store your data. There are various storage options to choose from in cloud data storage. Cloud data storage can store and transfer multiple business data, including sensitive data.
In addition, cloud data storage offers data accessibility from any device connected to the internet. This can be particularly useful for businesses that want to give their employees the freedom to work remotely.
How does Cloud Storage work?
Cloud storage works on a different mechanism as compared to traditional data storage. Cloud-based storage works on a multi-tenant architecture, meaning they have multiple clients accessing their servers from a shared environment. This can be compared to a hotel where all the guests have access to the same kitchen and dining area.
Cloud storage uses a single system for storing, managing, and protecting data for multiple clients. The system is highly scalable and can quickly expand to accommodate increased customer demand.
There are different types of storage offered by cloud providers. While some offer only storage services, others also provide backup services.
The General Architecture of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage architecture comprises applications, networks, operating systems, hypervisors, and storage.
Applications consist of software used in storing and managing data.
The network is the interconnection between the client, application, and data center.
Operating systems are software that controls the hardware and software of the computer.
Hypervisors are software applications that manage virtual machines. Finally, storage is the place where data is stored.
Types of Cloud Service
There are many cloud storage services:
Software as a Service (SaaS): This service is used for business software. The software is hosted in the cloud and accessed over the internet by users. Software as a Service (SaaS) includes marketing and sales automation, human resource software, financial management software, etc.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS is a cloud service that gives all the tools one needs to build and run an application. This includes a programming language, a code editor, a runtime, a database, a file system, and an execution environment.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS is a cloud service that provides the infrastructure needed to run an application. This includes virtual machines, networks, storage, and load balancers.
Cloud Storage Providers
Google - The most popular cloud storage service is Google Drive. Google Drive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage. Many users use Google Drive because of its simplicity and ease of use.
Amazon - Amazon comes with free cloud storage with 5 GB of free space for users. It also allows you to earn more free Amazon Drive space. You can earn up to 50 GB of free Amazon Drive space by participating in their referral program.
Microsoft - Microsoft OneDrive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage space. You can refer your friends and earn an additional 5 GB of space.
Advantages of Cloud Storage
Cost Effective - Cloud storage can be much less expensive than traditional data storage.
Scalability - Cloud storage can scale as your needs change.
Convenience - Cloud storage can be accessed from any device.
Security - Cloud storage offers a high level of security and compliance with industry standards.
No upfront cost - You don't have to spend money to implement an effective backup.
Available as a service - Companies that provide cloud storage services make their product available, so you only pay for what you use.
Offsite backup - Cloud storage offers a convenient way to keep your essential files safe during a natural disaster.
No equipment - You don't have to purchase the hardware to store data onsite.
No technical knowledge - You don't have to have any special knowledge to use cloud storage.
Safety - Cloud storage services keep your data in a remote location. Hence, they're safe in case of a fire or other disaster at your business.
Variety of providers - A variety of providers offer cloud storage services, so you have many options when choosing a provider.
Conclusion
Cloud storage has become an essential part of business operations. It has proven a reliable and cost-effective way to store and share data. The wide range of providers and the growing demand for cloud storage are indicators of the growth of this sector.
Cloud storage offers an easy way to share data with partners and co-workers. It also makes it easier for remote employees to access files from home. Cloud storage is helpful for businesses that need extra storage space, but don-t have room for servers.
It's also beneficial for people who need to store sensitive information on an external server. Cloud storage is widely used for storing personal data like photos, videos, and emails. In addition, cloud storage lets you access your data from anywhere, on any device. These benefits make cloud storage an excellent choice for anyone who needs to store data online.
Read More
Cloud Storage and its Importance
Cloud storage plays a vital role in our day-to-day lives. This is evident from the rapid growth of cloud storage providers. Cloud-based storage providers have transformed how we save data, store private information, and transfer files to other locations. Cloud storage is the new hot sector, with all the companies jumping on the bandwagon. In this digital age, where everything is online, we want to save and keep all our data safe. Unfortunately, there are many instances in which we might lose all our files or data if we don't have a good backup in place! But what exactly is cloud storage? How does it work? Continue the blog to learn about these.
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a type of computer storage that is accessible over the Internet. It is part of the cloud computing industry, including server hosting, network storage, and data management. Cloud storage differs from file servers and other types of centralized storage in that it is not owned by an organization or group but rather by a third-party provider who has access to your data as needed for their business purpose.
Cloud storage services typically allow users to store files in one place to access them anywhere on any device. They may also provide tools such as email, instant messaging, and calendars. Cloud storage can be accessed through web browsers or mobile apps on multiple computers and smartphones.
Cloud services are convenient because they allow you to store large amounts of data without worrying about maintaining physical space or spending money on hardware upgrades. Users can also pay only for what they use, unlike traditional methods where they purchase hard drives or other components upfront and pay for additional space yearly as their needs grow.
What is Cloud?
A cloud is a large data center that can be accessed remotely. It allows your application to run without the need for you to be physically present at a particular location.
For example, your software may only be used at home or work. You don't need to worry about transporting or storing data locally since it will all be stored in the cloud.
The benefit of using cloud computing is that you don't need to worry about storage space or maintenance costs since the company handling the storage and care will do it for you.
The Importance of Cloud Storage
Cloud data storage is generally less expensive than on-premises data storage. This is one of the most significant advantages of cloud data storage.
In addition, cloud data storage offers scalability for your business as your data storage needs increase. This also depends on which provider you choose to store your data. There are various storage options to choose from in cloud data storage. Cloud data storage can store and transfer multiple business data, including sensitive data.
In addition, cloud data storage offers data accessibility from any device connected to the internet. This can be particularly useful for businesses that want to give their employees the freedom to work remotely.
How does Cloud Storage work?
Cloud storage works on a different mechanism as compared to traditional data storage. Cloud-based storage works on a multi-tenant architecture, meaning they have multiple clients accessing their servers from a shared environment. This can be compared to a hotel where all the guests have access to the same kitchen and dining area.
Cloud storage uses a single system for storing, managing, and protecting data for multiple clients. The system is highly scalable and can quickly expand to accommodate increased customer demand.
There are different types of storage offered by cloud providers. While some offer only storage services, others also provide backup services.
The General Architecture of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage architecture comprises applications, networks, operating systems, hypervisors, and storage.
Applications consist of software used in storing and managing data.
The network is the interconnection between the client, application, and data center.
Operating systems are software that controls the hardware and software of the computer.
Hypervisors are software applications that manage virtual machines. Finally, storage is the place where data is stored.
Types of Cloud Service
There are many cloud storage services:
Software as a Service (SaaS): This service is used for business software. The software is hosted in the cloud and accessed over the internet by users. Software as a Service (SaaS) includes marketing and sales automation, human resource software, financial management software, etc.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS is a cloud service that gives all the tools one needs to build and run an application. This includes a programming language, a code editor, a runtime, a database, a file system, and an execution environment.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS is a cloud service that provides the infrastructure needed to run an application. This includes virtual machines, networks, storage, and load balancers.
Cloud Storage Providers
Google - The most popular cloud storage service is Google Drive. Google Drive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage. Many users use Google Drive because of its simplicity and ease of use.
Amazon - Amazon comes with free cloud storage with 5 GB of free space for users. It also allows you to earn more free Amazon Drive space. You can earn up to 50 GB of free Amazon Drive space by participating in their referral program.
Microsoft - Microsoft OneDrive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage space. You can refer your friends and earn an additional 5 GB of space.
Advantages of Cloud Storage
Cost Effective - Cloud storage can be much less expensive than traditional data storage.
Scalability - Cloud storage can scale as your needs change.
Convenience - Cloud storage can be accessed from any device.
Security - Cloud storage offers a high level of security and compliance with industry standards.
No upfront cost - You don't have to spend money to implement an effective backup.
Available as a service - Companies that provide cloud storage services make their product available, so you only pay for what you use.
Offsite backup - Cloud storage offers a convenient way to keep your essential files safe during a natural disaster.
No equipment - You don't have to purchase the hardware to store data onsite.
No technical knowledge - You don't have to have any special knowledge to use cloud storage.
Safety - Cloud storage services keep your data in a remote location. Hence, they're safe in case of a fire or other disaster at your business.
Variety of providers - A variety of providers offer cloud storage services, so you have many options when choosing a provider.
Conclusion
Cloud storage has become an essential part of business operations. It has proven a reliable and cost-effective way to store and share data. The wide range of providers and the growing demand for cloud storage are indicators of the growth of this sector.
Cloud storage offers an easy way to share data with partners and co-workers. It also makes it easier for remote employees to access files from home. Cloud storage is helpful for businesses that need extra storage space, but don-t have room for servers.
It's also beneficial for people who need to store sensitive information on an external server. Cloud storage is widely used for storing personal data like photos, videos, and emails. In addition, cloud storage lets you access your data from anywhere, on any device. These benefits make cloud storage an excellent choice for anyone who needs to store data online.
Google Cloud vs.AWS vs. Azure:Which One Should You Choose?
Google Cloud Vs. AWS Vs. Azure: Which one to choose?
Over the years, cloud platforms have become one of the most famous methods to interact with the cloud and build applications. Today, you have several cloud platforms to select from, but Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure are globally renowned as the top three cloud providers.
However, the question remains - which cloud computing is the best?
If you can choose just one, you would like to know more about these three before choosing one. Therefore, we have gathered a few points to differentiate these three cloud services, helping you select the best.
Google Cloud Vs. AWS Vs. Azure
- Security and Privacy
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) - An amazon.com subsidiary offers an on-demand Cloud Computing platform to people, organizations, and governments on a paid-subscription basis. It is the oldest and enterprise-ready supplier due to its simplicity in delivering top-notch privacy measures and security to the users. Moreover, AWS does a great job defaulting to secure options to ensure greater privacy. For instance, when introducing an EC2, it auto-defaults the networking access to off.
- Azure - Outperforms Google Cloud in security terms because of its cloud defender aspect. It's an AI-powered tool that can aid you in finding errors in the cloud configurations, enhance your security posture, and safeguard your multi-cloud and hybrid environments from new cyber dangers. For example, if you introduce a primary instance of a virtual machine, all the ports are open by default.
- Google Cloud - one of the most secure platforms that offer security factors like encryption and Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP).
- Fundamental Features
- Google Cloud - includes advanced data analytics and development tools. Apart from this, you can leverage its cloud SDK for interacting with Cloud APIs.
- AWS - has a 5-year head start and is more feature-rich, providing around 200 services compared to the other two.
- Azure - Having over 100 services, Azure's strength relies on its global reach and availability. Other than that, several tools to seamlessly manage the Azure cloud system. If you leverage Azure, you can move data between your sites without leaving the network, resulting in minimized latency, lower prices, and higher security.
- Compute Engines
- Google Cloud - Google's scalable virtualization network hosts Virtual Machines (VMs) in Google's data centers. This can start up swiftly, having a lot of storage space, and can be personalized according to client requirements.
- AWS – A primary compute offering of AWS is its customizable ECS instances. We can change storage, connect more models, adjust regions, and more. If you've no earlier experience in computing or are worried about high billing costs, start with Amazon Lightsail - a cheap, dependable virtual private server with serverless computing. An added advantage is to pay only for the computing capacity leveraged.
- Azure - Compute solution of Azure relies on VMs, with tools such as Resource Manager and Cloud Services to aid with cloud app deployment and Azure Autoscaling.
- Availability Zones
- Google Cloud - available in 20 regions globally and 3 more to come.
- AWS - 66 availability zones with 12 more following.
- Azure - available in 54 regions and 140 countries globally.
- Major Clients
- Google Cloud - Bloomberg, HSBC, Dominos, PayPal and 20th Century Fox.
- AWS - Zynga, Netflix, Samsung, Unilever, MI, Airbnb, and BMW
- Azure - Honeywell, Johnson Controls, HP, Polycom, Apple, and Fujifilm.
- Pricing
- Google Cloud - smallest instances containing 2 virtual CPUs and 8GB RAM is obtained at 25% cheaper rate (us $52/month). In case of larger instance (3.75TB RAM and 160vCPUs), you get for US $5.32/hour.
- AWS - The cost of basic instances (2 vCPUs and 8GB RAM) is over $69/month and larger instances (3.84TB RAM and 128 vCPUs) is $3.97/hour.
- Azure - For small instances (8GB RAM and 2 vCPUs) the cost is over $70/month and that of larger instances (128 vCPUs and 3.89TB RAM) is $6.79/hour.
- Hybrid & Multi Cloud Choices
- Google Cloud - Looker, Cloud Run for Anthos, Anthos, Cloud Build, Operation, and Traffic Director.
- AWS - Wavelength, Snowball, Local Zones, Amazon EKS Anywhere, VMware Cloud on AWS, Outposts, Snowcone.
- Azure - Centinel, Arc, Blob Storage, Active Directory, Stack, Backup and Security Center.
Which One to Choose?
Considering everything, we conclude that AWS is easier to learn if you have no earlier cloud expertise. AWS continues to set the standard for stability and potential in broad strokes.
It remains the undisputed market leader in quality, security, and features. However, you will have to pay a premium compared to the rest, which is why Microsoft Azure is suggested as the second-top option if you are in a tight expense spot.
Read More
Google Cloud Vs. AWS Vs. Azure: Which one to choose?
Over the years, cloud platforms have become one of the most famous methods to interact with the cloud and build applications. Today, you have several cloud platforms to select from, but Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure are globally renowned as the top three cloud providers.
However, the question remains - which cloud computing is the best?
If you can choose just one, you would like to know more about these three before choosing one. Therefore, we have gathered a few points to differentiate these three cloud services, helping you select the best.
Google Cloud Vs. AWS Vs. Azure
- Security and Privacy
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) - An amazon.com subsidiary offers an on-demand Cloud Computing platform to people, organizations, and governments on a paid-subscription basis. It is the oldest and enterprise-ready supplier due to its simplicity in delivering top-notch privacy measures and security to the users. Moreover, AWS does a great job defaulting to secure options to ensure greater privacy. For instance, when introducing an EC2, it auto-defaults the networking access to off.
- Azure - Outperforms Google Cloud in security terms because of its cloud defender aspect. It's an AI-powered tool that can aid you in finding errors in the cloud configurations, enhance your security posture, and safeguard your multi-cloud and hybrid environments from new cyber dangers. For example, if you introduce a primary instance of a virtual machine, all the ports are open by default.
- Google Cloud - one of the most secure platforms that offer security factors like encryption and Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP).
- Fundamental Features
- Google Cloud - includes advanced data analytics and development tools. Apart from this, you can leverage its cloud SDK for interacting with Cloud APIs.
- AWS - has a 5-year head start and is more feature-rich, providing around 200 services compared to the other two.
- Azure - Having over 100 services, Azure's strength relies on its global reach and availability. Other than that, several tools to seamlessly manage the Azure cloud system. If you leverage Azure, you can move data between your sites without leaving the network, resulting in minimized latency, lower prices, and higher security.
- Compute Engines
- Google Cloud - Google's scalable virtualization network hosts Virtual Machines (VMs) in Google's data centers. This can start up swiftly, having a lot of storage space, and can be personalized according to client requirements.
- AWS – A primary compute offering of AWS is its customizable ECS instances. We can change storage, connect more models, adjust regions, and more. If you've no earlier experience in computing or are worried about high billing costs, start with Amazon Lightsail - a cheap, dependable virtual private server with serverless computing. An added advantage is to pay only for the computing capacity leveraged.
- Azure - Compute solution of Azure relies on VMs, with tools such as Resource Manager and Cloud Services to aid with cloud app deployment and Azure Autoscaling.
- Availability Zones
- Google Cloud - available in 20 regions globally and 3 more to come.
- AWS - 66 availability zones with 12 more following.
- Azure - available in 54 regions and 140 countries globally.
- Major Clients
- Google Cloud - Bloomberg, HSBC, Dominos, PayPal and 20th Century Fox.
- AWS - Zynga, Netflix, Samsung, Unilever, MI, Airbnb, and BMW
- Azure - Honeywell, Johnson Controls, HP, Polycom, Apple, and Fujifilm.
- Pricing
- Google Cloud - smallest instances containing 2 virtual CPUs and 8GB RAM is obtained at 25% cheaper rate (us $52/month). In case of larger instance (3.75TB RAM and 160vCPUs), you get for US $5.32/hour.
- AWS - The cost of basic instances (2 vCPUs and 8GB RAM) is over $69/month and larger instances (3.84TB RAM and 128 vCPUs) is $3.97/hour.
- Azure - For small instances (8GB RAM and 2 vCPUs) the cost is over $70/month and that of larger instances (128 vCPUs and 3.89TB RAM) is $6.79/hour.
- Hybrid & Multi Cloud Choices
- Google Cloud - Looker, Cloud Run for Anthos, Anthos, Cloud Build, Operation, and Traffic Director.
- AWS - Wavelength, Snowball, Local Zones, Amazon EKS Anywhere, VMware Cloud on AWS, Outposts, Snowcone.
- Azure - Centinel, Arc, Blob Storage, Active Directory, Stack, Backup and Security Center.
Which One to Choose?
Considering everything, we conclude that AWS is easier to learn if you have no earlier cloud expertise. AWS continues to set the standard for stability and potential in broad strokes.
It remains the undisputed market leader in quality, security, and features. However, you will have to pay a premium compared to the rest, which is why Microsoft Azure is suggested as the second-top option if you are in a tight expense spot.
Top 12 Essential Cloud Computing Characteristics Unveiled
Top 12 Essential Characteristic of Cloud Computing
Continuous business growth and expansion demand massive computational power and a data storage framework. As Cloud Computing gains popularity in the modern world, companies leverage the technique that helps the firms expand and safely transfer data from physical locations to the cloud that can be accessed anywhere and anytime.
There are numerous aspects of Cloud Computing that make it one of the swift developing sectors. First, the flexibility offered by the Cloud services in the form of its evolving set of methods and tools has hastened its deployment in a wide range of industry verticals.
This article will walk you through the top 12 essential features of Cloud Computing, but before that, let's get familiar with the term Cloud Computing.
What is Cloud Computing?
It is defined as allocating computing resources such as software, applications, databases, storage, networking capabilities, and more through the internet by Cloud Service Providers (CSP) to their users.
Thus, people no longer require to depend on their software/hardware resources and can access programs, data, and services hosted on remote servers from any location.
CSP charges their end-users monthly or per the usage policy-oriented with the Cloud facility. As you only pay for the Cloud services you leverage, you can deduce the operational expenses and enhance the infrastructure efficiency.
12 Essential Cloud Computing Characteristics
1. Easy Maintenance
It is one of the most crucial aspects of Cloud Computing, controlled by the CSP, and users are never involved in any maintenance-based services. These services are well-planned so that the downtime remains significantly low. Further, the Cloud undergoes routine updates that aid in capability optimization.
2. Measured & Reporting Service
Cloud frameworks allow the meter to track, manage, and optimize Cloud resource leverage. We can portray this characteristic as a measured service. The metering capability is placed at a certain level of applicable service abstraction. Hence, this aspect enables transparency for the users and service providers.
3. On-demand Self-service
This is a primary feature of Cloud Computing that allows the end-users to continuously monitor the server uptime, capabilities, and allotted network storage. Moreover, this on-demand self-service feature also enables the client to likewise control the computing capabilities according to their requirements.
4. Flexibility
The clients benefit from the flexibility provided by the CSP when they host data in the assigned Cloud. This ensures that the client can do away from typical hosting methods wherein they have to switch the service providers more often.
5. Remote Working
Cloud Computing promotes the characteristic of remote working, where clients can function, work, or deliver services from any location. Hence, users can access organizational data even on their smart devices, thus, enabling them to connect swiftly.
6. Wide Network Access
Cloud Computing is attained through a typical computing approach, and this aspect help advances heterogeneous thick and thin client platforms. Examples of such media include smartphones, assigned workstations, laptops, and tablets. Moreover, proficiency is delivered across various networks. Therefore, Cloud Computing helps break obstacles and boundaries as they work across myriad geographies.
7. Economical & Security
Economical feature of Cloud Computing aids in minimizing the IT expenses of the companies. Here, the client needs to pay the administration for the space they have utilized, and no additional payments are charged. Therefore, the administration is economical, and more often, some spaces are given for free.
When it comes to security, Cloud services create a stored data copy to prevent data loss. If a server misses out on the data, the copy version is restored from the other server. This characteristic comes in handy when many users work on a particular file, and it suddenly gets corrupted.
8. Automation
IT teams and developers modify Cloud services through automation. When a Cloud system is in place, it ensures less interaction with humans. The configurations are installed to ensure the maintenance and monitoring of Cloud Computing, and such arrangements are mostly automated. Hence, automation in Cloud Computing facilitates the swift expansion of its services.
9. Service Excellence
Cloud Computing ensures that people receive the highest service level possible. The advantages highlighted in Service Legal Agreements must have constant availability and comprehensive resources, capacity, and performance. Any compromise on these services leads to the loss of clients and popularity.
10. Multi-tenancy
Multi-Tenancy is one of the top features of Cloud Computing - a software architecture that allows a single program instance to offer numerous user groups. Several Cloud provider customers share the same computing resources; however, each customer's data is entirely separated and maintained safely.
11. Flexible Payment Structure
Cloud Computing provides a comfortable payment structure that plays a vital role in companies' cost-cutting. Due to the additional functionality, Cloud Computing selections come at different prices. Users find the payment choice to be streamlined and simple to leverage, and it enables them to save time when making regular payments.
12. Resilience
Resilience in Cloud Computing indicates the potential of the service to recover from any disruption swiftly. A Cloud's resilience is estimated by how rapidly its databases, servers, and network framework restarts and recover from any damage. The CSP also creates plans that enhance disaster management, attained by maintaining backup Cloud nodes.
Why Use Cloud Computing?
The following are the reasons why one must leverage Cloud Computing:
- Deliver scalable business solutions
- Minimize expenses in terms of procuring new hardware/software
- Provide security and make easy access to Computing resources
- Helps to increase the capacity to adapt to the increasing business demands of huge companies
- Help enterprise clients to assess apps and services seamlessly.
- It is reliable as they provide backup and affordable methods for data recovery.
Read More
Top 12 Essential Characteristic of Cloud Computing
Continuous business growth and expansion demand massive computational power and a data storage framework. As Cloud Computing gains popularity in the modern world, companies leverage the technique that helps the firms expand and safely transfer data from physical locations to the cloud that can be accessed anywhere and anytime.
There are numerous aspects of Cloud Computing that make it one of the swift developing sectors. First, the flexibility offered by the Cloud services in the form of its evolving set of methods and tools has hastened its deployment in a wide range of industry verticals.
This article will walk you through the top 12 essential features of Cloud Computing, but before that, let's get familiar with the term Cloud Computing.
What is Cloud Computing?
It is defined as allocating computing resources such as software, applications, databases, storage, networking capabilities, and more through the internet by Cloud Service Providers (CSP) to their users.
Thus, people no longer require to depend on their software/hardware resources and can access programs, data, and services hosted on remote servers from any location.
CSP charges their end-users monthly or per the usage policy-oriented with the Cloud facility. As you only pay for the Cloud services you leverage, you can deduce the operational expenses and enhance the infrastructure efficiency.
12 Essential Cloud Computing Characteristics
1. Easy Maintenance
It is one of the most crucial aspects of Cloud Computing, controlled by the CSP, and users are never involved in any maintenance-based services. These services are well-planned so that the downtime remains significantly low. Further, the Cloud undergoes routine updates that aid in capability optimization.
2. Measured & Reporting Service
Cloud frameworks allow the meter to track, manage, and optimize Cloud resource leverage. We can portray this characteristic as a measured service. The metering capability is placed at a certain level of applicable service abstraction. Hence, this aspect enables transparency for the users and service providers.
3. On-demand Self-service
This is a primary feature of Cloud Computing that allows the end-users to continuously monitor the server uptime, capabilities, and allotted network storage. Moreover, this on-demand self-service feature also enables the client to likewise control the computing capabilities according to their requirements.
4. Flexibility
The clients benefit from the flexibility provided by the CSP when they host data in the assigned Cloud. This ensures that the client can do away from typical hosting methods wherein they have to switch the service providers more often.
5. Remote Working
Cloud Computing promotes the characteristic of remote working, where clients can function, work, or deliver services from any location. Hence, users can access organizational data even on their smart devices, thus, enabling them to connect swiftly.
6. Wide Network Access
Cloud Computing is attained through a typical computing approach, and this aspect help advances heterogeneous thick and thin client platforms. Examples of such media include smartphones, assigned workstations, laptops, and tablets. Moreover, proficiency is delivered across various networks. Therefore, Cloud Computing helps break obstacles and boundaries as they work across myriad geographies.
7. Economical & Security
Economical feature of Cloud Computing aids in minimizing the IT expenses of the companies. Here, the client needs to pay the administration for the space they have utilized, and no additional payments are charged. Therefore, the administration is economical, and more often, some spaces are given for free.
When it comes to security, Cloud services create a stored data copy to prevent data loss. If a server misses out on the data, the copy version is restored from the other server. This characteristic comes in handy when many users work on a particular file, and it suddenly gets corrupted.
8. Automation
IT teams and developers modify Cloud services through automation. When a Cloud system is in place, it ensures less interaction with humans. The configurations are installed to ensure the maintenance and monitoring of Cloud Computing, and such arrangements are mostly automated. Hence, automation in Cloud Computing facilitates the swift expansion of its services.
9. Service Excellence
Cloud Computing ensures that people receive the highest service level possible. The advantages highlighted in Service Legal Agreements must have constant availability and comprehensive resources, capacity, and performance. Any compromise on these services leads to the loss of clients and popularity.
10. Multi-tenancy
Multi-Tenancy is one of the top features of Cloud Computing - a software architecture that allows a single program instance to offer numerous user groups. Several Cloud provider customers share the same computing resources; however, each customer's data is entirely separated and maintained safely.
11. Flexible Payment Structure
Cloud Computing provides a comfortable payment structure that plays a vital role in companies' cost-cutting. Due to the additional functionality, Cloud Computing selections come at different prices. Users find the payment choice to be streamlined and simple to leverage, and it enables them to save time when making regular payments.
12. Resilience
Resilience in Cloud Computing indicates the potential of the service to recover from any disruption swiftly. A Cloud's resilience is estimated by how rapidly its databases, servers, and network framework restarts and recover from any damage. The CSP also creates plans that enhance disaster management, attained by maintaining backup Cloud nodes.
Why Use Cloud Computing?
The following are the reasons why one must leverage Cloud Computing:
- Deliver scalable business solutions
- Minimize expenses in terms of procuring new hardware/software
- Provide security and make easy access to Computing resources
- Helps to increase the capacity to adapt to the increasing business demands of huge companies
- Help enterprise clients to assess apps and services seamlessly.
- It is reliable as they provide backup and affordable methods for data recovery.
ITIL V3 evolves to V4: Transforming IT service management
ITIL is updating! Version 3 to V4 | ITIL
So, ITIL is upgrading to V4
ITIL 4 is an evolution from ITIL v3, providing a practical and flexible transition that allows organizations
to adopt the new ways of working required by the modern digital world.
What’s different in ITIL 4
ITIL 4 reflects and introduces the modern methods of digital transformation like DevOps, Agile and Lean IT.
The ITIL version 3 has a different lifecycle and credit system as compared to the newly launched version
4. The ITIL 4 Foundation was successfully launched in the month of February 2019 as per Axelos release statement.
ITIL evolution
ITIL ® V1
– Focus on systems Mgmt
– Business support focus
ITIL ® V2
– Focus on processes Mgmt for IT Services
– Business alignment focus
ITIL ® V3
– Focus on service lifecycle Mgmt with the help of processes
– Business Integration focus
ITIL ® V4
– Focus Digital transformation & New ways of working
– Integration & Coordination Focus
ITIL 3
ITIL Qualification Structure
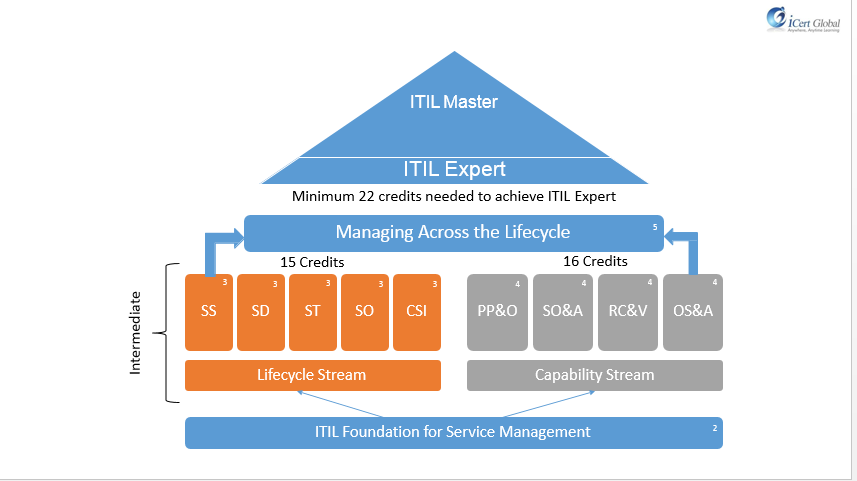
ITIL 4
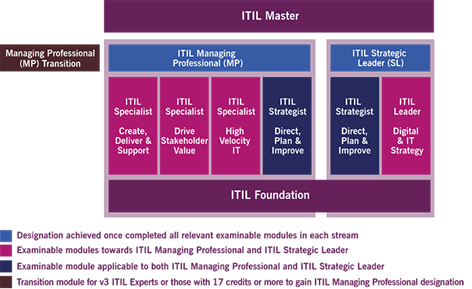
ITIL V4 Certification
In case you are doing ITIL V3, do not worry as your learning will be still be valuable but just hold it a
moment in pursuing further as ITIL 4 has a different pathway altogether. Remember, regardless of
ITIL V3 or V4, the core remains the same as we start off with Foundation Module and end up in Masters.
The modules in between changes.
As per the Axelos in their official page have reported that ITIL 4 expands on previous versions and
provides an end-to-end IT/digital operating model for the delivery and operation of tech-enabled
products and services.
Read More
ITIL is updating! Version 3 to V4 | ITIL
So, ITIL is upgrading to V4
ITIL 4 is an evolution from ITIL v3, providing a practical and flexible transition that allows organizations
to adopt the new ways of working required by the modern digital world.
What’s different in ITIL 4
ITIL 4 reflects and introduces the modern methods of digital transformation like DevOps, Agile and Lean IT.
The ITIL version 3 has a different lifecycle and credit system as compared to the newly launched version
4. The ITIL 4 Foundation was successfully launched in the month of February 2019 as per Axelos release statement.
ITIL evolution
ITIL ® V1
– Focus on systems Mgmt
– Business support focus
ITIL ® V2
– Focus on processes Mgmt for IT Services
– Business alignment focus
ITIL ® V3
– Focus on service lifecycle Mgmt with the help of processes
– Business Integration focus
ITIL ® V4
– Focus Digital transformation & New ways of working
– Integration & Coordination Focus
ITIL 3
ITIL Qualification Structure

ITIL 4

ITIL V4 Certification
In case you are doing ITIL V3, do not worry as your learning will be still be valuable but just hold it a
moment in pursuing further as ITIL 4 has a different pathway altogether. Remember, regardless of
ITIL V3 or V4, the core remains the same as we start off with Foundation Module and end up in Masters.
The modules in between changes.
As per the Axelos in their official page have reported that ITIL 4 expands on previous versions and
provides an end-to-end IT/digital operating model for the delivery and operation of tech-enabled
products and services.
ITSM: Unlocking Value Beyond Just Service Management!!!
There is also a misconception that IT Systems pertains to the software industry. The perception should ‘wherever IT Systems are deployed’; it calls for managing and maintenance of IT Systems. Automation is again big time in the software industry. Check out and you will find them more IT-services based.
Who will manage the IT Services?
Of course, IT Service Management team, that could include IT System Managers, IT Administrators, System Administrators, IT Quality Specialists, IT Audit, IT System Analysts and Quality Control who are either responsible for streamlining the IT Systems or part of IT Service Management team, Quality Assurance teams responsible for software and infrastructure.
Who will manage the people handling IT Services?
IT is ubiquitous. It’s almost everywhere. So, IT Service management is indispensable because there is no sphere of our life which IT has not shaped up. So you need people who are skilled in managing and handling IT systems. The need for ITIL® Certifications is more as a test of competency and validation of expertise in handling critical scenarios.
Why ITIL® Certifications
IT Service setup can be simple or complicated, and more often not, the complexity varies in severity. Hence, most companies prefer skilled people with experience and rich expertise in entrusting the systems. Just like mirror servers, company don’t prefer to depend on any particular team, rather they prefer a mix of teams who can be deployed and pressed in to service should a situation arise. This is the very reason why the ITIL® Certifications have gained prominence in the recent times as professionals start at foundation level and then move on to the intermediate modules – which can be either lifecycle modules best suited for professional pursuing management of services and the other is capability modules, which is apt for professionals preferring the process, and the next level of certification is the MALC ( Managing Across the Lifecycle) and clearance will lead to ITIL Expert. So given the mix of management and process in the intermediate levels, companies also use a judicious mix of people capable of handling management or process related issues.
In case of any faulty issues or malfunction, the troubleshooting will be addressed by the maintenance crew who are always on standby. Expecting the unexpected is a good maxim and mostly followed by all the companies that have deployed IT Systems. Maintenance is a critical and crucial as managing project. The prerequisites, qualifications, certification and validation in terms of capability and competency remain the same.
image:http://www.web-techsupport.com/images/ourservices.jpg
Read More
ITIL® – Define IT success through effective service strategy
A gaze into the future. That sounds exciting in terms of prospects and expectation. We seem to be advancing at an incredible speed. Technology is spearheading and impacting our lives in ways we would have imagined. According to Gartner’s prediction for 2016, some interesting insights that probably upped the ante would be
• By 2018, 6 billion connected things will be requesting support.
• In Gartner's IoT forecast, by 2020, more than 35 billion things will be connected to the Internet
• by 2021, 1 million IoT devices will be purchased and installed every single hour.
Of course, we expect smartness not just from people but in the products made by the people. When a solution is proposed, we pay attention and give equal weightage to the service aspect as well. Going by the statistics presented, there is going to an increased dependence on human intervention.
The stress on system and humans is significant to assess the way things will turnaround tomorrow. And that suggests the need of qualified professionals in ITSM. If the numbers in the forecasts are mind boggling, think about the demand that will be generated as a result and in terms of readiness what it takes to be prepared to face the challenges ahead. Looking forward, specialization and skills in service management will prove crucial and critical.
The advice to aspirants, especially those engaged in handling and managing of IT systems is to step out of the comfort zone and step up their credentials, wherein training and certification will establish credibility. ITIL and COBIT come across as commendable certification that should bolster your candidature. The digital divide is blurred and soon the switch to digital is expected to be complete attributing to the spike in the number presented.
By 2018, 2 million employees will be required to wear health and fitness tracking devices as a condition of employment.’ From a service perspective, for the system to be up and running, downtime is just unthinkable and SLAs charted will determine the uptime expected, which should be '200%'. So where are we heading? And how are we placed should the prediction come true? It might be baffling but to disbelieve would be disastrous.
It’s a clear indicator that systems would go up and so will the coordination to streamline. IT Services would hold a prominent portfolio. And if you are service personnel, its time to roll up your sleeves and start preparing to face tomorrow.
image courtesy: goo.gl/YX82HX
Read More
PRINCE2® 2017 – Stay updated on the latest exam changes.
Continuing with our previous blog post about the changes in the PRINCE 2017 Release, this posting covers the exam details for both Foundation Exam and Practitioner exam.
The details are provided from the Axelos site to preserve integrity of the data, and also avoid unnecessary ambiguity
Foundation Examination Design
Exam Design
• Number of questions reduced to 60 (previously 75 with trial questions), and no trial questions
• Exam duration unchanged (1 hour)
• (Pass mark may be adjusted following standard setting)
• Negative questions removed, except where it is part of the learning outcome to know that something shouldn’t occur (e.g. NOT, FALSE, INCORRECT)
• Number of list and missing word questions reduced, i.e. more standard questions
Foundation Exam Structure
• 5 Questions on key concepts
• 8 questions on principles
• 28 questions on themes
• 3-5 questions on each theme
• 19 questions on processes
• 2-3 questions on each process.
Practitioner Examination Design
Exam Design - Questions
• Number of questions (marks) reduced to 75 (previously 80)
• Exam duration unchanged (2.5 hours)
• (Pass mark may be adjusted following standard setting)
• Question styles removed:
• Multiple response
• Assertion reason
• Question styles retained:
• Matching (for BL3) – max 3 marks with 5-6 tokens
• Classic (for BL4) e.g. Yes, because…..
Practitioner Examination Design
Exam Design – Scenario/Information
Candidates will only need to refer to:
• A one-page project scenario
• One page of additional information for the organization theme (person profiles)
• Approx. 4 lines of information before the question stem to provide the context (especially BL4 questions).
In other words:
• No separate lengthy additional information (except for organization theme)
• No ‘delete entry 1’, ‘amend entry 1’ questions’!!
please watch this space for more update. We will keep you posted more about the developments about PRINCE 2-2017 release.
Wishing you good lucl in your endevaors.
image courtesy: goo.gl/XrGZEt
Read More
Continuing with our previous blog post about the changes in the PRINCE 2017 Release, this posting covers the exam details for both Foundation Exam and Practitioner exam.
The details are provided from the Axelos site to preserve integrity of the data, and also avoid unnecessary ambiguity
Foundation Examination Design
Exam Design
• Number of questions reduced to 60 (previously 75 with trial questions), and no trial questions
• Exam duration unchanged (1 hour)
• (Pass mark may be adjusted following standard setting)
• Negative questions removed, except where it is part of the learning outcome to know that something shouldn’t occur (e.g. NOT, FALSE, INCORRECT)
• Number of list and missing word questions reduced, i.e. more standard questions
Foundation Exam Structure
• 5 Questions on key concepts
• 8 questions on principles
• 28 questions on themes
• 3-5 questions on each theme
• 19 questions on processes
• 2-3 questions on each process.
Practitioner Examination Design
Exam Design - Questions
• Number of questions (marks) reduced to 75 (previously 80)
• Exam duration unchanged (2.5 hours)
• (Pass mark may be adjusted following standard setting)
• Question styles removed:
• Multiple response
• Assertion reason
• Question styles retained:
• Matching (for BL3) – max 3 marks with 5-6 tokens
• Classic (for BL4) e.g. Yes, because…..
Practitioner Examination Design
Exam Design – Scenario/Information
Candidates will only need to refer to:
• A one-page project scenario
• One page of additional information for the organization theme (person profiles)
• Approx. 4 lines of information before the question stem to provide the context (especially BL4 questions).
In other words:
• No separate lengthy additional information (except for organization theme)
• No ‘delete entry 1’, ‘amend entry 1’ questions’!!
please watch this space for more update. We will keep you posted more about the developments about PRINCE 2-2017 release.
Wishing you good lucl in your endevaors.
image courtesy: goo.gl/XrGZEt
The Importance Of IT Service Management.
Does artificial intelligence fall under the ambit of IT services? Yes, so long they are used for IT related projects and programs. Automation is again big time in the software industry. Check out and you will find them more IT-services based.
Failed computer replaced during U.S. astronauts' spacewalk [source- Reuters]that doesn’t speak of IT Service Management? News like and a horde of such articles and news items in the public domain only stresses the importance of IT Service management.
Who will manage the IT Services?
Of course, IT Service Management team, that could include IT System Managers, IT Administrators, System Administrators, IT Quality Specialists, IT Audit, IT System Analysts and Quality Control who are either responsible for streamlining the IT Systems or part of IT Service Management team, Quality Assurance teams responsible for software and infrastructure.
Who will manage the people handling IT Services?
The reiteration IT Service management is because there is no sphere of our life which IT has not shaped up. IT is ubiquitous. It’s almost everywhere. So you need people who are skilled in managing and handling IT systems. The need for ITIL® Certifications is more as a test of competency and validation expertise in handling critical scenarios. IT Service setup can be simple or complicated, and more often not, the complexity varies in severity, and you can take it for granted that any IT System will be complex. Hence, most companies prefer skilled people with experience and rich expertise in entrusting the systems. Just like mirror servers, company don’t prefer to depend on any particular team, rather they prefer a mix of teams who can be deployed and pressed in to service should a situation warrant. This is the very reason why the ITIL® Certifications have gained prominence in the recent times as professionals start at foundation level and then move on to the intermediate modules – which can be either Lifecycle modules best suited for professional pursuing management of services and the other is capability modules, which is apt for professionals preferring the process, and the next level of certification is the MALC ( Managing Across the Lifecycle) and clearance will lead to ITIL Expert. So given the mix of management and process in the intermediate levels, companies also use a judicious mix of people capable of handling scenarios pertaining to management or process or both.
Who will maintain the IT Systems?
It is an interesting poser. Maintenance of IT Systems need not be the same as the one managing the IT Systems. There can be a dedicated team exclusively for IT system maintenance. The prerequisites, qualifications, certification and validation in terms of capability and competency remain the same. Maintenance is a critical and crucial as managing. In case of any faulty issues or malfunction, troubleshooting will be taken care by the maintenance crew who are always on standby. Expecting the unexpected is a good maxim and mostly follow b all the companies that have deployed IT Systems. There is also a misconception that IT Systems pertains to the software industry. The perception should ‘wherever IT Systems are deployed’, it calls for managing and maintenance of IT Systems.
Read More
Boost your career with ITIL certification and earned credits
According to information published in 2012 by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job outlook for computer and information systems managers is projected to increase by 15% through 2022. ITIL® (IT Service Management) is the most recognized framework for IT service management in the world. The opportunities presented are plenty – and subjective to a professional’s preference. Professionals inclined more towards managing and leading teams are recommended to pursue the Lifecycle Modules; for those who are process oriented and wish to play an active in service management then it is strongly suggested to take up Capability modules. Certification & Credits ITIL® is undoubtedly one of the most recognized and accredited IT Service framework and helps professionals to pursue career goals. More often not, ITIL certification is understood for service management exclusively. While that’s true, ITIL also complements Project Management. So the scope is quite broad and left to the individual’s preference about career path. How many Credits do I need to become ITIL® Expert? ITIL® certification commences with Foundation and moves forward with Lifecycle or Capability Modules, which eventually will make you qualify to appear for the MALC certification. You need 22 credits to qualify for the expert level – which is usually achieved by becoming certified as Foundation level and earn 2 credit followed by Intermediate Modules and then MALC. Foundation (2 credits) + 5 Lifecycle Modules (each module is worth 3 credits and hence 5 x 3 =15 credits) + MALC (5 credits) =22 credits. Or Foundation (2 credits) + 4 Capability Modules (each module is worth 4 credits and hence 4x4 =16 credits) + MALC (5 credits)=23 credits. The criteria set are to earn 22 credit to become an Expert. You can learn more about the Credit system , please visit Axelos link. Career Advancement Excellent. For a qualified professional, the prospects can be just amazing. Evaluating studies from payscale.com offer valuable insights about the Employees with a Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Expert Level Certification: There is an increasing need and growing demand for this certification and indicators from the public domain forecast a trend of capitalizing on IT Service Management. ITIL professionals with more certifications earn on average 13% more in US, according to the ITSM Salary Survey by Plexent. According to the survey, certifications really do pay: in 2011, an ITIL Expert made on average $122,000 and an ITIL Service Manager $125,000 in US.
Read More
According to information published in 2012 by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job outlook for computer and information systems managers is projected to increase by 15% through 2022. ITIL® (IT Service Management) is the most recognized framework for IT service management in the world. The opportunities presented are plenty – and subjective to a professional’s preference. Professionals inclined more towards managing and leading teams are recommended to pursue the Lifecycle Modules; for those who are process oriented and wish to play an active in service management then it is strongly suggested to take up Capability modules. Certification & Credits ITIL® is undoubtedly one of the most recognized and accredited IT Service framework and helps professionals to pursue career goals. More often not, ITIL certification is understood for service management exclusively. While that’s true, ITIL also complements Project Management. So the scope is quite broad and left to the individual’s preference about career path. How many Credits do I need to become ITIL® Expert? ITIL® certification commences with Foundation and moves forward with Lifecycle or Capability Modules, which eventually will make you qualify to appear for the MALC certification. You need 22 credits to qualify for the expert level – which is usually achieved by becoming certified as Foundation level and earn 2 credit followed by Intermediate Modules and then MALC. Foundation (2 credits) + 5 Lifecycle Modules (each module is worth 3 credits and hence 5 x 3 =15 credits) + MALC (5 credits) =22 credits. Or Foundation (2 credits) + 4 Capability Modules (each module is worth 4 credits and hence 4x4 =16 credits) + MALC (5 credits)=23 credits. The criteria set are to earn 22 credit to become an Expert. You can learn more about the Credit system , please visit Axelos link. Career Advancement Excellent. For a qualified professional, the prospects can be just amazing. Evaluating studies from payscale.com offer valuable insights about the Employees with a Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Expert Level Certification: There is an increasing need and growing demand for this certification and indicators from the public domain forecast a trend of capitalizing on IT Service Management. ITIL professionals with more certifications earn on average 13% more in US, according to the ITSM Salary Survey by Plexent. According to the survey, certifications really do pay: in 2011, an ITIL Expert made on average $122,000 and an ITIL Service Manager $125,000 in US.
Enhancing automation, collaboration, and customer experience
The Internet growth has reshaped service and its outlook. The ITSM best practices and processes put in place so that organization can step-up potential, performance and profit. The service aspect, unlike the software, is not the cynosure yet the product lifecycle will be incomplete, if not, stunted without service in its place. More often, repeat orders [read as customers] are the key business drivers, and in order to gain confidence and increase traction, improve service. In the ITSM realm, the stress of service is on information and technology (IT) – as the definition states design, delivery, manage and improve IT services within an organization to meet its business goals. Process optimization: The most pressing issue as highlighted by a number of service management experts is Process Optimization. How can you maximize efficiency at minimum cost? Process Optimization. The key is to identify the areas which have the best impossible impact to effect. A typical scenario to understand optimization is automation. Setting auto-response to any query, instead of acknowledging receipt manually is the basic automation that goes unnoticed but very effective. Process optimization will ensure compliance adherence, increased accountability and avoid wastage. Self-service: Self-service is a hard-biting issue that still finds itself lagging and lacking for want of a better system. ITSM should be optimized to offer the experience of self-satisfaction. While customer-satisfaction is paramount, the interest of the self shouldn’t be delayed or discarded. The Self-service issue was a priority in the previous year 2015 which went unaddressed as expected and given the lacuna, the need to close the gap and plug holes took precedence over other priorities for 2016. Any issue important can be read as a good opportunity to make the most and hence focus is on improving the service standards. IT – business alignment: The synergy between IT and Business always results in a greater yield. to understand IT-Business alignment, you need to understand how and where does IT and Business connect. How are your meeting with customer captured? And how does technology enable business? You might want to look at dashboards that typically summarize the events and present critical information to empower informed decision-making. Its very much a strategic call, like IT Governance with risk and compliance management. The insights posited as trends or ‘Opportunities’ for 2016 is more of reflection from the remnant and projections for future. While Process Optimization was closely followed by self-service, the value of aligning business needs to increased customer satisfaction too was a pronounced call for action. Strong indication was sounded for Automation mainly to streamline process and resources and avoid waste of time and material. The list also featured Budgets, Digitization ESM and ITAM. While Budget and Digitization are prospects, ESM and ITAM stem from the remnants of 2015. The Status of 2015: The trends of 2015 was studied to understand the reach and addressal; and the understanding is that Services found wanting and fell short on Self-service, Service beyond management and IT Asset Management. The table below depicts the findings. Self Service: When user is self-empowered, the dependence on others can be cut down to improve productivity. Usually time-chokers, when issues have to be resolved by ‘someone’ always burdens the user with increased reliance on resources. Instances when access to a particular site is blocked that not only interrupts your work but arrests the thought flow, scuttling spontaneity and slowing work as a result, all in the aspect of security? There is always a better way to get things done without compromising security and still serving the self-service. The ITSM can step-in to sort out the mess and streamline flow to avoid interruption and enhance engagement. The service desk inexplicably, fails to empower self-service Service management beyond IT: It is also known as Enterprise Service Management (ESM), which can optimize service management to pass on benefits to other departments like Human Resources, Finance, to improve delivery. If you have to follow-up on a leave request or a loan applied, will it not be necessary to touch base with HR for eligibility and approval, and pass the request to Finance to disbursement? The services that can make the entire process seamless, cutting out the delay and accelerating the request-response will result in greater satisfaction. IT Asset Management (ITAM): Software management is significant because of its need and value, and also the adherence, compliance and audit check makes it increasingly important to manage your assets. Its observed from industry practice and use that aligning asset management with service management will result in substantial cost reduction. You will be able to better control and become cost-effective through screening and shortlisting to prioritize and take preventive measures to ac\void any attack or breaches in safeguarding your assets and value. Some of the critical shortcoming in 2015 were lined up for redressal and remedy in 2016 and prominently featured were self-service and IT Asset Management. You may please access the white paper which requires registration. For more information about our ITSM programs, we request you to visit our website http://www.icertglobal.com/ all-courses or call the nearest branch close to your locality.
Read More
The Internet growth has reshaped service and its outlook. The ITSM best practices and processes put in place so that organization can step-up potential, performance and profit. The service aspect, unlike the software, is not the cynosure yet the product lifecycle will be incomplete, if not, stunted without service in its place. More often, repeat orders [read as customers] are the key business drivers, and in order to gain confidence and increase traction, improve service. In the ITSM realm, the stress of service is on information and technology (IT) – as the definition states design, delivery, manage and improve IT services within an organization to meet its business goals. Process optimization: The most pressing issue as highlighted by a number of service management experts is Process Optimization. How can you maximize efficiency at minimum cost? Process Optimization. The key is to identify the areas which have the best impossible impact to effect. A typical scenario to understand optimization is automation. Setting auto-response to any query, instead of acknowledging receipt manually is the basic automation that goes unnoticed but very effective. Process optimization will ensure compliance adherence, increased accountability and avoid wastage. Self-service: Self-service is a hard-biting issue that still finds itself lagging and lacking for want of a better system. ITSM should be optimized to offer the experience of self-satisfaction. While customer-satisfaction is paramount, the interest of the self shouldn’t be delayed or discarded. The Self-service issue was a priority in the previous year 2015 which went unaddressed as expected and given the lacuna, the need to close the gap and plug holes took precedence over other priorities for 2016. Any issue important can be read as a good opportunity to make the most and hence focus is on improving the service standards. IT – business alignment: The synergy between IT and Business always results in a greater yield. to understand IT-Business alignment, you need to understand how and where does IT and Business connect. How are your meeting with customer captured? And how does technology enable business? You might want to look at dashboards that typically summarize the events and present critical information to empower informed decision-making. Its very much a strategic call, like IT Governance with risk and compliance management. The insights posited as trends or ‘Opportunities’ for 2016 is more of reflection from the remnant and projections for future. While Process Optimization was closely followed by self-service, the value of aligning business needs to increased customer satisfaction too was a pronounced call for action. Strong indication was sounded for Automation mainly to streamline process and resources and avoid waste of time and material. The list also featured Budgets, Digitization ESM and ITAM. While Budget and Digitization are prospects, ESM and ITAM stem from the remnants of 2015. The Status of 2015: The trends of 2015 was studied to understand the reach and addressal; and the understanding is that Services found wanting and fell short on Self-service, Service beyond management and IT Asset Management. The table below depicts the findings. Self Service: When user is self-empowered, the dependence on others can be cut down to improve productivity. Usually time-chokers, when issues have to be resolved by ‘someone’ always burdens the user with increased reliance on resources. Instances when access to a particular site is blocked that not only interrupts your work but arrests the thought flow, scuttling spontaneity and slowing work as a result, all in the aspect of security? There is always a better way to get things done without compromising security and still serving the self-service. The ITSM can step-in to sort out the mess and streamline flow to avoid interruption and enhance engagement. The service desk inexplicably, fails to empower self-service Service management beyond IT: It is also known as Enterprise Service Management (ESM), which can optimize service management to pass on benefits to other departments like Human Resources, Finance, to improve delivery. If you have to follow-up on a leave request or a loan applied, will it not be necessary to touch base with HR for eligibility and approval, and pass the request to Finance to disbursement? The services that can make the entire process seamless, cutting out the delay and accelerating the request-response will result in greater satisfaction. IT Asset Management (ITAM): Software management is significant because of its need and value, and also the adherence, compliance and audit check makes it increasingly important to manage your assets. Its observed from industry practice and use that aligning asset management with service management will result in substantial cost reduction. You will be able to better control and become cost-effective through screening and shortlisting to prioritize and take preventive measures to ac\void any attack or breaches in safeguarding your assets and value. Some of the critical shortcoming in 2015 were lined up for redressal and remedy in 2016 and prominently featured were self-service and IT Asset Management. You may please access the white paper which requires registration. For more information about our ITSM programs, we request you to visit our website http://www.icertglobal.com/ all-courses or call the nearest branch close to your locality.
ITIL Foundation Certification and Training for success.
ITIL® Foundation The Foundation Level is the entry-level qualification that offers candidates a general awareness of the key elements, concepts, and terminology used in the ITIL® Service Lifecycle, including the linkages between Lifecycle stages, the processes used and their contribution to Service Management practices. Why should I take ITIL® Foundation? Upon successful completion of the education and examination components related to this qualification, candidates can expect to gain a general overview, and basic knowledge and understanding of ITIL®. the qualification also fulfills the prerequisite entry criteria for the next level of study within the ITIL® qualifications scheme, the ITIL® Intermediate Level. Is it right for me? This qualification is primarily aimed towards: those who require a basic understanding of the ITIL® framework; those who need an understanding of how ITIL® can be used to enhance the quality of IT service management within an organization; IT professionals or others working within an organization that has adopted and adapted ITIL® who need to be informed about, or contribute to an ongoing service improvement program. The ITIL® qualification is open to any individuals who may have an interest in the subject. The ITIL® Foundation qualification is not intended to enable the holders of the qualification to apply the ITIL® practices for Service Management without further guidance. For more information and to register for ITIL Foundation Please click on below register button. images courtesy: goo.gl/NVVU7g
Read More
ITIL® Foundation The Foundation Level is the entry-level qualification that offers candidates a general awareness of the key elements, concepts, and terminology used in the ITIL® Service Lifecycle, including the linkages between Lifecycle stages, the processes used and their contribution to Service Management practices. Why should I take ITIL® Foundation? Upon successful completion of the education and examination components related to this qualification, candidates can expect to gain a general overview, and basic knowledge and understanding of ITIL®. the qualification also fulfills the prerequisite entry criteria for the next level of study within the ITIL® qualifications scheme, the ITIL® Intermediate Level. Is it right for me? This qualification is primarily aimed towards: those who require a basic understanding of the ITIL® framework; those who need an understanding of how ITIL® can be used to enhance the quality of IT service management within an organization; IT professionals or others working within an organization that has adopted and adapted ITIL® who need to be informed about, or contribute to an ongoing service improvement program. The ITIL® qualification is open to any individuals who may have an interest in the subject. The ITIL® Foundation qualification is not intended to enable the holders of the qualification to apply the ITIL® practices for Service Management without further guidance. For more information and to register for ITIL Foundation Please click on below register button. images courtesy: goo.gl/NVVU7g
Study ITIL basics, join a course, and ace practice tests!
Want to get certified in first attempt in ITIL Foundation certification exam? Well then, how do you prepare for the exam? This article will walk you through some insights considered critical and vital to successfully crack the exam. ITIL is considered as the best-practice service management framework across the industry, especially for IT service and governance. If your field of interest and area of expertise happens to center around IT services management, and serious about shaping a career, then we strongly recommend you to take up ITIL® certification. The certification will accelerate your career path and professional advancement. Now that you are sure of your interest and inclination, the stepping stone towards the ITIL® certification is the ITIL Foundation. Start your research Before enrolling to ITIL Foundation course, do a bit of research to gain a basic understanding about ITIL Foundation. This will help you to assess and analyze the knowledge gap as some topics might be familiar, which is a shot in the arm and makes you more confident. It presents an idea of your own appetite as well. Scout for a good learning providerExtend your research to check the available learning academies in and around your place. Alternatively, check and confirm if other modes of learning like instructor-led online class or e-learning can take the place of physical classroom. If your employment comes in the way of attending regular classroom training, other options should be open for consideration. So factor these aspects in your search ad don’t prioritize based on just proximity hoping to catch up on shortfall later. It should be well searched and informed decision before you can make your move. Sign up Once you screen and settle on a service provider, sign up after checking your calendar to ensure there are no planned events that might impact or interfere with your training dates. A dedicated effort always calls for a detailed plan. A systematic approach and meticulous plan and good balance bring in the much desired discipline. Make sure everything in its place before the course begins. There are tons of literatures available in the public domain. Read and upgrade. Study The relentless pursuit of learning leaves you rich and rewarding. So scratching the surface won’t suffice, instead dig deep and deeper and find roots. Study every chapter and summarize your learning. The Foundation course will be more about terminology, core concepts, process, lifecycles stages and links within. The course summary for every chapter will help you in identifying the learned and missed. If required, start all over again until you are satisfied and confident to close. Always question and seek greater clarity through illustration and examples. Try to reinforce learning through workplace experience and scenarios. After the completion of every chapter, attempt without fail the chapter test as this exercise will help you close the gaps that may exist and provide you the opportunity to assess your own standing based on the test outcome. Self-study Classroom study must be supplemented with self-study. The chapter tests taken in classroom can be replicated through tests available online. Today, the internet presents a wealth of information and poses hundreds of questions to test your skills and strength and as part of self-study, attempt as many as you can in the time available – that’s why the need for the systematic study and meticulous plan to apportion time accordingly. Usually, candidates are provided some time after the course completion to schedule the exam. Use this time effectively. Self-assessment The mock-exam or final test will be a comprehensive question papers simulating the severity of the Certification exam. You must endeavor to take as many as possible. Further, the official site hosts mock exam for participants to prepare themselves. Become conversant with course by scoring more than 90% in your mock exam. The ITIL Foundation is an objective-type 40 questions, and its possible to get all 40 correct. Your score above 90 must become a pattern from the series of mock exam attended. The score is a clear indicator of your learning and in case the score dips below 90, then restart by revisiting the chapters where the marks went missing. It’s plugging the holes and closing gaps that one scales. It’s very much possible and, with effort, achievable. Sit for the examination With the kind of strenuous preparation, just keep your cool and calmly appear for the exam. Make sure you read all the answers and most importantly understand the answers from the perspective of the question, and not misunderstand with your professional experience. Often candidates confuse the questions with scenarios experience in their professional front and as a result get sidetracked and struggle to find our way back. The percentage of pass is 65% which is answering 26 question correctly out of 40. The insistence in scoring 90 and above successively in a series of mock exam is to make oneself fluent and assure a safe passage to the subsequent level of certification exam, namely ITIL Intermediate. Wish you well in your endeavors. As the next step in your professional ITIL certification, you can either opt for Intermediate-Lifecycle modules for those wanting to pursue managerial openings or Intermediate-Capability modules for those who wish to involve with process or mix of both Lifecycle and Capability. About ITIL® ITIL®, an acronym of Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a collection of best practice in IT service management. ITIL is considered as the best-practice service management framework across the industry, especially for IT service and governance. If your area field of interest and area of expertise happens to center around IT services management, then we strongly recommend you to take up ITIL certification. There are currently six levels for the ITIL® Qualification Scheme (ITIL® Certification): § ITIL® Foundation Level § ITIL® Practitioner (newly added in 2016) § ITIL® Intermediate Level (Lifecycle Stream / Capability Stream) § ITIL® Managing Across the Lifecycle § ITIL® Expert § ITIL® Master The ITIL certification is a platform independent, vendor neutral and non-prescriptive credential, that’s widely accepted and recognized across the industry with regard to IT management and service advancement initiatives.
Read More
Want to get certified in first attempt in ITIL Foundation certification exam? Well then, how do you prepare for the exam? This article will walk you through some insights considered critical and vital to successfully crack the exam. ITIL is considered as the best-practice service management framework across the industry, especially for IT service and governance. If your field of interest and area of expertise happens to center around IT services management, and serious about shaping a career, then we strongly recommend you to take up ITIL® certification. The certification will accelerate your career path and professional advancement. Now that you are sure of your interest and inclination, the stepping stone towards the ITIL® certification is the ITIL Foundation. Start your research Before enrolling to ITIL Foundation course, do a bit of research to gain a basic understanding about ITIL Foundation. This will help you to assess and analyze the knowledge gap as some topics might be familiar, which is a shot in the arm and makes you more confident. It presents an idea of your own appetite as well. Scout for a good learning providerExtend your research to check the available learning academies in and around your place. Alternatively, check and confirm if other modes of learning like instructor-led online class or e-learning can take the place of physical classroom. If your employment comes in the way of attending regular classroom training, other options should be open for consideration. So factor these aspects in your search ad don’t prioritize based on just proximity hoping to catch up on shortfall later. It should be well searched and informed decision before you can make your move. Sign up Once you screen and settle on a service provider, sign up after checking your calendar to ensure there are no planned events that might impact or interfere with your training dates. A dedicated effort always calls for a detailed plan. A systematic approach and meticulous plan and good balance bring in the much desired discipline. Make sure everything in its place before the course begins. There are tons of literatures available in the public domain. Read and upgrade. Study The relentless pursuit of learning leaves you rich and rewarding. So scratching the surface won’t suffice, instead dig deep and deeper and find roots. Study every chapter and summarize your learning. The Foundation course will be more about terminology, core concepts, process, lifecycles stages and links within. The course summary for every chapter will help you in identifying the learned and missed. If required, start all over again until you are satisfied and confident to close. Always question and seek greater clarity through illustration and examples. Try to reinforce learning through workplace experience and scenarios. After the completion of every chapter, attempt without fail the chapter test as this exercise will help you close the gaps that may exist and provide you the opportunity to assess your own standing based on the test outcome. Self-study Classroom study must be supplemented with self-study. The chapter tests taken in classroom can be replicated through tests available online. Today, the internet presents a wealth of information and poses hundreds of questions to test your skills and strength and as part of self-study, attempt as many as you can in the time available – that’s why the need for the systematic study and meticulous plan to apportion time accordingly. Usually, candidates are provided some time after the course completion to schedule the exam. Use this time effectively. Self-assessment The mock-exam or final test will be a comprehensive question papers simulating the severity of the Certification exam. You must endeavor to take as many as possible. Further, the official site hosts mock exam for participants to prepare themselves. Become conversant with course by scoring more than 90% in your mock exam. The ITIL Foundation is an objective-type 40 questions, and its possible to get all 40 correct. Your score above 90 must become a pattern from the series of mock exam attended. The score is a clear indicator of your learning and in case the score dips below 90, then restart by revisiting the chapters where the marks went missing. It’s plugging the holes and closing gaps that one scales. It’s very much possible and, with effort, achievable. Sit for the examination With the kind of strenuous preparation, just keep your cool and calmly appear for the exam. Make sure you read all the answers and most importantly understand the answers from the perspective of the question, and not misunderstand with your professional experience. Often candidates confuse the questions with scenarios experience in their professional front and as a result get sidetracked and struggle to find our way back. The percentage of pass is 65% which is answering 26 question correctly out of 40. The insistence in scoring 90 and above successively in a series of mock exam is to make oneself fluent and assure a safe passage to the subsequent level of certification exam, namely ITIL Intermediate. Wish you well in your endeavors. As the next step in your professional ITIL certification, you can either opt for Intermediate-Lifecycle modules for those wanting to pursue managerial openings or Intermediate-Capability modules for those who wish to involve with process or mix of both Lifecycle and Capability. About ITIL® ITIL®, an acronym of Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a collection of best practice in IT service management. ITIL is considered as the best-practice service management framework across the industry, especially for IT service and governance. If your area field of interest and area of expertise happens to center around IT services management, then we strongly recommend you to take up ITIL certification. There are currently six levels for the ITIL® Qualification Scheme (ITIL® Certification): § ITIL® Foundation Level § ITIL® Practitioner (newly added in 2016) § ITIL® Intermediate Level (Lifecycle Stream / Capability Stream) § ITIL® Managing Across the Lifecycle § ITIL® Expert § ITIL® Master The ITIL certification is a platform independent, vendor neutral and non-prescriptive credential, that’s widely accepted and recognized across the industry with regard to IT management and service advancement initiatives.
ITIL 2011 Foundation Workshop INCL Certification Exam
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a set of globally recognized best practices for IT Service Management that can be tailored to any organization. ITIL provides the foundation for quality IT Service Management through documented, proven processes that cover the entire Service Lifecycle. It is easy for organizations to learn, tailor, and implement ITIL to suit their environment. A complete ITIL philosophy has grown around the guidance contained within the ITIL books and the supporting certification and qualification scheme. ITIL is the most widely adopted approach for IT Service Management in the world. It provides a practical, no-nonsense framework for identifying, planning, delivering and supporting IT services to the business. The ITIL Foundation Course is an entry-level certification. It introduces the Lifecycle of managing IT Services to deliver to business expectations and provides an approach to learning the core disciplines of ITIL best practices. The ITIL Foundation Course is a stepping-stone for everyone who is interested in learning more about ITIL best practices. The audience includes all IT professionals who work in or plan to work in an ITIL supported environment as well as in key business areas.
images courtesy: goo.gl/HFDBU3
Read More
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a set of globally recognized best practices for IT Service Management that can be tailored to any organization. ITIL provides the foundation for quality IT Service Management through documented, proven processes that cover the entire Service Lifecycle. It is easy for organizations to learn, tailor, and implement ITIL to suit their environment. A complete ITIL philosophy has grown around the guidance contained within the ITIL books and the supporting certification and qualification scheme. ITIL is the most widely adopted approach for IT Service Management in the world. It provides a practical, no-nonsense framework for identifying, planning, delivering and supporting IT services to the business. The ITIL Foundation Course is an entry-level certification. It introduces the Lifecycle of managing IT Services to deliver to business expectations and provides an approach to learning the core disciplines of ITIL best practices. The ITIL Foundation Course is a stepping-stone for everyone who is interested in learning more about ITIL best practices. The audience includes all IT professionals who work in or plan to work in an ITIL supported environment as well as in key business areas.
images courtesy: goo.gl/HFDBU3
Enroll in ITIL Certification Course in Bangalore Today!
Enroll for ITIL training in Bangalore..!!! Contact info@icertglobal.com with your Name and Phone Number.. Hurry UP ..Limited Slots.. Enroll for ITIL training in Bangalore..!!! Contact info@icertglobal.com with your Name and Phone Number.. Hurry UP ..Limited dates..
Read More
Enroll for ITIL training in Bangalore..!!! Contact info@icertglobal.com with your Name and Phone Number.. Hurry UP ..Limited Slots.. Enroll for ITIL training in Bangalore..!!! Contact info@icertglobal.com with your Name and Phone Number.. Hurry UP ..Limited dates..
Service Strategy Qualification: Key to ITSM Success & Growth
The Service Strategy module is one of the ITIL Service Lifecycle modules, and will be of interest to candidates looking to focus on the use of process and practice elements used, and the management capabilities needed to deliver quality Service Management practices. Is it right for me? As with any of the Intermediate modules, it is recommended that candidates have exposure to basic concepts in IT and at least two years professional experience working in IT Service Management. The Service Strategy qualification would suit candidates in the following IT professions or areas: IT Management IT Finance Manager Supplier Relationship Management We have provided this list as a guide only, and choices will depend on the candidate's individual career goals and objectives.
image courtesy: goo.gl/dxHNqp
Read More
The Service Strategy module is one of the ITIL Service Lifecycle modules, and will be of interest to candidates looking to focus on the use of process and practice elements used, and the management capabilities needed to deliver quality Service Management practices. Is it right for me? As with any of the Intermediate modules, it is recommended that candidates have exposure to basic concepts in IT and at least two years professional experience working in IT Service Management. The Service Strategy qualification would suit candidates in the following IT professions or areas: IT Management IT Finance Manager Supplier Relationship Management We have provided this list as a guide only, and choices will depend on the candidate's individual career goals and objectives.
image courtesy: goo.gl/dxHNqp
ITIL Service Operation Certification: Complete Guide & Prep
ITIL Service Operation Purpose of Service Operation: Purpose of Service Operation is to make sure services are delivered at agreed levels. Its purpose is to also manage the technology, infrastructure and applications implemented in organization in order to meet customers' needs. In fact this is the the stage in the whole life cycle where services basically deliver the value to the business because from business point of view this stage has the highest visibility. It is Service Operation staff responsibility to ensure that the value to the business is delivered. At this stage there may be some conflicting goals appear and it is important to know how to balance this. Some examples are: - technological, internal IT perception versus external business point of view. - stability versus responsiveness. - quality versus time to deliver versus cost of service. - reactive attitude to support services versus proactive activities. All the conflicts mentioned above are just examples. In practice there are much more of them and each one has to be balanced and maintained by the Service Operation staff. Excessive focus on one side without balancing another side will result in poor service.
images courtesy:goo.gl/fMKeZL
Read More
ITIL Service Operation Purpose of Service Operation: Purpose of Service Operation is to make sure services are delivered at agreed levels. Its purpose is to also manage the technology, infrastructure and applications implemented in organization in order to meet customers' needs. In fact this is the the stage in the whole life cycle where services basically deliver the value to the business because from business point of view this stage has the highest visibility. It is Service Operation staff responsibility to ensure that the value to the business is delivered. At this stage there may be some conflicting goals appear and it is important to know how to balance this. Some examples are: - technological, internal IT perception versus external business point of view. - stability versus responsiveness. - quality versus time to deliver versus cost of service. - reactive attitude to support services versus proactive activities. All the conflicts mentioned above are just examples. In practice there are much more of them and each one has to be balanced and maintained by the Service Operation staff. Excessive focus on one side without balancing another side will result in poor service.
images courtesy:goo.gl/fMKeZL
ITIL Qualification Scheme:Certification & Pathways Explained
ITIL Qualification Scheme The ITIL Qualifications scheme provides a modular approach to the ITIL framework, and is comprised of a series of qualifications focused on different aspects of ITIL Best Practice, to various degrees of depth and detail. These are the levels of qualifications within the scheme: ITIL Foundation ITIL Intermediate Level ITIL Managing Across the Life cycle ITIL Expert Level ITIL Master Qualification The modular, tiered structure of the qualification not only offers candidates the flexibility in relating to the different disciplines and areas of ITIL, but generally makes ITIL qualifications more accessible and achievable.
images courtesy: goo.gl/asmH3z
Read More
ITIL Qualification Scheme The ITIL Qualifications scheme provides a modular approach to the ITIL framework, and is comprised of a series of qualifications focused on different aspects of ITIL Best Practice, to various degrees of depth and detail. These are the levels of qualifications within the scheme: ITIL Foundation ITIL Intermediate Level ITIL Managing Across the Life cycle ITIL Expert Level ITIL Master Qualification The modular, tiered structure of the qualification not only offers candidates the flexibility in relating to the different disciplines and areas of ITIL, but generally makes ITIL qualifications more accessible and achievable.
images courtesy: goo.gl/asmH3z
IT Service Management
ITIL Foundation
The Foundation Level is the entry level qualification which offers candidates a general awareness of the key elements, concepts and terminology used in the ITIL Service Life cycle, including the linkages between Life cycle stages, the processes used and their contribution to Service Management practices.
Why should I take ITIL Foundation?
Upon successful completion of the education and examination components related to this qualification, candidates can expect to gain a general overview, and basic knowledge and understanding of ITIL.
Successful completion of the Foundation qualification also fulfils the prerequisite entry criteria for the next level of study within the ITIL qualifications scheme, the ITIL Intermediate Level .
images courtesy: goo.gl/LFf5uh
Read More
images courtesy: goo.gl/LFf5uh





.jpg)


.webp)
.webp)
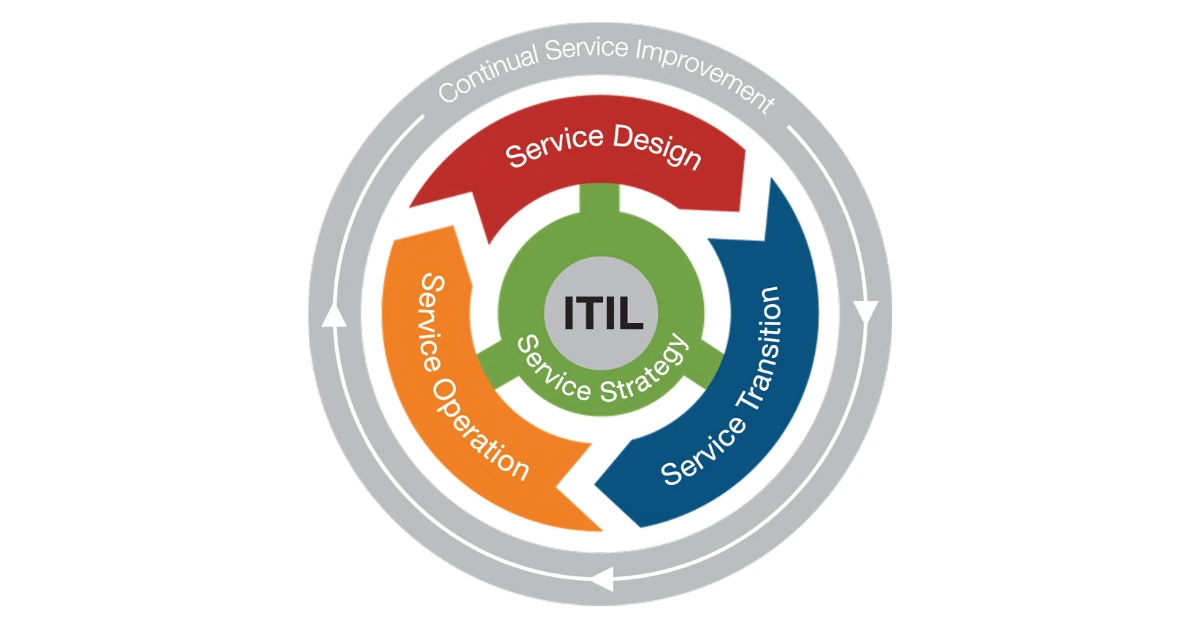


.webp)
.webp)
.webp)











.webp)

























.webp)











.png)






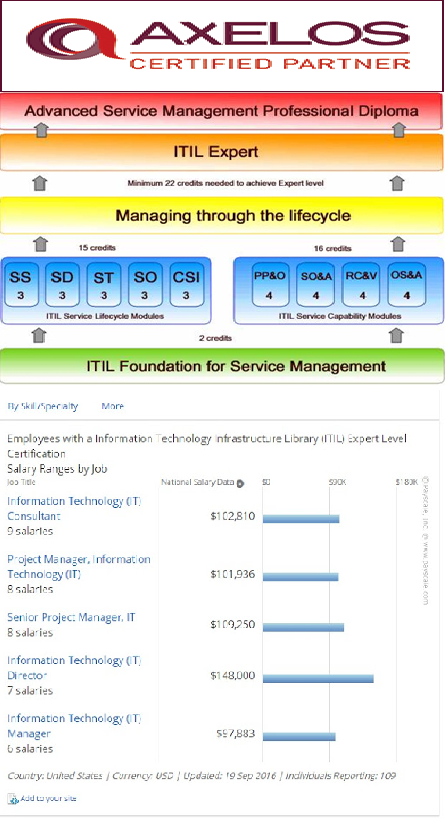
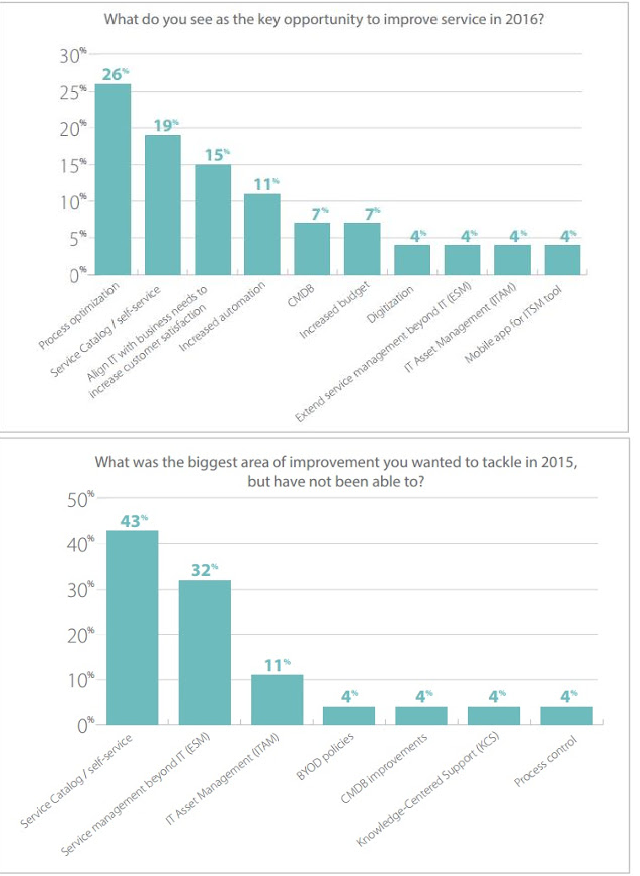







.png)
